* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 12
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroprosthetics wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
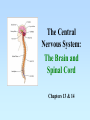
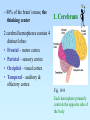
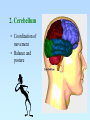
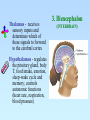
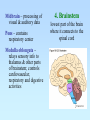
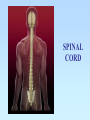
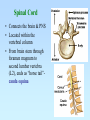
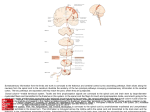
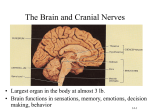
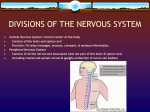
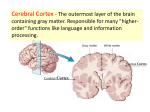
The Central Nervous System: The Brain and Spinal Cord Chapters 13 & 14 BRAIN The Brain • 100 billion neurons • 1.6 kg in males/1.45 kg in females (size is not representative of intelligence, only overall average body size) • Complexity dictates processing power Major Subdivisions of the Brain 1. Cerebrum 2. Cerebellum 3. Diencephalon – thalamus – hypothalamus 4. Brain stem – midbrain – pons – medulla oblongata Fig. 14-2 No functional area of the brain works alone ~ 80% of the brain’s mass; the thinking center 1. Cerebrum 2 cerebral hemispheres contain 4 distinct lobes: • Frontal – motor cortex • Parietal – sensory cortex • Occipital – visual cortex • Temporal – auditory & olfactory cortex Fig. 14-8 Each hemisphere primarily controls the opposite side of the body 2. Cerebellum • Coordination of movement • Balance and posture Thalamus - receives sensory inputs and determines which of these signals to forward to the cerebral cortex Hypothalamus - regulates the pituitary gland, body T, food intake, emotion, sleep-wake cycle and memory; controls autonomic functions (heart rate, respiration, blood pressure) 3. Diencephalon (INTERBRAIN) Limbic System • The “emotional” center, important for perception of pleasure and pain & functions in memory formation • Includes hypothalamus, hippocampus (longterm memory formation), amygdala (processing of emotions) Midbrain – processing of visual & auditory data Pons – contains respiratory center Medulla oblongata – relays sensory info to thalamus & other parts of brainstem; controls cardiovascular, respiratory and digestive activities 4. Brainstem lowest part of the brain where it connects to the spinal cord Protection of the Brain Several different mechanisms: • Skull & scalp hair • Meninges (connective tissue membranes wrapping the CNS) • Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cushions and nourishes the brain • Blood-brain barrier - separation of the CNS from general circulation; composed of the least permeable capillaries; helps to maintain homeostasis in the brain SPINAL CORD Spinal Cord • Connects the brain & PNS • Located within the vertebral column • From brain stem through foramen magnum to second lumbar vertebra (L2), ends as “horse tail”cauda equina