* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3C/D Worksheet KEY
Survey
Document related concepts
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Perception of infrasound wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus modality wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
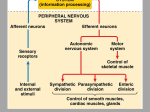
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Motor cortex wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
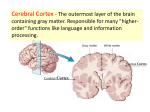
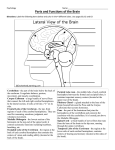
Unit 3C/D Answers 1) The cerebral hemispheres function differently: Left Hemisphere (in most) Right Hemisphere (in most) Right hand control (body) Left hand control (body) Language Music & Art Numeric & Scientific skill Space & Pattern Perception Reasoning Insight Comparing 2) The White Matter of the Cerebrum contains Association fibers found between gyri in the same hemisphere, they do not exist in the cerebral hemisphere, while Commissural fibers found in the corpus callosum connect the right and left hemispheres, and finally the Projection fibers connect the cerebrum to the rest of the brain and spinal cord.3C 8 3) The Cerebral Nuclei or Basal Ganglia are composed of gray matter deep inside the cerebrum. Interneurons provide connection of the cerebral cortex with the brainstem, the thalamus and the hypothalamus. Its functions are to influence muscular activity, regulate attention and cognition, also regulate the intensity of slow or stereotyped movements and inhibit antagonistic and unnecessary movements. 3C 8-9 4) The Diencephalon is made up of the Thalamus, Hypothalamus and the Epithalamus. 3C 9 5) The thalamus gland is the relay station for sensory input, except for smell, to the cerebrum. Its role is in mediating sensation, motor activities, cortical arousal, learning, and memory. It has four groups of nuclei on each side: anterior, ventral, dorsal, and posterior.3C 9 6) The Hypothalamus senses sound, taste, smell, and somatic sensations. It monitors the body providing homeostasis and connects the nervous system to the endocrine system and controls it. 7) The epithalamus region is located on the roof of the third ventricle. The pineal gland is found here and is part of the endocrine system and it secretes the hormone melatonin. The choriod plexus also forms CSF from the blood. 3C 9 8) The midbrain contains cerebral peduncles which are located on the ventral side and are composed of white matter. This contains motor fibers from the cerebral cortex that go to the pons and the spinal cord and also sensory fibers from the spinal cord to the thalamus for sorting. The tectum is located on the dorsal side and contains reflex centers that receive visual input and cause head and neck movement and receive auditory input that causes head and trunk movement. 9) The midbrain also contains the cell bodies for cranial nerves such as Oculomotor III, Trochlear, and Abducens VI nerve. 3C 10 10) The pons connects the medulla oblongata, and the spinal cord to the brain, it is in control of respiration with the medullary respiratory center. Nuclei for cranial nerves within the pons are the Trigeminal V, the Adbucens VI, the Facial VII, the Vestibulocochlear VIII. 3C10 11) In the Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) motor neurons innervate the viscera of smooth and cardiac muscle and also glands, as it regulates the viscera to ensure homeostasis during body activities. It is very hard to override the ANS voluntarily as it operates subconsciously. 12) The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) has two branches, the Sympathetic and the Parasympathetic. The Sympathetic NS which is referred to as the Fight or Flight response called for during exercise, excitement, emergencies, and embarrassment. It works with the Somatic Nervous System (SNS) to provide oxygen and fuel to the skeletal muscles. While the Parasympathetic NS is referred to as the rest and digest, which conserves energy during relaxation, mostly controlling digestion, defecation, and diuresis. 3D1