* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download interactions among organisms
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
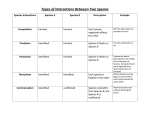
SUBMITTED BY, MARY JOEMA JOSE OPTIONAL: NATURAL SCIENCE REG.NO : 13385007 INTRODUCTION Ecology is the study of organisms and the living and non-living parts of their environment. There are many levels of organization in ecology. They are: The Biosphere – All the area on the surface of earth and in the atmosphere that supports life. Ecosystem – A group of organisms living together and the environment around them. Community – All of the interacting populations in an area Population – All of the organisms of the same species living in an area Organism – A single living thing On the basis of the benefits and harmful effects of organisms , relations can be categorized into : POSITIVE INTERACTION NEGATIVE INTERACTION Interactions in which either both the organisms or one of the organism is benefitted and the other is not harmed. Positive interactions are of two types. They are : Mutualism Commensalism In mutualism, both organisms benefit from one another .For example a heron feeds on the small insects in the rhino’s body , so that the rhino will get clean and the heron get its food. In commensalism, one organism benefits from the other. The other organism is not benefitted or harmed. For example vanda grows with the support of the mango tree but prepares its own food. Interactions in which one of the organism is harmed and the other being won or benefitted. Negative interaction is of three types .They are: PREDATION . PARASITISM. COMPETITION In this type of relationship ,one is benefitted and the other is harmed. For example a tiger feeds on a zebra for its food by chasing it . In this type of interaction, one is benefitted by taking the nutrients or made up food from the host The organism that benefits is called the parasite The organism that is harmed is called the host. Competition is a negative interaction that occurs among organisms whenever two or more organisms require the same limited resource.