* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
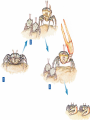
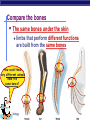
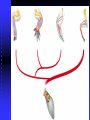
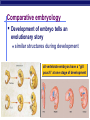
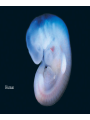
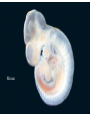
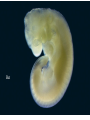
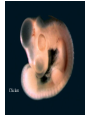
EVOLUTION Charles Darwin Question for Thought Earth has millions of other kinds of organisms of every imaginable shape, size, and habitat. This variety of living things is called biodiversity. How did all these different organisms arise? How are they related? In your own words, describe what YOU think the theory of evolution means… Darwin’s Theory of Evolution Evolution, or change over time, is the process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms. A scientific theory is a well-supported testable explanation of phenomena that have occurred in the natural world. How do you think Darwin came up with his theory? Voyage of Beagle Dates: February 12th, 1831 Captain: Charles Darwin Ship: H.M.S. Beagle Destination: Voyage around the world. Findings: evidence to propose a revolutionary hypothesis about how life changes over time The Galapagos Islands The smallest, lowest islands were hot, dry, and nearly barren-Hood Island-sparse vegetation The higher islands had greater rainfall and a different assortment of plants and animals-Isabela- Island had rich vegetation. The Galapagos Islands Darwin was fascinated in particular by the land tortoises and marine iguanas in the Galápagos. Giant tortoises varied in predictable ways from one island to another. The shape of a tortoise's shell could be used to identify which island a particular tortoise inhabited. Animals found in the Galapagos Land Tortoises Darwin Finches Blue-Footed Booby Marine Iguanas Animals The Journey Home Darwin Observed that characteristics of many plants and animals vary greatly among the islands Hypothesis: Separate species may have arose from an original ancestor Lamarck Population Growth Thomas Malthus19th century English economist If population grew (more babies born than die) Insufficient living space Food runs out Darwin applied this theory to animals Natural Selection & Artificial Selection Natural selection-differences among individuals of a species caused by nature Artificial selection- nature provides the variation among different organisms, and humans select those variations they find useful. Evolution by Natural Selection The Struggle for Existence-members of each species have to compete for food, shelter, other life necessities Survival of the Fittest-Some individuals better suited for the environment Natural Selection Over time, natural selection results in changes in inherited characteristics of a population. These changes increase a species fitness in its environment Evidence of Evolution The Fossil Record Geographic Distribution of Living Things Homologous Body Structures Similarities in Early Development We found the fossil — no joke! Land Mammal ? ? ? Complete series of transitional fossils Someone’s idea of a joke! Regents ButBiology the joke’s on them!! Ocean Mammal ? Evolution from sea to land 2006 fossil discovery of early tetrapod 4 limbs Missing link from sea to land animals Regents Biology 3. Anatomical record Animals with different structures on the surface But when you look under the skin… It tells an evolutionary story of common ancestors Regents Biology Compare the bones The same bones under the skin limbs that perform different functions are built from the same bones How could these very different animals have the same bones? Regents Biology Homologous structures Structures that come from the same origin homo- = same -logous = information Forelimbs of human, cats, whales, & bats same structure on the inside same development in embryo different functions on the outside evidence of common ancestor Regents Biology But don’t be fooled by these… Analogous structures look similar on the outside same function different structure & development How is a bird like a bug? on the inside different origin no evolutionary relationship Solving a similar problem with a similar solution Regents Biology Analogous structures Dolphins: aquatic mammal Fish: aquatic vertebrate both adapted to life in the sea not closely related Watch the tail! Regents Biology Vestigial structures Hind leg bones on whale fossils Why would whales have pelvis & leg bones if they were always sea creatures? Because they used to walk on land! Regents Biology Vestigial structures Structures on modern animals that have no function remains of structures that were functional in ancestors evidence of change over time some snakes & whales have pelvis bones & leg bones of walking ancestors eyes on blind cave fish human tail bone Regents Biology Comparative embryology Development of embryo tells an evolutionary story similar structures during development all vertebrate embryos have a “gill pouch” at one stage of development Regents Biology Comparative Embryology Human Mouse Bat Chicken Alligator 3. Molecular record Comparing DNA & protein structure everyone uses the same genetic code! DNA Human Macaque Dog Bird Frog Lamprey 8 32 45 67 125 compare common genes compare common proteins number of amino acids different from human hemoglobin 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 Regents Biology Building “family” trees Closely related species are branches on the tree — coming from a common ancestor Regents Biology Artificial selection How do we know natural selection can change a population? we can recreate a similar process “evolution by human selection” “descendants” of wild mustard Regents Biology Selective Breeding Humans create the change over time Regents Biology “descendants” of the wolf Artificial Selection …and the examples keep coming! I liked breeding pigeons! Regents Biology Artificial Selection gone bad! Unexpected consequences of artificial selection Pesticide resistance Antibiotic resistance Regents Biology Insecticide resistance Spray the field, but… insecticide didn’t kill all individuals What caused the variation? mutation resistant survivors reproduce resistance is inherited insecticide becomes Regents Biology less & less effective Regents Biology Any Questions?? Regents Biology