* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Media Selection in Advertising
Atheist Bus Campaign wikipedia , lookup
Social media marketing wikipedia , lookup
Radio advertisement wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of advertising wikipedia , lookup
Advertising to children wikipedia , lookup
Ad blocking wikipedia , lookup
Advertising management wikipedia , lookup
Targeted advertising wikipedia , lookup
False advertising wikipedia , lookup
Online advertising wikipedia , lookup
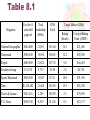
Media Selection in Advertising Chapter 8 What kinds of ads get your attention? Are they found in “traditional” media like television or unusual places? Where is the most unique or “oddest” place that you have seen an ad? Media Planning • Focus on consumer behavior • Create plans that reflect purchase process (Chapter 3) • Influence consumer in the marketplace Components of a Media Plan • • • • • Marketing analysis Advertising analysis Media strategy Media schedule Justification and summary Factors that have changed the role of Media • IMC – more than just mass advertising now • Cost factors • Globalization • Complexity of the media function • Profitability FIGURE 8.5 Developing Logical Combinations of Media Media Selection Factors • • • • • • Organizational Objectives Target market(s) Costs Message Theme Constraints Product/Service considerations Media Selection Factors • Advertising Objectives • • • • Reach Frequency/OTS Gross Rating Points = Reach X OTS Cost per Thousand (CPM) = Cost/Total audience X 1000 • Cost per rating point (CPRP) = Cost of media/rating Rating number of household turned to a program total number of households in a market • Gross impressions – audiences total exposure to a communication • Continuity – exposure schedule/pattern used in the campaign Table 8.1 Cost for 4color full page ad Total readership (000's) CPM Total National Geographic $346,080 21,051 Newsweek $780,180 People Magazine Target Market (20M) Rating (Reach) Cost per Rating Point (CPRP) $16.44 16.1 $21,496 15,594 $50.03 12.2 $63,949 $605,880 21,824 $27.76 9.4 $64,455 Southern Living $11,370 5,733 $1.98 2.4 $4,738 Sports Illustrated $965,940 13,583 $71.11 10.5 $91,994 $1,324,282 21,468 $61.69 15.9 $83,288 Travel & Leisure $183,216 2,205 $83.09 2.3 $79,659 U.S. News $100,740 8,929 $11.28 8.3 $12,137 Time Ad Campaign Continuity Continuous campaign Advantages: • Serves as a constant reminder to the customer • Covers the entire buying cycle Disadvantages: • Higher costs • Potential for overexposure Flighting Campaign Advantages: • Cost efficiency of advertising, only used during purchase cycles • Allows for more than one medium or vehicle on limited budgets Disadvantages: • Lack of awareness, interest, retention or promotional message during non-scheduled times – could lead to decay Pulsating Campaign Advantages: • Same as the two previous methods Disadvantage: • Not required for seasonal products, or other cyclical products Selecting Media • • • • • • • • • Television Radio Transit Billboard Internet Magazines Newspapers Direct Mail Alternate media Alternative Media Leaflets, brochures, and carry-home menus Ads on carry-home bags Ads on clothing and caps Ads on movie trailers (theater and rentals) Yellow pages Ads sent by fax Video replay and signage at sporting events Ads on walls in airports, subways, etc. Guerrilla marketing Product placements This ad for a portable e-mail device is aimed at busy travelers looking for convenience. http://www.billboardinfo.com How Important Is Advertising to Magazines? The chart below shows the top five magazines and the percentage of their revenues generated by advertising, subscriptions and newsstand sales TV Guide People Time Sports Illustrated Better Homes & Garden Total Revenue Advertising Subscribers Newstand $1,172,127,000 41.9% 43.2% 14.9% $1,155,395,000 61.8% 18.9% 19.3% $962,651,000 68.4% 27.2% 4.4% $905,313,000 67.8% 28.6% 3.6% $595,667,000 74.6% 23.0% 2.4% Source: Http://www.adage.com (1999 figures) Media Mix - United States Radio 3% Magazines 20.9% Outdoor 2.2% Newspapers 21.4% Internet 5.3% Television 47.2% Source: “100 Leading National Advertisers,” Advertising Age (June 29, 2004), pp. 1-5. Achieving Advertising Objectives 1. Three-exposure hypothesis • Intrusion value • Takes a minimum of three exposures for an ad to be effective • Effective frequency – number of times that one must be exposed to message to achieve its objective • Effective reach - % of target market that must be exposed to ad to achieve its objective Achieving Advertising Objectives 2. Recency theory • Effective the closer to a purchase • States that consumers use selective retention when they consider ads. • Advertising is a waste of money when intended market is not reached