* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 - Net Start Class
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
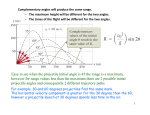
Physics 12 WK DCA Review – Forces & Projectiles 1. Which of the following statements are true of projectiles? List all that apply. a. A projectile is a free-falling object. b. A projectile experiences negligible or no air resistance. c. A projectile must be moving in the downward direction. d. A projectile must be accelerating in the downward direction. e. A projectile does not have to have horizontal motion. f. A projectile could begin its projectile motion with a downward velocity. g. A projectile does not need to be "falling." 2. Which of the following statements are true of the time of flight for a projectile? List all that apply. a. The time that a projectile is in the air is dependent upon the horizontal component of the initial velocity. b. The time that a projectile is in the air is dependent upon the vertical component of the initial velocity. c. For a projectile which lands at the same height that it is projected from, the time to rise to the peak is equal to the time to fall from its peak to the original height. d. For the same upward launch angles, projectiles will stay in the air longer if the initial velocity is increased. e. Assume that a kicked ball in football is a projectile. If the ball takes 3 seconds to rise to the peak of its trajectory, then it will take 6 seconds to fall from the peak of its trajectory to the ground. 3. Vector A is directed northward and vector B is directed eastward. Which of the following vector addition diagrams best represent the addition of vectors A and B and the subsequent resultant? 4. What is the velocity of a projectile with a vertical velocity of 25.0 m/s and a horizontal velocity of 18.0 m/s? a. 7.00 b. 21.56 c. 30.8 d. 35.8 m/s m/s m/s m/s 5. Which of the following is true for an object in freefall? a. Speed increases b. Acceleration increases Use the following choices to answer questions 6-8. a. entirely b. entirely horizontal vertical c. both 6. A football is kicked into the air at an angle of 45 degrees with the horizontal. At the very top of the ball's path, its velocity is ___. 7. A football is kicked into the air at an angle of 45 degrees with the horizontal. At the very top of the ball's path, its acceleration is _______. (Neglect the effects of air resistance.) 8. A football is kicked into the air at an angle of 45 degrees with the horizontal. At the very top of the ball's path, the net force acting upon it is _______. (Neglect the effects of air resistance.) 9. At what point in its path is the horizontal component of the velocity (vx) of a projectile the smallest? 10.At what point in its path is the vertical component of the velocity (vy) of a projectile the smallest? 11.As you roll a bowling ball off a table, what happens to the horizontal component of its velocity? 12.A bullet is fired horizontally and hits the ground in 0.5 seconds. If it had been fired with twice the speed in the same direction, it would have hit the ground in ____. (Assume no air resistance.) 13.Two projectiles are fired at equal speeds but different angles. One is fired at angle of 30 degrees and the other at 60 degrees. Which projectile will hit the ground first? 14.Consider the trajectory diagrams shown below for two different projectiles. The first is launched horizontally, and the second is launched at an angle. On the diagrams, draw vector arrows representing the vx and vy velocity components during the course of the motion. The length of the arrows should represent the magnitude of the velocity components. Label each component. (Note that the velocity components are already shown for the first position.) 15.The launch velocity and angle is given for three different projectiles. Use trigonometric functions to resolve the velocity vectors into horizontal (vx) and vertical (vy) velocity components. Then use kinematic equations to determine the time that the projectile is in the air, the maximum height, and the range that it travels. Launch Angle Launch Velocity 30⁰ 30 m/s 45⁰ 60⁰ 30 m/s 30 m/s 2 16.If a projectile is launched horizontally with a speed of 12.0 m/s from the top of a 24.6meter high building. Determine the horizontal displacement of the projectile. 17.A projectile is launched with an initial speed of 21.8 m/s at an angle of 35.0-degrees above the horizontal. a. Determine the time of flight of the projectile. b. Determine the peak height of the projectile. c. Determine the horizontal displacement of the projectile. 18.A projectile is launched horizontally from the top of a 45.2-meter high cliff and lands a distance of 17.6 meters from the base of the cliff. Determine the magnitude of the launch velocity. 19.Construct free-body diagrams for the following physical situations. a. A ball is dropped from rest from the top of a building. Assume negligible air resistance. b. After being thrown, a football is moving upwards and rightwards towards the peak of its trajectory. Assume negligible air resistance. c. After reaching a terminal velocity, a falling skydiver then opens up the parachute. d. An air track glider (frictionless) is gliding to the right at constant velocity. e. A car is skidding to a stop while traveling to the right. 20.Which of the following are always true of an object that is at equilibrium? a. All the forces acting upon the object are equal. b. The object is at rest. c. The object is moving and moving with a constant velocity. d. The object has an acceleration of zero. e. There is no change in the object's velocity. f. The sum of all the forces is 0 N. g. All the forces acting upon an object are balanced. 21.Which of the following are never true of an object that is at equilibrium? a. The object is accelerating. b. The object is at rest. c. The object is moving in a circle at constant speed. d. All the forces acting upon the object are equal. e. The object is in free-fall. f. The object is falling and has reached its terminal velocity. g. There is a net force acting upon the object. h. The object is moving and moving with a constant velocity. i. The object is at rest. 22.How much force is needed to accelerate a car with a mass of 1000 kilograms from a full stop to 50 m/s in 10 seconds if the rate of acceleration is constant? a. 1000 N b. 2000 N c. 5000 N d. 10,00N 3 23.A car accelerates at a constant rate of 3 m/s2. A continuous force of 3000 N along the direction of motion is responsible for this acceleration. What is the mass of the car? a. 3000 kg c. 1000 kg b. 9000 kg d. 500 kg 24.In a tug of war game, one team pulls to the east with a force of 500 N while the other team pulls west with a force of 300 N. If the ropes of each team are attached to a cart in the center that has a mass of 50 kg, what will be the acceleration of the cart? a. 10 m/s2, East c. 4 m/s2, East b. 10 m/s2, West d. 4 m/s2, West 25.According to Newton’s 2nd Law, what is the relationship between mass and acceleration? a. mass and acceleration are directly proportional b. mass and acceleration are inversely proportional c. there is no relationship 26. Forces F1 and F2 are applied simultaneously to the same point on a large crate resting on a frictionless surface. Which diagram shows the forces positioned to give the crate the greatest acceleration? 27.A different force is applied to each of four 1 kg blocks to slide them across a uniform surface at constant speed as shown below. In which diagram is the coefficient of friction between the block and the surface the greatest? 28.A rubber ball weighs 49N. It is thrown upward with a force of 89 N. What is the acceleration of the ball? a. 30 m/s2 b. 5 m/s2 c. 8 m/s2 d. 4 m/s2 4