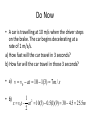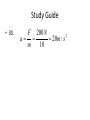* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab Mirterm Review PPT
Frictional contact mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Mass versus weight wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
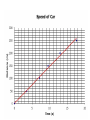
Midterm Review Do Now • A car is travelling at 10 m/s when the driver steps on the brake. The car begins decelerating at a rate of 1 m/s/s. a) How fast will the car travel in 3 seconds? b) How far will the car travel in those 3 seconds? • a) v v0 at 10 1(3) 7 m / s • b) 1 2 x v0t at 10(3) 0.5(1)(9) 30 4.5 25.5m 2 Object Thrown Up • What is the instantaneous speed at the highest point? • 0 • What is the instantaneous speed of the object at points of equal elevation? • The same. • Is acceleration different when the object moving upward or downward? • The same -9.8 m/s/s. Independence of Horizontal and Vertical Motion Demo • Two balls released simultaneously. One ball dropped freely, another projected horizontally. • Which ball will hit the ground faster? • Both balls fall the same vertical distance in equal times. Projectile Launched at an Angle • The horizontal motion of a projectile is independent of its vertical motion. • The horizontal velocity of a projectile is constant (a never changing in value). • The vertical velocity of a projectile changes by 9.8 m/s each second. Newton’s Laws of Motion • 1. Every object continues in a state of rest, or of uniform speed in a straight line, unless acted on by a nonzero net force. • 2. The acceleration produced by a net force on an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. F a m F ma • 3. Forces are always paired. The mutual forces of action and reaction between two bodies are equal in size and opposite in direction. Study Guide • 30. F 200 N 2 a 20m / s m 10 Friction • Friction = µN=µmg • µ-coefficient of friction • N-normal force • Frictional force always directed opposite to the motion. • The magnitude of the frictional force depends on the nature of the surfaces in contact. • Frictional force is independent of • the amount of surface in contact • relative speed of the objects Study Guide • 38. Friction = µN=µmg = = 0.3 x 1.5kgx10m/s/s/= 4.5N • Describe velocity and acceleration of each segment of the graph. Accuracy and Precision. • _________________describes how close a measured value is to the true value. • Accuracy • _________________describes the degree of exactness to which the measurement of a quantity can be reproduced. Motion Maps • If the distance between dots increasing, the object is speeding up or accelerating. • If the distance between dots decreasing, the object is slowing down or decelerating.