MathEngine KarmaTM User Guide - Unreal Engine 4 Documentation
... To explain the potential of physics engines, we need to consider the current solution to handling object behavior in a simulated game environment. This falls into two categories, namely scripted behavior (animation), and bespoke solutions: Scripted behavior is a predefined sequence of events used to ...
... To explain the potential of physics engines, we need to consider the current solution to handling object behavior in a simulated game environment. This falls into two categories, namely scripted behavior (animation), and bespoke solutions: Scripted behavior is a predefined sequence of events used to ...
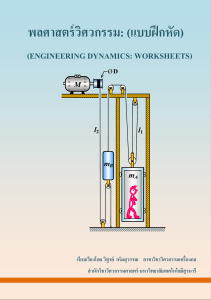
Problem 14.1 In Active Example 14.1, suppose
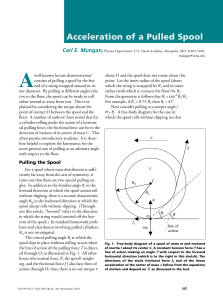
... Problem 14.20 The engineers conducting the test described in Problem 14.19 want to express the total force on the helicopter at t = 6 s in terms of three forces: the weight W , a component T tangent to the path, and a component L normal to the path. What are the values of W , T , and L? Solution: I ...
... Problem 14.20 The engineers conducting the test described in Problem 14.19 want to express the total force on the helicopter at t = 6 s in terms of three forces: the weight W , a component T tangent to the path, and a component L normal to the path. What are the values of W , T , and L? Solution: I ...
Vectors and Moments
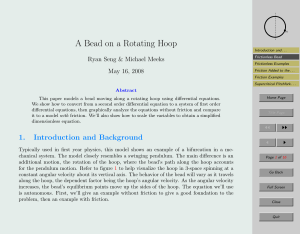
... are the angular velocity of a rigid body and a torque applied to a rigid body. The effect of the action of a force on a rigid body depends on the former’s line of action. As discussed in Chapter 1, Newton’s third law states, among other things, that, given two particles P and Q, the force exerted, sa ...
... are the angular velocity of a rigid body and a torque applied to a rigid body. The effect of the action of a force on a rigid body depends on the former’s line of action. As discussed in Chapter 1, Newton’s third law states, among other things, that, given two particles P and Q, the force exerted, sa ...
Ch 5
... Frictional force depends on the materials that the surfaces are made of. For example, there is more friction between skis and concrete than there is between skis and snow. The normal force between the two objects also matters. The harder one object is pushed against the other, the greater the force ...
... Frictional force depends on the materials that the surfaces are made of. For example, there is more friction between skis and concrete than there is between skis and snow. The normal force between the two objects also matters. The harder one object is pushed against the other, the greater the force ...
Laws Of Motion - Physics With Pradeep
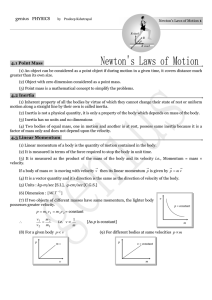
... (iii) Tension : The force exerted by the end of taut string, rope or chain against pulling (applied) force is called the tension. The direction of tension is so as to pull the body. T=F ...
... (iii) Tension : The force exerted by the end of taut string, rope or chain against pulling (applied) force is called the tension. The direction of tension is so as to pull the body. T=F ...
Acta Materialia_60_16_2012
... and therefore selects the particular combinations of active slip systems in the transmitted grain [19]. Later work by Clark et al. [20] improved on their model by noting that accurate prediction of the transmitted slip system, observed with a transmission electron microscope (TEM), also required the ...
... and therefore selects the particular combinations of active slip systems in the transmitted grain [19]. Later work by Clark et al. [20] improved on their model by noting that accurate prediction of the transmitted slip system, observed with a transmission electron microscope (TEM), also required the ...
Frictional contact mechanics

Contact mechanics is the study of the deformation of solids that touch each other at one or more points. This can be divided into compressive and adhesive forces in the direction perpendicular to the interface, and frictional forces in the tangential direction. Frictional contact mechanics is the study of the deformation of bodies in the presence of frictional effects, whereas frictionless contact mechanics assumes the absence of such effects.Frictional contact mechanics is concerned with a large range of different scales. At the macroscopic scale, it is applied for the investigation of the motion of contacting bodies (see Contact dynamics). For instance the bouncing of a rubber ball on a surface depends on the frictional interaction at the contact interface. Here the total force versus indentation and lateral displacement are of main concern. At the intermediate scale, one is interested in the local stresses, strains and deformations of the contacting bodies in and near the contact area. For instance to derive or validate contact models at the macroscopic scale, or to investigate wear and damage of the contacting bodies’ surfaces. Application areas of this scale are tire-pavement interaction, railway wheel-rail interaction, roller bearing analysis, etc. Finally, at the microscopic and nano-scales, contact mechanics is used to increase our understanding of tribological systems, e.g. investigate the origin of friction, and for the engineering of advanced devices like atomic force microscopes and MEMS devices.This page is mainly concerned with the second scale: getting basic insight in the stresses and deformations in and near the contact patch, without paying too much attention to the detailed mechanisms by which they come about.