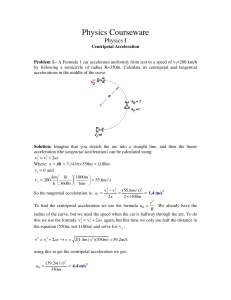
1. Give the magnitude and direction of the net force acting on (a) a
... The particle, if unrestrained by the string, will continue to move in a straight line without any change in velocity. The inertia force is internal to the particle. The weight of the particle = mg and the corresponding reaction of the table are balancing each other and do not figure in the net force ...
... The particle, if unrestrained by the string, will continue to move in a straight line without any change in velocity. The inertia force is internal to the particle. The weight of the particle = mg and the corresponding reaction of the table are balancing each other and do not figure in the net force ...
Dynamics Chapter Problems
... 83. A crate with a mass of 45 kg is suspended from a massless rope that runs vertically upward over a light pulley. The other end of the rope is connected to a 35 kg crate, which lies on a tabletop. The coefficients of the kinetic friction and the static friction between the crate and the surface ar ...
... 83. A crate with a mass of 45 kg is suspended from a massless rope that runs vertically upward over a light pulley. The other end of the rope is connected to a 35 kg crate, which lies on a tabletop. The coefficients of the kinetic friction and the static friction between the crate and the surface ar ...
STATIC AND KINETIC FRICTION
... normal force on the block. In each run, you will pull the block as before, but by changing the masses on the block, you will vary the normal force on the block. ...
... normal force on the block. In each run, you will pull the block as before, but by changing the masses on the block, you will vary the normal force on the block. ...
2007 The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. 13
... Impulsive Motion • Force acting on a particle during a very short time interval that is large enough to cause a significant change in momentum is called an impulsive force. • When impulsive forces act on a particle, ...
... Impulsive Motion • Force acting on a particle during a very short time interval that is large enough to cause a significant change in momentum is called an impulsive force. • When impulsive forces act on a particle, ...
Lecture 13 - University of Oklahoma
... Let’s first consider problems of static equilibrium Equilibrium corresponds to the case that the object has zero ~ net = 0 net force acting on it F Two types of equilibrium conditions Static equilibrium corresponds to the case when the object is at rest Dynamic equilibrium corresponds to the case wh ...
... Let’s first consider problems of static equilibrium Equilibrium corresponds to the case that the object has zero ~ net = 0 net force acting on it F Two types of equilibrium conditions Static equilibrium corresponds to the case when the object is at rest Dynamic equilibrium corresponds to the case wh ...
Frictional contact mechanics

Contact mechanics is the study of the deformation of solids that touch each other at one or more points. This can be divided into compressive and adhesive forces in the direction perpendicular to the interface, and frictional forces in the tangential direction. Frictional contact mechanics is the study of the deformation of bodies in the presence of frictional effects, whereas frictionless contact mechanics assumes the absence of such effects.Frictional contact mechanics is concerned with a large range of different scales. At the macroscopic scale, it is applied for the investigation of the motion of contacting bodies (see Contact dynamics). For instance the bouncing of a rubber ball on a surface depends on the frictional interaction at the contact interface. Here the total force versus indentation and lateral displacement are of main concern. At the intermediate scale, one is interested in the local stresses, strains and deformations of the contacting bodies in and near the contact area. For instance to derive or validate contact models at the macroscopic scale, or to investigate wear and damage of the contacting bodies’ surfaces. Application areas of this scale are tire-pavement interaction, railway wheel-rail interaction, roller bearing analysis, etc. Finally, at the microscopic and nano-scales, contact mechanics is used to increase our understanding of tribological systems, e.g. investigate the origin of friction, and for the engineering of advanced devices like atomic force microscopes and MEMS devices.This page is mainly concerned with the second scale: getting basic insight in the stresses and deformations in and near the contact patch, without paying too much attention to the detailed mechanisms by which they come about.