* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Projectile Motion
Introduction to general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Pioneer anomaly wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
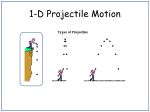
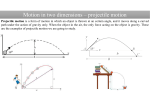
PROJECTILE MOTION PROJECTILES Projectile: any object that is launched with an initial velocity and continues to move; affected only by the force of gravity. Trajectory: the path a projectile follows. Usually parabolic Range: horizontal distance covered by a projectile Height: the maximum vertical distance reached by a projectile PROJECTILES Motion in the x-direction Forces: NONE! Velocity: Constant Acceleration: ZERO! Displacement: object will move equal distances every second. Motion in the y-direction Forces: GRAVITY! Velocity: Changes (gets faster going down) Acceleration: -9.81m/s2 Displacement: the object will move more distance each second. HORIZONTALLY LAUNCHED When a projectile is launched horizontally, all of its initial velocity is in the x-direction. vx is constant, so the distance in the x-direction is the same every second vy is increasing due to the force of gravity, so the distance in the y-direction increases every second. LAUNCHED AT AN ANGLE On the Way Up: •vy decreases •ay is constant (g = -9.81 m/s2) •dy decreases each second At the Top: •vy = 0 •ay is constant (g = -9.81 m/s2) •vx = only velocity; constant On the Way Down: •vy increases •ay is constant (g = -9.81 m/s2) •dy increases each second EFFECT OF VARIOUS LAUNCH ANGLES