* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Yr 9 Science ECOLOGY - Ecological succession
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Deep ecology wikipedia , lookup
Agroecology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological economics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
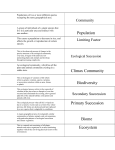
Yr 9 Science ECOLOGY - Ecological succession 1. Define the term ecological succession. Ecological succession is a process by which the structure of a biological community changes over time. 2. Rank these four ponds from oldest to most recent. BCAD 3. Describe what is meant by pioneers when discussing ecological succession. Pioneers are the first population to colonise an abiotic ecosystem or a previously damaged ecosystem and starting a chain of ecological succession that culminates in a biodiverse stable ecosystem. 4. Given the following facts, construct a story that demonstrates the development of ecological succession. Identify which are the pioneers and which are the climax populations. Without grazing, vegetation is left to grow unabated. (3) White pine grows slowly and tolerates shade very well. (6) A farmer has a flock that graze on his farm. (1) Birds and small mammals feed only upon plant seeds. (9) Predators like using thick forest for refuge and shelter. (11) Larger birds feed on tree buds, acorn and nuts. (10) Maple, red pines and poplars grow very fast but they don’t like shaded conditions. They thrive in sunlight. (5) The trees are only a part of this story of ecological succession. (7) Animal populations also go through change. (8) Poison ivy, wild grapes and creepers make use of sunlight and open spaces. (4) A virus wiped out all of his stock. (2) The pioneers here are the vines and poison ivy. The climax population is the white pines because they are the last to grow.