* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Natural selection File
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Inbreeding avoidance wikipedia , lookup
Group selection wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Selective breeding wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Peppered moth evolution wikipedia , lookup
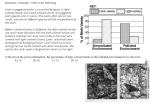
NATURAL SELECTION IGCSE Biology Revision Notes Darwin’s Original Idea 1. Individuals in a species show a wide range of variation 2. Variation is caused by differences in their genes 3. Individuals with characteristics best adapted to the environment are more likely to survive and reproduce 4. These individuals’ genes are passed to their offspring. 5. Individuals that are poorly adapted to their environment are less likely to survive and reproduce. 6. Their genes will be less common in the next generation. 7. Given enough time, a species will gradually evolve. Standard modern version 1. The environment creates selection pressure by limiting the resources available to individuals (e.g. food, shelter, protection from predators) 2. Mutations and meiosis create genetic variation 3. Organisms in a species are in competition – characteristics that are well adapted create a selective advantage 4. Individuals with the characteristics best adapted to the environment are more likely to survive and reproduce: they are selected for 5. These individuals’ genes are passed to their offspring. 6. Individuals that are poorly adapted to their environment are less likely to survive and reproduce: they are selected against. 7. Their genes will be less common in the next generation. Examples: Peppered Moth • Industrial pollution in the 19th Century killed light-coloured lichens and made trees dark. That created a selection pressure as the kind camouflage needed to avoid detection by birds changed • Dark moths had a selective advantage and so were selected for, and more of the alleles responsible for the dark colour were present in the next generation • Light moths had a selective disadvantage and so were selected against, so fewer of the alleles responsible for the light colour were present in the next generation • In industrial areas, dark moths became common and light moths became rare Example: Antibiotic resistance • Selection pressure: Antibiotic that kill bacteria or prevent • • • • • • them reproducing Selective advantage: Resistance to antibiotic Selected for: Bacteria that are resistant Selective disadvantage: Susceptibility to antibiotic Selected against: Bacteria that are susceptible Result: When a new antibiotic is introduced to the environment, after some time there are more resistant bacteria and fewer susceptible bacteria in the population Problem: There are now many, many antibiotic-resistant bacteria, and fewer effective antibiotics available!