* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Disorders of memory overview
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
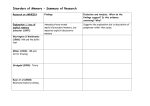
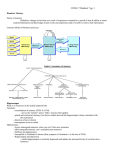
Disorders of memory overview AMNESIA Amnesia is a partial or total loss of memory o Retrograde vs anterograde o HM and Clive Wearing Explanation 1: loss of explicit memory o Schacter (1987): Amnesiacs have normal implicit/procedural memory, but impaired explicit/declarative memory Warrington & Weiskrantz (1968): HM and the Gollin test Milner (1962): HM and mirror drawing Stickgold (2000): Tetris o However, this is a descriptive rather than explanatory explanation Ryan et al (2000): Relational memory binding Explanation 2: Inability to consolidate new memories o Issac and Mayes (1999): amnesiacs could retrieve but not consolidate memories The temporal gradient: evidence for consolidation o Consolidation issues caused by damage to hippocampus HM and Clive Wearing Gabrieli (1998): damage to CA1 (hippocampus) causes anterograde amnesia. Reed and Squire (1998): MRI scans on amnesiacs Remondes & Scman (2004): damage to rats’ hippocampus ALZHEIMER’S Progressive form of dementia. Causes problems with memory Explanation 1: β-amyloids, plaques and tangles o Amyloid precursor protein broken down into β-amyloid protein 42 causing the build up of plaques Selkoe (2000): causes damage to cerebral cortex and hippocampus Berntson et al (2002): causes damage to basal forebrain Murphy & LeVine (2010): β-amyloid starts chain of events which leads to alzheimer’s o β-amyloid interferes with normal brain function Synder (2005): β-amyloid interferes with NDMA neurotransmitter Cleary et al (2005): rats injected with β-amyloid have memory disruption o Tangles: structure of cell body disintegrates sue to build up of tau protein Explanation 2: Genes o Alzheimer’s can be explained by a genetic predisposition. These genes play a role in producing β-amyloid Lott (1982): Early onset Alzheimer’s linked to chromosome 21 (down’s syndrome) Levy-Lahad eta al (1995): Early onset Alzheimer’s gene found on chromosome 1 Schellenberg et al (1992): Early onset Alzheimer’s gene found on chromosome 14 Ertekin-Taner et al (2000): Gene for later onset Alzheimer’s found on chromosome 10 o Genes do not provide a full explanation St George-Hislop (2000): Half of all Alzheimer’s patients have no relatives with the illness Hendrie (2001): Yoruba people have Alzheimer’s genes, but much lower rates of the illness.