* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 18 clicker questions
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
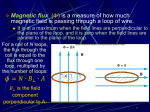
Chapter 18 Clickers Electromagnetic Induction Prepared by Dedra Demaree, Georgetown University © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question If explanation 2 is correct, then if a bar magnet is placed near a coil but is not moving, such that the magnetic field lines of the bar magnet pass through the coil but are unchanging: a) A constant current will be induced. b) No current will be induced. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question If explanation 2 is correct, then if a bar magnet is placed near a coil but is not moving, such that the magnetic field lines of the bar magnet pass through the coil but are unchanging: a) A constant current will be induced. b) No current will be induced. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question Which of the loops immediately experiences a changing number of field lines as they move to the right? a) All of them b) 1, 2, and 4 c) 3 d) 1 and 2 © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question Which of the loops immediately experiences a changing number of field lines as they move to the right? a) All of them b) 1, 2, and 4 c) 3 d) 1 and 2 © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question A current will be induced in a coil of wire if: a) The area of the coil is changed. b) The orientation of the magnetic field relative to the coil is changed. c) The strength of the magnetic field in the vicinity of the coil is changed. d) All of the above. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question A current will be induced in a coil of wire if: a) The area of the coil is changed. b) The orientation of the magnetic field relative to the coil is changed. c) The strength of the magnetic field in the vicinity of the coil is changed. d) All of the above. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question The magnetic flux increases if: a) The strength of the magnetic field increases. b) The area of the loop decreases. c) The angle between the normal vector of the loop and the magnetic field increases. d) All of the above. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question The magnetic flux increases if: a) The strength of the magnetic field increases. b) The area of the loop decreases. c) The angle between the normal vector of the loop and the magnetic field increases. d) All of the above. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question If the north pole of a bar magnet moves away from a loop of wire, the flux in the wire: a) Increases. b) Decreases. c) Does not change. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question If the north pole of a bar magnet moves away from a loop of wire, the flux in the wire: a) Increases. b) Decreases. c) Does not change. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question If the flux in a loop of wire increases, the induced magnetic field in the wire must: a) Point in the same direction as the external magnetic field. b) Point in the opposite direction as the external magnetic field. c) There is no induced magnetic field. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question If the flux in a loop of wire increases, the induced magnetic field in the wire must: a) Point in the same direction as the external magnetic field. b) Point in the opposite direction as the external magnetic field. c) There is no induced magnetic field. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question If the flux in a loop of wire decreases, the induced magnetic field in the wire must: a) Point in the same direction as the external magnetic field. b) Point in the opposite direction as the external magnetic field. c) There is no induced magnetic field. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question If the flux in a loop of wire decreases, the induced magnetic field in the wire must: a) Point in the same direction as the external magnetic field. b) Point in the opposite direction as the external magnetic field. c) There is no induced magnetic field. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question The emf induced in a coil increases if: a) The area of the loop decreases. b) The time it takes for the magnetic flux to change increases. c) The change in magnetic flux increases. d) All of the above. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question The emf induced in a coil increases if: a) The area of the loop decreases. b) The time it takes for the magnetic flux to change increases. c) The change in magnetic flux increases. d) All of the above. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question A single loop of wire is oriented so that the magnetic field is parallel to the normal vector of the loop. If the magnetic field changes from 0 T to 4 T in 2 s, and the area of the loop is 0.5 m2, what is the emf induced in the loop? a) 0.5 V b) 1 V c) 2 V d) 4 V © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question A single loop of wire is oriented so that the magnetic field is parallel to the normal vector of the loop. If the magnetic field changes from 0 T to 4 T in 2 s, and the area of the loop is 0.5 m2, what is the emf induced in the loop? a) 0.5 V b) 1 V c) 2 V d) 4 V © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question Motional emf will be larger if: a) The rod is moved faster. b) The magnetic field is stronger. c) The rod is longer. d) All of the above. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question Motional emf will be larger if: a) The rod is moved faster. b) The magnetic field is stronger. c) The rod is longer. d) All of the above. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question A 1-m-long rod is moving perpendicular to a magnetic field with a constant speed of 10 m/s. The magnitude of the magnetic field is 2 T. What is the motional emf? a) 0 V b) 5 V c) 10 V d) 20 V © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question A 1-m-long rod is moving perpendicular to a magnetic field with a constant speed of 10 m/s. The magnitude of the magnetic field is 2 T. What is the motional emf? a) 0 V b) 5 V c) 10 V d) 20 V © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question A simple electric generator works by: a) Changing the area of a loop in an external magnetic field. b) Changing the magnitude of the external magnetic field through a loop. c) Changing the orientation of a loop in an external magnetic field. d) None of the above. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question A simple electric generator works by: a) Changing the area of a loop in an external magnetic field. b) Changing the magnitude of the external magnetic field through a loop. c) Changing the orientation of a loop in an external magnetic field. d) None of the above. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question The induced emf in an electric generator decreases if: a) The loop rotates faster. b) There are more coils of wire in the loop. c) The area of the loop gets bigger. d) The external magnetic field gets smaller. e) None of the above. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question The induced emf in an electric generator decreases if: a) The loop rotates faster. b) There are more coils of wire in the loop. c) The area of the loop gets bigger. d) The external magnetic field gets smaller. e) None of the above. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question The induced current in a generator is: a) Alternating because the coil continuously rotates, flipping its orientation with respect to the external magnetic field every half-turn. b) Constant because the flux constantly changes as the coil continuously rotates. c) Neither of the above. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question The induced current in a generator is: a) Alternating because the coil continuously rotates, flipping its orientation with respect to the external magnetic field every half-turn. b) Constant because the flux constantly changes as the coil continuously rotates. c) Neither of the above. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question Your laptop requires a 20−V emf to function. What should be the ratio of the primary coil turns to the secondary coil turns if this transformer is to be plugged into a standard house AC outlet (120−V emf)? a) 6 b) 20 c) 120 d) 2400 © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question Your laptop requires a 20−V emf to function. What should be the ratio of the primary coil turns to the secondary coil turns if this transformer is to be plugged into a standard house AC outlet (120−V emf)? a) 6 b) 20 c) 120 d) 2400 © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question Which of the following statements is correct? a) A moving electric charge produces a magnetic field. b) An electric charge has a corresponding electric field. c) A changing magnetic field produces an electric field. d) All of the above are correct. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Voting question Which of the following statements is correct? a) A moving electric charge produces a magnetic field. b) An electric charge has a corresponding electric field. c) A changing magnetic field produces an electric field. d) All of the above are correct. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc.