* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam 2 - Wake Forest University
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Woodward–Hoffmann rules wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
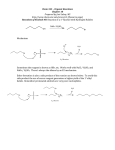
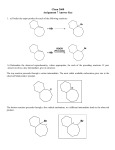
Exam 2 Chemistry 122 March 24, 2003 Do not open or begin this exam until instructed. This exam consists of 5 pages plus the cover page. Before starting the exam, check to make sure that you have all of the pages. The exam has a total of 100 points and includes 13 questions. Only legible answers written on the exam will be considered for grading. All pertinent information needed for the exam is given. Notes and textbooks are not permitted. This exam is administered under the Wake Forest Honor Code. Name_______________________________________ 1. (4 points) Provide an IUPAC name for the following molecule. Include stereochemistry in the name if necessary. OH 2. (5 points) Provide a structure of (Z)-2-bromo-3-ethyl-4-methyl-2-pentene. 3. (3 points) Provide the structure of an amine. (Do not include multiple functional groups in the molecule you draw.) 4. (3 points) Which of the following alkenes will release the most heat upon catalytic hydrogenation? 1-hexene 2,3-dimethyl-1-butene 2,3-dimethyl-2-butene 5. (5 points) What would be formed as a result of the given electron-pushing arrows? + O N O 6. (2 points) Circle the strongest acid. CH3OH BrCH2OH Br2CHOH 1 7. (4 points) Circle the strongest base in each set. a. CH3CH3 CH3OLi CH3NHNa b. CH3CH2OH CH3CH2ONa O CH3 C ONa 8. (15 points) For each of the following Bronsted-Lowry acid/base reactions a. provide products that would form if the reaction proceeds as written b. label the acid and base on each side of the reaction c. draw an arrow indicating which way the equilibrium actually lies CH3CH2C CLi + CH3CH3 (CH3CH2)2NCH3 + H2SO4 O O + F OH ONa Cl 9. (6 points) The following alcohols may look similar on paper, but they behave quite differently in acid/base reactions. One has a pKa of 10 and the other has a pKa of 16. Which compound has which pKa? In the space provided explain your reasoning. OH OH 2 10. (12 points) For each pair, circle the reaction that proceeds the fastest by the given mechanism. a. CH3OH Br OCH3 SN1 CH3OH Br OCH3 SN1 b. CH3CH2Br + NaN3 CH3CH2N3 + NaBr SN2 O CH3CH2OSCH3 O + NaN3 CH3CH2N3 + SN2 O NaOSCH3 O c. CH3CHBrCH3 + NaNH2 CH3CHBrCH3 + NaNH2 25 oC E2 75 oC E2 CH3CH=CH2 + NaBr + NH3 CH3CH=CH2 + NaBr + NH3 11. (21 points, 3 each) Provide the major organic products for each of the following reactions. Include stereochemistry where necessary. If the predominant reaction pathway is an elimination pathway, list all the alkenes that will be formed and indicate which one will be formed in highest yield. OTs + NaOCH3 CH3OH OH + HBr 3 Br D + H2 Pt 25 oC I CH3CH2OH (CH3)3COK Cl OH (CH3)3COH + O Cl S O pyridine Br + NaI acetone 12. (5 points) Provide an acceptable structure for the missing starting material. CH3I + CH3SCH2CH(CH3)2 4 13. (15 points) Provide an electron-pushing mechanism and a fully labeled reaction energy diagram for the following reaction. (Include structures at every maximum and minimum energy on the diagram.) You may assume the reaction is exothermic. Br + NaCN DMSO CN + NaBr 5