* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Different Kinds of Cells Make Up Our Bodies
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Stem-cell therapy wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
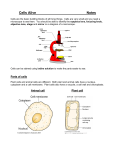
Different Kinds of Cells Make Up Our Bodies By Cindy Grigg When you were made, a tiny cell from your father joined with another tiny cell from your mother. Those cells began to divide, making new cells. First there was one cell, then it divided and there were two. Each of those cells divided, and then there were four. Each of those divided, and then there were eight. In the beginning, all of those cells looked alike. Then when those eight cells divided, the new cells began to look different from each other. Some cells became bone cells that made up your skeleton. Some became blood cells, some muscle cells. Some of those muscle cells specialized, and they became your heart muscle. Some cells became nerve cells. There are over two hundred different types of cells in your body. Each kind of cell is shaped differently because it has a different job to do. Each of these cells looks very, very different from each other. 1 On the outside of your body, you have skin cells. Skin cells protect your body by keeping out rain, dirt, and germs. Skin holds together all your separate body parts. Skin protects you from heat, cold, and sharp or hard objects. You wouldn't want to walk barefoot without skin! Skin cells stack in layers of about ten cells thick, always making new skin cells on the inside layer, and then moving outward as the cells get older and tougher. When they die, they flake off and form dust. Millions of skin cells die every day. Skin cells give people's bodies their color. Everybody's skin cells are exactly the same, except they make different amounts of two substances called melanin and carotene. These two substances give skin its color. If you go out in the sun, your skin cells make more melanin. That's what causes your skin to "tan." Too much sun is not good for skin. It can cause skin to wrinkle, and it can also cause skin cancer. 2 Because cells are alive, they need nutrients to survive. Blood cells carry nutrients and oxygen into your body. Blood looks red because of the red blood cells in it. Red blood cells look red because they have a chemical called hemoglobin in them. They are the cells that carry oxygen to your cells. Without oxygen, all your cells would die. When you breathe in, you take air into your lungs. The hemoglobin in blood gets oxygen from the lung cells and takes it through your bloodstream to all the cells in your body. Red blood cells also take the carbon dioxide out of the cells into the blood, where it goes into the lungs again and is breathed out of the body. Blood also contains white blood cells. The white blood cells are the defenders of your body. They fight bacteria and viruses that might make you sick. When your skin is injured and you have a scab, you might see the dead white blood cells under a scab that has been scratched off too soon. They look white or greenish color. They have been fighting the germs that came into your body when the skin was injured. Your body makes about one hundred fifty million (150,000,000) blood cells every minute of your life to replace the ones that die. 3 Your bones are made of cells, too. Minerals such as calcium surround the cell and make the bone hard. Bone cells make up the 206 bones in an adult's body. Our bones give our body support and protect our internal organs. Ever notice how your ribs circle around your heart and lungs? Bones also help make new cells in the bone marrow and work with our muscles to help us move. 4 Nerve cells are unusual. Some of them look like a tree with many branches. The nerve cells that control your arm and leg muscles are as wide as other cells in your body, but they may be as long as one meter! Nerve cells live a long time; some of them live as long as sixty years! Nerve cells send messages through your body to and from your brain. They work by sending tiny electrical impulses along thin parts of the cell called axons. Some nerve cells in your brain keep parts of your body working without you thinking about it, even when you are asleep. You don't have to think about making your heart beat or breathing when you are sleeping. 5 Every part of your body is made of tiny "building blocks" called cells. Your body has many other types of cells in your stomach, your intestines, your teeth, nails, and hair. Each kind of cell is different because it has a different job to do. The nerves that help you see, feel, hear, smell, and taste things are made of cells. The bones that hold your body up are made of cells. The muscles that make you move, the skin that protects your body, and the hair on your head are all made of cells. 6 Copyright © 2010 edHelper Name _____________________________ Date ___________________ Different Kinds of Cells Make Up Our Bodies 1. How many different types of cells are found in the human body? About 100 About 200 About 150,000,000 About 1,000 2. How does skin protect your body? It keeps blood inside your body. It keeps your temperature even. It keeps out rain, dirt, and germs. 3. What do your skin cells make when you go out in the sun? Melanin Sun block Carotene 4. What kind of cells takes nutrients and oxygen throughout your body? Lung cells Nerve cells Blood cells 5. What do white blood cells do? They fight bacteria and viruses. They carry oxygen. They have hemoglobin. 6. Some nerve cells may be as long as ______. A meter A centimeter A millimeter A kilometer 7. Nerve cells may live as long as ______. 8. Every part of your body is made of A year ______. 60 years Skin 6 months Cells 30 days Muscle Melanin Different Kinds of Cells Make Up Our Bodies By Cindy Grigg outward layers causes separate lung nerves support lungs wrinkle nerve carbon bloodstream ribs beginning cause layer flake skeleton began axons Directions: Fill in each blank with the word that best completes the reading comprehension. When you were made, a tiny cell from your father joined with another tiny cell from your mother. Those cells began to divide, making new cells. First there was one cell, then it divided and there were two. Each of those cells divided, and then there were four. Each of those divided, and then there were eight. In the (1) _______________________ , all of those cells looked alike. Then when those eight cells divided, the new cells (2) _______________________ to look different from each other. Some cells became bone cells that made up your (3) _______________________ . Some became blood cells, some muscle cells. Some of those muscle cells specialized, and they became your heart muscle. Some cells became (4) _______________________ cells. There are over two hundred different types of cells in your body. Each kind of cell is shaped differently because it has a different job to do. Each of these cells looks very, very different from each other. On the outside of your body, you have skin cells. Skin cells protect your body by keeping out rain, dirt, and germs. Skin holds together all your (5) _______________________ body parts. Skin protects you from heat, cold, and sharp or hard objects. You wouldn't want to walk barefoot without skin! Skin cells stack in (6) _______________________ of about ten cells thick, always making new skin cells on the inside (7) _______________________ , and then moving (8) _______________________ as the cells get older and tougher. When they die, they (9) _______________________ off and form dust. Millions of skin cells die every day. Skin cells give people's bodies their color. Everybody's skin cells are exactly the same, except they make different amounts of two substances called melanin and carotene. These two substances give skin its color. If you go out in the sun, your skin cells make more melanin. That's what (10) _______________________ your skin to "tan." Too much sun is not good for skin. It can cause skin to (11) _______________________ , and it can also (12) _______________________ skin cancer. Because cells are alive, they need nutrients to survive. Blood cells carry nutrients and oxygen into your body. Blood looks red because of the red blood cells in it. Red blood cells look red because they have a chemical called hemoglobin in them. They are the cells that carry oxygen to your cells. Without oxygen, all your cells would die. When you breathe in, you take air into your lungs. The hemoglobin in blood gets oxygen from the (13) _______________________ cells and takes it through your (14) _______________________ to all the cells in your body. Red blood cells also take the (15) _______________________ dioxide out of the cells into the blood, where it goes into the (16) _______________________ again and is breathed out of the body. Blood also contains white blood cells. The white blood cells are the defenders of your body. They fight bacteria and viruses that might make you sick. When your skin is injured and you have a scab, you might see the dead white blood cells under a scab that has been scratched off too soon. They look white or greenish color. They have been fighting the germs that came into your body when the skin was injured. Your body makes about one hundred fifty million (150,000,000) blood cells every minute of your life to replace the ones that die. Your bones are made of cells, too. Minerals such as calcium surround the cell and make the bone hard. Bone cells make up the 206 bones in an adult's body. Our bones give our body (17) _______________________ and protect our internal organs. Ever notice how your (18) _______________________ circle around your heart and lungs? Bones also help make new cells in the bone marrow and work with our muscles to help us move. Nerve cells are unusual. Some of them look like a tree with many branches. The nerve cells that control your arm and leg muscles are as wide as other cells in your body, but they may be as long as one meter! Nerve cells live a long time; some of them live as long as sixty years! Nerve cells send messages through your body to and from your brain. They work by sending tiny electrical impulses along thin parts of the cell called (19) _______________________ . Some nerve cells in your brain keep parts of your body working without you thinking about it, even when you are asleep. You don't have to think about making your heart beat or breathing when you are sleeping. Every part of your body is made of tiny "building blocks" called cells. Your body has many other types of cells in your stomach, your intestines, your teeth, nails, and hair. Each kind of cell is different because it has a different job to do. The (20) _______________________ that help you see, feel, hear, smell, and taste things are made of cells. The bones that hold your body up are made of cells. The muscles that make you move, the skin that protects your body, and the hair on your head are all made of cells. Copyright © 2010 edHelper Name _____________________________ Date ___________________ Different Kinds of Cells Make Up Our Bodies 1. How many different types of cells are found in the human body? About 1,000 About 100 About 150,000,000 About 200 2. How does skin protect your body? It keeps out rain, dirt, and germs. It keeps blood inside your body. It keeps your temperature even. 3. What do your skin cells make when you go out in the sun? Sun block Carotene Melanin 4. What kind of cells takes nutrients and oxygen throughout your body? Blood cells Lung cells Nerve cells 5. What do white blood cells do? They carry oxygen. They have hemoglobin. They fight bacteria and viruses. 6. Some nerve cells may be as long as ______. A meter A kilometer A centimeter A millimeter 7. Nerve cells may live as long as ______. 8. Every part of your body is made of A year ______. 60 years Muscle 6 months Cells 30 days Melanin Skin Name _____________________________ Date ___________________ (Key 1 - Answer ID # 1066650) Crack the code! Write the real word that each of the codes represent. Each letter in the real word has been changed to another letter. For example, a B in the code might really mean C. Once you figure out the code for one letter, the same code is used for all the words on this sheet. Code: A C D E F G I J K M N O P Q R U V W Y Z B R G A O Letter: 1. DKIOCOE 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. APEMCARZ DKGGWIY MEZRJCJ RNWJD DVEZEYWJ KJKDKRZ MCZZCWJ FEQCJJCJQ UZRVE Different Kinds of Cells Make Up Our Bodies - Answer Key 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 About 200 It keeps out rain, dirt, and germs. Melanin Blood cells They fight bacteria and viruses. A meter 60 years Cells Different Kinds of Cells Make Up Our Bodies By Cindy Grigg Answer Key When you were made, a tiny cell from your father joined with another tiny cell from your mother. Those cells began to divide, making new cells. First there was one cell, then it divided and there were two. Each of those cells divided, and then there were four. Each of those divided, and then there were eight. In the (1) beginning , all of those cells looked alike. Then when those eight cells divided, the new cells (2) began to look different from each other. Some cells became bone cells that made up your (3) skeleton . Some became blood cells, some muscle cells. Some of those muscle cells specialized, and they became your heart muscle. Some cells became (4) nerve cells. There are over two hundred different types of cells in your body. Each kind of cell is shaped differently because it has a different job to do. Each of these cells looks very, very different from each other. On the outside of your body, you have skin cells. Skin cells protect your body by keeping out rain, dirt, and germs. Skin holds together all your (5) separate body parts. Skin protects you from heat, cold, and sharp or hard objects. You wouldn't want to walk barefoot without skin! Skin cells stack in (6) layers of about ten cells thick, always making new skin cells on the inside (7) layer , and then moving (8) outward as the cells get older and tougher. When they die, they (9) flake off and form dust. Millions of skin cells die every day. Skin cells give people's bodies their color. Everybody's skin cells are exactly the same, except they make different amounts of two substances called melanin and carotene. These two substances give skin its color. If you go out in the sun, your skin cells make more melanin. That's what (10) causes your skin to "tan." Too much sun is not good for skin. It can cause skin to (11) wrinkle , and it can also (12) cause skin cancer. Because cells are alive, they need nutrients to survive. Blood cells carry nutrients and oxygen into your body. Blood looks red because of the red blood cells in it. Red blood cells look red because they have a chemical called hemoglobin in them. They are the cells that carry oxygen to your cells. Without oxygen, all your cells would die. When you breathe in, you take air into your lungs. The hemoglobin in blood gets oxygen from the (13) lung cells and takes it through your (14) bloodstream to all the cells in your body. Red blood cells also take the (15) carbon dioxide out of the cells into the blood, where it goes into the (16) lungs again and is breathed out of the body. Blood also contains white blood cells. The white blood cells are the defenders of your body. They fight bacteria and viruses that might make you sick. When your skin is injured and you have a scab, you might see the dead white blood cells under a scab that has been scratched off too soon. They look white or greenish color. They have been fighting the germs that came into your body when the skin was injured. Your body makes about one hundred fifty million (150,000,000) blood cells every minute of your life to replace the ones that die. Your bones are made of cells, too. Minerals such as calcium surround the cell and make the bone hard. Bone cells make up the 206 bones in an adult's body. Our bones give our body (17) support and protect our internal organs. Ever notice how your (18) ribs circle around your heart and lungs? Bones also help make new cells in the bone marrow and work with our muscles to help us move. Nerve cells are unusual. Some of them look like a tree with many branches. The nerve cells that control your arm and leg muscles are as wide as other cells in your body, but they may be as long as one meter! Nerve cells live a long time; some of them live as long as sixty years! Nerve cells send messages through your body to and from your brain. They work by sending tiny electrical impulses along thin parts of the cell called (19) axons . Some nerve cells in your brain keep parts of your body working without you thinking about it, even when you are asleep. You don't have to think about making your heart beat or breathing when you are sleeping. Every part of your body is made of tiny "building blocks" called cells. Your body has many other types of cells in your stomach, your intestines, your teeth, nails, and hair. Each kind of cell is different because it has a different job to do. The (20) nerves that help you see, feel, hear, smell, and taste things are made of cells. The bones that hold your body up are made of cells. The muscles that make you move, the skin that protects your body, and the hair on your head are all made of cells. Answers to Reading Comprehension Questions 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 About 200 It keeps out rain, dirt, and germs. Melanin Blood cells They fight bacteria and viruses. A meter 60 years Cells Answer Key 1066650 Key # 1 Crack the code! Write the real word that each of the codes represent. Each letter in the real word has been changed to another letter. For example, a B in the code might really mean C. Once you figure out the code for one letter, the same code is used for all the words on this sheet. Code: A C D E F G I J K M N O P Q R U V W Y Z Letter: C I S E B P R N U M X V H G A F K O T L 1. DKIOCOE 2. APEMCARZ 3. DKGGWIY SUPPORT 4. MEZRJCJ MELANIN 5. RNWJD 6. DVEZEYWJ 7. KJKDKRZ UNUSUAL 8. MCZZCWJ MILLION 9. FEQCJJCJQ 10. UZRVE SURVIVE CHEMICAL AXONS SKELETON BEGINNING FLAKE