LIEDER Prepared Microscope Slides Multimedia
... LIEDER prepared microscope slides are made in our laboratories under scientific control. They are the product of long experience in all spheres of preparation techniques. Microtome sections are cut by highly skilled staff, cutting technique and thickness of the sections are adjusted to the objects. ...
... LIEDER prepared microscope slides are made in our laboratories under scientific control. They are the product of long experience in all spheres of preparation techniques. Microtome sections are cut by highly skilled staff, cutting technique and thickness of the sections are adjusted to the objects. ...
- studijní a informační středisko vfu brno
... the first meiotic division and become primary oocytes which are diploid (period of growth). They become arrested at the diplotene phase. A primary oocyte surrounded by a single layer of squamous follicular cells is known as a primordial follicle. The primordial follicles present the pool of quiescen ...
... the first meiotic division and become primary oocytes which are diploid (period of growth). They become arrested at the diplotene phase. A primary oocyte surrounded by a single layer of squamous follicular cells is known as a primordial follicle. The primordial follicles present the pool of quiescen ...
Introduction
... in the space provided for observations and documentation or in your notebook. The sequence of different observations is indicated by numbers 1,2,3 etc. Record observations in the correct sequence. Try noting down the observations then and there instead of doing it later. Draw the diagrams as you act ...
... in the space provided for observations and documentation or in your notebook. The sequence of different observations is indicated by numbers 1,2,3 etc. Record observations in the correct sequence. Try noting down the observations then and there instead of doing it later. Draw the diagrams as you act ...
Unit 2 Key areas
... 3. identify different structural features of specialised plant cells. 4. identify different structural features of specialised animal cells. 5. relate the structure of cells to their function. 6. identify tissues and organs from the specialised cells that make them. ...
... 3. identify different structural features of specialised plant cells. 4. identify different structural features of specialised animal cells. 5. relate the structure of cells to their function. 6. identify tissues and organs from the specialised cells that make them. ...
Lec 06 - Development of e
... differences among them exposed hereunder. Differentiation: The term differentiation is used in many different senses in biology. In broad sense, it is defined as the process by which meristematic cells are converted into two or more types of cells, tissues or organs which are qualitatively different ...
... differences among them exposed hereunder. Differentiation: The term differentiation is used in many different senses in biology. In broad sense, it is defined as the process by which meristematic cells are converted into two or more types of cells, tissues or organs which are qualitatively different ...
AQA GCSE (9-1)
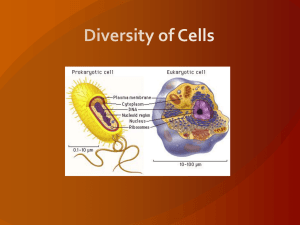
... Overview of the unit In this unit, students will learn about the structure of plant, animal, prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms, and the functions of major structures. They will compare the level of detail revealed by light and electron microscopes, calculating magnifications. Students will descri ...
... Overview of the unit In this unit, students will learn about the structure of plant, animal, prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms, and the functions of major structures. They will compare the level of detail revealed by light and electron microscopes, calculating magnifications. Students will descri ...
Different Kinds of Cells Make Up Our Bodies
... Nerve cells are unusual. Some of them look like a tree with many branches. The nerve cells that control your arm and leg muscles are as wide as other cells in your body, but they may be as long as one meter! Nerve cells live a long time; some of them live as long as sixty years! Nerve cells send mes ...
... Nerve cells are unusual. Some of them look like a tree with many branches. The nerve cells that control your arm and leg muscles are as wide as other cells in your body, but they may be as long as one meter! Nerve cells live a long time; some of them live as long as sixty years! Nerve cells send mes ...
Licensed to: iChapters User
... cells, nerve cells, and gland cells. Each human organism begins when an egg and sperm unite to form a single new cell, which multiplies and forms a growing mass through myriad cell divisions. If cell multiplication were the only process involved in development, all the body cells would be essentiall ...
... cells, nerve cells, and gland cells. Each human organism begins when an egg and sperm unite to form a single new cell, which multiplies and forms a growing mass through myriad cell divisions. If cell multiplication were the only process involved in development, all the body cells would be essentiall ...
Chordate ancestry of the neural crest: New insights from ascidians
... migrate singly rather than in streams. During migration they are morphologically distinct from any other cell in the larva [46]. Three migratory pathways were detected (Fig. 3G–J): (1) anterior toward the oral siphon primordium, (2) posterior toward the anal siphon primordium, and (3) ventral into t ...
... migrate singly rather than in streams. During migration they are morphologically distinct from any other cell in the larva [46]. Three migratory pathways were detected (Fig. 3G–J): (1) anterior toward the oral siphon primordium, (2) posterior toward the anal siphon primordium, and (3) ventral into t ...
Using food and controlling growth - Delivery guide
... This section can prove to be quite difficult for some learners to understand so using models, videoclips, animations and diagrams will be useful. There are a number of learning objectives that are a series of sequential steps such as those found in mitosis and the formation of cancers. Activities in ...
... This section can prove to be quite difficult for some learners to understand so using models, videoclips, animations and diagrams will be useful. There are a number of learning objectives that are a series of sequential steps such as those found in mitosis and the formation of cancers. Activities in ...
Malaysian Guidelines for Stem Cell Research and Therapy
... tract plus various accessory organs like the lungs and liver. Much of the proposed research on stem cells centers upon the early human embryo. ...
... tract plus various accessory organs like the lungs and liver. Much of the proposed research on stem cells centers upon the early human embryo. ...
DEVELOPMENT OF MESODERM,
... At the end of lecture students should be able to know, What is gastrulation. Development of mesoderm. Somitogenesis. Formation of cartilage. ...
... At the end of lecture students should be able to know, What is gastrulation. Development of mesoderm. Somitogenesis. Formation of cartilage. ...
GCSE Biology Textbook sample
... HOW DO WE DEVELOP INTO A COMPLEX ORGANISM FROM JUST A FERTILISED EGG CELL? • The body’s cells divide and the newly formed cells are identical to the existing cells. • Cells differentiate to become specialised, and specialised cells are organised. • When cell division accelerates out of control, ...
... HOW DO WE DEVELOP INTO A COMPLEX ORGANISM FROM JUST A FERTILISED EGG CELL? • The body’s cells divide and the newly formed cells are identical to the existing cells. • Cells differentiate to become specialised, and specialised cells are organised. • When cell division accelerates out of control, ...
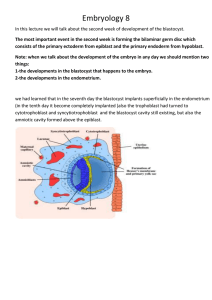
Embryology 8
... Trophoblastic lacunae will be formed at abembryonic pole and the syncytiotrophoblast will penetrate large area of the endometrium ,also the dilated and encouraged blood vessels grow up to maternal sinusoids at the embryonic pole Sinusoids: large spaces filled with maternal bloods in the endometrium ...
... Trophoblastic lacunae will be formed at abembryonic pole and the syncytiotrophoblast will penetrate large area of the endometrium ,also the dilated and encouraged blood vessels grow up to maternal sinusoids at the embryonic pole Sinusoids: large spaces filled with maternal bloods in the endometrium ...
Leukaemia Section Chronic myelogenous leukaemia (CML) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... haematological relapse; 2-The most primitive stem cells seem to be resistant to IM therapy at least in vitro ; 3-The resistance to IM-therapy has been found to be associated, especially in patients who received it as second line treatment, with the occurrence of mutations in the ABL-kinase domain, i ...
... haematological relapse; 2-The most primitive stem cells seem to be resistant to IM therapy at least in vitro ; 3-The resistance to IM-therapy has been found to be associated, especially in patients who received it as second line treatment, with the occurrence of mutations in the ABL-kinase domain, i ...
Slides - Workforce Development in Stem Cell Research
... from the morula 2. ES cells are normally derived from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst 3. ES cells can be derived from primordial germ cells ...
... from the morula 2. ES cells are normally derived from the inner cell mass of the blastocyst 3. ES cells can be derived from primordial germ cells ...
Organism: Homo sapiens sapiens http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki
... Blastula develops into a tube shaped "trochophore" larva, mouth forming FIRST. Bilateral symmetry (you could draw a line down the middle). Has a head and tail. Chitinous cuticle as an exoskeleton. Sheds the cuticle as it grows larger. Coelem partially formed. Most of the inside is called a haemocoel ...
... Blastula develops into a tube shaped "trochophore" larva, mouth forming FIRST. Bilateral symmetry (you could draw a line down the middle). Has a head and tail. Chitinous cuticle as an exoskeleton. Sheds the cuticle as it grows larger. Coelem partially formed. Most of the inside is called a haemocoel ...
Question paper - Unit B731/02 - Modules B1, B2, B3 - Higher
... Your quality of written communication is assessed in questions marked with a pencil ( The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. The total number of marks for this paper is 75. This document consists of 24 pages. Any blank pages are indicated. ...
... Your quality of written communication is assessed in questions marked with a pencil ( The number of marks is given in brackets [ ] at the end of each question or part question. The total number of marks for this paper is 75. This document consists of 24 pages. Any blank pages are indicated. ...
Platyhelminthes
... Members of the phylum Platyhelminthes are dorsoventrally flattened with body composed of three different tissue layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and the mesoderm. These animals are bilaterally symmetrical. This phylum demonstrates an organ-system level of organization. The front or anterior portion of th ...
... Members of the phylum Platyhelminthes are dorsoventrally flattened with body composed of three different tissue layers: ectoderm, endoderm, and the mesoderm. These animals are bilaterally symmetrical. This phylum demonstrates an organ-system level of organization. The front or anterior portion of th ...
Primer - Workforce Development in Stem Cell Research
... precursors begin to acquire cardiogenic potential (i.e. the ability to become heartproducing cells), they begin to express two important transcription factors (i.e. DNA binding proteins): Nkx2.5 and Isl1. Progenitor cells that will give rise to the left ventricle are called the 1st heart field proge ...
... precursors begin to acquire cardiogenic potential (i.e. the ability to become heartproducing cells), they begin to express two important transcription factors (i.e. DNA binding proteins): Nkx2.5 and Isl1. Progenitor cells that will give rise to the left ventricle are called the 1st heart field proge ...
Implantation2008-11-04 07:213.1 MB
... (blastocele) appears inside morula Blastomeres are separated into: Outer cell layer, the trophoblast, which gives rise to embryonic part of placenta Centrally located, inner cell mass (embryoblasts) which gives rise to embryo ...
... (blastocele) appears inside morula Blastomeres are separated into: Outer cell layer, the trophoblast, which gives rise to embryonic part of placenta Centrally located, inner cell mass (embryoblasts) which gives rise to embryo ...
File
... 5. Ahmad has to make a model of body tissue. He knows that a body tissue is made up of many cells that have specific characteristics. Which of the following statements describes the characteristics of the cells that make up a tissue? F. The cells have similar structures and similar ...
... 5. Ahmad has to make a model of body tissue. He knows that a body tissue is made up of many cells that have specific characteristics. Which of the following statements describes the characteristics of the cells that make up a tissue? F. The cells have similar structures and similar ...
Stem cell

Stem cells are undifferentiated biological cells that can differentiate into specialized cells and can divide (through mitosis) to produce more stem cells. They are found in multicellular organisms. In mammals, there are two broad types of stem cells: embryonic stem cells, which are isolated from the inner cell mass of blastocysts, and adult stem cells, which are found in various tissues. In adult organisms, stem cells and progenitor cells act as a repair system for the body, replenishing adult tissues. In a developing embryo, stem cells can differentiate into all the specialized cells—ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm (see induced pluripotent stem cells)—but also maintain the normal turnover of regenerative organs, such as blood, skin, or intestinal tissues.There are three known accessible sources of autologous adult stem cells in humans: Bone marrow, which requires extraction by harvesting, that is, drilling into bone (typically the femur or iliac crest). Adipose tissue (lipid cells), which requires extraction by liposuction. Blood, which requires extraction through apheresis, wherein blood is drawn from the donor (similar to a blood donation), and passed through a machine that extracts the stem cells and returns other portions of the blood to the donor.Stem cells can also be taken from umbilical cord blood just after birth. Of all stem cell types, autologous harvesting involves the least risk. By definition, autologous cells are obtained from one's own body, just as one may bank his or her own blood for elective surgical procedures.Adult stem cells are frequently used in medical therapies, for example in bone marrow transplantation. Stem cells can now be artificially grown and transformed (differentiated) into specialized cell types with characteristics consistent with cells of various tissues such as muscles or nerves. Embryonic cell lines and autologous embryonic stem cells generated through Somatic-cell nuclear transfer or dedifferentiation have also been proposed as promising candidates for future therapies. Research into stem cells grew out of findings by Ernest A. McCulloch and James E. Till at the University of Toronto in the 1960s.