* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DEVELOPMENT OF MESODERM,
Retinal waves wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Bone morphogenetic protein 4 wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Somatic cell nuclear transfer wikipedia , lookup
Paolo Macchiarini wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
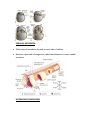
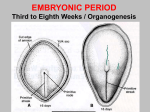
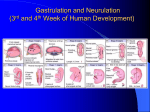
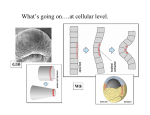
DEVELOPMENT OF MESODERM, PARAXIAL MESODERM AND SCLEROMYOTOME AND FORMATION OF CARTILAGES LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of lecture students should be able to know, What is gastrulation. Development of mesoderm. Somitogenesis. Formation of cartilage. GASTRULATION( Week 3-8) • Gastulation is the process which establishes the formation of three germ layered embryo: – Ectoderm – Mesoderm – Endoderm • Formation of trilaminar embryonic disc by day 21. THE THREE GERM LAYERS The three germ layers are the derivatives of epiblast The three germ layers give rise to all the tissues and organs of the body. DEVELOPMENT OF MESODERM Paraxial mesoderm Intermediate mesoderm Lateral mesoderm PARAXIAL MESODERM Thick plate of mesoderm located on each side of midline Becomes organized into segments called somatomeres in cranio-caudal sequence. INTERMEDIATE MESODERM Longitudinal dorsal ridge of mesoderm located between paraxial and lateral mesoderm This ridge forms the Urogenital ridge Urogenital ridge forms the future kidneys and gonads LATERAL MESODERM Thin plate of mesoderm located along the lateral side of embryo. Large spaces develop in the lateral plate mesoderm and coalesce to form intraembryonic coelom Intraembryonic coelom divides lateral mesoderm into: Intraembryonic somatic mesoderm Intraembryonic visceral mesoderm SOMITOGENESIS Process of segmentation development of axial system vertebrae, muscles and innervations. Somites form from paraxial mesoderm in anterior-posterior gradient, begins at neurulation. Two parallel columns of mesodermal cells form along the longitudinal axis, on each side of the notochord and neural tube. Transverse fissures form in the columns forming somitomeres in cranio caudal direction. SOMITOMERES Somitomere 1-7 do not form somites, but contribute mesoderm to pharyngeal arches The remaining somitomeres condense in cranio-caudal sequence forming 41-42 pairs of somites. SOMITES Somites differentialte into: Sclerotome Forms cartilage and bone component of veebral column Myotome Forms epimeric and hypomeric muscles Dermatome Forms dermis and subcutaneous area of skin SUMMARY OF MESODERMAL DEVELOPMENT FORMATION OF CARTILAGE Cartilage is derived from mesenchyme Avascular mesenchyme contains stem cells embedded in a delicate collagen matrix CHONDROBLAST Mesenchyme cells begin to differentiate into protochondral cells Protochondral cells divide to produce chondroblasts CARTILAGE DEVELOPMENT The center fills with chondroblasts as the top and bottom edges continue to differentiate. Stem cells remain on the edges Chondroblasts remain in the center and produce cartilage matrix. Stem cells at the edges produce fibroblasts and make the fibrous perichondrium Chondroblasts in the center continue to divide THANK YOU