Specialized Plant and Animal Cells
... Process whereby a body part is replaced or re-grown through the process of mitosis The liver is the only human organ that can naturally regenerate Research continues in the field of regeneration of organs ...
... Process whereby a body part is replaced or re-grown through the process of mitosis The liver is the only human organ that can naturally regenerate Research continues in the field of regeneration of organs ...
What are Stem Cells? - Science and Today`s Headlines
... cells in the development of a human being. They have an amazing ability to develop into multiple different cell types and they can remain, without a specific function, in the human body. These cells can also regenerate and repair organs at an unlimited rate. The fact that these cells can develop int ...
... cells in the development of a human being. They have an amazing ability to develop into multiple different cell types and they can remain, without a specific function, in the human body. These cells can also regenerate and repair organs at an unlimited rate. The fact that these cells can develop int ...
stem cell
... potential to become any type of cell. Under the proper conditions the stem cells can become specialized cells. The ability to direct stem cell development could help to treat many injuries and diseases. ...
... potential to become any type of cell. Under the proper conditions the stem cells can become specialized cells. The ability to direct stem cell development could help to treat many injuries and diseases. ...
N5- Unit 2 MO1-Cells, tissues, organs, stem cells and meristems 1
... Adaptations: contains haemoglobin to carry oxygen, large surface area to allow diffusion, flexible to go through capillaries. 7.What are stem cells? 8. What can happen to a stem cell went it divides? 9. What are stems cells needed for? 10. Give examples of the use of stem cells in medicine 11. What ...
... Adaptations: contains haemoglobin to carry oxygen, large surface area to allow diffusion, flexible to go through capillaries. 7.What are stem cells? 8. What can happen to a stem cell went it divides? 9. What are stems cells needed for? 10. Give examples of the use of stem cells in medicine 11. What ...
Biology Review
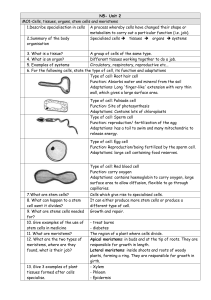
... 12. Identify these specialized cells from the descriptions of their functions (p.55). Cells that move bones Cells that cover the body and help keep moisture inside Cells that distribute oxygen and remove carbon dioxide Cells that transmit electrical signals from the brain ...
... 12. Identify these specialized cells from the descriptions of their functions (p.55). Cells that move bones Cells that cover the body and help keep moisture inside Cells that distribute oxygen and remove carbon dioxide Cells that transmit electrical signals from the brain ...
View Press Release
... neurogenesis. Neuronascent's scientists aim to enhance neurogenesis to promote greater numbers of mature neurons that will subsequently promote cognitive improvement in patients with Alzheimer's disease, stroke or depression. Neuronascent has laboratories in Rockville and Walkersville, Maryland. Int ...
... neurogenesis. Neuronascent's scientists aim to enhance neurogenesis to promote greater numbers of mature neurons that will subsequently promote cognitive improvement in patients with Alzheimer's disease, stroke or depression. Neuronascent has laboratories in Rockville and Walkersville, Maryland. Int ...
PowerPoint #1
... Stem cell research for Type I Diabetes: The end goal of researchers in this field is to differentiate stem cells into glucose-responsive, insulin-producing pancreatic ß cells. It is hoped that these cells will be able to replace pancreatic ß cells that are destroyed in T1D, which would be the ideal ...
... Stem cell research for Type I Diabetes: The end goal of researchers in this field is to differentiate stem cells into glucose-responsive, insulin-producing pancreatic ß cells. It is hoped that these cells will be able to replace pancreatic ß cells that are destroyed in T1D, which would be the ideal ...
Ch 10 Cell Growth and Division
... stage of development most multicellular organisms pass through ...
... stage of development most multicellular organisms pass through ...
Document
... Where are embryonic stem cells found? How does their ability to differentiate change ...
... Where are embryonic stem cells found? How does their ability to differentiate change ...
Biology 10.3 and 10.4 Review
... Totipotent: Able to become all cells Pluripotent: Able to become most cells Multipotent: Able to become few cells B. Come up with an easy way to remember these terms. Toti = total = all Pluri = plural/plethora = many/most Multi = multiples = few ...
... Totipotent: Able to become all cells Pluripotent: Able to become most cells Multipotent: Able to become few cells B. Come up with an easy way to remember these terms. Toti = total = all Pluri = plural/plethora = many/most Multi = multiples = few ...
Slide 1
... Direct microinjection of a chosen gene construct from another member of the same species or from a different species, into the pronucleus of a fertilized ovum. ...
... Direct microinjection of a chosen gene construct from another member of the same species or from a different species, into the pronucleus of a fertilized ovum. ...
Stem cell

Stem cells are undifferentiated biological cells that can differentiate into specialized cells and can divide (through mitosis) to produce more stem cells. They are found in multicellular organisms. In mammals, there are two broad types of stem cells: embryonic stem cells, which are isolated from the inner cell mass of blastocysts, and adult stem cells, which are found in various tissues. In adult organisms, stem cells and progenitor cells act as a repair system for the body, replenishing adult tissues. In a developing embryo, stem cells can differentiate into all the specialized cells—ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm (see induced pluripotent stem cells)—but also maintain the normal turnover of regenerative organs, such as blood, skin, or intestinal tissues.There are three known accessible sources of autologous adult stem cells in humans: Bone marrow, which requires extraction by harvesting, that is, drilling into bone (typically the femur or iliac crest). Adipose tissue (lipid cells), which requires extraction by liposuction. Blood, which requires extraction through apheresis, wherein blood is drawn from the donor (similar to a blood donation), and passed through a machine that extracts the stem cells and returns other portions of the blood to the donor.Stem cells can also be taken from umbilical cord blood just after birth. Of all stem cell types, autologous harvesting involves the least risk. By definition, autologous cells are obtained from one's own body, just as one may bank his or her own blood for elective surgical procedures.Adult stem cells are frequently used in medical therapies, for example in bone marrow transplantation. Stem cells can now be artificially grown and transformed (differentiated) into specialized cell types with characteristics consistent with cells of various tissues such as muscles or nerves. Embryonic cell lines and autologous embryonic stem cells generated through Somatic-cell nuclear transfer or dedifferentiation have also been proposed as promising candidates for future therapies. Research into stem cells grew out of findings by Ernest A. McCulloch and James E. Till at the University of Toronto in the 1960s.