* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Unit Interactive Notes
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
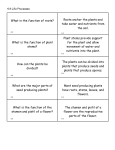
Plant Unit Interactive Notes Plant Unit Table of Contents….6 Illustrations: Parts of a Plant….7 Notes: Parts of a Plant….8 Illustrations: Seeds and Spores….9 Notes: Seeds and Spores…10 Illustrations: Parts of a Flower….11 Notes: Parts of a Flower….12 Illustrations: Pollination and Fertilization….13 Notes: Pollination and Fertilization….14 Illustrations: Photosynthesis….15 Notes: Photosynthesis….16 Illustrations: Plant Adaptations….17 Notes: Plant Adaptations….18 Parts of a Plant Have you ever thought about how a plant works? Usually we just look at a plant and think it looks pretty, but we don’t think about its parts. Green plants have 4 basic anatomical structures that help it survive. First, the plant needs a way to get nourishment. Roots anchor the plant in the ground and take water and nutrients from the soil. Second, the plant needs something to help it stand up straight and move water to the rest of the plant. The stem supports the plant and allows water and nutrients to move to all the other parts of the plant. Next, the plant needs a place to make its food. The leaf is like the kitchen of the plant. This is where the plant makes the sugars that it uses as food. Finally, the plant needs a way to make new plants. Plant reproduction takes place in the flower of the plant. Seeds and Spores Plants can be divided into two groups: those that produce seeds and those that produce spores. A seed is an undeveloped plant with stored food sealed in a protective covering. This package has a hard shell that protects the tiny plant and is called the seed coat. Inside of the seed is an undeveloped baby plant, or embryo. The embryo is surrounded by food for the new plant to use that that it can begin to grow its first root, stem, and leaves. Seeds can grow into small plants, with roots, stems, leaves, and flowers, when given water and light. Some plants do not bloom, or grow flowers. Since these plants do not grow flowers, they do not have a way to make seeds. Instead, they make spores. Each spore is produced by just one plant. Spores are formed in tiny sacks on the leaves and stems of plants. Spores are different from seeds in many ways. Spores are smaller than even the smallest seed. Spores do not have a hard shell outside. They also do not have a little plant or food for it inside. But spores are like seeds in one way… they can grow into new plants. Ferns, mosses, and mushrooms grow from spores. Parts of a Flower Have you ever taken apart a flower? If you have you may have noticed that it has many different parts. These parts work together to help the flower make seeds. The bottom of the flower is covered by the sepals. The sepals are the small leaves that protect the developing flower. Most people love the flower’s petals the best. The petals are the colorful part of the flower. Their function is to attract birds and insects to the flower for pollination. The pistil is a single stalk in the center part of the flower. It is the female reproductive part of the flower. At the top of the pistil is the stigma. The stigma is the sticky, top part of the pistil that the pollen sticks to. Located at the bottom of the pistil is the seed. The seed is the undeveloped plant with stored food sealed in a protective covering. The stamen are the skinny stalks that surround the pistil. They are the male reproductive part of the flower. In the stamen, pollen is made. Pollination and Fertilization The reproductive process of flowering plants, pollination, is how new plants are made. How does pollination happen? Well, let’s find out! First, birds and bees are attracted to the beautifully, brightly colored petals. They fly over to the petals and drink the sweet nectar in the flower. While they are drinking the sweet nectar, pollen from the stamen gets onto various parts of the bee’s or bird’s body. Second, the bee or the bird travels to another flower (of the same kind) or remains at the same flower. While they continue looking for more sweet nectar, they rub against the stigma, rubbing pollen off of their bodies and onto the stigma. Third, the pollen travels from the stigma, down the pistil, to the seed. Fourth, fertilization takes place when the pollen gets inside the seed. The seed, now fertilized, becomes an embryo. With the right conditions, the embryo grows into a new plant. Photosynthesis Like all living things, you eat food and drink water to get energy. However, plants make their own food. This food making process for plants is called photosynthesis. First, sunlight shines down on the plant. The green leaves of the plant contain cells of chlorophyll. This chlorophyll makes leaves green and traps the sunlight to be used during the process. Second, energy from the sunlight is used to mix the water (that traveled to the leaf through the stem) and carbon dioxide (the gas in the air that plants need to breathe, which gets into the air because humans and animals breathe it out) within the leaf. Third, once the mixing of the water and carbon dioxide is done, what is left is sugar (plant food) and oxygen (gas that humans need to breathe). Fourth, the sugar is carried to all parts of the plant for food. This is the same sugary taste found in fruit. The oxygen is released into the air for humans and animals to breathe in. Plant Adaptations Plants, like animals and humans, make adaptations during their lifetime. An adaptation is a change that occurs to make sure a living thing survives. A common plant adaptation is dormancy. Think about your yard in the winter. The grass is brown and dry and the trees are bare and leafless. Are they dead? No! They are in a state called dormancy. The word dormancy comes from the French word dormir, which means to sleep. When some plants do not have the right conditions for making food and growing, they go into a state of dormancy, meaning they go to sleep. When environmental conditions change, they start making their own food and growing again. Sometimes plants go dormant in the summer. Think about your lawn. Sometimes it becomes brown and dry and stops growing even though it is summer. This is because it is not getting enough water to make its food. However, once it rains again and the lawn gets enough water, it will make its own food again and turn bright green. Your lawn wasn’t dead. It was dormant!