* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit Genetics Test Review
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
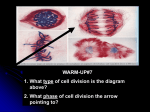
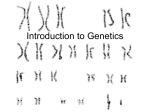
Name _____________________________ Unit Genetics Test Review 1. Heterozygous – 2 different alleles for a trait. Homozygous – 2 identical alleles for a trait 2. What are hybrids? The offspring from crosses between parents with different traits are hybrids 3. What are the offspring of the F1 generation called? F2 4. Genes are chemical factors that determine traits. The different forms of a gene are called Alleles 5. The physical appearance of an organism is its phenotype 6. Define each: a) Principle of Dominance - some alleles are dominant and some are recessive b) Principle of Independent Assortment - the alleles for different genes usually segregated independently of one another (i.e. hair color and eye color are not linked together) c) Principle of Segregation - in most sexually reproducing organisms, each adult has two copies of each gene. These genes are segregated from each other when gametes are formed. 7. When Mendel crossed true-breeding tall plants with true-breeding short plants, all the offspring of the F1 generation were tall and the alleles for tall plants are dominant (heterozygous) 8. If blue eyes are recessive, how many alleles for that trait does a person have to have in order to have blue eyes? 2 9. when you roll a dice, what is probability of getting either a 2 or a 6? (which rule will you apply – addition or multiplication) . 1/3 10. What is the probability of getting tails 4 times in a row when you flip a coin? (which rule will you apply – addition or multiplication)1/16 11. What is the probability it will tails on the 5th flip as a separate event. 1/2 12. What is incomplete dominance? Give an example. where one allele is not completely dominant over another; the heterozygous phenotype is in between the two homozygous (parents) phenotypes. Mirabilis plants (red flower X white flower = pink flower) 13. What is codominance? Give an example both alleles are expressed. Roan colored cattle. 14. Give an example of a polygenic trait Wide range of skin color in humans and multiple alleles human genes for blood type 15. Cells that contain only one set of chromosomes (i.e. sex cells/gametes) are said to be haploid. 16. Cells that contain two sets of chromosomes (i.e. somatic cells) are said to be diploid 17. If an organism’s diploid number is 90, what is its haploid number?45 18. What process cuts chromosome number in ½ and produces gametes? meiosis 19. List four differences between mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis Meiosis All somatic cells Only sex cells 2 daughter cells – exactly identical to each other and parent cell 4 daughter cells – genetically different from each other and parent cell # of chromosomes remains same Diploid Diploid 4 phases # of chromosomes is cut in half Diploidhaploid 8 phases 20. For an organism with a diploid number of 4 (2n=4), draw all 8 steps of meiosis? 21. What is shown in following figure on the right? Chromosomes exchange portion of chromatids (alleles) “crossing over” 22. Between what genes will crossing over most likely occur on a gene map? Genes that are farther apart are more likely to be separated by a crossover in meiosis. 23. Meiosis results in production of gametes in males and females. Label (in the above diagrams), which cells are haploid and which cells are diploid. 24. A corresponding pair of maternal and paternal chromosomes (from each parent) in a human karyotype that are of the same length and have genes for the same trait at the same loci is called homologous. 25. How many chromosomes are shown in a normal human karyotype 46 26. What are all the chromosomes EXCEPT the sex chromosomes called? Autosomes What are the sex chromosomes for males? XYAnd Females? XX 27. What is the gender of the person in the karyotype in the picture above male 28. Male diploid cell = 46XY Sperm = 23X or 23Y Sperm are haploid. 50 % of sperm carry X chromososme and 50 % of sperm carry Y chromosome. 29. What chromosomal disorder is present in the karyotype above - Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome) Explain what causes it. Nondisjunction - failure of one or more homologous chromosomes (pairs) to separate during meiosis. 30. In a pedigree, what does a shaded circle represent? Female with a trait or disorder This pedigree shows inheritance of the hemophilia (a sex linked trait) XH = normal Xh = hemophiliac 31. How many males in this pedigree are hemophiliac? 10 32. Carrier female(s) are not shaded in the diagram. Is queen Victoria a carrier? Yes 33. What is a genotype of Beatrice - XH Xh or XH XH Study your notes, labs, and assignments and read chapter 11 & 14 from the book. Study from the genetics problems packet. Be able to do Punnett sq - monohybrid, dihybrid, incomplete, codominance, sex linked and give the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring.