* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Organic Families: Summary Chart
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
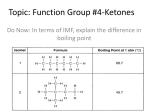
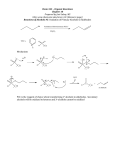
Organic Families: Summary Chart Organic Family Hydrocarbons o Alkanes (single-bond) o Alkenes (double-bond) o Alkynes (triple-bond) Alcohols Structural Formula(s) Properties The more C atoms present, the harder it is to break the bonds. The more C atoms, the higher the boiling point. Alkenes and alkynes are more reactive than alkanes due to their double/triple bonds (unsaturated). Presence of OH group makes alcohol more polar than hydrocarbons. Therefore, boiling point is considerably higher than boiling points of comparable alkanes. Commercial Uses Crude oil extracted from petroleum: - gasoline & fuel - kerosene - plastics - waxes (eg. candles) - asphalt for roads - liquors (ethanol) - rubbing alcohol - car antifreeze The longer the molecule, the higher the boiling point. Ethers Combust with O2 to form CO2 and H2O. Presence of O atom makes them more polar than hydrocarbons, but ethers are less polar than alcohols. Boiling points are higher than hydrocarbons but less than alcohols. - anaesthetic - insectides and fumigants Organic Family Structural Formula(s) Properties Lower boiling points than alcohols of similar sizes, due to presence of O atom. Aldehydes Commercial Uses Smaller aldehydes: - antiseptics - disinfectants - preservatives Larger aldehydes: - essential oils Lower boiling points than alcohols of similar sizes, due to presence of O atom. - nail polish remover (acetone) - pheromones Ketones Carboxylic Acids Esters Turn blue litmus paper into red; - acetic acid (vinegar) react with bases - citric acid (sour taste in fruits) - ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) Presence of O atom and OH - acetylsalicylic acid (ASA, molecular makes them polar. aspirin) - oxalic acid (rust removers and The more COOH groups, the brass cleaners) higher the melting point. Lower melting and boiling - natural and synthetic odours points than carboxylic acids. - perfumes - artificial and natural food flavourings - cosmetics