* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ethers - ThinkChemistry
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Polythiophene wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
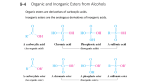
Alcohols and Ethers AH Chemistry Unit 3(b) Alcohols Physical properties • When comparing the boiling point of ethanol with an alkane, which alkane would you compare it with? • Which would have the higher boiling point? • Why? • Alcohols exhibit hydrogen bonding. • As a result, they exhibit higher boiling points than (most) other organic compounds of similar molecular mass. • Which is more soluble in water: ethanol or hexan-1-ol? • Why? • The lower alcohols are miscible with water but as their chain length increases their solubility in water decreases. Preparation of alcohols • There are 2 principle methods for producing alcohols in industry. What are they? 1. Acid-catalysed hydration of alkenes (electrophilic addition) 2. Nucleophilic substitution of halogenoalkanes Reactions of alcohols • With metals – produces alkoxides • Dehydration – produces alkenes • With carboxylic acids – produces esters, slowly • With acid chlorides – produces esters, more vigorously Acid chlorides Carboxylic acids can be converted into acid chlorides by reaction with: – Thionyl chloride – Phosphorus(III) chloride – Phosphorus(v) chloride Producing esters • Use full structural formulae to illustrate how ethyl propanoate can be produced from an alcohol and an acid chloride. • What type of reaction is this? Ethers General formula Uses • Solvents • Reasons: – Dissolve many organic compounds – Volatile (so removed easily by distillation) Preparation of ethers • Q: How can you prepare an ether in the lab? • A: Reaction of a halogenoalkane with a metal alkoxide. • Q: What type of reaction is this? • A: Nucleophilic substitution Naming ethers Methoxyethane Methoxymethane Ethoxypropane Naming Ethers • Name the longest continuous chain e.g. pentane • Name the alkoxy group by removing “yl” from the substituent name and adding “oxy” e.g. propyl becomes propoxy • Add the appropriate number in front of the substituent if the ether is branched e.g. 3 • Name a halogenoalkane and metal alkoxide combination you could use to prepare ethoxybutane. • Name a halogenoalkane and metal alkoxide combination you could use to prepare 2-ethoxybutane. • Name the ether produced by reacting 1chloropropane with sodium ethoxide. Physical properties – mp / bp • How do the melting and boiling points of ethers compare to alcohols? • Why? Physical properties - solubility • Why are ethers of low molecular mass soluble in water? Chemical properties • Flammable • Form peroxides on exposure to air / light (these are unstable and explosive) e.g. ethoxyethane peroxide