* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Peptidoglycans - Sigma
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
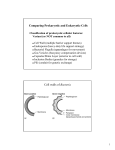
GLY FINAL 1207 PGD cleanxrefs2 Peptidoglycans Peptidoglycans Structure Bacterial Components The basic structure of peptidoglycan (PGN) contains a carbohydrate backbone of alternating units of N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and Nacetylmuramic acid, with the N-acetylmuramic acid residues cross-linked to peptides. Peptidoglycan provides rigidity to the cell wall; the cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria may contain up to 40 layers of peptidoglycan, conferring significant mechanical strength.1 Structurally, bacteria resemble primitive plants in that the cellular contents are surrounded by an inner peptidoglycan cell wall in addition to an inner plasma membrane and, in Gram-negative bacteria, an outer lipid bilayer (see Figure 2). In Gram-negative bacteria, peptidoglycans make up about 10% of the cell wall dry weight; while in Gram-positive bacteria the thicker peptidoglycan layer contains about 20% of the cell wall dry weight. Although the peptidoglycan is responsible for the mechanical strength and shape of bacterial cells, it has sufficient plasticity and dynamic turnover to allow cell growth and division. Gram-Positive Bacterial Cell Wall Gram-Negative Bacterial Cell Wall Lipoteichoic Acid Outer Lipid Membrane Peptidoglycan Cell Wall Peptidoglycan Plasma Membrane Plasma Membrane Alternating copolymer of b(14)-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid Pentaglycine cross-link L-Ala-D-GluL-Lys-D-Ala tetrapeptide Figure 2. The basic structure of bacterial peptidoglycan and the cell wall structures of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. Biosynthesis and Degradation The peptidoglycan biosynthetic pathway begins in the cytoplasm with the synthesis of a muramyl peptapeptide precursor containing a terminal D-AlaD-Ala. L-Alanine is converted to D-alanine by racemase, with subsequent assembly of D-alanyl-D-alanine by D-Ala-D-Ala ligase. In the cytoplasm, the muramyl pentapeptide precursor is anchored via a water-soluble UDP-glucosamine moiety. In the second phase of peptidoglycan construction, the muramyl pentapeptide N-acetylglucosamine is transferred to a C55 undecaprenyl phosphate with the release of UMP to form a Lipid I intermediate. An additional glycosylation step completes the peptidoglycan unit, which is then transported via its C55 lipid tail to the external periplasmic surface of the membrane, where the peptidyglycan unit becomes integrated into the cell wall matrix. Several transpeptidases and transglycosylases connect the newly formed peptidoglycan structures to the cell wall peptidoglycan matrix. Inhibitors of peptidoglycan biosynthesis act as antibiotics in that they lead sequentially to the loss of peptidoglycan, loss of cell wall integrity, and lysis. Peptidoglycan degradation is catalyzed by glycosidases, peptidases, and amidases, including lysing enzymes such as lysozyme, that are commonly used for degrading cell walls. Specific antibacterial compounds that contain a β-lactam structure, such as penicillin, interfere with the synthesis of the cell wall, weakening the peptidoglycan scaffold within the bacterial wall so the structural integrity eventually fails. Since mammalian cells have a plasma membrane but lack the peptidoglycan wall structure, this class of antibacterials selectively targets bacteria with no significant negative effect on the cells of the mammalian host. The specificity of β-lactam antibacterials is due to their structural similarity to the D-alanyl-D-alanine group, allowing them to compete for the binding sites of transpeptidases and prevent the assembly of peptidoglycan layers in both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. 30 sigma.com/glycobiology For Technical Service, call your local office or visit sigma.com/techinfo GLY FINAL 1207 PGD cleanxrefs2 Peptidoglycans Functions References: 1. Stewart-Tull, D.E.S., Major component of the cell wall in Gram positive organisms. Consists of a glycan backbone with alternating β(1,4) linked residues of N-acetyl-Dglucosamine and muramic acid. The immunological activities of bacterial peptidoglycans. Ann. Rev. Microbiol., 34, 311 (1980). 2. Schleifer, K.H., and Kandler, O., Peptidoglycan types of bacterial cell walls and their taxonomic implications. Bact. Rev., 36, 407 (1972). 3. Wheat, L.J., et al.,Antibody response to peptidoglycan during staphylococcal infections. J. Inf. Dis., 147, 16 (1983). 4. Doyle R.J., Dziarski R., in Molecular Medical Microbiology (Susmsman M., ed.) pp. 137‑153, Academic Press (2001). 5. Alexopoulou, L., et al., Recognition of double-stranded RNA and activation of NF-κB by Toll-like receptor 3. Nature, 413, 732 (2001). 6. Zhou, R., et al., Substrate for the determination of lysostaphin activity. Anal. Biochem., 171, 141 (1988). The Antibiotic Explorer The Antibiotic Explorer connects you to products for your specific applications, including: Cell Culture Gene Regulation and Expression Studies ■ Analytical Reference Standards Plasmid Selection Plant Tissue Culture ■ Research Antibiotics ■ ■ ■ ■ Bacterial Components The primary immune recognition is based on structures common among invading pathogens. Surface molecules, such as lipopolysaccharide (LPS), peptidoglycans, and peptidoglycan recognition protein (PGRP), are known to elicit immune reactions ranging from cytokine release to fever.2‑4 Peptidoglycans activate the Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2), that is present in mammalian cells, and they can be used for the stimulation of lymphocytes. Peptidoglycans also function as antagonists of Poly(I:C).5 Peptidoglycans may be used to estimate the activity of lysing enzymes such as lyticase.6 Peptidoglycans Name Cat. No. Peptidoglycan from Bacillus subtilis 69554-10MG-F Peptidoglycan from Methanobacterium sp. 78721-10MG-F Peptidoglycan from Micrococcus luteus 53243-10MG-F Peptidoglycan from Saccharomyces cerevisiae 72789-10MG-F Peptidoglycan from Staphylococcus aureus 77140-10MG 77140-25MG Peptidoglycan from Staphylococcus staphylolyticus 08678-10MG-F Peptidoglycan from Streptomyces sp. 79682-10MG-F To access the largest selection of research antibiotics, visit sigma-aldrich.com/antibiotic sigma-aldrich.com Your Favorite Gene™, Your Comprehensive Gene Search Tool, visit sigma.com/yfg 31