* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Crusades - Cobb Learning
Second Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Fourth Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Kitab al-I'tibar wikipedia , lookup
First Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Church of the Holy Sepulchre wikipedia , lookup
Kingdom of Jerusalem wikipedia , lookup
Northern Crusades wikipedia , lookup
Barons' Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1291) wikipedia , lookup
Third Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Arsuf wikipedia , lookup
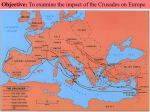
CRUSADES = Standards: SSWH5e Describe the impact of the Crusades on both the Islamic World and Europe. What am I learning: How did the Crusades impact Europe and the Middle East? What will I do to show I have learned it? I will complete the guided notes and participate in class discussion Chivalry:_____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ Goal of Crusades:______________________________________________________ Causes of the Crusades Specific Crusades 1st Crusade- 2nd Crusade- 3rd Crusade- Results of the Crusades “Then the French entered the city [of Jerusalem] at the noonday hour of Friday, the day of the week when Christ redeemed the whole world on the cross. . .All the heathen, completely terrified, changed their boldness to swift flight the narrow streets of the city. . . some fled into the Tower of David; others shut themselves in the temple of the Lord and of Solomon, where in the halls a very great attack was made on them. . . Within this Temple, about ten thousand were beheaded. Not one of them was allowed to live. They did not spare the women and children.” Chronicle of the First Crusade, M.E. McGinty, trans., 1941 This document refers to Saladin’s takeover of Jerusalem in the Third Crusade Saladin decided that neither Frankish Christians, nor the ones of oriental heritage should be pursued. Saladin placed guards around the church of the Holy grave as well as other holy places belonging to the non-Muslims, to avoid them being destroyed. Saladin encouraged the Franks to stay, and invited Jewish families to move back in to Jerusalem. Saladin’s tax collectors were shocked by the fact that their leader allowed Franks, and others who wanted to leave Jerusalem, to depart without returning goods they had stolen. Firstly, Saladin said, it will be difficult to prove what is actually plundered, and secondly; he had not taken the city to enrich himself on material wealth. Saladin let al-Aqsa, which was previously turned into a church, once again become a mosque after having the walls sprinkled with rose-water. Then Saladin let the slaves free without them having to pay, further on he pro-claimed that he would not take a ransom for the richest. Some of his trusted men objected loudly. Saladin answered them: “Christians throughout the world will remember the good deeds we have done for them." In your Reading Guide Books Read 131-134 ANSWER QUESTIONS AND FILL OUT CHART BELOW Key Word Guild Commercial Revolution Vernacular Common Law Magna Carta Parliament Definition Impact on Society