* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER SEVEN Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization
Islamic terrorism wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Iran wikipedia , lookup
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Somalia wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Hizb ut-Tahrir in Central Asia wikipedia , lookup
Censorship in Islamic societies wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Abbasid Caliphate wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
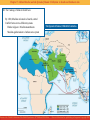
CHAPTER SEVEN Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia World Civilizations, The Global Experience AP* Edition, 5th Edition Stearns/Adas/Schwartz/Gilbert *AP and Advanced Placement are registered trademarks of The College Entrance Examination Board, which was not involved in the production of, and does not endorse, this product. Copyright 2007, Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Longman Chapter 7: Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia I. The Islamic Heartlands in the Middle and Late Abbasid Eras II. An Age of Learning and Artistic Refinements III. The Coming of Islam to South Asia IV. The Spread of Islam to Southeast Asia Stearns et al., World Civilizations, The Global Experience, AP* Edition, 5th Edition Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Longman, Copyright 2007 Chapter 7: Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia I. The Islamic Heartlands in the Middle and Late Abbasid Eras Abbasid empire weakened, 9th-13th centuries peasant revolts Al-Mahdi (775-785) Shi-a unreconciled succession not secure The Abbasid Empire at Its Peak Stearns et al., World Civilizations, The Global Experience, AP* Edition, 5th Edition Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Longman, Copyright 2007 Chapter 7: Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia I. The Islamic Heartlands in the Middle and Late Abbasid Eras A. Imperial Extravagance and Succession Disputes Harun al-Rashid son of al-Mahdi The Thousand and One Nights Barmicides Persian advisors death followed by civil war al-Ma'mun B. Imperial Breakdown and Agrarian Disorder Civil unrest Caliphs build lavishly tax burden increases agriculture suffers The Abbasid Empire at Its Peak Stearns et al., World Civilizations, The Global Experience, AP* Edition, 5th Edition Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Longman, Copyright 2007 Chapter 7: Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia I. The Islamic Heartlands in the Middle and Late Abbasid Eras C. The Declining Position of Women in the Family and Society Seclusion, veil Polygyny D. Nomadic Incursions and the Eclipse of Caliphal Power Former provinces threaten Abbasids Buyids, Persia take Baghdad, 945 Sultans Seljuk Turks 1055, defeat Buyids Sunnis Shi'a purges defeat Byzantines, Egypt The Abbasid Empire at Its Peak E. The Impact of the Christian Crusades 1096, Western European Christian knights small kingdoms established Saladin retakes lands last in 1291 Stearns et al., World Civilizations, The Global Experience, AP* Edition, 5th Edition Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Longman, Copyright 2007 Chapter 7: Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia II. An Age of Learning and Artistic Refinements Urban growth Merchants thrive A. The Full Flowering of Persian Literature Persian the court language administration, literature Arabic in religion, law, sciences Calligraphy Firdawsi Shah-Nama epic poem Sa'di Omar Kayyan Rubaiyat Stearns et al., World Civilizations, The Global Experience, AP* Edition, 5th Edition Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Longman, Copyright 2007 Chapter 7: Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia II. An Age of Learning and Artistic Refinements B. Achievements in the Sciences Math build on Greek work Chemistry experiments Al-Razi Al-Biruni specific weights Medicine hospitals courses of study Stearns et al., World Civilizations, The Global Experience, AP* Edition, 5th Edition Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Longman, Copyright 2007 Chapter 7: Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia C. Religious Trends and the New Push for Expansion Sufis mysticism Ulama conservative against outside influence Greek philosophy rejected Qur'an sufficient Al-Ghazali synthesis of Greek, Qur'anic ideas opposed by orthodoxy D. New Waves of Nomadic Invasions and the End of the Caliphate Mongols Chinggis Khan Hulegu 1258, Baghdad falls last Abbasid killed Stearns et al., World Civilizations, The Global Experience, AP* Edition, 5th Edition Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Longman, Copyright 2007 Chapter 7: Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia III. The Coming of Islam to South Asia By 1200, Muslims rule much of north, central Conflict between two different systems Hindu religion v. Muslim monotheism Muslim egalitarianism v. Indian caste system The Spread of Islam, 10th-16th Centuries Stearns et al., World Civilizations, The Global Experience, AP* Edition, 5th Edition Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Longman, Copyright 2007 Chapter 7: Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia III. The Coming of Islam to South Asia A. Political Divisions and the First Muslim Invasions First Muslims as traders, 8th century attacks lead to invasion Muhammad ibn Qasim Umayyad general takes Sind, Indus valleys Indians treated as dhimmi The Spread of Islam, 10th-16th Centuries B. Indian Influences on Islamic Civilization Math, medicine, music, astronomy India influences Arab Stearns et al., World Civilizations, The Global Experience, AP* Edition, 5th Edition Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Longman, Copyright 2007 Chapter 7: Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia III. The Coming of Islam to South Asia C. From Booty to Empire: The Second Wave of Muslim Invasions 10th century, Turkish dynasty established in Afghanistan Mahmud of Ghazni begins invasion of India Muhammad of Ghur Persian state in Indus valley thence to Bengal his lieutenant, Qutb-ud-Din Aibak forms state at Delhi Delhi sultanate rules for 300 years D. Patterns of Conversion Converts especially among Buddhists, lower castes, untouchables also conversion to escape taxes Muslims fleeing Mongols, 13th, 14th centuries Stearns et al., World Civilizations, The Global Experience, AP* Edition, 5th Edition Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Longman, Copyright 2007 Chapter 7: Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia III. The Coming of Islam to South Asia E. Patterns of Accommodation High-caste Hindus remain apart Muslims also often fail to integrate F. Islamic Challenge and Hindu Revival Bhakti devotional cults emotional approach caste distinctions dissolved Shiva, Vishnu, Kali especially Mira Bai, Kabir, songs in regional languages G. Stand-off: The Muslim Presence in India at the End of the Sultanate Period Brahmins v. ulama > separate communities Stearns et al., World Civilizations, The Global Experience, AP* Edition, 5th Edition Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Longman, Copyright 2007 Chapter 7: Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to South and Southeast Asia IV. The Spread of Islam to Southeast Asia Shrivijaya A. Trading Contacts and Conversion Trading leads to peaceful conversion Sufis important starting with Sumatran ports The Spread of Islam, 10th-16th Centuries Malacca thence to Malaya, Sumatra, Demak (Java) Coastal cities especially receptive Buddhist elites, but population converts to Islam B. Sufi Mystics and the Nature of Southeast Asian Islam Important mystical strain Women in a stronger position matrilineal Stearns et al., World Civilizations, The Global Experience, AP* Edition, 5th Edition Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Longman, Copyright 2007