* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Angle and Regular Polygon Review
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Coxeter notation wikipedia , lookup
Mirror symmetry (string theory) wikipedia , lookup
Event symmetry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Regular polytope wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
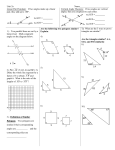
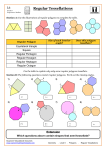
Line Symmetry / Reflection Symmetry Review Questions Draw a square and draw all lines of symmetry on this 2-d shape. What kinds of lines of symmetry does the square have? Now draw a triangle that has all interior angles the same size and all sides the same size. What kinds of lines of symmetry does this special triangle have? Which of these terms may confuse children? What is the name of this special triangle? 3 lines of symmetry are shown below for the triangle The lines are referred to as l, m, and n. 2 colors are added here to show half the triangle folds onto the other colored half. Assume the original interior was white in color. The red half folds onto the orange half so that both halves match. This makes m a line of symmetry. What kind of line symmetry is this? l m n Do all triangles have 3 lines of symmetry? If not, draw ones with 0, 1, 2, and 4 lines of symmetry. (if possible) Use drawing and the Mira or paper folding and cutting to study the lines of symmetry of famous quadrilaterals. Some Famous quadrilaterals - 4-sided polygons a) Described related to number of parallel sides Trapezoid Right trapezoid Isosceles trapezoid Parallelogram b) Described related to all angles being congruent ? c) Described related to all sides being congruent ? d) Described related to both b and c being true ? Make a Venn diagram showing the relationship of all trapezoids, parallelograms, and rectangles in the universe of quadrilaterals. Angle and Regular Polygon Review A popular measurement unit is the degree. There are 360 degrees in a circle (full turn). There are half as many degrees in a half circle. So 180 degrees in a straight angle. A quarter circle has one-fourth the degrees of a full circle. Such a 90 degree angle is called a right angle. It is often shown with a small square corner near the vertex of a right angle. Angles that are less than 90 degrees are called _?_angles. Draw such an angle: Angles that are greater than 90 degrees are called _?_angles. Some curricula also define __?__ angles as larger than 180 degrees. Between 90 and 180 Greater than 180 Polygon Terms Review Polygons: simple closed 2-d shapes made up of straight line segments for sides. Famous Triangles 3-sided polygons named for kinds of angles acute triangles right triangles obtuse triangles named for possible congruent side lengths scalene triangle – no sides are congruent isosceles triangle - 2 sides are congruent equilateral triangle – all 3 sides are congurent These may be combined for more detailed descriptions. Draw an obtuse isosceles triangle. Regular Polygons A regular polygon is a polygon where all the interior angles are congruent (same measurement) and all the sides are congruent. Regular triangle: Draw a regular 2d shape An equiangular polygon is a polygon where all the interior angles are congruent (same measurement). An equilateral polygon is a polygon where all the sides are congruent (same length measurement). Sketch examples to help you decide which of these are true statements. (may want to focus on quadrilaterals and triangles first) 1. A regular polygon is equilateral or equiangular. 2. A regular polygon is equilateral and equiangular. 3. All equilateral polygons are regular polygons. 4. All equiangular polygons are regular polygons. 5. All equilateral polygons are equiangular polygons. Draw a Venn diagram showing the relationship of regular polygons, equiangular polygons, and equilateral polygons. Use the universe of all polygons. Next draw an example sketch of a polygon that would go into each region of the Venn diagram.