* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The subject of " Engineering Materials " deals with the study of
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Self-healing material wikipedia , lookup
Flux (metallurgy) wikipedia , lookup
Thermal spraying wikipedia , lookup
De re metallica wikipedia , lookup
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Strengthening mechanisms of materials wikipedia , lookup
Alkaline earth metal wikipedia , lookup
Superplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Electroactive polymers wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Shape-memory alloy wikipedia , lookup
Thermoelectric materials wikipedia , lookup
Materials science wikipedia , lookup
Heavy metals wikipedia , lookup
Ceramic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
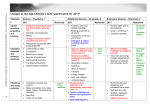
The subject of " Engineering Materials " deals with the study of materials in respect of the following : Sources , composition , properties , manufacturing methods and testing , Applying in the varions fields of Engineering and Technology , modern techniques for handling and using materials with economical and safer design of structurs . and machines . Classification of Eng. Materials : A : 1- civil Eng. Materials : suchas classification According to Application Building stones .bricks and clay products , time, cement , concrete , mortar , timber ….. 2- Electrical Eng. materials : Copper , aluminum , iron , and steel … conductors . Silicon , germanium , Asbestos , Bakelite , mice , varnishes , air…………. In sulators . Iran , nickel , cobalt , ………… magnetic materials. 3- Mechanical Eng. Materials : Cast iron , steel , lubricating , materials . B. 1- Classification according to structure Metals : Iron , Aluminum , copper , Zinc ……….. metals may be subdivided as :. (1) Ferrous metals ( cast iron , wrought iron and steel ) and alloys ( silicon steel , high speed steel , spring steel ). (2) Non-Ferrous metals ) copper , Aluminium , Zinc ……. ) and alloys ( brass ,bronze , duralumin a ) . 2- Non metals : Building stones , cement , concrete , plastics , asbestos . General classification C. 1- metais and alloys . 2- Ceramics 3- Organic polymers The Differences between metals and Non-metals Property 1- Structure 2- Excitation of Valence electron by E.M.F. ( Electromotive force ) 3- State Metals Non-metals All solid metals have They exist crystalline structure anamorphic or mesomorphic forms Easy Difficult Generally solids at room temperature 4- Luster Possess metallic luster 5- Conductivity Good conductor of heat and electricity Gases and solids at ordinary temperatures Do not possess metallic luster ( except iodine and graphite ) Bad conductor of heat and electricity 6- Malleability 7- Ductility 8- Hardness 9- Electrolysis 10- Density 1- Metals and alloys : Malleable Ductile Generally hard Form anions High density Not Malleable Not ductile Hardness Varies Form anions Low density Metals are polycrystalline bodies consisting of a great number of fine crystals differently oriented with respect to one another (10-1 – 10-4 c, size ) . Depending on the mode of crystallization , there are crystals of regular shapes which called crystallites or grains of the metal . Metals in the solid state , and to same extent in the liqnid state possess high thermal and electrical conductivity . the electrical resistance of pure metals increases with the temperature Many metals display duper conductivity at temperatures near absolute Zero where their electrical resistance drops abruptly to extremely low values . All metals are capable of thermionic emission ( the emission of electrons when being heated , they are good reflectors of light and lend them selves to plastic deformation . Pure metals are of low string the and do not possess the required physiochemical and technological properties for some definite purpose , so they are seldom used in Eng. The majority of metals used are alloys . Alloys are produced by melting or sintering twoor more metals , or metals and anon-metal together . An Alloy can consist of twoor more components . Examples : steels , super alloys , brass , bronze 2- Ceramic Materials : these materials are non-metallic solids made of inorganic compounds such as oxides , nitrides , borides , silicates , carbides . They are fabricated by first shaping the powder with or without the application of pressure in to a compact , which is subsequently subjected to a high temp . treat ment called sintering . Traditional ceramics have been used in the manufacture of pottery , porcelain , cement and silicate glasses . New ceramics possess exceptional electrical , magnetic , chemical , structural , and thermal properties . such ceramics are now extensively used in the electronic control devices. Computers , nuclear Eng. And aerospace fields . Examples : silica , soda lime glass . concrete , cement . Ferrites , granite , Mgo , Cds , Zno , Sic . 3- Organic materials : these materials are derived directly from carbon where carbon is chemically combined with hydrogen , oxygen , or other non-metallic Substances and their structure is complex . Organic materials are termed polymers be cansee they are formed by polymerization reaction in which simple molecules are chemically combined into massive long chain molecules or three – dimensional structures . Examples : phalstics ( PVC , PE , PTFE ) : Fibers ( nylon , cotton , terylene ) : Natural and synthetic rubbers , leather . Examples of compsites ; 1- Metals and alloys with ceramics : (1) Steel reinforced concrete . (2) Dispersion hardened alloys . 2- Metals and alloys with organic polymers : (1) Vinyl – coated steel (2) Whisker reinforced plastics 3- Ceramics and organic polymers : (1) Fiber – reinforced plastics . (2) Carbon – reinforced rubber.