* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Module 2 Biochemical bases of proliferation, intercellular
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Specialized pro-resolving mediators wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Glyceroneogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Module 2 Biochemical bases of proliferation, intercellular connections and physiological
functions of organs and tissues. Bases of pharmaceutical biochemistry
Test questions in text form
1. 2, 4-Dioxypyrimidine is
A. Thymine
B. Cystosine
C. * Uracil
D. Guanine
E. None of these
2. A cofactor in the conversion of dihydroorotate to orotic acid, catalysed by the enzyme
dihydroorotate dehydrogenase is
A. FAD
B. FMN
C. * NAD
D. NADP
E. PLP
3. A nucleoside consists of
A. Nitrogenous base
B. * Purine or pyrimidine base + sugar
C. Purine or pyrimidine base + phosphorous
D. Purine + pyrimidine base + sugar +Phosphorous
E. All of these
4. A substituted pyrimidine base of pharmacological value is
A. 5-Iododeoxyuridine
B. Cytisine arabinoside
C. * 5-Fluorouracil
D. All of these
E. None of these
5. A substrate for enzymes of pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis is
A. * Allopurinol
B. Tetracylin
C. Chloramphenicol
D. Puromycin
E. All of these
6. Adenine is
A. * 6-Amino purine
B. 2-Amino-6-oxypurine
C. 2-Oxy-4-aminopyrimidine
D. 2, 4-Dioxypyrimidine
E. None of these
7. All following are naturally occurring nucleotides except
A. Cyclic AMP
B. ATP
C. * DNA
D. Inosine monophosphate
E. GTP
8. All of the following can occur in Lesch-Nyhan syndrome except
A. Gouty arthritis
B. Uric acid stones
C. * Retarted growth
D. Self-mutiliating behaviour
E. Both a and B
9. All of the following occur in orotic aciduria except
A. * Increased synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides
B. Increased excretion of orotic acid in urine
C. Decreased synthesis of cytidine triphosphate
D. Retardation of growth
E. None of these
10. All of the following statements about allopurinol are true except
A. * It is a structural analogue of uric acid
B. It can prevent uric acid stones in the kidneys
C. It increases the urinary excretion of xanthine and hypoxanthine
D. It is a competitive inhibitor of xanthine oxidase
E. Both a and B
11. All of the following statements about primary gout are true except
A. Uric acid stones may be formed in kidneys
B. Arthritis of small joints occurs commonly
C. * Urinary excretion of uric acid is decreased
D. It occurs predominantly in males
E. Both C and D
12. All of the following statements about thioredoxin reductase are true except:
A. * It requires NADH as a coenzyme
B. Its substrates are ADP, GDP, CDP and UDP
C. It is activated by ATP
D. It is inhibited by dADP
E. Both A and C
13. All the enzymes required for de novo synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides are cytosolic
except
A. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase
B. Aspartate transcarbamoylase
C. Dihydro-orotase
D. * Dihydro-orotate dehydrogenase
E. Both C and D
14. Amethopterin and aminopterin decrease the synthesis of
A. * TMP
B. UMP
C. CMP
D. All of these
E. Both A and B
15. An autosomal recessive disorder, xanthinuria is due to deficiency of the enzymes:
A. Adenosine deaminase
B. * Xanthine oxidase
C. HGPRTase
D. Transaminase
E. Xanthine reductase
16. An enzyme of pyrimidine nucleotides biosynthesis regulated at the genetic level by
apparently coordinate repression and derepression is
A. * Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase
B. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
C. Thymidine kinase
D. Deoxycytidine kinase
E. Carbamoyl phosphatase
17. Aspartate amino transferase uses the following for transamination:
A. Glutamic acid and pyruvic acid
B. * Glutamic acid and oxaloacetic acid
C. Aspartic acid and pyruvic acid
D. aspartic acid and keto adipic acid
E. None of these
18. Aspartate contributes the following carbon atoms of the pyrimidine nucelus:
A. C2 and C4
B. C5 and C6
C. C2, C4 and C6
D. * C4, C5 and C6
E. C4 and C5
19. Aspartate transcarbamoylase is inhibited by
A. * CTP
B. PRPP
C. ATP
D. TMP
E. AMP
20. Complete absence of hypoxanthine guanine phospharibosyl transferase causes
A. Primary gout
B. Immunodeficiency
C. Uric acid stones
D. * Lesh-Nyhan syndrome
E. All of these
21. 5 year old sick boy whith Lesch-Nyhan syndrome suffers from hyperuricemia and gout,
caused by accumulation:
A. * Hypoxanthine
B. Adenine and guanine
C. Cytosine and uracil
D. Thymine
E. Hypoxanthine and adenine
22. Excessive consumption of purine rich products by the 46 year old patient caused
alimentary hyperuricemia. These products are:
A. Coffee, tea
B. Liver
C. Meat, especially young bird meat
D. East
E. * all above correct
23. For treatment of gout was prescribed allopurinol, which is the competitive inhibitor of
enzyme:
A. Inosinekinase
B. * Xanthinoxsidase
C. Transformilase
D. Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
E. Ribonucleotidecarboxidase
24. In the chemotherapy of tumor inhibitors of nucleotides synthesis are used. They are the
followings substanses except:
A. 5-ftoruracil
B. * Cocarboxylase
C. 5-ftordeoxyuridin
D. Aminopterin
E. Pteroylglutaminate
25. Malignant cells have high speed of proliferation, therefore for treatment of oncology
diseases used:
A. Inhibitors of trypsin
B. Inhibitors of cytochrome oxidase
C. * Inhibitors of nucleotides synthesis
D. Inhibitors of proteins biosynthesis
E. Activators of proteolytic enzymes
26. Medicine, which is used for treatment of gout is the structural analogue of hypoxanthine,
it:
A. Salts of lithium
B. Anturan
C. * Allopyrinol
D. Uridine
E. Acetilisoniazid
27. ?Prof. I.Horbachevskiy offered and grounded the theory of biosynthesis of uric acid in
the organism of mammals. Choose precursor of uric acid:
A. Urea and proteins
B. Proteins and nucleic acids
C. Lipids and nucleic acids
D. Glycoproteins and fatty acids
E. * Nucleic acids at the degradation of nucleincontaining cells
28. Prof. I.Horbachevskiy’s investigations about purine metabolism are widely known in the
world. Why I. Gorbachevskiy was not awarded with the Nobel prize:
A. Nobel prize was not yet
B. Gorbachevskiy was not nominated
C. He lived in Czekh republic, and the synthesis of uric acid was carried out in
Austria
D. The scientific world did not estimate the role of I.Horbachevskiy’s investigations
for the future of medicine and biology
E. * all above correct
29. Syndrome of Lesch-Nyhan – hard hyperuricemia is the genetic deficiency of such
enzyme:
A. Xantine oxidase
B. Adenosine deaminase
C. Hypoxanthine oxidase
D. Phosphorylase
E. * Hypoxanthine – guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
30. The 3 year old child suffers from orotic acid aciduria. Orotaciduriya is accompanied the
followings symptoms:
A. Dermatitis of the opened areas of body
B. Bleeding, disorders of growth
C. Disorders of mental development, galactosemia
D. * Disorders of physical and mental development, megaloblastic anemia
E. Diarrhea, dermatitis, demention
31. The 45 year old patient suffers from gout. Symptoms of gout are heavy pain syndrome
and inflammation, caused deposition in joints, cartilages and other tissues:
A. Oxalates
B. Gomogentizic acid
C. Orotates
D. Phosphates
E. * Urates
32. The 5 year old child suffers from orotic acid aciduria. Deficiency of which of below
mentioned enzyme causes orotaciduria?
A. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase ІІ
B. Aspartate carbamoyl transferase
C. * Orotate phosphoribosyl transferase
D. Orotate carboxylase
E. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
33. The 5 year old child suffers from physical and mental underdevelopment, megaloblastic
anemia. It was diagnozed orotic acid aciduria. Orotic aciduria type I reflects the
deficiency of enzymes:
A. * Orotate phosphoribosyl transferase and orotidylate decarboxylase
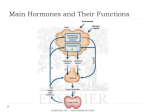
B. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
C. Dihydroorotase
D. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase
E. Xanthine oxidase
34. The 50 year old patient suffers from hyperuricemia. Hyperuricemia is increase of uric
acid level more than:
A. * 0,5 mmol/l
B. 0,1 mmol/l
C. 10 mmol/l
D. 1 mmol/l
E. 2 mmol/l
35. The 55 year old male suffers from hyperuricemia. Hyperuricuria is observed at all of
diseases which are accompanied the increased disintegration:
A. Glycoproteins
B. Phosphoproteins
C. * Nucleoproteins
D. Lipoproteins
E. Chromoproteins
36. The 56 year old patient suffers from hyperuricemia. Uric acid is the product of
disintegration of purine nucleotides, in composition of which are the following
nitrogenous bases:
A. Adenine or thymine
B. Thymine or uracil
C. Guanine or cytosine
D. * Adenine or guanine
E. Cytosine or uracil
37. The 6 year old boy suffers from Lesch-Nyhan syndrome. Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, the sex
linked, recessive absence of HGPRTase, may lead to
A. * Compulsive self destructive behaviour with elevated levels of urate in serum
B. Hypouricemia due to liver damage
C. Failure to thrive and megaloblastic anemia
D. Protein intolerance and hepatic encephalopathy
E. Both A and D
38. The 6 year old child suffers from physical and mental underdevelopment, megaloblastic
anemia. It was diagnozed orotic acid aciduria. Biochemical index, which characterizes
the genetic disorder of UMP biosynthesis is following:
A. Aspartataciduria
B. * Orotaciduria
C. Gomogentisinuria
D. Uraciluria
E. Cytosinuria
39. The 6 year old child suffers from physical and mental underdevelopment, megaloblastic
anemia. It was diagnozed orotic acid aciduria. To prevent formation of orotic acid excess
it is possible the use:
A. Adenine
B. Thymine
C. Guanine
D. * Uridine
E. Aspartate
40. Uric acid is the end product of purine as well as protein catabolism in
A. Man
B. Fish
C. * Birds
D. All of these
E. None of these
41. Usage in the metabolic reactions of free hypoxanthine and guanine („salvage pathway”)
catalyses enzyme:
A. Xanthine oxidase
B. Phosphorylase
C. * Hypoxanthine – guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
D. Hypoxanthine oxidase
E. Guanosine deaminase
42. What is a way of synthesis of pentoses from glucose metabolites?
A. Glycolysis
B. Gluconeogenesis
C. Pentose Phosphate Pathway
D. Krebs’s cycle
E. Cory cycle
43. What is the main pathway for providing of human organism with nitrogenous bases for
formation of nucleotides and nucleic acids:
A. Citrate cycle
B. Ornithine cycle
C. * Synthesis of purine and pyrimidine bases
D. Synthesis of fatty acids
E. Disintegration of glycogen
44. What prevents hyperuricemia:
A. Disorders of urinary acid excretion
B. Disintegration of DNK
C. Radiation defeat of cell
D. Toxemia of pregnancy
E. Application of structural analogue of hypoxanthine
45. Where in a cell is located synthesis of pyrimidine bases?
A. Nucleus
B. * Cytoplasm
C. Mitochondria
D. Microtome
E. Endoplasmic reticulum
46. Where nucleic acids hydrolysis takes place?
A. In liver
B. In stomach
C. In small intestine
D. In a pancreas
E. In muscles
47. Which medicine is used to increase solubility of urates - salts of uric acid for patients
with gout:
A. Allopurinol
B. Chenodesoxycholic acid
C. Cholic acid and Allopyrinol
D. * Salts of lithium and anturan
E. Solutin of NaCl
48. Which of following nucleotides are purine:
A. AMP and TMP
B. * AMP and GMP
C. AMP and UMP
D. UMP and TMP
E. CMP and GMP
49. Which of the following amino acids produce a vasoconstrictor on decarboxylation?
A. Histidine
B. * Tyrosine
C. Threonine
D. Arginine
E. All of these
50. Which of the following is absent in the structure of mononucleotides?
A. Nitrogenous base
B. Ribose
C. Desoxyribose
D. * Nitric acid
E. Phosphoric acid
51. Which of the following reaction does not include into purine nucleotides disintegration:
A. Splitting of phosphate group with formation of adenosine and guanosine
B. Deamination
C. Splitting of D-ribose from nucleotides
D. * Degradation of alanine to CO2 and N2O
E. Catabolism of hypoxanthine or xanthine with formation of uric acid
52. Which one of the following contributes nitrogen atoms to both purine and pyrimidine
rings?
A. * Aspartate
B. Carbanoyl phosphate
C. Carbondioxide
D. Tetrahydrofolate
E. Ammonia
53. Which products can be used at gout and hyperuricemia:
A. Liver, fish
B. Meat, yeasts
C. Milk, cheese, eggs
D. Coffee, tea
E. Meat, liver
54. Which substance causes the decrease of level of uric acid in blood and urine:
A. Antimycin
B. Аminopterin
C. Barbiturates
D. * Allopurinol
E. AMP
55. Which substance gives only one nitrogen atom for purine ring:
A. alanine
B. glutamine
C. * aspartate
D. methenil-THF
E. formyl -THF
56. Which substance is formed at 11th reaction of synthesis of purine nucleotides:
A. Adenylate
B. Uric acid
C. * Inosine monophosphate
D. Hypoxanthine
E. Xanthine
57. Which substance is precursor of ? –alanine in the reactions of pyrimidine bases
transformation:
A. Thymine
B. * Uracil
C. Cytosine
D. Adenine
E. Guanine
58. Which substance is the source of ribose and desoxyribose in purine and pyrimidine
nucleotides?
A. * Glucose
B. Cholesterol
C. Vitamin С
D. Vitamin D
E. Arabinose
59. Which substance is utilized in xanthineoxidase’s reactions as oxidant and reduses to
N2O2:
A. N2O
B. * O2
C. HNO3
D. HCO3
E. Cu(OH)2
60. Which substanse does not take part in the biosynthesis of purine nucleotides?
A. Glycine
B. Tetragidrofolat
C. Arginine
D. Aspartate
E. Glutamine
61. Which substrate donates 2 carbon atoms for the biosynthesis of purine simultaneously for
it’s pyrimidine and imidazole rings:
A. glutamine
B. * glycine
C. aspartate
D. methionine
E. CO2
62. Which substrates take part in the second reaction of formation of purine:
A. Fructosepyrophosphate + glycine
B. Ribosopyrophosphate + glycine
C. * Phosphoribosepyrophosphate + glutamine
D. Ribose-5-phosphate + glycine
E. Pyrimidine + diazole
63. Which vitamin donates 2 carbon atoms for the biosynthesis of purine?
A. Vitamin B1
B. Vitamin B6
C. Ascorbic acid
D. Vitamin Н
E. * Vitamin B10
64. Who synthesized uric acid artificially from glycine and urea in 1882:
A. German scientist Veller
B. German scientist Fisher
C. Polish-Russian scientist Nenskiy
D. Austrian physiologist Maresh
E. * Ukrainian scientist I. Horbachevskiy
65. Why constant excessive consumption of meat and glandular tissues for some people
causes hyperuricemia and formation of kidney’s stones:
A. these products reduce solubility of uric acid
B. decrease excretion of urates
C. effect on a genetic apparatus, stimulating the biosynthesis of purine nucleotides
D. * contain a lot of nucleoproteins and nucleotides, which catabolism is
accompanied with formation of uric acid
E. stimulate transformation of urea to uric acid
66. Why the constant excessive consumption of coffee and tea can cause hyperuricemia and
appearance of kidney’s stones:
A. components of coffee decrease solubility of uric acid in blood
B. components can stimulate formation of uric acid
C. coffee and tea do not effect on formation of uric acid
D. it is possible at the simultaneously excessive consumption of meat
E. * the excessive consumption of coffee and tea can activate the enzyme
demethilase, which leads to hyperuricemia
67. Xanthineoksidase is FAD-depending enzyme, flavoprotein which contains such ions:
A. * Fe and Mo
B. Fe and Cu
C. Zn and Mo
D. Mg and Cu
E. Zn and Fe
68. Xanthosine monophosphate is an intermediate during de novo synthesis of
A. TMP
B. CMP
C. AMP
D. * GMP
E. All of these
69. Which of the following is not an essential attribute that a biological molecule would need
to be a useful genetic material?
A. * It must carry all of the information needed to direct the specific organization
and metabolic activities of the cell
B. It must replicate accurately so that the information it contains is precisely
inherited by the daughter cells
C. It must be capable of undergoing occasional mutations, such that the information
it carries is altered in a heritable way
D. It must have highly repetitive DNA sequences.
E. All are essential attributes of useful genetic material.
70. ____ regulate which genes or subsets of genes are transcribed in a particular cell type.
A. * Transcription factors
B. Chaperone proteins
C. RNA polymerases
D. Transcription is not regulated
E. All of the above
71. _______________ join DNA fragments to the lagging strand.
A. A.Telomeres
B. Centromeres
C. Helicase
D. * Ligases
E. Antiparallel strands
72. A DNA strand with the sequence AACGTAACG is transcribed. What is the sequence of
the mRNA molecule synthesized?
A. AACGTAACG
B. UUGCAUUGC
C. AACGUAACG
D. * TTGCATTGC
E. None of the above
73. A molecule of DNA is a polymer composed of
A. Glucose
B. Amino acids
C. Fatty acids
D. * Nucleotides
E. Vitamins
74. A reaction of the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids in the process of
translation is catalyzed by:
A. * Peptydyltransferase
B. Aminoacylsynthetase
C. Peptidylligase
D. Peptidase
E. Peptydylhydrolase
75. According to Chargaff's rule, the following proportion exists in DNA
A. * C=G
B. C»T
C. C»G
D. C=T
E. None of the above
76. All of the below mentioned are the components of the protein synthesis system, except:
A. Ribosomes
B. m-RNA
C. t-RNA
D. Regulatory proteins
E. * DNA
77. Amino acid during synthesis of proteins bounds to the:
A. * 33-end of t-RNA
B. Anticodon
C. Codon
D. 55-end of t-RNA
E. 33-end of m-RNA
78. Areas of a eukaryotic gene that are represented in the final protein product are termed
__________.
A. Introns
B. Mutons
C. Recons
D. * Exons
E. Cistrons
79. Binding of RNA-polymerase to DNA-matrix takes place in specific areas of genome.
What is the name of these areas?
A. Active centers
B. Contact areas
C. * Promotors
D. Catalytic areas
E. There is not correct answer
80. Biosynthesis of proteins is related to the following organelles:
A. Mitochondria
B. Lysosomes
C. Microsomes
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
E. * Ribosomes and nucleus
81. By convention, the sequence of bases in a nucleic acid is usually expressed in the
_________ direction
A. 3' to 1'
B. 3' to 5'
C. 1' to 3'
D. * 5' to 3'
E. Clockwise
82. By which mechanism the synthesis of RNA is inhibited by actinomycin D?
A. * Penetration inside the double strand of DNA between G-C with local
deformation of DNA matrix
B. Inhibition of RNA synthesis initiation
C. Associates with A-subunit
D. Ingibition of elongation process of RNA synthesis
E. Oppression of synthesis of matrix RNA
83. Clusters of highly repetitive DNA located near the centromeres and telomeres are called
A. * Nucleosomes
B. Euchromatin
C. Chromatids
D. Heterochromatin
E. 30 nm chromatin
84. Codons are composed of:
A. * Triplet sequences of nucleotide bases in mRNA
B. Triplet sequences of nucleotide bases in DNA
C. Triplet sequences of amino acids in polypeptide chains
D. Triplet sequences of deoxyribose sugars in DNA
E. None of the above
85. Common mechanisms of action of tetracyclin, streptomycin and levomycitin:
A. All these antibiotics ingibit replication
B. All these antibiotics ingibit transcription
C. * All these antibiotics ingibit translation
D. All these antibiotics stimulate the synthesis of protein
E. All these antibiotics ingibit posttraslation modifications of protein
86. Conformity of A-T, G-C in the DNA molecule is defined as a rule of:
A. Watson
B. Crick
C. * Chargaphe
D. Jakob
E. Starling
87. Decide whether each statement is true (T) or false (F). Place your answer in the blank
space given. A. A-T is a possible base pair in a DNA molecule.
A. * A-C is a possible base pair in a DNA molecule
B. C-A is a possible base pair in a DNA molecule.
C. A-G is a possible base pair in a DNA molecule.
D. G-A is a possible base pair in a DNA molecule.
88. DNA is made up of a phosphate group, an organic base, and:
A. A protein
B. * A sugar
C. A molecule of ATP
D. A fat
E. None of the above
89. DNA replication is called semiconservative because _______________ of the original
duplex appears in the duplex formed in replication.
A. * None
B. Most
C. Half
D. Hardly any
E. All
90. DNA–polymerase can show except polymerase activity:
A. * Exonuclease activity
B. Endonuclease activity
C. Intranuclease activity
D. Glyconuclease activity
E. Liponuclease activity
91. Each individual zone of a chromosome replicates as a discrete section called
A. Telomere
B. Euchromatin
C. * Okazaki fragment
D. Replication unit
E. Linker DNA
92. Each unit of a nucleic acid consisting of a sugar, attached phosphate group, and base is a
A. Nucleolus
B. * Nucleotide
C. Nucleosome
D. Histone
E. Genetisome
93. Enzyme which catalyses replication of both chains in eukaryotes:
A. DNA – polymerase 4
B. * DNA – polymerase A
C. DNA – polymerase D
D. DNA – polymerase D
E. DNA – ligase
94. First stage of proteins biosynthesis – activation of amino acids is catalyzed by:
A. Aminoacyl-kinase
B. Aminoacyl- transferases
C. Aminoacyl-t-RNA- hydrolases
D. * Aminoacyl-t-RNA- synthetases
E. Аміноаcyl-t-RNA- lyases
95. For the activation of amino acids in the first stage of proteins biosynthesis the following
ion is needed:
A. Ca2+
B. Na+
C. K+
D. ClE. * Mg2+
96. For the process of transcription the followings components are needed, except:
A. DNA-matrix
B. DNA-depending-RNA-polymerase
C. Nucleoside triphosphates
D. Ions of Mg2+
E. * Ions of Zn2+
97. Genetic code is informative only when it is read in direction:
A. 55 – 3
B. From right to left
C. Direction is not important
D. 33 – 4
E. * 33 – 5
98. Give the definition of transcription term:
A. * A biosynthesis of RNA on DNA-matrix
B. Synthesis of daughter molecules of DNA
C. Synthesis of proteins, the amino acid sequence of which is determined by the
nucleotide sequence of mRNA
D. Enzymatic deleting and repeating synthesis of areas of DNA
E. Moving of gene or groups of genes
99. How does protein synthesis begin?
A. * The cell divides
B. Multiple cells join
C. The DNA unzips
D. The DNA zips up
E. Nothing happens
100.
How many combinations of DNA nitrogen bases are possible in a DNA triplet
code?
A. * 20
B. 32
C. 64
D. 128
E. 19
101.
How many molecules of histons does a nucleus of every nucleosome have?
A. 2
B. 4
C. 6
D. * 8
E. 10
102.
If one side of a DNA molecule contains the following sequence of nucleotides,
AGTCCG, the complementary sequence on the other side would be:
A. GCCTGA
B. AGTCCG
C. * TCAGGC
D. CTGAAT
E. None of the above
103.
In a double stranded molecule of DNA, the ratio of purines : pyrimidines is:
A. Variable
B. Determined by the base sequence in RNA
C. Genetically determined
D. * Always 1:1
E. Determined by the number of purines in the sense strand of the DNA
104.
In DNA guanine always pairs with
A. Adenine
B. Cytosine
C. Guanine
D. * Thymine
E. Uracil
105.
In DNA, thymine always pairs with
A. * Adenine
B. Cytosine
C. Guanine
D. Thymine
E. Uracil
106.
In nucleic acids, the free hydroxyl group is attached to the _______________
carbon of the sugar.
A. 5'
B. 4'
C. * 3'
D. 2'
E. 1'
107.
In nucleic acids, the phosphate group is attached to the ___ carbon of the sugar.
A. * 5'
B. 4'
C. 3'
D. 2'
E. 1'
108.
In replication of DNA, the helix is opened and untwisted by
A. Ribase
B. Ligase
C. Deoxase
D. * Helicase
E. Polymerase
109.
In the DNA molecule:
A. * Adenine pairs with thymine
B. Guanine pairs with thymine
C. Cytosine pairs with thymine
D. Adenine pairs with cytosine
E. All of the above are possible.
110.
In the process of elongation there is untwisting of the double-helical DNA areas
with formation of the bonds in polyribonucleotide chain. What bonds are formed?
A. 1,6-glycosidic
B. B-1,4- glycosidic
C. * 3'-5'- phosphodiester
D. Disulfide
E. Ionic
111.
Indicate the difference between RNA transcription and DNA replication:
A. * In RNA transcription as a matrix only 1 chain of DNA is used
B. In RNA transcription as a matrix 2 chains of DNA are used
C. In RNA transcription ions of Zn2+ are necessary
D. In RNA transcription the factors of replisome are necessary
E. In RNA transcription the whole DNA molecule is transcribed
112.
Initiation aminoacyl-t-RNA in eukaryotes is:
A. Alanine-t-RNA
B. Histidine –t-RNA
C. * Methionine –t-RNA
D. Glycine- t-RNA
E. Cysteine- t-RNA
113.
lustersWhat is the percentage of thymine in the DNA molecule, if the content of
cytosine is 22%?
A. 38
B. * 28
C. 22
D. 44
E. 11
114.
Main enzyme which catalyzes the reaction of synthesis of both chains of DNA in
prokaryotes:
A. DNA - ligase
B. DNA – polymerase D
C. DNA - synthetase
D. * DNA - polymerase 3
E. DNA - ligase 5
115.
Name nitrogen bases that enter to the structure of DNA:
A. Guanine, uracil, thymine
B. Cytosine, uracil, thymine
C. Uracil, adenine, guanine
D. * Adenine, thymine, guanine
E. Thymine, adenine, uracil
116.
Name nitrogenous bases included into the structure of RNA:
A. Guanine, uracil, thymine
B. Cytosine, adenine, thymine
C. * Uracil, adenine, guanine
D. Adenine, thymine, guanine
E. Thymine, adenine, uracil
117.
Name process which is catalyzed by aminoacyl-t-RNA synthetases?
A. * Recognition and joining of amino acids to t-RNA
B. Initiation of translation
C. Elongation of polypeptide chain
D. Termination of translation
E. Synthesis of t-RNA
118.
Name proteins that take part in the regulation of transcription in eukaryotes?
A. Albumins
B. Globulins
C. Immunoglobulins
D. * Histons
E. Cathepsins
119.
Name the mechanism of DNA replication:
A. * Semiconservative
B. Conservative
C. Depressive
D. Repressive
E. Replicative
120.
Named the structural monomers of DNA molecule:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
121.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
122.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
123.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
124.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
125.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
126.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
127.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
128.
A.
B.
C.
D.
* Mononucleotides
Nucleosides
Nitric bases
Polynucleotides
Peptides
Normal self-termination of transcription occurs due to the presence of
Stem-loop sequences in mRNA
Termination proteins
* Multiple RNA polymerase molecules
Polyribosome formation
All of the above
?Nucleic acids are:
Mononucleotides
Nucleosides
Nucleoproteins
* Polynucleotides
Dinucleotides
Nutritional mutants
Grow on minimal medium
* Lack an essential metabolic protein
Are also called prototrophs
Are the same as carbon-source mutants
Are usually antibiotic resistant
Okazaki fragments are used to elongate
The leading strand toward the replication fork
The lagging strand toward the replication fork
Both strands in both directions
* The leading strand away from the replication fork
The lagging strand away from the replication fork
On which of the following molecules would you find a codon?
* Messenger RNA
Ribosomal RNA
Transfer RNA
Small nuclear RNA
Big nuclear RNA
On which of the following molecules would you find an anticodon?
Messenger RNA
Ribosomal RNA
* Transfer RNA
Small nuclear RNA
Big nuclear RNA
Polymerase III is actually a complex containing
* Сatalytic subunits
Proofreading subunits
"Sliding clamp" subunits
All of the above
None of the above
Polysomes - are structures which are formed during translation from:
tRNA and one ribosome
* One molecule of mRNA and several ribosomes
A few molecules of mRNA and a few ribosomes
A few molecules of mRNA and one ribosome
E. A few molecules of tRNA, mRNA and few ribosomes
129.
Primer is synthesized by specific:
A. * Primase
B. DNA – ligase
C. RNA – ligase
D. RNA - polymerase
E. None of above
130.
Properties of genetic code are all below, except:
A. Universality
B. * Interruption
C. Nonoverlapping
D. Degeneration
E. Specificity
131.
Proteins are made from amino acids by the process of
A. * Hydrolysis
B. Pinocytosis
C. Active transport
D. Dehydration synthesis
E. All of the above
132.
Proteins that block the passage of RNA polymerase are called:
A. Operons
B. Activators
C. * Repressors
D. Enhancers
E. Promoters
133.
Regulatory domains of most activators interact with
A. The transcription factor complex
B. * RNA polymerase
C. Repressors
D. The regulatory factor complex
E. The DNA binding domain
134.
Regulatory proteins of the protein synthesis system on ribosomes are all below,
except:
A. Factors of initiation
B. * Factors of polymerization
C. Releasing-factors
D. Factors of elongation
E. Factors of termination
135.
Replication fork has configuration like:
A. W
B. R
C. C
D. * V
E. T
136.
Represors of proteins synthesis on the level of transcription are:
A. Protamines
B. Glutelins
C. * Prolamines
D. Scleroproteins
E. Histons
137.
Reverse transcriptase (revertase or RNA-depending-DNA-polymerase) catalyzes:
A. * Synthesis of і-RNA on the DNA
B.
C.
D.
E.
Synthesis of DNA on the DNA
Synthesis of tRNA on the DNA
Synthesis of DNA on the RNA matrix
Synthesis of DNA on the ribosome
138.
RNA contains which bases?
A. Adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine, uracil
B. Adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine
C. Thymine, guanine, cytosine, uracil
D. * Adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil
E. None of the above
139.
RNA synthesis on a DNA template is called __________.
A. Transformation
B. Translation
C. Transduction
D. * Transcription
E. Transfection
140.
Since the first nucleotides cannot be linked in a newly synthesized strand in DNA
replication, ___________ is required
A. A DNA primer
B. * DNA polymerase
C. Ligase
D. An RNA primer
E. Helicase
141.
Synthesis of daughter molecules of DNA, identical to maternal DNA, is named:
A. Reverse transcription
B. Transcription
C. Replication of RNA
D. * Replication of DNA
E. Translation
142.
The acceptor region of t-RNA contains such terminal sequence of nucleotides:
A. * CCA
B. CAC
C. CCU
D. GCA
E. CGA
143.
The actual synthesis of DNA in E. coli is the function of
A. * Polymerase I
B. Primase
C. Polymerase III
D. DNA ligase
E. Hirase
144.
The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide chain comprises the ____ structure of
the protein.
A. * Primary
B. Secondary
C. Tertiary
D. Quaternary
E. Presecondary
145.
The amino acids are transported to the place of synthesis of proteins in the cells
by:
A. Proteins-carryer
B. r-RNA
C. * t-RNA
D. Lipoproteins
E. m-RNA
146.
The base thymine is always paired with ___.
A. * Adenine
B. Guanine
C. Cytosine
D. Thymine
E. Uracil
147.
The component of the protein synthesis system on ribosomes is:
A. Nucleus
B. * mRNA
C. RNA- primer
D. DNA- primer
E. DNA
148.
The double strand model of DNA was proposed by:
A. Mitchel
B. Krebs
C. * Watson – Crick
D. Knoop
E. Nirenberg
149.
The effort to decipher the genetic code was led by ____ who was awarded a Nobel
Prize for his work.
A. * Nirenberg
B. Lederberg
C. Watson
D. Crick
E. Van-Helmont
150.
The first mRNA codon to specify an amino acid is always
A. TAC
B. * UAA
C. UAG
D. AUG
E. UGA
151.
The following compounds are formed in complete hydrolysis of nucleic acids,
except:
A. Phosphoric acid
B. Pentoses
C. Purine bases
D. * Acetic acid
E. Adenine
152.
The four ribonucleotide triphosphates incorporated into mRNA are
A. Inosine, Guanine, Uracil, Thymine
B. Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine
C. * Cytosine, Uracil, Adenine, Guanine
D. Thymine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine
E. Inosine, Guanine, Adenine, Cytosine
153.
The genetic code is considered "degenerate" because __________.
A. The code originated from bacterial genomes
B. DNA is unstable
C. Degenerate is the name of the person who deciphered the code
D. * More than one nucleotide triplet codes for the same amino acid
E. None of the above
154.
The initiation of synthesis of RNA is started from the including of first nucleotide
into the chain. What nucleotide does begin this process in pro- and in eukaryotes?
A. Pyrimidine nucleosidtriphosphate
B. Urydinmonophosphate
C. Desoxyribonucleosidtriphosphate
D. * Purine nucleosydtriphosphate
E. Cytidyltriphosphate
155.
The mode of action of a steroid hormone involves:
A. * Binding to a cell membrane receptor
B. Activation of protein kinases
C. Binding to calmodulin
D. Covalent modification of enzyme activity
E. Modifaing gene transcription
156.
The Okazaki fragment is synthesized in direction:
A. Along the movement of replication fork
B. 3'-5'
C. * Oppositely to the movement of replication fork
D. Antiparallely to the daughter chain
E. Proportionally to the movement of new synthesized daughter chain
157.
The operon that controls tryptophan producing genes in E. coli consists of
_______________ .
A. Only one gene
B. * Two genes
C. Three genes
D. Four genes
E. Five genes
158.
The presence of DNA is important for cellular metabolic activities because DNA
A. Directs the production of enzymes
B. Is a structural component of cell walls
C. Directly increases the solubility of nutrients
D. * Is the major component of cytoplasm
E. Nonproduction f enzymes
159.
The process of copying a gene's DNA sequence into a sequence of RNA is called
A. Replication
B. * Transcription
C. Translation
D. PCR
E. Posttranslation modification
160.
The process of DNA synthesis, the nucleotides sequence of which is
complementary to the sequence of RNA, is named:
A. * Reverse transcription
B. Transcription
C. Replication of RNA
D. Replication of DNA
E. Translation
161.
The process of producing a RNA polymer from a DNA template is called __.
A. Replication
B. * Transcription
C. Translation
D. Duplication
E. Iniciation
162.
The process of producing an amino acid polymer (polypeptide) from a RNA
template is called _.
A. Replication
B. * Transcription
C. Translation
D. Duplication
E. Transreplication
163.
The process of the exchange of genetic materials between the different DNA
molecules is named:
A. Replication of RNA
B. Reverse transcription
C. * Recombination
D. Reparation
E. Transposition
164.
The process of translation requires the presence of:
A. * mRNA, tRNA and ribosomes
B. mRNA, ribosomes and RNA polymerase
C. DNA, mRNA and RNA polymerase
D. Chromatin, DNA and amino acids
E. Free nucleotide bases, amino acids and ribosomes
165.
The stages of replication include:
A. Recognition of the point of replication beginning
B. Untwisting of double spiral of matrix DNA
C. Formation of fragments for the imitation synthesis of daughter's chains
D. Elongation of synthesis and termination
E. * All of the above
166.
The synthesis of new chains during replication takes place in such direction:
A. 4' – 5'
B. 7' - 8'
C. * 5' - 3'
D. 2' - 6'
E. 9' - 4'
167.
The synthesis of Okazaki fragments begins from:
A. Homonucleotide
B. Mononucleotide
C. Heteronucleotide
D. Polynucleotide
E. * Primer
168.
The synthesis of primer - fragment of RNA - takes a place in:
A. Transcription
B. Recognition
C. Reparation
D. * Replication
E. Translation
169.
The total length of all DNA of human cell is:
A. 20 sm
B. * 2
C. 2 sm
D. 0,2 sm
E. 20 m
170.
The transcribing enzyme is
A. Ligase.
B.
C.
D.
E.
DNA polymerase.
* RNA polymerase.
Amino-acyl transferase.
Hydrolases
171.
The transcription of DNA to a molecule of messenger RNA occurs:
A. * On the ribosomes
B. In the cytosol
C. In the nucleus
D. Only during cell division
E. When amino acids are made available by transfer RNA
172.
Theory of induction-repression of genes activity or theory of operon was
developed by:
A. Crick and Watson
B. Mitchel and Knoop
C. * Jakob and Monod
D. Krebs and Knoop
E. Gorbachevsky and Parnass
173.
There is the dynamic equilibrium between subunits and full ribosomes in the cells.
Full ribosomes are formed mainly in period of:
A. Transcription
B. Activation of amino acids
C. * Translation
D. Posttranslation modifications
E. Posttranslation modification of RNA
174.
Three types of RNA involved in comprising the structural and functional core for
protein synthesis, serving as a template for translation, and transporting amino acid,
respectively, are:
A. * mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
B. rRNA, tRNA, mRNA
C. tRNA, mRNA, rRNA
D. tRNA, rRNA, mRNA
E. rRNA, mRNA ,tRNA
175.
To describe the genetic code as degenerate indicates that
A. mRNA is rapidly degraded
B. The code is not universal among organisms
C. * Some amino acids have more than one codon
D. Frameshift mutations are tolerated
E. Stop codons may have corresponding tRNA molecules
176.
To which of the following does guanine form hydrogen bonds in DNA?
A. Adenine
B. Thymine
C. * Cytosine
D. Guanine
E. Uracyl
177.
Transcription factors appear to be unable to bind to a nucleosome because
A. Activators are inhibited by the configuration
B. * Of inhibition of RNA polymerase
C. Of histones positioned over promoters
D. Nucleosomes are especially vulnerable to repressors
E. Operators are placed in an inaccessible position
178.
Transcription is:
A. Activation of amino acids
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Rewriting of information to RNA on the matrix DNA
Process of formation of functional ribosome
Process of elongation of polypeptide chain
Processing of m-RNA
179.
Transcription occurs along a ____ template forming an mRNA in the ____
direction.
A. 5' to 3'; 5' to 3'
B. * 5' to 3'; 3' to 5'
C. 3' to 5'; 5' to 3'
D. 3' to 5'; 3' to 5'
E. None of the above
180.
Transfer RNA's bind during translation by the
A. Codon
B. * Anticodon
C. Template
D. Operon
E. None of the above
181.
Translation repressor proteins may shut down translation of processed mRNA
transcripts by
A. * Binding with the poly-A tail
B. Resetting the reading frame
C. Reinserting introns into the transcript
D. Excising a short sequence of nucleotides
E. Excising a short sequence of nucleosides
182.
What amino acid is coded by the triplet of bases UAU?
A. * Phenylalanine
B. Serine
C. Tyrosine
D. Cysteine
E. Lusine
183.
What are the two processes of protein synthesis in order?
A. Meiosis, Translation
B. Translation, Transcription
C. Replication, Mitosis
D. * D.Transcription, Translation
E. Protein, Synthesis
184.
What does a ribosome do?
A. Calls the xRNA with no codons
B. * Helps create the mRNA
C. Nothing
D. Calls the tRNA with the appropriate codon
E. Explodes
185.
What does the speed of initiation process depend of?
A. * Structures of promotors sequences
B. Nucleotide sequences
C. Amount of RNA-depending-DNA-polymerase
D. The presence of 3'-5'-phosphodiester bonds
E. The structure of coplement dNМP in the coding chain of DNA
186.
What form of DNA is a left-handed spiral?
A. B
B. С
C. Т
D. A
E. * Z
187.
What function of gene-operator in the structure of operon?
A. On the gene-operator mRNA is transcribed that serves as a matrix for the
synthesis of protein-repressor
B. * Regulates (turns on) transcription on the structural genes
C. On the gene-operator mRNA is transcribed that serves as a matrix for the
synthesis of proteins which are necessary for cell
D. On the gene-operator mRNA is transcribed that serves as a matrix for the
synthesis of protein-inductor
E. On the gene-operator rRNA transcribed
188.
What happens in Transcription?
A. The xRNA is destroyed
B. The rRNA is destroyed
C. * The mRNA is synthesized
D. The mRNA is destroyed
E. The xRNA is made
189.
What happens in Translation?
A. The xRNA is destroyed
B. Translation doesn't exist
C. The tRNA is called and the protein is made
D. * The mRNA creates amino acids
E. Amino Acids cause a nuclear reaction
190.
What is a polypeptide?
A. A strand of DNA
B. * An incomplete strand of protein (amino acids and enzymes)
C. A strand of mRNA
D. An RNA molecule
E. It doesn't exist
191.
What is operon?
A. Area of mRNA which codes the synthesis of one protein
B. Area of DNA in which the information about the synthesis of one protein is coded
C. * Area of DNA which consists of gene-operator and a few structural genes
D. Area of DNA which consists of gene-regulator and promoter
E. Area of DNA which consists of gene-regulator and structural genes
192.
What is protein made up of?
A. Enzymes and DNA
B. Happiness and Sadness
C. Meat
D. * Enzymes and Amino Acids
E. Amino Acids and Hydroclorich
193.
What is the function of gene-regulator in accordance with the theory of Jakob and
Monod?
A. * On the gene-regulator mRNA is transcribed that serves as a matrix for the
synthesis of protein-repressor
B. Directly regulates (turns on) transcription on structural genes
C. On the gene-regulator mRNA is transcribed that serves as a matrix for the
synthesis of necessary for cell proteins
D. On the gene-regulator mRNA is transcribed that serves as a matrix for the
synthesis of protein-inductor
E. On the gene-regulator rRNA transcribed
194.
What is the function of tRNA?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Transport of amino acids
Transferring of genetic information
Formation of ribosomes
Storage of genetic information
Transport of mononucleotides
195.
What is the polysome?
A. Conglomerate containing few ribosomes
B. A few mRNA, that combined with one ribosome
C. * Many ribosomes that accommodate on one matrix RNA
D. A few tRNA transporting one amino acid to ribosome
E. A few amino acids which are transported by one tRNA to ribosome
196.
What is the terminal signal in the synthesis of polypeptide chain on ribosome?
A. Deficit of ATP energy in a cell
B. * Meeting of A-center of ribosome with terminal codon of mRNA
C. Dissociation of large and small subunits of ribosome
D. Decreasing of the amount of elongation factors in the cell
E. Placing methionine of tRNA in the P-center of ribosome
197.
What methods of DNA replication do you know?
A. * Conservative and semiconservative
B. Complete and incomplete
C. Completed and uncompleted
D. Determined and nondetermined
E. Temporal and permanent
198.
What of the following changes have relation to posttranslation modification of
proteins?
A. Formation of disulfide bonds between residues of cystein
B. Adding of cofactors or prosthetic groups
C. Formation of oligomers from a few polypeptide chains
D. Phosphorylation of some amino acids residues
E. * All of the above
199.
What role does messenger RNA play in the synthesis of proteins?
A. It catalyses the process.
B. It provides the genetic blueprint for the protein.
C. * It translates the genetic code to a specific amino acid.
D. It modifies messenger RNA molecules prior to protein synthesis.
E. None of the above
200.
What role does mRNA play in protein synthesis?
A. It explodes
B. It blows up
C. It helps form ribosomes
D. Nothing
E. * It is what the tRNA matches up to in order to form protein
201.
What role does small nuclear RNA play in the synthesis of proteins?
A. It catalyses the process.
B. * It provides the genetic blueprint for the protein
C. It translates the genetic code to a specific amino acid.
D. It modifies messenger RNA molecules prior to protein synthesis.
E. None of the above
202.
What role does the rRNA play in protein synthesis?
A. It is part of a ribosome that calles the tRNA molecules
B. It forms the mRNA
C. It creates DNA
D. It is a harmful molecule that is associated with protein synthesis
E. * Play role as adaptor
203.
What sequence on the template strand of DNA corresponds to the first amino acid
inserted into a protein?
A. TAC
B. UAA
C. UAG
D. * AUG
E. UUA
204.
What term is used to describe the process by which a segment of DNA is copied
to produce a molecule of messenger RNA?
A. Reproduction
B. Replication
C. Translation
D. * Transcription
E. Recombination
205.
What term is used to describe the process by which proteins are synthesised from
a genetic code?
A. Reproduction
B. Replication
C. * Translation
D. Transcription
E. Recombination
206.
What type of DNA, except nuclear, are in the eukaryotic cells:
A. * Mitochondrial
B. Lisosomal
C. Endoplasmic
D. Ribosomal
E. Mesosomal
207.
What type of enzyme is used in recombinant DNA technology to split a specific
sugar phosphate bond in each strand of a DNA double helix?
A. * Esterase
B. Restriction enzyme
C. Lipase
D. Ligase
E. Transferase
208.
Which enzyme catalyzes transcription of RNA on DNA matrix?
A. * DNA-depending-RNA-polymerase
B. DNA-polymerase II
C. DNA-polymerase III
D. DNA-ligase
E. RNA-depending-DNA-polymerase
209.
Which ions are needed for DNA replication?
A. Ca2+ and Na+
B. Mg2+ and Mn2+
C. Zn2+ and K+
D. Na+ and Ca2+
E. * Mg2+ and Zn2+
210.
Which is not part of the lac operon?
A. * Repressor
B. Activator protein
C. Operator
D. Promotor
E. Structural gene
211.
Which mode of information transfer usually does not occur?
A. DNA to DNA
B. DNA to RNA
C. * DNA to protein
D. All occur in a working cell
E. None of the above
212.
Which molecule contains the genetic code?
A. DNA
B. * mRNA
C. tRNA
D. rRNA
E. dRNA
213.
Which nitrogenous bases make up DNA nucleotides?
A. * Adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine
B. Adenine, uracil, guanine and cytosine
C. Adenine, thymine, uracil, and cytosine
D. Adenine, thymine, guanine, and uracil
E. Adenine, thymine, uracil, guanine
214.
Which nucleic acids contain the lowest number of nucleotides?
A. DNA
B. * t-RNA
C. m-RNA
D. r-RNA
E. і-RNA
215.
Which of the following are not matched correctly?
A. Exon splicing-occurs in nucleus
B. Post-translational modifications-phosphorylation
C. SnRNA-splice out exons from transcript
D. Activated enhancers-trigger transcription
E. * All are matched correctly
216.
Which of the following does NOT involve introns?
A. Alternative splicing
B. * Ribozymes
C. Intervening sequences
D. Heteroduplexes
E. Antisense oligonucleotides
217.
Which of the following features is common to both DNA replication and
transcription?
A. Nucleotides are added to the 5' end of the newly synthesized strand
B. * A sugar-phosphate bond is formed between the 3' hydroxyl and the 5' phosphate
C. Deoxyribonucleotides are incorporated into the growing sequence
D. Both RNA and DNA polymerase require oligonucleotide priming
E. Both RNA and DNA polymerase initiate at promoter sequences
218.
Which of the following is an example of the degeneracy of the genetic code?
A. * A given amino acid has more than one codon
B. Each codon specifies more than one amino acid
C. The first two bases specify the amino acid
D. The genetic code is not degenerate
E. None of the above
219.
Which of the following is part of an operon?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
220.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
221.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
222.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
223.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
224.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
225.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
226.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
227.
A.
B.
C.
D.
Structural genes
An operator
A promoter
A CAP binding site
* All of the above
Which of the following is true regarding RNA processing?
Spliceosomes are present in organelles and nuclei
Involves removal of exons
Involves removal of one or more introns.
Occurs in prokaryotes
* None of the above
Which of the following is true regarding the machinery of translation?
* Initiation usually begins at an AUG codon
Eukaryotes have nuclear ribosomes
Polycistronic mRNA usually has a single ribosome binding site
tRNAs released from the ribosome are degraded
Termination is at inverted repeats
Which of the following is unique to eukaryotic mRNA synthesis?
Polycistronic mRNA
* Coupled transcription-translation
Removal of introns
Polysomes
All of the above
Which of the following is unique to prokaryotic mRNA synthesis?
Coupled transcription-translation
Exon processing
3' polyadenylation
mRNA capping
* Promoter sequences
Which of the following molecules does not form part of DNA?
Purine
Pyrimidine
Deoxyribose
* Amino acid
Phosphate
Which of the following nucleotide bases is not found in RNA?
* Thymine
Adenine
Uracil
Guanine
Cytosine
Which of the following statements is true regarding introns?
* Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated.
Introns have no function.
In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms
Introns may be involved in exon shuffling.
None of the above
Which of the following statements is true regarding transposons?
* They are sequences of mRNA that can move around in the genome
They exist in corn, but are not found in the human genome
They are the most abundant type of repeat in the genome
All of the above are true regarding transposons
E. None of the above
228.
Which of the statements below is false?
A. The genetic code is overlapping
B. The genetic code is universal
C. Degenerate codons specify the same amino acids
D. * The genetic code is triplet
E. None of the above
229.
Which process is the first stage of biosynthesis of proteins?
A. * Activation of amino acids
B. Elongation
C. Termination
D. Transcription
E. Translation
230.
Which statement about the elongation of the lagging strand during DNA
replication is correct?
A. * It is synthesized in a 3' --> 5' direction.
B. It progresses (grows) toward the replication fork.
C. It requires a short RNA primer to proceed.
D. It is synthesized by DNA ligase.
E. It is synthesized continuously.
231.
Which subunits do ribosomes of eukaryotes reversibly dissociate to?
A. * 60s and 40s
B. 60s and 80s
C. 40s and 45s
D. 40s and 40s
E. 60s and 20s
232.
With few exceptions, all nucleic of eukaryotes contain
A. Genes to specify the portion of the organism in which they are found
B. All the information needed for growing the whole organism
C. All of the chromosomes except sex chromosomes which are restricted to sex
organs
D. * Single stranded DNA
E. Only euchromatin except in the case of the Y-chromosome
233.
All of the following help to explain the mechanism for releasing insulin from
beta-cells in response to the concentration of blood glucose - EXCEPT
A. The important regulator of glycolysis in beta cells is the concentration of glucose
reacting with glucokinase
B. ATP is made in proportion to the rate of glycolysis
C. The rate of K+ leaving the cell through a potassium channel is a major
determinant of the polarization of the cell membrane
D. ATP inhibits the K+-channel, the more ATP, the less K+ leaving the cell, and the
less polarized (more depolarized) the cell membrane
E. * Depolarization causes Ca++ to exit the cell and insulin leaves the cell through
the insulin transporter
234.
During an overnight fast, the major source of blood glucose is
A. Dietary glucose from the intestine
B. * Hepatic glycogenolysis
C. Gluconeogenesis
D. Muscle glycogenolysis
E. Glycerol from lipolysis
235.
Inhibitory factors of hypothalamus are:
A. somatostatin, melanostatin, folliclestatin
B.
C.
D.
E.
* somatostatin, melanostatin, prolactostatin
A. somatostatin, prolactostatin, folliclestatin
prolactostatin, folliclestatin, luteostatin
melanostatin, folliclestatin, thyrostatin
236.
The absorption of glucose from the gut into intestinal mucosal cells is coupled to
Na?,K?-ATPase. In contrast, the movement of glucose from the intestinal epithelial cells
into the submucosal bloodstream occurs through passive transport. Given these facts,
which of the following statements can be true at one time or another?
A. Cytosolic levels of glucose in intestinal mucosal cells are regulated by levels of
glucose in skeletal muscle cells
B. Free glucose levels in the lumen of the intestine can never be higher than levels in
intestinal cells
C. Plasma glucose levels are much higher than intestinal cell cytosolic levels of
glucose
D. Levels of glucose in the intestinal lumen are always higher than those in the
cytosol of intestinal epithelial cells
E. * Levels of plasma glucose are approximately equal to levels in the cytosol of
intestinal epithelial cells
237.
A 62 yaears old woman has cataract (lenticular opacity) by diabetes mellitus.
Which process increase by diabetes is the reason for lenticular opacity?
A. ketogenesis
B. lipolysis
C. protein proteolysis
D. * protein glycosylation
E. gluconeogenesis
238.
A dysfunction of Langergans islets results in the decline of such hormones:
A. * Glucagon and insulin
B. Thyroxin and calcitonin
C. Insulin and epinephrine
D. Callicrein and angiotensin
E. Parathormone and cortisol
239.
A hormone that secreted in the pancreatic duct is
A. Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Somatostatin
D. * Lipocain
E. Cortisol
240.
A man after 1,5 litres blood loss has suddenly reduced diuresis. The increased
secretion of what hormone caused such diuresis alteration?
A. Corticotropin
B. Natriuretic
C. Parathormone
D. Cortisol
E. * Vasopressin
241.
A patient has such sympthoms as hyperglycaemia, glucosuria, increased urine
density, thirst, acidosis. What from below mentioned disorders can result in such state?
A. * Insufficiency of insulin
B. Hyperproduction of insulin
C. Insufficiency of vasopressin
D. Hyperproduction of glucocorticoids
E. Insufficiency of glucagon
242.
A patient has such sympthoms as polyuria, decreased urine density, thirst. What
from below mentioned disorders can result in such state?
A. Insufficiency of insulin
B. Hyperproduction of insulin
C. * Insufficiency of vasopressin
D. Hyperproduction of glucocorticoids
E. Insufficiency of glucagon
243.
A patient, which visited a doctor, has increased level of glucose in blood and
urine. Diabetes mellitus is suspected. What changes in lipid metabolism causes this
disease?
A. hyperketonemia
B. hypercholesterolemia
C. * hypoketonemia, ketonuria
D. hyperphospholipidemia, hyperketonemia
E. hypophospholipidemia , hypoketonemia
244.
A typical symptom of cholera is a body water loss and sodium ions loss. The
biochemical mechanisms of choleric toxin action is:
A. Activation of synthesis of atrial natriuretic factor
B. * Activation of adenylate cyclase in small intestine
C. Decrease of synthesis of antidiuretic hormone in a hypothalamus
D. D. Activation of secretion renin by the cells of yukstaglomerular aparatus
E. Oxydation of aldosterone in the adrenal cortex
245.
ACTH- hormone of the adenohypophysis. Per oral introduction of ACTH as
medical preparation ineffective because this hormone is:
A. * Decomposed with the proteolytic enzymes
B. Does not absorbed in the intestine
C. Inactivated in the cells of intestinal wall
D. Inactivated in a liver
E. Does not transferred with blood
246.
After meal an alimentary hyperglycemia stimulates the secretion of such
hormone:
A. Cortisol
B. Glucagon
C. Epinephrine
D. Norepinephrine
E. * Insulin
247.
Alfa-cells of pancreas synthesize the glucagon, which participates in the
metabolism of carbohydrates. Which process in a liver it effects.
A. Inhibits glycogenolysis
B. Activates glycolysis
C. * Activates a glycogenolysis
D. Ingibits glycolysis
E. Activates lipogenesis
248.
All other things being constant, an increase in stress hormones would result in an
increase in:
A. Fatty acid synthesis in adipose tissue
B. * Blood amino acids for gluconeogenesis
C. Malonyl CoA concentrations in liver
D. Protein synthesis in muscle
E. Glycogen synthesis in muscle
249.
All the following are important in the glucagon second messenger cascade
EXCEPT
A. Glucagon binds causing the dissociation of GDP from and the association of GTP
with the G-protein
B. Adenylate cyclase catalyzes the conversion of ATP to cAMP
C. Phosphodiesterase catalyzes the conversion of cAMP to AMP
D. * The receptor for glucagon undergoes an autophosphorylation which activates
adenylate cyclase
E. The cAMP binds to Protein Kinase A regulatory subunits, releasing catalytic
subunits
250.
All the following statements about serotonin are true except
A. * It causes vasolidatation
B. It causes bronchoconstriction
C. It is metabolized by monoamine oxidase
D. Its metabolite is 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid
E. Both A and B
251.
Alpha – cells of pancreas produse such hormon as:
A. Insulin
B. * Glucagon
C. Somatostatin
D. Lipocain
E. Cortisol
252.
As a medical preparations derivates of amino acids are widely used. Which from
the below mentioned hormones is derivative of amino acid?
A. * Thyroid hormones
B. Glucocorticoids
C. Androgens
D. Hormones of hypophysis
E. Estrogens
253.
As a result of insulin binding to the insulin receptor, the GRB protein binds to the
IRS. The binding of the GRB adaptor protein occurs because the IRS contains
A. * A phosphorylated tyrosyl residue
B. A phosphorylated seryl residue
C. A src homology binding domain (SH2 domain)
D. Bound inositol trisphosphate
E. An alpha-1 receptor
254.
At emotional stress in adipocytes hormone sensitive threeacylglycerollipase is
activated. What second mediator does take part in this process?
A. * cАМP
B. cGМP
C. AMP
D. Diacylglycerol
E. Ions of Ca2+
255.
At pheochromocytoma (adrenal glands medullary substance tumour) epinephrine
synthesis is increased. Which of the mentioned changes is observed in such conditions?
A. hard hypoglycemia
B. * hyperglycemia
C. normal glucose amount
D. hyperproteinemia
E. hypercholesterolemia
256.
Ca2+ ions - are an evolutional oldest secondary messenger in cells. They are the
activators of glycogenolysis, if cooperate with:
A. Calcitonin
B. * Calmodulin
C. Calciferol
D. Kinase of light chains of myosin
E. Phosphorylase C
257.
Chemical nature of ACTH:
A. simple protein
B. derivative of amino acid
C. derivative of unsaturated fatty acid
D. * hormone of peptide structure
E. steroid hormone
258.
Chemical nature of glucagon is:
A. * Peptide
B. Protein
C. Steroid
D. Derivative of amino acid
E. Derivative of arachidonic acid
259.
Chemical nature of growth hormone:
A. * simple protein
B. derivatives of amino acid
C. derivatives of unsaturated fatty acid
D. hormone of peptide structure
E. steroid hormone
260.
Chemical nature of insulin is:
A. * Protein
B. Derivative of amino acid of thyrosin
C. To the derivates of arachidonic acid
D. Oligopeptide
E. Steroid
261.
Choose a stimulus for rennin formation
A. * Diminishing of kidney blood flowing
B. Increase of kidney blood flowing
C. Adrenocorticotropic hormone
D. Aldosterone
E. Hypoglycemia
262.
Choose a substance which carries out the role of the secondary mediator at the
membrane-intracellular mechanism of action of hormones:
A. UMP
B. GTP
C. Oleic acid
D. Arachidonic acid
E. * Cyclic АМP
263.
Choose from below mentioned compouds statins of hypothalamus:
A. Thyrostatin, prolactostatin, melanostatin
B. Somatostatin, thyrostatin, melanostatin
C. Somatostatin, prolactostatin, thyrostatin
D. Thyrostatin, lipostatin, melanostatin
E. * Somatostatin, prolactostatin, melanostatin
264.
Choose from the below mentioned effects of insulin:
A. Represses oxidization of glucose in glycolysis, represses a PPP, activates
glycogen synthase (synthesis of glycogen)
B. Activates oxidization of glucose in glycolysis, represses a PPP, represses
glycogen synthase (synthesis of glycogen)
C. Represses oxidization of glucose in glycolysis, activates a PPP, represses
glycogen synthase (synthesis of glycogen)
D. * Activates oxidization of glucose in glycolysis, activates a PPP, activates
glycogen synthase (synthesis of glycogen)
E. Represses oxidization of glucose in glycolysis, inhibites PPP, represses glycogen
synthase (synthesis of glycogen)
265.
Choose, which biogenic аmines are the derivates of tryptophane:
A. Serotonin and dopamine
B. Dopamine and melatonin
C. * Serotonin and melatonin
D. Dopamine and histamine
E. Serotonin and histamine
266.
Cooperating of catecholamines with the beta - adrenoreceptors increases the level
of cАМP in the cells. Which enzyme catalyses the reaction of cАМP formation:
A. * Adenylatecyclase
B. Phosphodiesterase
C. Phosphatase
D. Guanilatciclase
E. Creatinkinase
267.
Cooperating of catecholamines with the beta - adrenoreceptors promotes the level
of cАМP in the cells. Name an enzyme which catalyzes the reaction of cАМP formation:
A. Creatinkinase
B. Phosphodiesterase
C. Phosphatase
D. Guanilatcyklase
E. * Adenylatecyclase
268.
Cyclic nucleotides (cАМP and cGМP) is the secondary mediators at transfer of
information. Witch their role as a regulators?
A. * Activating of specific proteincinases.
B. Phosphorylating of histons.
C. Activating of neiromediators.
D. Stimulation of CNS
E. Stimulation of transcription and translation.
269.
Delta cells of pancreas produse such hormon as:
A. Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. * Somatostatin
D. Lipocain
E. Cortisol
270.
Dopamine is biogenic amine which is intermediate in a synthesis:
A. * Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
B. Serotonin
C. Serotonin and melatonin
D. Insulin
E. All of above correct
271.
During stress there takes place a rapid output of glucose into blood with the
purpose of providing of organism energy. It takes a place due to:
A. * Increased secrection epinephrine which splits a glycogen in a liver and muscles
B. Increased secrection of thyroxine, which promotes absorption of glucose in an
intestine
C. Increased secrection of glucocorticoids which activate formation of glucose from
noncarbohydrate components
D. Increased secrection of epinephrine which activates a gluconeogenesis
E. To the increased secrection of epinephrine which promotes absorption of glucose
in an intestine
272.
During the series of events following an increase in insulin, all of the following
occur EXCEPT:
A. Insulin binds its receptor, causing the autophosphorylation of receptor subunits
B. Active protein kinases can cause the induction/repression of genes
C. Glucagon-stimulated phosphorylation is reversed by the effects of insulin
D. Phosphorylation results in more glucose transporters in adipose tissue cells
E. * Phosphorylation inhibits 3', 5'-phosphodiesterase
273.
Effect of epinephrine on a lipid metabolism is:
A. Inhibits a tissue lipase and mobilization of fat from a depot;
B. * Activates a tissue lipase and mobilization of fat from a depot;
C. Inhibits lipids oxidation
D. Stimulates converting of fats into carbohydrates
E. Stimulates transformation of fats into proteins
274.
Effect of insulin on a carbohydrate metabolism is:
A. * Activates transfer of glucose through the cells membranes
B. Activates glucokinase
C. Activates glycogensynthase
D. Activates a gluconeogenesis
E. Inhibits transfer of glucose through the cells membranes
275.
Effect of insulin on a lipid metabolism is:
A. * Activates the synthesis of fatty acids
B. Inhibits the synthesis of fatty acids
C. Activates converting of fatty acids into carbohydrates
D. Inhibits convention of fatty acids into carbohydrates
E. Stimulates transformation of lipids into proteins
276.
Effect of insulin on a proteins metabolism is:
A. * Activation of the synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids
B. Repression of the synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids
C. Reducing of permeability of cells membranes for amino acids
D. Activation of conversion of amino acids into glucose
E. Activation of conversion of amino acids into lipids
277.
Effect of somatotropic hormone on a proteins metabolism:
A. Represses entering of amino acids into cells
B. Represses the biosynthesis of proteins, DNA, RNA
C. Activates conversion of amino acids into fats
D. Stimulates conversion of amino acids into glucose
E. * Activates the biosynthesis of proteins, DNA, RNA
278.
Epinephrine increases the glucose level in the blood by activation of:
A. * glycogenolysis
B. glycolysis
C. ketolysis
D. gluconeogenesis
E. glycogenesis
279.
Epinephrine increases the glucose level in the blood by activation of:
A. * glycogenolysis
B. glycolysis
C. ketolysis
D. gluconeogenesis
E. glycogenesis
280.
Epinephrine stimulates a glycogenolysis by:
A. * Activation of glycogenphosphorylase
B. Inhibition of glycogenphosphorylase
C. Activation of glycogensynthase
D. Activation of hexokinase
E. Inhibition of hexokinase
281.
Epinephrine stimulation of lipolysis in adipocytes is thought to differ from
epinephrine stimulation of glycogenolysis in the liver in which way?
A. Glucagon, not epinephrine, stimulates lipolysis in adipocytes
B. The mechanism of hormone-receptor interaction is thought to be fundamentally
different in each tissue
C. Phosphorylase kinase is activated directly by a second messenger in adipocytes,
but not in the liver
D. Adenosine 3?,5?-cyclic monophosphate (cyclic AMP) is the second messenger in
adipocytes, but not in the liver
E. * Only protein kinase is interposed as an amplification factor between the second
messenger and the physiologically important enzymes in adipocytes
282.
Excess accumulation of which biogenic аmine in the areas of inflammation and
areas of cooperation an antigen-antibody is one of mechanisms of development of
allergic reactions:
A. Serotonin
B. Dopamine
C. * Histamine
D. Melatonin
E. Epinephrine
283.
Following release of norepinephrine by sympathetic nerves and epinephrine by
the adrenal medulla, which of the following metabolic processes is decreased?
A. * Glycolysis
B. Lipolysis
C. Gluconeogenesis
D. Glycogenolysis
E. Ketogenesis
284.
For what from the following hormones are specific such effects as activation of
decomposition of glycogen in a liver, activation of lipolysis, stimulation of
gluconeogenesis.
A. Insulin
B. * Glucagon
C. Epinephrine
D. Cortisol
E. Testosteron
285.
For what glycolysis enzyme the activator is insulin?
A. * hexokinase
B. B.glucose-6-phosphatase, phosphoglucom
C. C.glucose-6-phosphate-isomerase, aldolase
D. aldolase, lactate dehydrogenase
E. phosphoglucomutase, aldolase
286.
Formation of insulin is increased at:
A. During starvation
B. During the physical loading
C. At emotional stress
D. * After meal
E. At a flu
287.
Glucocorticoids increase the level of glucose in the blood by activation of:
A. glycogenogenesis
B. glycogenolysis
C. * gluconeogenesis
D. ketogenesis
E. glycolysis
288.
Histamine responsible for all of physiological effects, except:
A. * Narrowing of peripheral vessels
B. Dilatation of peripheral vessels
C. Stimulation of secretion of HCl in a stomach
D. Narrowing of bronchus
E. Participating is in immunological reactions.
289.
Hormone, which increase the activity of lipolysis in fatty tissue:
A. * epinephrine
B. parathyroid hormone
C. insulin
D. B. vasopressin
E. prostaglandins
290.
Hormones regulate the numeral processes of metabolism. Which from the below
mentioned hormones has аnabolic action:
A. * Insulin
B. Epinephrine
C. Vasopresin
D. Glukagon
E. Oxytocin
291.
How can be diabetic tendency detected?
A. Determinating the level of 17-ketosteroids in blood .
B. * By the glucose-tolerance test.
C. Determinating the glucose level in blood.
D. Determinating the glucose level in urine
E. Determinating the level of cholesterol in blood
292.
How could be an inactive kininogens converted into an active kinins?
A. Under the action of rennin
B. Under the action of angiotensin
C. Under the action of prostaglandins
D. Under the action of somatotropin
E. * Under the action of kallikreins
293.
How do catecholamins influence on a carbohydrate metabolism?
A. Activate decomposition of glycogen in a liver
B. * Activate decomposition of glycogen in a liver and muscles
C. Activate a gluconeogenesis
D. Activate suction of glucose in an intestine
E. Activate the synthesis of glycogen
294.
How do catecholamins influence on a lipids metabolism?
A. * Activate mobilization and oxidization of fats
B. Activate lipogenesis
C. Activate synthesis of phospholipids in a liver
D. Activate formation of transport forms of lipids in a liver
E. Promote formation of chylomicrons in the wall of intestine
295.
How do catecholamins influence on a protein metabolism?
A. Promote synthesis of proteins
296.
297.
298.
299.
300.
301.
302.
B. Promote synthesis of proteins in a liver and activate its decomposition in
connective tissue
C. * Promote in a proteins catabolism
D. Activate convertion of proteins into carbohydrates
E. Activate transformation of carbohydrates into a proteins
How does glucagon influence on a carbohydrate metabolism?
A. Activates the synthesis of glycogen in a liver
B. Activates the synthesis of glycogen in a liver and muscles
C. Activates decomposition of glycogen in a liver and muscles
D. * Activates decomposition of glycogen in a liver
E. Activates the transport of glucose across cellular membranes
How does insulin influence on a lipid metabolism?
A. Represses synthesis of fats, activates a gluconeogenesis
B. * Activates synthesis of fats, represses a gluconeogenesis
C. Activates synthesis of fats, activates a gluconeogenesis
D. Represses synthesis of fats, represses a gluconeogenesis
E. Participates in converting of lipids into carbohydrates, activates oxidization of
fatty acids
How does insulin influence on a mineral metabolism?
A. Regulates calcium-phosphate metabolism
B. * Activates a transport of potassium into a cells, and sodium from the cells
C. Activates insertionof iron into hemoglobin
D. Regulates metabolism of copper in an organism
E. Instrumental in insertion of iodine in tyrosine
How does insulin influence on a protein metabolism?
A. * Promotes permeability of membranes for amino acid, activates the synthesis of
proteins and nucleic acids, represses a gluconeogenesis
B. Reduces permeability of membranes for amino acid, represses the synthesis of
proteins and nucleic acids, represses a gluconeogenesis
C. Reduces permeability of membranes for amino acid, represses the synthesis of
proteins and nucleic acids, activates a gluconeogenesis
D. Promotes permeability of membranes for amino acid, represses the synthesis of
proteins and nucleic acids, activates a gluconeogenesis
E. Promotes permeability of membranes for amino acid, activates the synthesis of
proteins and nucleic acids, activates a gluconeogenesis
How is active insulin formed in a pancreas?
A. From the protein - precursor by phosphorylation
B. From the protein - precursor by acetylation
C. * From the protein - precursor by partial proteolysis
D. From the protein - precursor by the methylation
E. It formed in an active form
How is insulin catabolised after its action?
A. Excreted from an organism in an unchanging form with urine
B. Excreted from an organism in an unchanging form with a bile
C. Excreted from an organism with a bile after oxidization in a liver
D. * By the enzyme of insulinase to amino acids
E. By lysosomal enzymes in all of rissues
How is regulated intensity of insulin secretion?
A. By insulinotropin - a hormone of hypophysis
B. By insulinoliberin of hypothalamus
C. * By the concentration of glucose in blood
D. By the somatic nervous system
E. By the concentration of calcium and phosphorus in blood
303.
How many gramms of glucose is it necessary to eat for a patient half-starving to
perform a method of sugary loading aiming to reveal the hidden form of diabetes
mellitus?
A. * 1 g per 1 kg of weight
B. 100 g
C. 20 g
D. 50 g
E. 10 g
304.
Impairment in the synthesis of dopamine by the brain is a major causative factor
for the disorder:
A. * Parkinson’s disease
B. Addison’s disease
C. Cushing’s syndrome
D. Goiter
E. Insulin-dependent diabetes
305.
In stress the level of glucose increases in blood. Which hormone does result in it
with the activating of glycogenolysis?
A. Parathyroid hormone
B. Aldosterone
C. * Epinephrine
D. Vasopressin
E. Progesterone
306.
In diabetes mellitus the tissues of organism have heavy deficit of oxidative
substratum, as they can not assimilate glucose. Gluconeogenesis increases and ketone
bodies become the main substratum for oxidation. What is one of the reasons for
ketonuria by diabetes mellitus?
A. lack of HS-CoA
B. lactate excess
C. * lack of oxaloacetate
D. glucose formation
E. polyuria
307.
In emotional stress threeacylglycerollipase is activated in adipocytes.
Concentration of which secondary messenger increases?
A. * cАМP
B. cGМP
C. AMP
D. Diacylglycerol
E. Ca2+
308.
In liver and muscle, glycogen degradation is characterized by all of the following
EXCEPT:
A. * The activation by insulin of glycogen phosphorylase
B. The yielding of glucose-1-phosphate residues by the enzyme glycogen
phosphorylase
C. The activity of a 4: 4- transferase to ensure the debranching
D. The activity of a specific alpha-1, 6- glucosidase that yields free glucose residues
E. The use of inorganic phosphate by glycogen phosphorylase
309.
In pheochromocytoma (adrenal glands medullary substance tumour) increase
epinephrine synthesis. Which of the mentioned changes is observed by such conditions?
A. hard hypoglycemia
B. * hyperglycemia
C. normal glucose amount
D. hyperproteinemia
E. hypercholesterolemia
310.
In the blood of the patient the amount of glucose half-starving is 5,6 mmol/l, in an
hour after sugary loading – 13,8 mmol/l, in two hours – 9,2 mmol/l. Such figures are
typical for:
A. healthy man
B. patient with thyrotoxicosis
C. * patient with hidden form of diabetes mellitus
D. patient with Cushing's syndrome
E. patient with acromegaly
311.
In the synthesis of Insulin, which of the following is NOT TRUE?
A. * The alpha-cells of the pancreas are centered such that blood flow carries new
glucagon over the beta-cells explaining the inhibitory effect of glucagon on
insulin release
B. Glucose is a major regulator of insulin release
C. Cleavage of proinsulin to insulin yields a C-Peptide
D. The chains of insulin are held together and in active conformation by disulfide
bridges
E. The A chain of insulin is shorter than the B chain
312.
Increace of insulin secretion takes place in a pancreas after the carbohydrate meal.
Activity of which enzymes of glycolisis regulates insulin:
A. * Glucokinase, phоsphоfructokinase, pyruvatkinase
B. Aldolase, LDH, enolase
C. Phosphoglyceromutase, LDH, phosphoglucomutase
D. Enolase, аldolase, hexokinase
E. Phosphoglycerokinase, pyruvatkinase, enolase
313.
Increased blood insulin specifically plays a major role in all of the following
EXCEPT:
A. Glucose storage as glycogen in liver and muscle
B. * Conversion of glucose to triacylglycerols in liver
C. Amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in skeletal muscle
D. Promotion of the sparing of glucose utilized for energy in the brain during a fast
E. Stimulation of transport of glucose into muscle and adipose tissue
314.
Increased reabsorption of water from the kidney is the major consequence of
which of the following hormones?
A. Cortisol
B. Insulin
C. * Vasopressin
D. Glucagon
E. Aldosterone
315.
Insulin decreases the level blood glucose by means of:
A. gluconeogenesis activation
B. gluconeogenesis oppression
C. * glucose phosphorylation oppression
D. glucose with urine excretion
E. adrenalin excretion decrease
316.
Insulin effects on the metabolism of carbohydrates, stimulates the transport of
glucose from extracellulary space through cellular membranes inside the cells. Which
cells are the target – cells for insulin?
A. * Myocytes, adipocytes
B. Neurons, myocytes
C. Neurons, red blood cells
D. Hepatocytes, neurons
E. Lymphocytes, red blood cells
317.
Insulin has many direct effects on various cell types from such tissues as muscle,
fat, liver, and skin. Which of the following cellular activities is decreased following
exposure to physiologic concentrations of insulin?
A. Plasma membrane transfer of glucose
B. Glucose oxidation
C. * Gluconeogenesis
D. Lipogenesis
E. Formation of ATP, DNA, and RNA
318.
Insulin is secreted by the B-cells of the pancreas into the hepatic portal vein.
Which of the following regarding insulin synthesis is FALSE:
A. The active form of insulin is composed of two polypeptide chains linked by two
interchain disulfide bonds
B. The A-Chain has an intrachain disulfide bond
C. Insulin is synthesized as a preprohormone which is converted to proinsulin
D. * Stimulation of A-cells by glucose causes exocytosis of the insulin storage
vesicles
E. Cleavage of proinsulin to insulin yields a C-peptide
319.
Introduction of epinephrine to the organism increases the level of glucose in
blood. What process is activated mainly?
A. * Disintegration of glycogen
B. Synthesis of glycogen
C. Cycle of Krebs
D. Pentosophosphate cycle
E. Alcoholic fermentation
320.
Introduction of epinephrine to the organism results in the increase of glucose level
in blood. Which process is activates mainly?
A. Alcoholic fermentation
B. Synthesis of glycogen
C. Cycle of Krebs
D. Pentose phosphate cycle
E. * Disintegration of glycogen
321.
Melatonin responsible for all of physiological effects, except:
A. Synchronization of endogenous biorhythms in an organism
B. Adjusting of “sleep-wake” activity
C. * Activation of immune reactions
D. Inhibition of secretion somatotropic and gonadotropic hormones
E. Inhibition of free radical oxidization reactions
322.
Name the hormone, predominantly produced in response to fight, fright and flight:
A. Thyroxine
B. * Epinephrine
C. Aldosterone
D. ADH
E. Insulin
323.
One of the following hormones is an amino acid derivate:
A. Epinephrine
B. Norepinephrine
C. Thyroxine
D. * All of them
E. Insulin
324.
One of the ways of glucose oxidation is pentose-phosphate cycle. What is the
main destination of this process?
A. * formation of NADPH2 and pentose
B. formation of NADPH2 and gluconic acid
C. glycogen synthesis in the liver
D. acetyl CoA formation
E. formation of NADH2
325.
Oversecretion of which hormone causes higher growth, unproportionally large
hands?
A. * Somatotropic hormone
B. Epinephrine
C. Thyroxin
D. Antidiuretic hormone
E. Melanocytostimulation hormone
326.
Patient is in condition of constant stress, what caused the violation of lipid
metabolism. Characteristic for this condition are the following features, but:
A. hyperglycemia
B. hyperketonemia
C. decrease of total lipids in blood
D. organism emaciation
E. * fatty liver degeneration
327.
Prostaglandins are inactivated by
A. * 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase
B. Cyclo-oxygenase
C. Lipo-oxygenase
D. None of these
E. Both B and C
328.
Prostaglandins have a common structure based on prostanoic acid which contains
carbon atoms:
A. 12
B. 16
C. 18
D. * 20
E. 32
329.
Specify chemical nature of hormones of a neurohypophysis:
A. * Cyclic peptides
B. Simple proteins
C. Derivates of tyrosine
D. Derivates of fatty acids
E. Glycoproteins
330.
The B-cells of endocrine portion of pancreas are selectively damaged by alloxan
poisoning. How will it be reflected in blood plasma?
A. The content of fibrinogen decrease
B. The content of albumins decreases
C. * The content of sugar increases
D. The content of globulins decreases
E. The level of sugar decreases
331.
The cause of insulin dependent diabetes (type II) is:
A. * malfunction of structure and insulin receptors function
B. decreased insulin synthesis
C. increased insulin synthesis
D. increased epinephrine synthesis
E. decreased epinephrine synthesis
332.
The cause of insulin-dependent diabetes (type I) is:
A. * decreased insulin synthesis
B. increased insulin synthesis
C. increased glucocorticoids synthesis
D. increased glucagon synthesis
E. decreased glucagon synthesis
333.
The chemical nature of tropic hormones of adenohypophysis is:
A. Simple proteins
B. * Glycoproteins
C. Lipoproteins
D. Derivates of fatty acids
E. Derivates of amino acid
334.
The feature of tyrosine metabolism is its including in the process of hormones
synthesis. Choose one of them that synthesizes in the adrenal medulla.
A. Thyroxin
B. Glucagon
C. * Epinephrine
D. Histamine
E. Serotonin
335.
The following are all effects of insulin EXCEPT
A. Stimulation of acetyl CoA carboxylase
B. * Stimulation of the lipolytic activity of hormone sensitive lipase (HSL)
C. Stimulates adipose cells to synthesize and secrete LPL (lipoprotein lipase)
D. Stimulates the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
E. Increase in the number of glucose transporters in adipose cell membranes
336.
The hormone, that depresses lipolysis in fatty tissue:
A. * insulin
B. epinephrine
C. glucagon
D. thyroxine
E. adrenocorticotropin
337.
The hormones of protein – peptide nature regulate biochemical processes with
activating of adenylatecyclase. Choose the substance which appears as a result of this
enzyme action.
A. cCМP
B. cGМP
C. * cАМP
D. cТМP
E. cUМP
338.
The hypersecretion of which hormone causes development of hyperglycemia?
A. * Glucagon
B. Insulin
C. Somatomedine
D. Melanotropin
E. Vasopressin
339.
The level of glucose in blood of a patient increases. Excess of which hormone
could results such effect?
A. * Epinephrine
B. Insulin
C. Testosteron
D. Norepinephrine
E. Oxytocin
340.
The level of glucose in blood of a patient increased. Excess of which hormone
could result in such effect?
A. Oxytocin
B. Insulin
C. Testosterone
D. Norepinephrine
E. * Epinephrine
341.
The patient complains for undue fatiguability after working day, constant thirst. A
doctor suspected diabetes mellitus. Choose the blood plasma glucose concentration,
which proves the diagnosis:
A. * 8,5 mmol/l
B. 2 mmol/l
C. 4,5 mmol/l
D. 5 mmol/l
E. 3,3 mmol/l
342.
The patient complains of polyuria. The pathological components in urine are not
detected. The deficiency of what hormone can result in such state?
A. Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Epinephrine
D. * Vasopressin
E. Cortisol
343.
The patient with diabetes mellitus has hypoglycemic coma. The reasons for this
can be:
A. * overdosage of insulin
B. starvation
C. dehydration of the organism
D. pancreatic islet adenoma
E. Addison's disease
344.
The patient with diabetes mellitus has hypoglycemic coma. The reasons for this
can be:
A. * overdosage of insulin
B. starvation
C. dehydration of the organism
D. pancreatic islet ?-cells adenoma
E. Addison's disease
345.
The precursor of what bioactive substanse is thyrosine?
A. Bensoic acid
B. Androsteron
C. Insulin
D. * Epinephrine
E. Bilirubin
346.
The products of hydrolysis and modification of some proteins are biologically
active substances – hormones. Which from the below mentioned proteins is precursor for
lipotropin, corticotropin, melanotropin and endorphin?
A. * Proopiomelanocortin (POMC).
B. Neuroalbumin
C. Neurostromin
D. Neuroglobulin
E. Thyreoglobulin
347.
The prostaglandins are synthesized from
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Arachidonic acid
Oleic acid
Linoleic acid
Linolenic acid
Both C and D
348.
The secondary mediator in the mechanism of action of epinephrine is:
A. cCMP
B. cGMP
C. cUMP
D. cTMP
E. * cAMP
349.
The secondary mediator in the mechanism of epinephrine action is:
A. cGМP
B. * cАМP
C. cUМP
D. cТМP
E. cCМP
350.
The secondary messenger in the mechanism of ACTH action is:
A. cТМP
B. cGМP
C. cUМP
D. * cАМP
E. cCМP
351.
The secretion of glucagon is increased at:
A. In a postabsorptive period (after meal)
B. * At starvation
C. At the use of plenty of carbonhydratess
D. At the use of plenty of lipids
E. At stress
352.
The usage of glucose takes a place with its transport from intracellular space
across cell membrane inside cells. This process stimulates such hormone:
A. * Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Thyroxin
D. Aldosterone
E. Epinephrine
353.
There is only one hormone among the neurohormones which refers to the
derivatives of amino acids according to classification. Point it out:
A. Oxytocin
B. * Melatonin
C. Vasopressin
D. Thyroliberin
E. Somatotropin
354.
These compounds relax a smooth muscles of blood vessels and reduce a blood
pressure, promote permeability of capillaries and take part in development of
inflammatory reactions. Choose this hormones (hormonoids)?
A. Renin and angiotensin
B. * Kinins
C. Prostaglandins
D. Glucocorticoids
E. Corticosteroids
355.
This hormone narrows vessels and promotes a blood pressure, increases a pulse,
relaxes a smooth muscles of bronches and intestine. Choose this hormone:
A. Thyroxine
B. Somatotropic hormone
C. Cortisol
D. Testosteron
E. * Epinephrine
356.
Transfer of information from the hormones of peptide nature on intracellular
secondary messenger takes place with participation of adenylatecyclase. Which reaction
is catalyzed with adenylatecyclase?
A. * Breaking up of ATP with formation of cАМP and pyrophosphate.
B. Breaking up ATP with formation ADF and phosphorus inorganic.
C. Synthesis ATP from AMF and pyrophosphate.
D. Breaking up of ADP with formation of AMF and inorganic phosphate.
E. Breaking up ATP with formation of AMP and pyrophosphate.
357.
?Tryptophan could be considered as precursor of
A. * Melanotonin
B. Thyroid hormones
C. Melanin
D. Epinephrine
E. Both A and B
358.
Tumor of adenohypophysis caused disorders of tropic hormones synthesis.
Choose, high level of which hormone causes acromegalia?
A. Melanocytostimulating
B. CTH
C. Luteinizing
D. * Somatotropic
E. Folikulostimulating
359.
Tumors of endocrine glands enhance amounts of hormones in blood as a rule.
What biochemical changes in blood can be at a tumor of adenohypophysis?
A. Hypoglycemia
B. * Hyperglycemia
C. Hypercholesterolemia
D. Ketoacidosis
E. Acetonuria
360.
Vasopressin has a strong antidiuretic action, stimulates the reabsorbtion of water
through the membranes of kidney canaliculies. What is its chemical nature?
A. * Peptide
B. Carbohydrate
C. Steroid
D. Lipid
E. Derivate of amino acid
361.
What from below mentioned hormones is antagonist of insulin?
A. Somatotropic hormone
B. Thyrotropic hormone
C. Calcitonin
D. * Glucagon
E. Parathormone
362.
What amino acid is a precursos for epinephrine and norepinephrine synthesis?
A. Lysin
B. * Tyrosine
C. Alanine
D. Glutamic acid
E. Aspartic acid
363.
What are effects of the kallikrein-kinin system action?
A. * Relaxion of the smooth muscles of blood vessels, reducing of blood pressure,
promotes permeability of capillaries, takes part in development of inflammatory
reactions
B. Inhibits lipase activity, regulates calcium metabolism, inhibits a gastric secretion,
stimulates a lipogenesis
C. Narrows vessels, increases a blood pressure, stimulates a secretion of aldosteron
D. Promotes glucosemia, activates a gluconeogenesis, stimulates glycogenolysis in a
liver
E. Rises a blood pressure, a pulse, promotes contractive activity of myocardium.
364.
What are effects of the rennin-angiotensin system action?
A. Vasoconstriction, oppression of secretion of aldosteron
B. * Vasoconstriction, stimulation of secretion of aldosteron
C. Relaxion of vessels, oppression of secretion of aldosteron
D. Relaxionof vessels, stimulation of secretion of aldosteron
E. Stimulation of reabsorption of sodium and potassium in kidney tubulis
365.
What biochemical symptoms are specific for diabetes insipidus?
A. Hyperglycemia, glucosuria, polyuria, decreased density of urine
B. Hypoglycemia, glucosuria, polyuria, increased density of urine
C. Normoglycemia, glucosuria, normal density of urine
D. Normoglycemia, polyuria, decreased density of urine, acidosis
E. * Normoglycemia, polyuria, decreased density of urine
366.
What biochemical symptoms are specific for diabetes mellitus?
A. Hyperglycemia, glucosuria, decreased urine density
B. Hypoglycemia, glucosuria, increased urine density, acidosis
C. Hypoglycemia, glucosuria, normal urine density
D. Hyperglycemia, glucosuria, decreased urine density, acidosis
E. * Hyperglycemia, glucosuria, increased urine density, acidosis
367.
What changes in lipid metabolism may be caused by insufficiency of
somatotropin excretion?
A. emaciation
B. fatty liver degeneration
C. atherosclerosis
D. * obesity
E. ketonemia
368.
What from below mentioned effects are specific for insulin?
A. Increases permeability of cellular membranes for glucose, activates enzymes of
Krebs cycle, activates a gluconeogenesis
B. Increases permeability of cellular membranes for glucose, represses the Krebs
cycle, inhibites a gluconeogenesis
C. * Increases permeability of cellular membranes for glucose, activates enzymes of
Krebs cycle, inhibites a gluconeogenesis
D. Diminishes permeability of cellular membranes for glucose, activates enzymes of
of Krebs cycle, inhibites a gluconeogenesis
E. Diminishes permeability of cellular membranes for glucose, inhibites enzymes of
of Krebs cycle, activates a gluconeogenesis
369.
What from next hormones has anabolic effects?
A. * Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Epinephrine
D. Thyroxine in high concentrations
E. Norepinephrine
370.
What from the below mentioned hormones are catecholamins?
A. Cortisol, hydrocortisol
B. Thyroxine
C. Estriol, estradiol
D. * Epinephrine, Norepinephrine
E. Insulin, glucagon
371.
What from the below mentioned functions specific for lipocain?
A. Activates lipogenesis, inhibits lipolysis and mobilization of fats from a depot
B. Activates oxidization of fatty acids, promotes converting of carbohydrates into
lipids
C. * Activates formation of phosphotids in a liver, stimulates the action of lipotropic
food’s factors
D. Inhibits formation of phospholipids in a liver, assists in the fatty degeneration of
liver
E. Stimulates formation of triacylglycerols in the wall of intestine, activates the
synthesis of chylomicrons in an intestine
372.
What from the below mentioned hormones activate formation of phospholipids in
a liver?
A. Somatostatin
B. Insulin
C. Lipotropnic hormone
D. Thyroxine
E. * Lipocain
373.
What from the below mentioned hormones are catabolics?
A. Thyroxine
B. * Catecholamins
C. Glucocorticoids
D. Sex hormones
E. Insulin and glucagon
374.
What from the below mentioned hormones does reduce speed of lipolysis in fatty
tisuues?
A. Hydrocortison
B. Epinephrine
C. * Insulin
D. Somatotropin
E. Norepinephrine
375.
What from the below mentioned hormones is not produced in adenohypophysis?
A. Somatotropic.
B. Adrenocorticotropic.
C. * Melanotropin.
D. Thyrotropnin.
E. Prolactin.
376.
What from the transferred hormones is not secreted by a pancreas?
A. Somatostatin;
B. Glucagon;
C. * Somatomedin;
D. Insulin;
E. Lipocain.
377.
What hormone promotes glycogen synthesis?
A. Glucagon
B.
C.
D.
E.
378.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
379.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
380.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
381.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
382.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
383.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
384.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
385.
Epinephrine
Thyroxine
* Insulin
Parathormone
What hormone promotes lipogenesis?
Epinephrine
Thyroxine
Parathormone
Glucagon
* Insulin
What hormones are prodused in a pancreas?
Insulin, glucagon, somatomedins, lipotropic hormones
Insulin, glucagon, melanocytostimulation hormone, lipocain
Insulin, glucagon, liberines and statines
* Insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, lipocain
Insulin, glucagon, lipotropic hormone, oxytocin
What is a reason of acidosis development at I type of diabetes mellitus ?
Insufficiency of insulin results in the increased formation of pyruvate, which
transforms into acetyl CoA, which is utillized for the synthesis of ketone bodies
* Insufficiency of insulin results in oppression of formation of pyruvate which
determines insufficiency of oxaloacetate
Insufficiency of insulin results in activation of glycolysis and the synthesis of
ketone bodies is activated as a result
Insufficiency of insulin results in oppression of PPP and as a result to the
increased formation of ketone bodies
Insufficiency of insulin results in increasing of glucose in blood and it
transformation on ketone bodies
What is the chemical nature of catecholamins?
Proteins
Peptids
* Derivatives of amino acid
Steroids
Derivatives of arachidonic acid
What is the chemical nature of insulin?
Nucleotide
* Protein
Steroid
Carbohydrate
Lipid
What metal is needed for functioning of insulin?
Iron
Copper
Cobalt
Calcium
* Zinc
What substance is a precursor in the synthesis of prostaglandins in the organism?
Linolic acid
Palmitic acid
Linolenic acid
Oleic acid
* Arachidonic acid
What types of metabolism does insulin influence on?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Only on carbohydrate
On carbohydrate and lipid
On carbohydrate and albumen
On carbohydrate, lipid and protein
* On carbohydrate, lipid, protein and mineral
386.
When epinephrine binds to alpha-1 receptors, one result is
A. The receptor binds to the IRS-protein
B. The receptor inhibits phospholipase-C
C. * The endoplasmic reticulum releases calcium ions
D. There is a reduction in the diacylglycerol concentration
E. Calmodulin dissociates from all the proteins to which it normally binds
387.
When the blood concentration of insulin is increases, less glucagon is produced
and there is a(n)
A. Increases in the activity of adenylate cyclase
B. * Increase in the activity of cAMP phosphodiesterase (3’, 5’-phosphodiesterase)
C. Increase in binding of cAMP to the inhibitory subunits of protein kinase A
D. Increase in cAMP
E. Increase in protein kinase A activity
388.
Where are catecholamins secrected?
A. In a thyroid gland
B. In a parathyroid glands
C. In the cortex of a suprarenal gland
D. * In the medulla of a suprarenal gland
E. In the islets of Langerhans of pancreas
389.
Where is insulin synthesized?
A. In alfa-cells of Langergans ilets
B. * In the beta-cells of Langergans ilets
C. In the delta-cells of Langergansa ilets
D. In the endothelial cells of conclusion channels of pancreas
E. In стромі of pancreas
390.
Where is rennin synthesized?
A. In a liver
B. In a pancreas
C. In a thyroid gland
D. * In kidneys
E. In a hypophysis
391.
Which from below mentioned hormones is a complex protein?
A. ACTH.
B. * Follicle stimulating hormone
C. Oxytocin
D. Glucagon
E. Somatostatin
392.
Which from below mentioned hormones is a derivate of amino acid?
A. Calcitonin
B. Adrencorticotropic hormone
C. Insulin
D. Vasopressin
E. * Epinephrine
393.
Which hormone does stimulate lipolysis in fatty tissue?
A. Oxytocin
B. * Epinephrine
C. Foliculotropin
394.
395.
396.
397.
398.
399.
400.
401.
402.
D. Melanotropin
E. Calcitonin
Which hormone does stimulate lipolysis in fatty tissue?
A. Folikulotropin
B. Oxytocin
C. * Epinephrine
D. Melanotropin
E. Kalcitonin
Which hormones effect on the cells genetic apparatus?
A. Protein nature
B. Peptide nature
C. Hormones - derivates of amino acids
D. * Steroid hormones
E. All of above
Which of the following action is improper for insulin?
A. Increases the permeability of cell membranes for glucose.
B. * Inhibits the first enzyme of glycolysis – glucokinase.
C. Activates some enzymes of Krebs cycle.
D. Activates the pentose phosphate cycle;
E. Activates some enzymes of glycolysis
Which of the following effect of insulin is correct?
A. Activates the oxidation of fatty acids.
B. Activates the lipolysis.
C. Inhibits the synthesis of lipids.
D. * Enhances the synthesis of lipids.
E. All of the above
Which of the following hormone acts on the cell genetic apparatus?
A. Insulin.
B. * Testosteron.
C. Thyroxin.
D. Epinephrine.
E. Glucagon
Which of the following hormone acts on the cell genetic apparatus?
A. Insulin.
B. * Testosteron.
C. Glucagon
D. Epinephrine.
E. Vasopressin
Which of the following hormone acts through the activation of adenilate cyclase?
A. * Epinephrine.
B. Estrol.
C. Testosteron.
D. Cortisol.
E. Aldosteron
Which of the following hormone acts through the activation of adenilate cyclase?
A. * Epinephrine.
B. Estrol.
C. Testosteron.
D. Cortisol.
E. Aldosteron
Which of the following hormones promotes hypoglycemia?
A. Epinephrine
B.
C.
D.
E.
Norepinephrine
* Insulin
Glucagon
Glucocorticoids
403.
Which of the following is NOT a result of insulin binding to its receptor on a
muscle cell?
A. The receptor undergoes a change in conformation
B. The receptor autophosphorylates tyrosyl residues
C. Phosphorylation of the insulin receptor substrate (IRS) is increased
D. More glucose transporters are inserted into the membrane
E. * G-protein and adenylate cyclase are activated
404.
Which of the following is not true?
A. Glucagon causes the breakdown of glycogen in liver to yield glucose to the blood
B. Insulin inhibits glycogenolysis in the liver
C. Epinephrine causes the glycogen in liver to be degraded to yield glucose to the
blood
D. Insulin causes the transport of glucose into muscle cells
E. * Epinephrine inhibits glycolysis of glucose in muscle cells
405.
Which of the following proteins is responsible for secretion of pancreatic juice
into the intestine?
A. Cholecystokinin
B. Gastrin
C. Insulin
D. Intrinsic factor
E. * Secretin
406.
Which of the following rules is correct for epinephrine?
A. Epinephrine promotes synthesis of proteins.
B. * Epinephrine promotes decomposition of proteins.
C. Epinephrine promotes synthesis of lipids.
D. Epinephrine promotes synthesis of glycogen.
E. Epinephrine promotes decomposition of glucose
407.
Which of the following rules is correct for epinephrine?
A. Epinephrine promotes synthesis of proteins.
B. * Epinephrine promotes decomposition of proteins.
C. Epinephrine promotes synthesis of lipids.
D. Epinephrine promotes synthesis of glycogen.
E. All correct
408.
Which of the following statements about prostaglandins is true?
A. They are precursors to arachidonic acid
B. They release arachidonic acid from membranes through the action of
phospholipase A
C. * They were first observed to cause uterine contraction and lowering of blood
pressure
D. Although found in many organs, they are synthesized only in the prostate and
seminal vesicles
E. They may be converted to leukotrienes by lipoxygenase
409.
Which of the following statements accurately describes sex hormones?
A. They bind specific membrane receptors
B. They interact with DNA directly
C. They cause release of a proteinaceous second messenger from the cell membrane
D. * They enhance transcription when bound to receptors
E. They inhibit translation through specific cytoplasmic proteins
410.
Which of the following statements correctly describes insulin?
A. It is an anabolic signal to cells that glucose is scarce
B. It is converted from proinsulin to insulin primarily following secretion from ?cells
C. It does not have a prohormone form
D. It is a small polypeptide composed of a single chain bridged by disulfide groups
E. * Its action is antagonistic to that of glucagon
411.
Which of the following tissues is capable of contributing to blood glucose?
A. Brain
B. Adipose tissues
C. Cardiac muscle
D. * Duodenal epithelium
E. Cartilage
412.
With the purpose of analgesia a substance, which imitates the effects of morphine,
but produced in CNS, can be used. Choose it.
A. Somatoliberin
B. Oxytocin
C. Vasopressin
D. Calcitonin
E. * Endorphin
413.
________ is a process in which hormones are made less active or are eliminated
by attaching water-soluble molecules such as sulfate or glucuronic acid groups to them in
the liver.
A. Active transport
B. * Conjugation
C. Excretion
D. Metabolism
E. Structural protection
414.
A dietary deficiency of iodine can:
A. Directly affect the synthesis of thyroglobulin on ribosomes
B. * Result in increased secretion of thyroid stimulating hormone
C. Result in decreased production of thyrotropin releasing hormone
D. Result in increased heat production
E. Result in decreased heat production
415.
A hormone that increases sodium loss and lowers blood pressure is
A. Aldosterone
B. * Atrial natriuretic peptide
C. Antidiuretic hormone
D. Calcitonin
E. Glucagon
416.
A key intermediate for the synthesis of both testosterone and cortisol from
cholesterol is:
A. 7-hydroxycholesterol
B. * Pregnenolone
C. Aldosteron
D. Retinoic acid
E. 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
417.
Action of parathormone is tightly connected with vitamin:
A. A. С
B. B. A
C. * C. D
D. D. Е
E. E. K
418.
Adrenaline is...
A. Produced by the adrenal cortex
B. * Also called epinephrine
C. Released when the parasympathetic nervous system is stimulated
D. None of the above
E. All of the above
419.
An example of a mineralocorticoid is:
A. Glucagon
B. Cortisol
C. * Aldosterone
D. Testosterone
E. Insulin
420.
Associated with increased TBG (thyroxine-binding globulin):
A. Androgens
B. Colestipol
C. * Interleukin 2
D. Amiodarone
E. Estrogens
421.
Biochemical manifestation of excessive secretion of calcitonin:
A. A. Hypercalciemia
B. * B. Hypocalciemia
C. C. Hyperphosphatemia
D. D. Hypophosphaturia
E. E. Hypernatriemia
422.
Chemical nature of calcitonin:
A. * A. Peptide
B. B. Steroid
C. C. Derivative of amino acid
D. D. Derivative of аrachidonic acid
E. E. Glycoprotein
423.
Chemical nature of parathormone:
A. * A. Protein
B. B. Steroid
C. C. Derivate of amino acid
D. D. Lipid
E. E. Derivate of arachidonic acid
424.
Chemical nature of sex hormones
A. A. Proteins
B. B. Peptides
C. * C. Steroids
D. D. Derivates of the unsaturated fatty acids
E. E. Derivates of amino acids
425.
Choose a male sex hormone:
A. A. Estradiole
B. * B. Testosterone
C. C. Cortizon
D. D. Progesterone
E. E. Cortikosterone
426.
Choose the correct name of the state of hyperglycemia and glucosuria that appears
in hypercorticism?
A. A. Diabetes mellitus
B.
C.
D.
E.
B. Diabetes insipidus
* C. Steroid diabetes
D. Kidney diabetes
E. Adrenal diabetes
427.
Choose the pair of hormones that have agonistic effects on blood sugar levels:
A. A. Calcitonin and PTH
B. * B. Adrenalin and Glucagon
C. C. Glucagon and Glucose
D. D. ADH and Aldosterone
E. E. Only A
428.
Choose the statement about steroid hormones that is incorrect
A. Steroids are lipids with complex ring structures.
B. * Steroids can pass through their target cell membrane and interact with receptors
in the nucleus.
C. Steroids employ first and second messengers that amplify the cellular response.
D. The estrogens and testosterone are examples of steroid hormones.
E. All of the above
429.
Chose the effects that are caused by parathormone?
A. A. Hypocalciemia, hypophosphatemia, hyperphosphaturia
B. * B. Hypercalciemia, hypophosphatemia, hyperphosphaturia
C. C. Hypocalciemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperphosphaturia
D. D. Hypercalciemia, hypophosphatemia, hypophosphaturia
E. E. Hypercalciemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypophosphaturia
430.
Competitive inhibition of iodide uptake by the thyroid:
A. Perchlorate
B. Pertechnetate
C. * Thiocyanate
D. A & C
E. A, B & C
431.
Cortisol is produced by the:
A. * Adrenal cortex
B. Adrenal medulla
C. Pancreas
D. Thyroid gland
E. Salivary gland
432.
Cyclic AMP functions as a(n) _______________ for _______________
hormones.
A. Binding site; nonsteroid
B. Membrane receptor; steroid
C. Activity site; G protein
D. * Second messenger; nonsteroid
E. All of the above
433.
Diabetes insipidus results from a lack of:
A. Glucagon
B. Aldosterone
C. Calcitonin
D. * Antidiuretic hormone
E. Insulin
434.
Displacement of thyroid hormones (thyroxine, triiodothyronine) from TBG; may
cause hyperthyroxinemia:
A. * Methadone
B. Sucralfate
435.
436.
437.
438.
439.
440.
441.
442.
443.
C. Lithium
D. Furosemide
E. None of the above
Down-regulation occurs because
A. * Both hormone and receptor are taken into the cell by phagocytosis
B. Receptor molecules are degraded more quickly
C. There is a decrease in the rate of receptor synthesis
D. All of these
E. None of thes
During emergencies, the "fight-or-flight" response
A. Decrease the heartrate
B. * Is caused by hormone secretions in the adrenal medulla
C. Is stimulated by cortisol
D. Is the result of aldosterone causing faster blood flow
E. Is ingibitad by cortisol
Effective hyperthyroidism on thyroxine (T4) metabolic clearance:
A. * Increased
B. Decreased
C. No change
D. C and B
E. Only B
Epinephrine, norepinephrine, and thyroid hormones are examples of
A. Proteins.
B. Glycoproteins
C. Polypeptides.
D. * Amino acid derivatives.
E. Steroids.
Estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, and glucocorticoids are all examples of
A. Proteins
B. Glycoproteins
C. Polypeptides
D. Amino acid derivatives
E. * Steroids
Excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland
A. Is called hypothyroidism
B. * Can cause nervousness, irregular heartbeat, and weight loss
C. Can cause stunted growth and retardation in children
D. Can cause a goiter
E. Can cause riskets
Functions of parathormone:
A. A. Promotes deposition of calcium in bones and decreases Ca in blood
B. * B. Promotes resorption of calcium from bones and increases in blood
C. C. Stimulates reabsorption of phosphorus in kidney
D. D. Stimulates reabsorbtion of sodium in kidney
E. E. Inhibits reabsorption of sodium in kidney
Functions of prostaglandins:
A. A. Regulate activity of dehydrogenase in liver
B. B. Regulate reabsorption of water in kidney
C. C. Regulate the functions of nervous system
D. * D. Regulate gastric secretion
E. E. Regulate activity of hydrolase in cells
Glands in the endocrine system
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
444.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
445.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
446.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
447.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
448.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
449.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
450.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
451.
A.
B.
C.
D.
Produce hormones that are secreted into the digestive tract
* Release hormones into the bloodstream or the fluid around cells
Release hormones as rapidly as nerve impulses are transmitted
None of the above
All of the above
Hormon, that binds to receptors on Leydig cells:
* Luteinizing hormone
Prolactin
Thyroid stimulating hormone
Growth hormone
Follicle stimulating hormone
Hormone associated with diuresis:
Oxytocin
* Vasopressin
Both oxytocine and vasopresine
Neither oxytocine nor vasopressin
ACTH
Hormone associated with induction of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase:
* Cortisol
Aldosteron
Both cortisol and aldosteron
Neither cortisol nor aldosterone
Prolactin
Hormone found associated with neurophysin in secretory granules:
Oxytocin
Vasopressin
* Both oxytocine and vasopresine
Neither oxytocine nor vasopressin
Melanotonin
Hormone produced by anterior pituitary:
Oxytocin
Vasopressin
Both oxytocine and vasopresine
* Neither oxytocine nor vasopressin
Melanotonin
Hormone secreted in response to angiotensin II
Cortisol
* Aldosteron
Both cortisol and aldosteron
Neither cortisol nor aldosterone
Prolactin
Hormone that binds to intracellular receptor:
Cortisol
Aldosteron
* Both cortisol and aldosteron
Neither cortisol nor aldosterone
Prolactin
Hormone that is incoded by the propiomelanocortin gene:
Luteinizing hormone
Follicle stimylating hormone
Growth hormone
* Melanocyte stimulating hormone
E. Thyroid hormones
452.
Hormone that mediates its action by the second messenger:
A. Cortisol
B. Aldosteron
C. Both cortisol and aldosteron
D. * Neither cortisol nor aldosterone
E. Testosterone
453.
Hormone that stimulates testosterone production:
A. * Luteinizing hormone
B. Follicle stimylating hormone
C. Growth hormone
D. Melanocitostimulating hormone
E. Thyroid hormones
454.
Hormone that stimulates the production of estradiol by the immature ovarian
follicle:
A. Luteinizing hormone
B. Prolactin
C. Thyroid stimulating hormone
D. Growth hormone
E. * Follicle stimulating hormone
455.
Hormone that stimulates the production of progesterone by the corpus luteum:
A. * Luteinizing hormone
B. Prolactin
C. Thyroid stimulating hormone
D. Growth hormone
E. Follicle stimulating hormone
456.
Hormones can be any of these types of molecules EXCEPT
A. Proteins
B. Glycoproteins
C. Polypeptides
D. * Glycolipids
E. Steroids
457.
Hormones released by nerve cells of the _______ regulate hormones secreted by
the ____________.
A. Hypothalamus, anterior pituitary
B. * Hypothalamus, posterior pituitary
C. Anterior pituitary, hypothalamus
D. Cerebellum, posterior pituitary
E. Posterior pituitary, anterior pituitary
458.
Hormones that bind to plasma proteins
A. Bind reversibly
B. Establish an equilibrium between free hormones and bound hormones
C. Must be free hormones to diffuse through the capillary walls.
D. * Usually bind only to specific types of plasma proteins.
E. All of these
459.
Hormones with a short half-life regulate activities that have a __________ onset
with a __________ duration.
A. Rapid, long
B. Rapid, short
C. Slow, long
D. * Slow, short
E. Only C
460.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
461.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
462.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
463.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
464.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
465.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
466.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
467.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
468.
Hormones'
Are not secreted at a constant rate
Function to regulate the rates of many activities in the body
Secretion rate is controlled by negative feedback mechanisms
Help maintain homeostasis
* All of these
How glucocorticoids affect carbohydrate metabolism?
Repress gluconeogenesis
* Activate gluconeogenesis
Activate glycolisis
Stimulate the transport of glucose into cells
Stimulate pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
How glucocorticoids affect lipid metabolism?
* Activate lypolysis and transformation of fats into carbohydrates
Inhibit lypolysis and transformation of fats into carbohydrates
Activate the synthesis of phospholipids and cholesterol in liver
Stimulate the synthesis of triacylglycerols and chylomicrones in the walls of
intestine
Activate oxidation of fatty acids and formation of ketone bodies
How glucocorticoids affect protein metabolism?
Promote the synthesis of proteins in all organs
* Promote the synthesis of proteins in liver and activate their decomposition in
connective and muscle tissues
Promote the proteolysis in all organs
Stimulate the transport of amino acids in cells
Activate the transformation of carbohydrates to proteins
How iodine containing hormones are transported in blood?
In the free state
* Connected with albumins
Connected with w-globulins
Connected with C-globulins
Connected with C-globulins
How many carbon atoms the molecules of euicosanoids contain?
15
18
* 20
22
24
How sex hormones affect the protein metabolism?
Stimulate disintegration of proteins
Activate conversion of proteins into carbohydrates
* Stimulate the synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids
Activate transaminases of amino acids
Activate the synthesis of urea
How thyroid hormones affect lipid metabolism?
Stimulate the synthesis of triacylglycerols
Stimulate lipogenesis and synthesis of cholesterol in liver
Activate formation of chylomicrones in intestine and VLDL in liver
* Activate mobilization of fats and their oxidation
Activate the synthesis of phospholipids in liver
How thyroid hormones affect protein metabolism?
A. * In normal concentration stimulate the synthesis of proteins, in increased –
decomposition.
B. In a small concentration stimulate decomposition of proteins, in increased their
synthesis
C. Stimulate the decomposition of proteins and their transformation into
carbohydrates
D. In certain organs stimulate the synthesis of proteins, in other - decomposition
E. Repress desamination and transamination of aminoacids
469.
Hypersecretion of Thyroxin would be caused by an increase in the release of:
A. FSH or LH
B. STHRH or STH
C. TSH or ACTH
D. * TRH or TSH
E. All of the above
470.
Hypofunction of thyroid gland in adults results in:
A. Cretinism
B. Dwarfing
C. Toxic goiter
D. * Mixedema
E. Acromegalia
471.
Hypofunction of thyroid gland in children results in:
A. Gigantism
B. Graves disease
C. Toxic goiter
D. Dwarfing
E. * Cretinism
472.
If there is a decrease in the specific plasma protein to which a hormone binds
A. More free hormone occurs
B. Less hormone binds to target cells
C. * Blood levels of the hormone increase
D. All of these
E. None of above
473.
In excess of this hormone uncoupling of the tissue respiration and oxidative
phosphorylation takes place. Decrease of ATP formation and increase of heat formation
occur. What hormone is it?
A. Cortizol
B. * Thyroxine
C. Progesteron
D. Parathormone
E. Glucagon
474.
In the "second messenger" theory, which is the first messenger?
A. cAMP
B. Hormone
C. Enzyme
D. * Receptor
E. All of the above
475.
In the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland is controlled by hormones made where?
A. * In the Hypothalamus
B. In the Adrenal Gland
C. In the Pancreas
D. In the Parathyroid
E. In the Anterior pituitary
476.
Increased blood glucose causes increased insulin secretion from the pancreas. This
is an example of
A. * Hormonal regulation of hormone secretion.
B. Neural regulation of hormone secretion.
C. Nonhormonal regulation of hormone secretion.
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
477.
Inhibition of thyroid hormone synthesis or release:
A. Amiodarone
B. * Lithium
C. Minoglutethimide
D. Iodides
E. E. All of the above
478.
Inhibits iodide transport into thyroid gland:
A. Ipodate
B. * Thiocyanate
C. Thioamides
D. A & C
E. A, B & C
479.
Intracellular hormone receptors are located
A. * Floating freely in the cytoplasm of target cells.
B. In the nucleus.
C. In the mitochondria.
D. In the endoplasmic reticulum.
E. Both a and b
480.
Lipid-soluble hormones
A. * Can bind to plasma proteins
B. Attach to intracellular receptors in target cells
C. Tend to have slower onset and longer duration
D. Include steroids
E. All of these
481.
More potent thyroid hormone:
A. T4
B. * T3
C. Equal potent
D. Vasopressin
E. Prolactin
482.
Name a biological active compound which is the derivative of arachidonic acid:
A. * Prostaglandin
B. Thyroxine
C. Noradrenaline
D. Cholin
E. Ethanolamine
483.
Name female sex hormones?
A. * Estradiol, estrione, estrole, progesterone
B. Testosterone, estrione, estrole
C. Cortisone, progesterone, estrione, estrole
D. Progesterone, corticosterone, estrione, estrole
E. Testosterone, estrole, corticosterone, estrione
484.
Name hormone that is synthesized from cholesterol by cells of the adrenal cortex:
A. Cortisol
B. Aldosteron
485.
486.
487.
488.
489.
490.
491.
492.
493.
C. * Both cortisol and aldosteron
D. Neither cortisol nor aldosterone
E. Prolactin
Name hormone that stimulates production of insulin-like growth factor:
A. Luteinizing hormone
B. Prolactin
C. Thyroid stimulating hormone
D. * Growth hormone
E. Follicle stimulating hormone
Name hormone that stimulates the synthesis of milk proteins:
A. Luteinizing hormone
B. * Prolactin
C. Thyroid stimulating hormone
D. Growth hormone
E. Follicle stimulating hormone
Name hormone which release is inhibited by thyroxine:
A. Luteinizing hormone
B. Prolactin
C. * Thyroid stimulating hormone
D. Growth hormone
E. Follicle stimulating hormone
Parathyroid hormone stimulates the formation of active form of vitamin D:
A. In liver
B. In blood
C. In brain
D. In intestine
E. * In kidneys
Parathyroid hormone stimulates the formation of active form of vitamin D:
A. In liver
B. In blood
C. In brain
D. In intestine
E. * In kidneys
Preparation of choice for thyroid replacement.
A. * Dessicated thyroid
B. Liothyronine
C. Levothyroxine
D. Propylthiouracil
E. Methimazole
Prostaglandins are ___________ substances that regulate neighboring cells.
A. Endocrine
B. * Paracrine
C. Eccrine
D. Glycoprotein
E. Lipoprotein
Prostaglandins are synthesized from:
A. Cholesterol
B. Amino Acids
C. Carbohydrates
D. * Fatty Acids
E. Vitamins
Sex hormones are secreted by ________________.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
494.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
495.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
496.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
497.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
498.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
499.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
500.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
501.
A.
B.
C.
D.
All endocrine tissues of the body
The inner cortex of the adrenal medulla
The inner cortex of the adrenal medulla and the gonads
* The gonads
Pancreas
Steroid hormones are synthesized from:
Fatty acids
* Cholesterol
Glucose
Phospholipids
Amino acids
Target organs for specific hormones are determined by
Whether the hormone is water-soluble or lipid-soluble
How close the target organ is to the endocrine gland that secretes that hormone
* The type of receptors on that organ
How much hormone is secreted
The blood supply to the specific organ
The body's normal metabolic rate is regulated by
* Thyroid hormones
Epinephrine
Metaboloxin
Prolactin
Vasopressin
The derivatives of which amino acid are iodthyronines?
Tryptophane
Histidine
Glutamic acid
Serine
* Tyrosine
The effect of thyroxine on carbohydrate metabolism:
* Activates decomposition of glycogen
Represses absorption of carbohydrates in intestine
Represses decomposition of glycogen
Represses gluconeogenesis
Activates the synthesis of glycogen
The following compound is a precursor for the synthesis of prostaglandins:
Tyrosine
Cholesterol
Acetyl-CoA
Glycerol
* Arachidonic acid
The followings hormones are synthesized in thyroid glands:
Parathormone and iodthyronines
* Calcitonin and iodthyronines
Thyrotropic hormone and iodthyronines
Thyrotropic hormone and calcitonin
Thyrotropic hormone and parathormone
The hormone _____ causes the contractions of labor.
Prolactin
Estrogen
* Oxytocin
Progesterone
E. Thyroid hormon
502.
The hormone Progesterone causes what to occur in women?
A. Follicle Development
B. Development of the Uterine Lining
C. Spermatogenesis
D. * Female Secondary Sex Characteristics
E. Only A
503.
The hypothalamus has a dual function in that it
A. * Sends nerve impulses and also makes hormones
B. Is both a nervous and olfactory organ
C. Belongs to both the nervous and circulatory systems
D. Is found connected to both kidneys
E. All of the above
504.
The insufficient production of mineralocorticoids (Addison diseases, bronze
diseases) is accompanied with muscle weakness. This is explained by the excretion with
urine increased amount of ions of:
A. * Na+
B. K+
C. H+
D. Ca2+
E. Mg2+
505.
The islets of Langerhans are found in the:
A. Kidney
B. Adrenal gland
C. * Pancreas
D. Pituitary gland
E. Liver
506.
The large gland located on either side of the larynx is the:
A. Parathyroid gland
B. Pituitary gland
C. * Thyroid gland
D. Adrenal gland
E. Pancreas
507.
The largest number of hormones binds to
A. Membrane-bound receptors and control ion channels.
B. Membrane-bound receptors and activate G proteins.
C. Membrane-bound receptors that phosphorylate intracellular proteins.
D. * Intracellular receptors.
E. Only C
508.
The lipid hormones are either __________ or derivatives of fatty acids.
A. Glycolipids
B. Phospholipids
C. * Steroids
D. Triglycerides
E. Glycerols
509.
The Pancreas produces which 2 hormones:
A. Epinephrine and Insulin
B. Melatonin and Glucagon
C. * Insulin and Glucagon
D. Glucagon and Norepinephrine
E. Glucagon and vasopressin
510.
The pineal gland has been implicated in the disorder
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Diabetes mellitus
Hypothyroidism
* Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) syndrome
None of the above
Scurvy
511.
The pituitary gland is controlled by the:
A. Anterior LobeB.
B. * Hypothalamus
C. Posterior Lobe
D. Frontal Cortex
E. All of thq above
512.
The stalk connecting the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland is called the:
A. * Pituitary cortex
B. Infundibulum
C. Anterior lobe
D. Hypophysis
E. Neurohypophysis
513.
The synthesis of sex hormones is controlled by:
A. Central nervous system
B. Neurophysin
C. Hormones of hypothalamus
D. Aldosterone
E. * Gonadotropic hormones of hypophysis
514.
The target of the hormone Erythropoietin is:
A. White Blood Cells
B. The Kidneys
C. * Bone Marrow
D. Right Atrium of the Heart
E. All of the above
515.
This hormone in a normal concentration stimulates the synthesis of proteins and
nucleic acids, in increased concentration – activates catalytic processes. What hormone is
it?
A. Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Somatotropic hormone
D. Testosteron
E. * Thyroxine
516.
This hormone promotes the transition of calcium from bones to blood, inhibits
reabsorption of phosphorus in kidneys and stimulates absorption of calcium in intestine.
Which hormone is it?
A. Calcitonin
B. Thyroxine
C. Triiodthyronine
D. * Parathormone
E. Thyrotropin
517.
This hormone promotes the transition of calcium from bones to blood, inhibits
reabsorption of phosphorus in kidneys and stimulates absorption of calcium in intestine.
Which hormone is it?
A. Calcitonin
B. Thyroxine
C. Triiodthyronine
D. * Parathormone
E. Thyrotropin
518.
This hormone stimulates the formation of 1,25- dihydroxycholecalciferol in
kidneys. What hormone is it?
A. Calcitonin
B. Thyroxine
C. Triiodthyronine
D. * Parathormone
E. Thyrotropin
519.
This hormone stimulates the formation of 1,25- dihydroxycholecalciferol in
kidneys. What hormone is it?
A. Calcitonin
B. Thyroxine
C. Triiodthyronine
D. * Parathormone
E. Thyrotropin
520.
Thyroid hormone more to be completely absorbed following oral administration
A. Thyroxine
B. Triiodothyronine
C. Both equally absorbed
D. * Neither absorbed orally, requires parenteral administration
E. Vasopressin
521.
Water-soluble hormones
A. Have a long half-life.
B. Have a short half-life.
C. * Bind to intracellular receptors.
D. Both a and c
E. Only A
522.
Water-soluble hormones, such as proteins, glycoproteins, epinephrine and
norepinephrine
A. Have relatively long half-lives.
B. * Are degraded rapidly by enzymes.
C. Have half-lives that increase and decrease slowly.
D. Regulate activities that have a long duration
E. A, c, and d
523.
What is a precursor for the synthesis of corticosteroids?
A. Tyrosine
B. Arachidonic acid
C. Phenylalanine
D. * Cholesterol
E. Glycerol
524.
What is another name for thyroxine?
A. * Tetraiodothyronine
B. Thyroid
C. Thymus
D. Triiodothyronine
E. Lipotropic hormon
525.
What is the function of aldosterone?
A. Represses reabsorption of sodium, activates reabsorption of water
B. * Activates reabsorption of sodium, activates reabsorption of water
C. Represses reabsorption of sodium, represses reabsorption of water
D. Represses the excretion of potassium ions from organism, activates reabsorption
of sodium
526.
527.
528.
529.
530.
531.
532.
E. Represses the excretion of potassium ions from organism, represses reabsorption
of sodium
What is the function of calcitonin?
A. Promotes the transition of calcium from bones to blood, inhibits reabsorption of
phosphorus in kidney
B. Promotes the transition of calcium from blood to bones, stimulates reabsorption
of phosphorus in kidney
C. * Promotes the transition of calcium from blood to bones, inhibits reabsorbtion of
phosphorus in kidney
D. Promotes the transition of calcium from bones to blood, stimulates reabsorption
of phosphorus in kidney
E. Inhibits the exit of calcium from bones, activates reabsorption of phosphorus in
kidney
What is the function of insulin?
A. Antagonistic to glucagon
B. Decreases glycogen storage in liver and muscle
C. Reduces hyperglycemia
D. * All of the above
E. None of the above
What is the function of parathormone?
A. * Promotes transition of calcium from bones to blood, inhibits reabsorbtion of
phosphorus in kidney
B. Promotes transition of calcium from blood to bones, stimulates reabsorption of
phosphorus in kidney
C. Promotes transition of calcium from blood to bones, inhibits reabsorbtion of
phosphorus in kidney
D. Promotes transition of calcium from bones to blood, stimulates reabsorption of
phosphorus in kidney
E. Inhibits the exit of calcium from bones, inhibits reabsorption of phosphorus in
kidney
What is the half-life time of iodine containing hormones?
A. 20 min
B. * 1 week
C. C. 20 sec
D. D. 60 min
E. E. 1 month
What is the name of disease that is developed in hyperfunction of thyroid glands:
A. A. Cretinism
B. B. Mixedema
C. C. Gigantism
D. * D. Graves disease
E. E. Dwarfism
What is the nature of iodthyronines?
A. A. Proteins
B. B. Peptids
C. * C. Derivatives of amino acid
D. D. Derivates of fatty acids
E. E. Steroids
What is the target of ACTH?
A. Most cells
B. Thyroid gland
C. Mammary glands
D. * Adrenal cortex
E. Adrenal medulla
533.
What is the ultimate purpose of hormones?
A. To maintain growth
B. To keep the brain functioning
C. * To stimulate metabolism
D. None of the above
E. All of the above
534.
Where is hormone calcitonin synthesized?
A. In parathyroid glands
B. In a hypophyses
C. * In a thyroid gland
D. In a pancreas
E. In adrenal glands
535.
Where progesterone is formed?
A. In follicles of ovaries
B. In adrenal cortex
C. In testicules
D. * By a yellow body and placenta
E. By follicles, adrenal cortex, testicules
536.
Which effects are specific for the thyroid hormones?
A. Stimulate the synthesis of glycogen, stimulate decomposition of proteins,
stimulate the synthesis of lipids
B. Stimulate lipogenesis, promotes the formation of ATP in mithochondria, at large
concentrations stimulate the synthesis of proteins
C. Activate lipolysis, activate the synthesis of cholesterol, activate a gluconeogenesis
D. Activate decomposition of proteins and stimulate a basic metabolism, repress
decomposition of fats, stimulate the synthesis of glycogen in muscles and liver
E. * Activate breaking up of glycogen and absorbtion of carbohydrates in intestine,
activate lipolysis and oxidation of fatty acids, in an increased concentration
stimulate the decomposition of proteins
537.
Which fatty acid is a precursor in the synthesis of such important compounds as
prostaglandins, leucotrienes and thromboxanes?
A. * Arachidonic
B. Linolic
C. Oleic
D. Stearic
E. Palmitooleic
538.
Which hormone directly affects blood pressure?
A. * ADH
B. Insulin
C. PTH
D. ACTH
E. Glucagon
539.
Which hormone has steroid nature?
A. Calcitonine
B. Parathormone
C. Norepinephrine
D. Epinephrine
E. * Estron
540.
Which hormone has the greatest effect on metabolism?
A. GH
B.
C.
D.
E.
541.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
542.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
543.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
544.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
545.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
546.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
547.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
548.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Thyroxine
TSH
ACTH
FSH
Which hormone has the greatest influence on the ability to secrete milk?
Oxytocin
Estrogen
* Prolactin
Progesterone
Vasopressin
Which hormone is mineralocorticoid?
Corticosteron
Cortison
Hydrocortisone
* Aldosterone
Progesteron
Which hormone is produced in the Beta cells of the islets of Langerhans:
Melatonin
Glucagon
* Insulin
Calcitonin
Vasopressin
Which hormone is the derivative of the unsaturated fatty acids?
Estradiol
Progesterone
Noradrenaline
Testosterone
* Prostaglandins
Which hormone opposes the effects of parathyroid hormone?
* Calcitonin
Glucagon
Growth hormone
Prolactin
Vasopressin
Which hormone stimulates the synthesis of W-lactalbumin:
Oxytocin
Aldosterone
Vasopressin
* Prolactin
Cortisol
Which hormone stimulates the uterine contraction:
* Oxytocin
Aldosterone
Vasopressin
Prolactin
Cortisol
Which hormone works antagonistically to parathormone:
Triiodothyronine
Insulin
Estrogen
* Calcitonin
Vasopressin
549.
Which hormones act on the genetic apparatus of cell?
A. Protein nature
B. Peptide nature
C. Hormones - derivates of amino acids
D. * Steroid nature
E. Polipeptide nature
550.
Which hormones are the derivates of cholesterol?
A. * Adrenal cortex, sex hormones
B. Tropic hormones of hypophysis
C. Vasopressine and oxytocine
D. Thyroid gland hormones
E. Glucagon and insulin
551.
Which hormones belong to glucocorticoids?
A. Cortison, hydrocortisone, aldosterone
B. * Cortison, hydrocortisone, corticosterone
C. Hydrocortisone, corticosterone, aldosterone
D. Estriole, corticosterone, aldosterone
E. Corticosterone, estradiol, corticosterone
552.
Which hormones regulate the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus?
A. Liberins and statins
B. * Parathormone and calcitonin
C. Thyroid hormones and glucagon
D. Calcitonin and somatostatin
E. Calcitonin and glucagon
553.
Which iodthyronines do you know?
A. A. Тriiodthyronine, diiodthyronine
B. * B. Tetraiodthyronine, triiodthyronine
C. C. Thyroxine, calcitonin
D. D. Calcitonin, parathormone
E. E. Thyroxine, diiodthyronine
554.
Which is not a function of the hypothalamus?
A. * Affect heart rate
B. Control temperature
C. Affect water balance
D. Secrete FSH
E. None of the above
555.
Which microelement is needed for the synthesis of hormones of thyroid glands?
A. A. Iron
B. B. Fluorine
C. * C. Iodine
D. D. Cobalt
E. E. Zinc
556.
Which of the following compounds increases the release of Ca2+ from the
endoplasmatic reticulum?
A. Diacylglycerol
B. * Inositol tryphosphate
C. Parathyroid hormone
D. 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
E. Retinol
557.
Which of the following effects are caused by calcitonin?
A. * A. Hypocalciemia, hypophosphatemia, hyperphosphaturia
B. B. Hypercalciemia, hypophosphatemia, hyperphosphaturia
558.
559.
560.
561.
562.
563.
564.
565.
566.
C. C. Hypocalciemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperphosphaturia
D. D. Hypercalciemia, hypophosphatemia, hypophosphaturia
E. E. Hypercalciemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypophosphaturia
Which of the following hormones is synthesized in the posterior pituitary?
A. * Antidiuretic hormone
B. Melatonin
C. Growth hormone
D. None of the above
E. Somatotropic hormon
Which of the following is MISMATCHED?
A. Oxytocin – hypothalamus
B. Insulin – pancreas
C. Glucagon – pancrease
D. * Thyroid hormone -- pituitary gland
E. Vasopressin – posterior pitutery gland
Which of the following is NOT a product of the adrenal gland?
A. Cortisol
B. * Aldosterone
C. Progesterone
D. Epinephrine
E. Insulin
Which of the following is true of epinephrine?
A. Acts only throught the phosphatidylinositol biphosphate system
B. * Is synthesized from tyrosine
C. Decreases the level of cAMP in liver cells
D. Functions like a steroid hormone
E. Is produced from estradiol
Which of the following is true of testosterone?
A. * May be converted to a more active androgen in its target cells
B. Acts by binding to receptors on the cell surface
C. Is produced from estradiol
D. Stimulates the synthesis of gonadotropin releasing hormone by the hypothalamus
E. Stimulates the synthesis of epinephrine
Which of these does not directly stimulate the gonads?
A. FSH
B. * TTH
C. LH
D. ACTH
E. All of the above
Which of these hormone types bind to intracellular receptors?
A. * Proteins
B. Glycoproteins
C. Polypeptides
D. Epinephrine
E. Steroids
Which of these hormones is made by the posterior pituitary?
A. FSH
B. LH
C. ACTH
D. * ADH
E. Prolactin
Which of these hormones is secreted in the liver?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Renin
* Somatomedin
Erythropoietin
Estrogen
Insulin
567.
Which of these is an example of positive-feedback regulation in the endocrine
system?
A. * An increase in blood glucose causes an increase in insulin secretion; insulin
moves glucose into cells.
B. An increase in TSH causes an increase in thyroid hormone secretion; thyroid
hormones inhibit TSH secretion.
C. Before ovulation, an increase in LH causes an increase in estrogen, which causes
an increase in LH.
D. An increase in TRH causes an increase in TSH secretion; thyroid hormone
inhibits TRH secretion.
E. An increase in blood calcium causes an increase in calcitonin secretion; calcitonin
moves calcium into the blood.
568.
Which of these is not an endocrine gland?
A. Pancreas
B. Testes
C. * Salivary gland
D. Parathyroid
E. All of the above
569.
Which statement is false?
A. The endocrine system is composed of ductless glands
B. Contents of the endocrine system are released into the bloodstream
C. * The mammory gland is part of the endocrine system
D. Exocrine glands are not part of the endocrine system
E. Non of the above
570.
Which symptoms are typical for hypofunction of thyroid gland?
A. A. Increase of body temperature, exophthalmia, loss of weight
B. B. Sweat, increased body temperature
C. * C. Lowering of basic metabolism, lowering of body temperature, and swelling.
D. D. Loss of weight, increase sweating, mucosa edema.
E. E. Hyperpigmentation, obesity
571.
Which two groups of hormones are synthesized by adrenal cortex?
A. A. Corticosteroids and mineralocorticoids
B. B. Corticosteroids and glucocorticoids
C. * C. Glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids
D. D. Catecholamines and corticosteroids
E. E. Catecholamines and glucocorticoids
572.
Which two hormones are released from the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland?
A. ADH and GH
B. ACTH and TSH
C. * ADH and oxytocin
D. TRH and CRH
E. Insulin and glucagon
573.
‘Burning foot syndrome’ has been described to the deficiency of:
A. * Pantothenic acid
B. Thiamin
C. Cobalamin
D. Pyridoxine
E. Ascorbic acid
574.
A deficiency of vitamin B12 causes
A. Beri-Beri
B. Scurvy
C. * Perniciuos anemia
D. Ricket
E. Pellagra
575.
A molecule of CO2 is captured by biotin when it acts as coenzyme for
carboxylation reaction. The carboxyl group is covalently attached to
A. * A nitrogen (N1) of the biotin molecule
B. Sulphur of thiophene ring
C. ?-Amino group of lysine
D. ?-Amino group of protein
E. All of these
576.
A provitamin D synthesized in human beings is
A. Ergosterol
B. * 7-Dehydrocholesterol
C. Cholecalciferol
D. 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol
E. All of these
577.
A vitamin which can be synthesized by human beings is:
A. Thiamin
B. * Niacin
C. Folic acid
D. Cyanocobalamin
E. Both B and C
578.
An important function of vitamin A is
A. To act as coenzyme for a few enzymes
B. To play an integral role in protein synthesis
C. To prevent hemorrhages
D. * To maintain the integrity of epithelial tissue
E. A and C only
579.
Anti-egg white injury factor is:
A. Pyridoxine
B. * Biotin
C. Thiamin
D. Liponic acid
E. All of these
580.
Ascorbic acid can reduce
A. 2, 6-Dibromobenzene
B. 2, 6-Diiodoxypyridine
C. * 2, 6-Dichlorophenol indophenol
D. 2, 4-Dinitrobenzene
E. All of the above
581.
Ascorbic acid is required to synthesise all of the following except:
A. Collagen
B. Bile acids
C. * Bile pigments
D. Epinephrine
E. Both B and C
582.
Biotin is a coenzyme for:
A. Pyruvate carboxylase
B.
C.
D.
E.
583.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
584.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
585.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
586.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
587.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
588.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
589.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
590.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Acetyl CoA carboxylase
Propionyl CoA carboxylase
* All of these
None of these
Biotin is a coenzyme of the enzyme:
* Carboxylase
Hydroxylase
Decarboxylase
Deaminase
Dehydrogenase
Biotin is required as a coenzyme by:
Anaerobic dehydrogenases
Decarboxylases
Aerobic dehydrogenases
* Carboxylases
All of these
Chemically, lipoic acid is:
Saturated fatty acid
Unsaturated fatty acid
Amino acid
* Sulphur containing fatty acid
Keto acid
Coenzyme A contains a nitrogenous base which is:
* Adenine
Guanine
Choline
Ethanolamine
Tymine
Conversion of all-trans-retinal into all-trans-retinol requires:
NAD
NADH
NADP
* NADPH
FAD
Conversion of folate into tetrahydrofolate requires:
NADH
* NADPH
FMNH2
FADH2
TPP
Conversion of retinal into retinol requires the presence of:
PLP
* NADPH
FADH2
Lipoic acid
Both B and C
Daily requirement of niacin is
5 mg
10 mg
* 20 mg
35 mg
20 g
591.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
592.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
593.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
594.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
595.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
596.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
597.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
598.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
599.
A.
B.
C.
Daily requirement of vitamin C in adults is about:
100 mg
25 mg
* 70 mg
100 mg
70 g
Deficiency of Vitamin A causes
* Xeropthalmia
Hypoprothrombinemia
Megaloblastic anemia
Pernicious anemia
Beri-Beri
Deficiency of vitamin B12 can occur because of:
Decreased intake of vitamin B12
Atrophy of gastric mucosa
Intestinal malabsorption
* All of these
None of these
Deficiency of vitamin C causes:
Beriberi
Pellagra
Pernicious anaemia
* Scurvy
Both A and D
Deficiency of vitamin D causes
* Rickets and osteomalacia
Tuberculosis of bone
Hypothyroidism
Skin cancer
Cretinism
Ergosterol is found in
Animals
* Plants
Bacteria
All of these
Both A and B
FAD is a coenzyme for
Succinate dehydrogenase
Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
Sphingosine reductase
* All of these
None of these
Fat soluble vitamins are
Soluble in alcohol
one or more Propene units
Stored in liver
* Cause hypervitaminosis
All these
Folic acid contains:
Pteridine
p-Amino benzoic acid
Glutamic acid
600.
601.
602.
603.
604.
605.
606.
607.
608.
D. * All of these
E. None of these
Function of Vitamin A:
A. Healing epithelial tissues
B. Protein synthesis regulation
C. Cell growth
D. * All of these
E. None of these
In the body 1 mg of niacin can be produced from:
A. 60 mg of pyridoxine
B. * 60 mg of tryptophan
C. 30 mg of tryptophan
D. 30 mg of pantothenic acid
E. 60 g of tryptophan
Intrinsic factor is chemically a:
A. Protein
B. * Glycoprotein
C. Mucopolysaccaride
D. Peptide
E. Amino acid
Lipoic acid is a conenzyme for:
A. Pyruvate dehydrogenase
B. ?-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
C. * Both (A) and (B)
D. Glutamate dehydrogenase
E. None of these
Methylcobalamin is required for formation of
A. Serin from glycine
B. Glycine from serine
C. * Methionine from homocysteine
D. All of these
E. Both (B) and (C)
NAD is required as a coenzyme for
A. * Malate dehydrogenase
B. Succinate dehydrogenase
C. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
D. HMG CoA reductae
Niacin can be synthesised in human beings from
A. Histidine
B. Phenylalanine
C. Tyrosine
D. * Tryptophan
E. Both (A) and (C)
Niacin contains a
A. Sulphydryl group
B. * Carboxyl group
C. Amide group
D. All of these
E. None of these
Niacin deficiency can occur in
A. * Hartnup disease
B. Phenylketonuria
609.
610.
611.
612.
613.
614.
615.
616.
617.
C. Alkaptonuria
D. None of these
E. Both (A) and (C)
Niacin deficiency is common in people whose staple food is
A. Wheat
B. Polished rice
C. * Maize and /or sorghum
D. None of these
E. Both (A) and (C)
Niacin is present in maize in the form of:
A. Niatin
B. Nicotin
C. * Niacytin
D. Nicyn
E. None of these
Niacin is synthesized in the body from:
A. * Tryptophan
B. Tyrosine
C. Glutamate
D. Aspartate
E. None of the above
Niacin or nicotinic acid is a monocarboxylic acid derivative of:
A. * Pyridine
B. Pyrimidine
C. Flavin
D. Adenine
E. A and B
On exposure to light rhodopsin forms
A. * All trans-retinal
B. Cis-retinal
C. Retinol
D. Retinoic acid
E. All of the above
One international unit (I.U) of vitamin D is defined as the biological activity of
A. * 0.025 µg of cholecalciferol
B. 0.025 µg of 7-dehydrocholecalciferol
C. 0.025 µg of ergosterol
D. 0.025 µg of ergocalciferol
Pantothenic acid contains an amino acid which is:
A. Aspartic acid
B. Glutamic acid
C. * Alanine
D. ?-Aminoisobutyric acid
E. None of these
Pellagra is caused due to the deficiency of:
A. Ascorbic acid
B. Pantothenic acid
C. Pyridoxine
D. * Niacin
E. C and D
Pellagra occurs in population dependent on:
A. Wheat
B.
C.
D.
E.
618.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
619.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
620.
A.
B.
C.
D.
621.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
622.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
623.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
624.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
625.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
626.
Rice
* Maize
Milk
B and C
Pellagra preventing factor is
Thiamin
Riboflavin
* Niacin
Pyridoxine
Both (A) and (C)
Precursor of Vitamin A is:
?-Carotene
?-Carotene
?-Carotene
* All of these
Both A and B
Preformed Vitamin A is supplied by Milk, fat and liver
* All yellow vegetables
All yellow fruits
Leafy green vegetables
All of the above
Provitamin D3 is
Cholecalciferol
Ergosterol
* 7-Dehydrocholesterol
Ergocaliferol
All of these
Provitamins A include
Retinal
Retionic acid
* Carotenes
Both B and C
All of these
Pyridoxal phosphate is a coenzyme for
Glutamate oxaloacetate transaminase
Glutamate pyruvate transaminase
Tyrosine transaminase
* All of these
None of these
Pyridoxal phosphate is required as a coenzyme in
Transamination
Transulphuration
Desulphydration
* All of these
Dehydrogenation
Pyridoxine deficiency can be diagnosed by measuring urinary excretion of
Pyruvic acid
Oxaloacetic acid
* Xanthurenic acid
None of these
All of these
Pyridoxine requirement depends upon the intake of
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Carbohydrates
* Proteins
Fats
All of these
None of these
627.
Retinoic acid participates in the synthesis of
A. Iodopsin
B. Rhodopsin
C. * Glycoprotein
D. Cardiolipin
628.
Retinol and retinal are interconverted requiring dehydrogenase or reductase in the
presence of
A. * NAD or NADP
B. NADH + H+
C. NADPH
D. FAD
E. PLP
629.
Retinol isomerase is present in:
A. Retina
B. * Liver
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Cornea
E. None of these
630.
Rhodopsin contains opsin and:
A. * 11-cis-retinal
B. 11-trans-retinal
C. All-cis-retinal
D. All trans-retinal
E. All of these
631.
Riboflavin deficiency can cause
A. Peripheral neuritis
B. Diarrhoea
C. * Angular stomatitis
D. None of these
E. Both (A) and (C)
632.
Riboflavin deficiency symptoms are:
A. Glossitis
B. Stomatis
C. Vomitting
D. * Both (A) and (B)
E. Diarrea
633.
Riboflavin is heat stable in
A. Acidic medium
B. Alkaline medium
C. Neutral medium
D. * Both (A) and (C)
E. Both (B) and (C)
634.
Scurvy is caused due to the deficiency of
A. Vitamin A
B. Vitamin D
C. Vitamin K
D. * Vitamin C
635.
636.
637.
638.
639.
640.
641.
642.
643.
E. B and D only
Sterilised milk lacks in
A. Vitamin A
B. Vitamin D
C. * Vitamin C
D. Thiamin
E. All of the above
Sulphydryl group of coenzyme a is contributed by:
A. Alanine
B. ?-Aminoisobutyric acid
C. Methionine
D. * Thioethanolamine
E. Both (A) and (D)
The central heavy metal cobalt of vitamin B12 is coordinately bound to
A. * Cyanide group
B. Amino group
C. Carboxyl group
D. Sulphide group
E. Hydroxyl group
The enzymes with which nicotinamide act as coenzyme are:
A. * Dehydrogenases
B. Transaminases
C. Decarboxylases
D. Carboxylases
E. A and B
The following is required for the formation of coenyzme A:
A. * ATP
B. GTP
C. CTP
D. None of these
E. AMP
The most important natural antioxidant is
A. Vitamin D
B. * Vitamin E
C. Vitamin B12
D. Vitamin K
E. All of these
The most potent Vitamin D metabolite is
A. 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol
B. * 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol
C. 24, 25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol
D. 7-Dehydrocholesterol
E. All of these
The pellagra preventive factor is:
A. Riboflavin
B. Pantothenic acid
C. * Niacin
D. Pyridoxine
E. Ascorbic acid
The requirement of vitamin E is increased with greater intake of
A. Carbohydrates
B. Proteins
644.
645.
646.
647.
648.
649.
650.
651.
652.
C. * Polyunsaturated fat
D. Saturated fat
E. A and B
The vitamin having the highest daily requirement among the following is:
A. Thiamin
B. Ribovflavin
C. Pyridoxine
D. * Ascorbic acid
E. Both A and D
Tocopherols prevent the oxidation of
A. * Vitamin A
B. Vitamin D
C. Vitamin K
D. Vitamin C
E. A and B
Two molecules of vitamin A can be formed from 1 molecule of:
A. ?-Carotene
B. * ?-Carotene
C. ?-Carotene
D. Both A and B
E. All of these
Vitamin A is stored in the body in:
A. * Liver
B. Adipose tissue
C. Reticuloendothelial cells
D. Both A and B
E. All of these
Vitamin B12 is synthesized by:
A. * Bacteria only
B. Plants only
C. Animals only
D. Both (A) and (C)
E. All of the above
Vitamin B12 is transported in blood by:
A. Albumin
B. Transcortin
C. Transcobalamin I
D. * Transcobalamin II
E. All of these
Vitamin B12 is:
A. Not stored in the body
B. Stored in bone marrow
C. * Stored in liver
D. Stored in RE cells
E. All of these
Vitamin C activity is present in:
A. D-Ascorbic acid
B. D-Dehydroascorbic acid
C. * L-Ascorbic acid
D. Both A and B
E. Both B and C
Vitamin C enhances the intestinal absorption of:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
653.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
654.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
655.
is
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Potassium
Iodine
* Iron
Calcium
None of these
Vitamin C is required for the synthesis of:
* Bile acids from cholesterol
Bile salts from bile acids
Vitamin D from cholesterol
All of these
None of these
Vitamin E reduces the requirement of
Iron
Zinc
* Selenium
Magnesium
Sodium
Vitamin required for the conversion of hydroxyphenylpyruvate to homogentisate
Folacin
Cobalamin
Ascorbic acid
* Niacin
Cholecalciferol
656.
Vitamin required in conversion of folic acid to folinic acid is
A. Biotin
B. Cobalamin
C. * Ascorbic acid
D. Niacin
E. Cholecalciferol
657.
1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol promotes absorption of:
A. P
B. Cu
C. Zn
D. Na
E. * Ca
658.
1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol promotes absorption of:
A. P
B. Cu
C. Zn
D. Na
E. * Ca
659.
A cofactor required in oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate is
A. * Lipoate
B. Pantothenic acid
C. Biotin
D. Para aminobenzoic acid
E. PLP
660.
A lot of biochemical functions of water soluble vitamins are related to their ability
to transform in cells in the proper coenzymes. Which from the below mentioned vitamins
is needed for formation of FMN and FAD?
A. Vitamin B6
B.
C.
D.
E.
Vitamin B1
Vitamin B5
Vitamin B3
* Vitamin B2
661.
A poor source of Vitamin D is
A. Egg
B. Butter
C. * Milk
D. Liver
E. All of these
662.
Absorption of Vitamin B12 requires the presence of:
A. Pepsin
B. Hydrochloric acid
C. Intrinsic factor
D. * Boh (B) and (C)
E. Rennin
663.
Absorption of vitamins depends on some factors. Which compound does prevent
absorption of biotin?
A. * Avidine
B. Albumin
C. Globulin
D. Transferrin
E. Ferritin
664.
Active coenzyme forms of vitamin B5:
A. FAD and FMN
B. Pyridoxal phosphate
C. * NAD and NADP
D. Pyridoxamine
E. Coenzyme A
665.
Anaemia can occur due to the deficiency of all the following except:
A. * Thiamin
B. Pyridoxine
C. Folic acid
D. Cyanocobalamin
E. Both A and B
666.
Analog of vitamin K:
A. * Dicumarol
B. Prothrombin
C. Fibrinogen
D. Proconvertin
E. Hesperedin
667.
Ascorbic acid is especially abundant in:
A. * Citrus fruits;
B. White bread;
C. Rice;
D. Yeast.
E. Plant oils
668.
At the tissue respiration the primary acceptor of hydrogen is pyridine dependent
dehydrogenase. Which from the below mentioned vitamins is needed for the coenzyme
NAD+?
A. * Vitamin PP
B. Vitamin C
669.
670.
671.
672.
673.
674.
675.
676.
C. Vitamin B1
D. Vitamin B2
E. Vitamin B3
Below named are the main clinical symptoms of scurvy, except:
A. Gums bleeding
B. Pain in heart
C. Tachycardia
D. * Xeroftalmia
E. Petechias
Calcitriol synthesis involves
A. * Both liver and kidney
B. Intestine
C. Adipose tissue
D. Muscle
E. Liver
Chemically, Extrinsic Factor of Castle is a:
A. Mucoprotein
B. Glycoprotein
C. Mucopolysaccharide
D. * Cyanocobalamin
E. Peptide
? Choose correct answer according to concept of “vitamins”:
A. Are inorganic substances that function in living cells in trace amounts and are
vital for many forms of life
B. * Are organic substances that function in living cells in trace amounts and are
vital for many forms of life
C. Are organic substances that function only in liver in trace amounts
D. Are inorganic substances that must acquire from endogenous sources
E. All answers correct
Choose physiological name of vitamin B2:
A. Antianemic
B. Antineuritic
C. Antipellagric
D. Antiscurvy
E. * Growth factor
Choose the active form of vitamin D, which has characteristics of hormone?
A. 7-dehydrocholesterol
B. * 1,25-dihydrocholecalciferol
C. 25- hydroxycholecalciferol
D. Ergocalciferol
E. Cholecalciferol
Choose the chemical nature of vitamin B5:
A. Amino acid
B. * Nicotinic acid
C. Pantothenic acid
D. Ascorbic acid
E. Citric acid
Clinical manifestation of riboflavin deficiency are all, except:
A. Growth inhibition
B. Loss of hair
C. Inflammatory processes of lips
D. * Defect of nervous system
E. Keratitis
677.
Consumption of raw eggs can cause deficiency of
A. * Biotin
B. Pantothenic acid
C. Riboflavin
D. Thiamin
E. Ascorbic acid
678.
Corneal vascularisation is found in deficiency of the vitamin:
A. B1
B. * B2
C. B3
D. B6
E. D
679.
Day necessity of thiamin:
A. 10-15 mg
B. 1-2 g/l
C. * 2-3 mg
D. 16-25 mg
E. 10-15 g
680.
Day's necessity of vitamin D for children:
A. 2-3 mg
B. 2-3 µg
C. С. 70-100 mg
D. * 10-15 µg
E. Е. 10-12 g
681.
Deficiency of vitamin B6 may occur in
A. Obese person
B. Thin person
C. * Alcoholics
D. Diabetics
E. All of these
682.
Differences of water-soluble vitamins from fat-soluble vitamins are all, except:
A. * Are included into coenzymes
B. Don't have provitamins
C. Are not included into the membranes
D. Hypervitaminoses are not peculiar for them
E. Usually have provitamins
683.
Early symptoms of vitamin A deficiency:
A. Muscle dystrophy
B. Lungs inflammation
C. Liver cancer
D. * Xerophthalmia ("dry eyes")
E. Petechias
684.
Epileptiform convulsion in human infants have been attributed to the deficiency of
the vitamin:
A. B1
B. B2
C. * B6
D. B12
E. D
685.
Flavoenzymes take part in the following biochemical processes, except:
A. Oxidative degradation of pyruvate
B.
C.
D.
E.
Oxidative degradation of fatty acids
Oxidative degradation of amino acids
* Serves as carrier of acyl groups
Take part in the process of electron transport.
686.
Folate as a coenzyme is involved in the transfer and utilization of
A. Amino group
B. Hydroxyl group
C. * Single carbon moiety
D. Amido group
E. All of these
687.
Folate deficiency causes
A. Microcytic anemia
B. Hemolytic anemia
C. Iron deficiency anemia
D. * Megaloblastic anemia
E. Scurvy
688.
Folic acid deficiency can be diagnosed by increased urinary excretion of
A. Methylmalonate
B. * Figlu
C. Cystathionine
D. Creatinine
689.
Folic acid or folate consists of the
A. Base pteridine, p-amino benzoic acid and asparate
B. Base purine, p-amino benzoic acid and glutamate
C. * Base pteridine, p-amino benzoic acid and glutamate
D. Base purine, p-hydroxy benzoic acid and glutamate
E. Base pyrimidine, p-amino benzoic acid and glutamate
690.
For absorption of which vitamin the Castle’s factor is need (glycoprotein which
produced by the cells of stomach)?
A. Vitamin B6
B. Vitamin E
C. Vitamin C
D. Vitamin B5
E. * Vitamin B12
691.
For hypovitaminosis of vitamin Е are proper such symptoms:
A. Xerophtalmia, keratomalacia
B. Dermatitis, dementia
C. Osteoporosis
D. Diarrhea, polyneuritis
E. * Atrophy of muscles
692.
Hydroxylation of vitamin D occurs in
A. Skin
B. * Liver
C. Kidneys
D. Intestinal mucosa
E. Pancreas
693.
Hypervitaminosis K in neonates may cause
A. Porphyria
B. * Jaundice
C. Pellagra
D. Prolonged bleeding
E. Scurvy
694.
In biochemical processes in the human organism all forms of vitamin A take part
except:
A. Retinol
B. Retinal
C. Retinoic acid
D. * Tocopherol
E. Esters forms of vitamin A
695.
In biotin-containing enzymes, the biotins bound to the enzyme by
A. An amide linkage to carboxyl group of glutamine
B. A covalent bond with CO2
C. * An amide linkage to an amino group of lysine
D. An amide linkage to carboxyl group of Protein
E. All of these
696.
In human body highest concentration of ascorbic acid is found in
A. Liver
B. * Adrenal cortex
C. Adrenal medulla
D. Spleen
E. Pancreas
697.
In the large intestine microorganisms synthesize vitamins which take part in the
biochemical processes of organism. Choose them:
A. * K, B12
B. D, C
C. E, H
D. B1, D
E. B6, E
698.
Increased glucose consumption increases the dietary requirement for
A. Pyridoxine
B. Niacin
C. Biotin
D. * Thiamin
E. Cholecalciferol
699.
Insufficiency of which vitamin does cause the inhibition of activity of
aminotransferase’s and decarboxylase?
A. B3
B. B2
C. * B6
D. B12
E. B15
700.
Lack of vitamin K causes:
A. Diarrhea
B. Kakheksiya
C. S. Growth retardation
D. * Hemorrhages
E. Steatoreya
701.
Lipid soluble vitamins are:
A. Coenzymes
B. * Modulators of cell membranes
C. Regulators of secretion of digestive juices
D. Transport of substances
E. Е. Mediators of nervous system
702.
Main function of bioflavonoids is:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
703.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
704.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
705.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
706.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
707.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
708.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
709.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
710.
A.
B.
C.
D.
Take part in metabolism of epinephrine
It necessary for hydroxylation of cholesterol
* Support the elasticity of capillaries
Reduce the disulfide bonds to sulphhydryl bonds
Participation in respiratory chain
Main function of coenzyme A is:
A carrier of methyl group
Removal of hydrogen atom from specific substrate
Catalyze reaction of carbohydrate metabolism
* A carrier of acyl groups
Participation in respiratory chain
Name biologicaly active form of vitamin D:
* Ergocalciferol
Cholecalciferol
7-dehydrocholesterol
25-hydroxycholecalciferol
1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
Name provitamins of vitamin A:
Flavonoids
Cholecalciferol
* Carotenoids
Hesperedin
Dehydroascorbic acid
Name the active coenzyme form of vitamin B2:
A.TMP, TDP
NAD, NADP
* FMN, FAD
Coenzyme A
THFA
One manifestation of vitamin A deficiency is
Painful joints
* Night blindness
Loss of hair
Thickening of long bones
All of these
Pantothenic acid is a constituent of the coenzyme involved in:
Decarboxylation
Dehydrogenation
* Acetylation
Oxidation
All of these
Pantothenic acid was identified as:
Coenzyme Q
Metalloenzyme
Flavoenzyme
* Coenzyme A
Pyridine coenzyme
Pyridoxal phosphate is central to:
Deamination
Amidation
Carboxylation
* Transamination
E. Oxidation
711.
Pyridoxal phosphate is the active coenzyme form of vitamin:
A. B1.
B. B2.
C. B3.
D. * B6.
E. B12
712.
pyridoxamine phosphate
A. Deamination of serine
B. Deamination of threonine
C. Conversion of pyridoxal phosphate to
D. * Methylation of homocystein to methionine
E. Hydroxilation of proline
713.
Pyridoxine can biologically convert into such compounds:
A. Pyridine and thiamin
B. Propionil and pyridine
C. * Pyridoxal and pyridoxamine
D. Nicotine and nicotinamide
E. Pyridine coenzyme
714.
RDA of vitamin Е is:
A. * A.20-50 mg
B. B.20-50 µg
C. С.45-60 mg
D. D.50-100 µg
E. Е.40-80 mg
715.
Retinal is a component of
A. Iodopsin
B. * Rhodopsin
C. Cardiolipin
D. Glycoproteins
E. Lipoproteins
716.
Retinal is reduced to retinol in intestinal mucosa by a specific retinaldehyde
reductase utilising
A. * NADPH + H+
B. FAD
C. NAD
D. NADH + H+
E. PLP
717.
Rhodopsin includes a protein:
A. Crioglobulin
B. * Opsin
C. Transpherin
D. Pepsin
E. Tyrosine
718.
Riboflavin deficiency causes
A. * Cheilosis
B. Loss of weight
C. Mental deterioration
D. Dermatitis
E. Beriberi
719.
Riboflavin is a coenzyme in the reaction catalysed by the enzyme
A. Acyl CoA synthetase
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Acyl CoA dehydrogenase
?-Hydroxy acyl CoA
Enoyl CoA dehydrogenase
All of these
720.
Richest source of Vitamin D is
A. * Fish liver oils
B. Margarine
C. Egg yolk
D. Butter
E. Meat
721.
Rod cells possess a trans-membrane protein which is
A. Adenylate cyclase
B. Transducin
C. * Rhodopsin
D. B as well as C
E. All of these
722.
Sequence of enzymatic reactions of visual cycle is catalyzed by two enzymes:
A. Lactate dehydrogenase and phosphatase
B. Alcohol dehydrogenase and lactate dehydrogenase
C. * Retinal-reductase and retinol-isomerase
D. Esterases and glycosidases
E. Retinal-reductase and retinol-transferase
723.
Subacute combined degeneration of cord is caused due to deficiency of
A. Niacin
B. * Cobalamin
C. Biotin
D. Thiamin
E. Ascorbic acid
724.
Sulpha drugs interfere with bacterial synthesis of
A. Lipoate
B. Vitamin E
C. * Tetrahydrofolate
D. Ascorbic acid
E. All of these
725.
The active form of vitamin D (1,25-dihydrocholecalciferol) maintain in an
organism a constant level of:
A. Potassium and phosphorus
B. * Calcium and phosphorus
C. S. Iron and calcium
D. Iron and magnesium
E. Magnesium and manganese
726.
The analogue of vitamin K which takes part in the tissue respiration is:
A. Vikasol
B. * Ubiquinone
C. Naphtoquinon
D. Tocopherol
E. Cytochrome
727.
The antivitamin of vitamin K is:
A. Vikasol
B. Cholecalciferol
C. * Dikumarol
D. Thiamin
E. Е. Cholin
728.
The biochemical function of water soluble vitamins depends on their ability to
convert into coenzyme forms. In which coenzyme the vitamin B2(riboflavin) transforms:
A. * FMN (flavin mononucleotide)
B. NAD+ (nicotine amide dinucleotide)
C. TMP (tiaminmonofosphate)
D. TDP (thiamine diphosphate)
E. PALP (pirodoxal phosphate)
729.
The central structure of B12 referred to as corrin ring system consists of
A. * Cobalt
B. Manganese
C. Magnesium
D. Iron
E. Potassium
730.
The coenzyme required for conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate is
A. FAD
B. NAD
C. TPP
D. * Biotin
E. PLP
731.
The cofactor or its derivative required for the conversion of acetyl CoA to
malonyl-CoA is
A. FAD
B. ACP
C. NAD+
D. * Biotin
E. TPP
732.
The component of rodopsin
A. Trans-retinol
B. * Cis-retinal
C. Yodopsin
D. Trans-retinal
E. Cis- retinol
733.
The daily requirement of riboflavin for adult in mg is
A. 0–1.0
B. * 1.2–1.7
C. 2.0–3.5
D. 4.0–8.0
E. 10.6-15.5
734.
The day requirement of vitamin C is:
A. 50-70 µg.
B. * 50-70 mg.
C. 50-70 g.
D. 500-700 mg.
E. 5-7 g
735.
The deficiency of thiamin causes disease:
A. Acute pancreatitis
B. * Beri-beri
C. Pellagra
D. Liver cancer
E. Loss of hair
736.
The deficiency of tocopherol causes many other symptoms, except:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Infertility in male and female
Degeneration of the kidneys
Necrosis of the liver
* Mental retardation
Dystrophy of skeletal muscles
737.
The derivates of vitamins are included in composition of coenzymes of respiratory
chain. The coenzyme form of what vitamin is NAD+?
A. B1
B. B2
C. B6
D. * PP
E. B3
738.
The derivates of vitamins carry out the role of coenzymes. The coenzyme form of
which vitamin is a thiamine pyrophosphate?
A. Vitamin B5
B. * Vitamin B1
C. Vitamin B2
D. Vitamin B3
E. Vitamin B6
739.
The disease pellagra is developed in the lack of vitamin:
A. Thiamin.
B. Riboflavin.
C. * Nicotinic acid.
D. Pantothenic acid.
E. Ascorbic acid
740.
The earliest symptoms of thiamin deficiency cause disorders of some system,
except:
A. Nervous.
B. Cardio-vascular
C. Respiratory
D. Muscular
E. * Digestive
741.
The function of coenzyme A is to take part in the following enzymatic reactions,
except:
A. Fatty acid synthesis
B. Fatty acid oxidation
C. * Hydrolysis of proteins
D. Pyruvate oxidation
E. Biological acetylations
742.
The main enzymatic reaction requiring pyridoxal phosphate as a coenzyme is :
A. Decarboxilation
B. * Transamination
C. Deamination
D. Reamination
E. Oxidation
743.
The molecule of vitamin A contains:
A. Benzene ring
B. * ?-Ionone ring
C. ?-Carotene ring
D. All of these
E. None of these
744.
The most specific symptoms of pellagra are all, except:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
745.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
746.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
747.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
748.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
749.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
750.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
751.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
752.
A.
B.
C.
D.
Dermatitis
Diarrhea
Dementia
* Muscle dystrophy
Photosensibility
The precursor of CoA is:
Riboflavin
Pyridoxamine
Thiamin
* Pantothenate
None of the above
The proteins present in maize are deficient in:
Lysine
Threonine
* Tryptophan
Tyrosine
C and D
The Vitamin B1 deficiency causes
Ricket
Nyctalopia
* Beriberi
Pellagra
Scurvy
The vitamin required as coenzyme for the action of transaminases is
Niacin
Pantothenic acid
* Pyridoxal phosphate
Riboflavin
Ascorbic acid
The vitamin required for the formation of hydroxyproline (in collagen) is
* Vitamin C
Vitamin A
Vitamin D
Vitamin E
Vitamin K
The Vitamin which does not contain a ring in the structure is:
* Pantothenic acid
Vitamin D
Riboflavin
Thiamin
A and D
Thiamin deficiency includes
Mental depression
Fatigue
Beriberi
Miscle atrophy
* All of these
Thiamin diphosphate is required for oxidative decarboxylation of
* ?-Keto acids
?-Amino acids
Fatty acids
Glycerol
E. All of these
753.
Thiamin is heat stable in
A. * Acidic medium
B. Alkaline medium
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Neutral medium
E. None of these
754.
Thiamin is oxidized to thiochrome in alkaline solution by
A. Potassium permanganate
B. * Potassium ferricyanide
C. Potassium chlorate
D. Potassium dichromate
E. All of these
755.
Thiamin occurs in cells mainly as its active coenzyme form:
A. NAD
B. FAD
C. NADP
D. * TPP
E. CoA
756.
Thiamin requirement is greater in
A. Non-vegetarians
B. Alcoholics
C. Pregnant women
D. * Both B and C
E. None of above
757.
To the group of fat soluble vitamins peculiar presence of provitamins. The
provitamin of vitamin D3 is:
A. Ergosterol
B. Cholesterol
C. * 7-dehydrocholesterol
D. 1,25-dihydrocholecalciferol
E. Ergocalciferol
758.
Tocopherols have such property:
A. * Antioxidant activity
B. Antidermatites activity
C. Antipellagric activity
D. Antixerophtalmic activity
E. Antianemic activity
759.
Two coenzymes – NAD and NADP are also referred to as:
A. * Pyridine coenzymes
B. Flavoenzymes
C. Thiamin coenzyms
D. Transaminase
E. Ligases
760.
Vitamin A or retinal is a
A. Steroid
B. * Polyisoprenoid compound containing a cyclohexenyl ring
C. Benzoquinone derivative
D. 6-Hydroxychromane
E. None of the above
761.
Vitamin B12 deficiency can be diagnosed by urinary excretion of
A. Pyruvate
B.
C.
D.
E.
762.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
763.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
764.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
765.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
766.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
767.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
768.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
769.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Methylmalonate
Malate
Lactate
All of these
Vitamin B12 forms coenzymes known as:
* Cobamide
Transcobalamin I
Transcobalamin II
Both (B) and (C)
All of these
Vitamin B12 has a complex ring structure (corrin ring) consisting of four
Purine rings
Pyrimidine rings
* Pyrrole rings
Pteridine rings
Bensol ring
Vitamin B12 is also known as:
Folic acid
* Cyanocobalamin
Piridoxine
Orotic acid
Biotin
Vitamin B6 deficiency may occur during therapy with
* Isoniazid
Terramycin
Sulpha drugs
Aspirin
All of these
Vitamin B6 includes:
Pyridoxal
Pyridoxamine
Pyridoxine
* All of these
Both A and B
Vitamin K is a cofactor for
* Gamma carboxylation of glutamic acid residue
?-Oxidation of fatty acids
Formation of ?-amino butyrate
Synthesis of tryptophan
Synthesis of fatty acids
Vitamin K is found in
* Green leafy plants
Meat
Fish
Milk
All of these
Vitamin K is required for normal:
* Blood-clotting time
Development of bones
Prevent blood clotting
Promotes absorption of Ca in intestine
Demineralisation
770.
Vitamin P - is the group of compounds, except:
A. Rutin
B. Hesperedin
C. Katechines
D. * Riboflavin
E. All of above
771.
Vitamin synthesized by bacterial in the intestine is
A. A
B. C
C. D
D. * K
E. B1
772.
Vitamins are
A. * Accessory food factors
B. Generally synthesized in the body
C. Produced in endocrine glands
D. Proteins in nature
E. All of the above
773.
Vitamins are classified into two large groups:
A. Organic and inorganic
B. Simple and complex
C. * Water-soluble and fat-soluble
D. Protein-soluble and fat-soluble
E. All of above
774.
Vitamins at their simultaneous usage can strengthen action of each other. Which
of following vitamins assist in anti-hyaluronidase activity of vitamin P?
A. Vitamin B2
B. Vitamin D
C. Vitamin B1
D. * Vitamin C
E. Vitamin A
775.
What disease is developed in the vitamin B12 deficiency?
A. * Pernicious anemia.
B. Pellagra.
C. Beri-beri.
D. Dermatitis.
E. Neuritis.
776.
What disease is developed in the vitamin C deficiency?
A. * Scurvy.
B. Pellagra.
C. Beri-beri.
D. Dermatitis.
E. Neuritis
777.
What forms of carotenes do you know?
A. A1, 2 2
B. a, b, с
C. * C, ,, ,
D. A1, A2
E. E, ,
778.
When light falls on rod cells:
A. All-cis-retinal is converted into all-trans-retinal
B. 11-cis-retinal is converted into 11-trans-retinal
C. 11-trans-retinal is converted into all-transretinal
D. * 11-cis-retinal is converted into all-trans-retinal
E. None of these
779.
?-Carotene, precursor of vitamin A, is oxidatively cleaved by
A. * ?-Carotene dioxygenase
B. Oxygenase
C. Hydroxylase
D. Transferase
E. ?-Carotene lyase
780.
______ is a measurement of the relative amount of immunoglobulin in the serum
A. * Gamma globulin
B. Secretory antibody
C. Antibody titer
D. Blast formation
E. Fibrinogen
781.
The two primary components of whole blood are plasma and
A. Serum
B. Platelets
C. * Formed elements
D. Dissolved proteins
E. Granular leukocytes
782.
____ are agents that stimulate the immune system to produce antibodies.
A. Alpha globulins
B. * Gamma globulins
C. Beta globulins
D. Antigens
E. Platelets
783.
____ is a hormone produced by the ____ when tissue levels of oxygen levels are
low.
A. Bilirubin stomach
B. * Bilirubin; bone marrow
C. Erythropoietin; kidneys
D. Erythropoietin; bone marrow
E. Hemoglobin; liver
784.
_____ are to blood clotting as neutrophils are to phagocytosis.
A. Eosinophils
B. * Platelets
C. Blymphocytes
D. Monocytes
E. Basophils
785.
A toxic gas that strongly binds to hemoglobin and deprives the body of oxygen is:
A. Hydrogen peroxide
B. * Carbon monoxide
C. Carbon dioxide
D. Sodium bicarbonate
E. Ctric acid
786.
Ability to link free haemoglobin and to transport her in the cells of RES at the
condition of physiological and pathological disintegration of erythtrosytes belongs:
A. Transferin
B. Crioglobulin
C. Ceruloplazmin
D. * Haptoglobin
787.
788.
789.
790.
791.
792.
793.
794.
795.
E. Ferritin
Acid-Base balance is important for:
A. Normal enzyme functions
B. Normal metabolite solubility
C. Normal membrane potentials
D. A and C
E. * All of the above
Acidosis results in increasing levels of what ion?
A. Calcium
B. Chloride
C. Sodium
D. Phosphorus
E. * Hydrogen
Albumin-globulin coefficient of blood plasma of healthy people compose:
A. 3,0-4,0
B. 1,0-1,5
C. 5,0-6,5
D. 8,0-10,0
E. * 1,5-2,0
All of the following are functions of blood except
A. Transportation of oxygen and carbon dioxide
B. Regulation of body temperature
C. * Synthesis of vitamins
D. Defense against infection
E. Maintenance osmotic pressure
All of the following are true of erythrocytes except
A. When mature, they have no nucleus or other organelles
B. Their plasma membrane contains many antigens (molecules projecting from the
surface)
C. They normally contain practically all of the hemoglobin that is present in blood
D. They transport oxygen from the lungs to body tissues
E. * They have a finite life span averaging about 60 days
An excessive number of white blood cells is called:
A. Lymphoma
B. Leukopenia
C. * Leukocytosis
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
Anemia resulting from iron deficiency is called :
A. Pernicious anemia
B. * Hemoffhagic anemia
C. Aplastic anemia
D. Sickle cell anemia
E. Nutritional anemia
Antibodies are plasma proteins that are classified as:
A. Albumins
B. * Globulins
C. Fibrinogen
D. All of the above
E. Prealbumins
Antibodies are produced as a reaction to the presence of :
A. Red blood cells
B.
C.
D.
E.
Haemoglobin
* Antigens
White blood cells
Platelets
796.
B cells function by promoting ____ .
A. * Phagocytosis
B. Antibody production
C. Release of histamine
D. Cell to cell killing of viral infected cells
E. The production of erythropoietin
797.
Blood fails to clot in the absence of :
A. Magnesium
B. * Calcium
C. Sulphur
D. Potassium
E. Cooper
798.
Blood is composed of :
A. Plasma and red blood cells
B. * Plasma and formed elements
C. Red and white blood cells
D. Red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets
E. Plasma and platelets
799.
Blood perform such functions:
A. Gas transport
B. Transport of nutritional substances
C. Regulative
D. Osmotic
E. * All of the above
800.
Blood platelets are:
A. * Cytoplasmic fragments
B. Free nuclei
C. A kind of red cell
D. Found only during clot formation
E. Mithochodrial fragment
801.
Blood transports dissolved gases, bringing oxygen from the lungs to the tissues
and carrying
A. * Carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lungs
B. Carbon dioxide from the lungs to the tissues
C. Carbon dioxide from the interstitial fluid to the cell
D. Carbon dioxide from one peripheral cell to another
E. None of the above
802.
Cell-to-cell killing is to T cells as antibody production is to :
A. Neutrophils
B. Basophils
C. Monocytes
D. * B cells
E. Eosinophils
803.
Ceruloplasmin is the protein of:
A. A-globulin fraction.
B. B1-globulin fraction.
C. * C2-globulin fraction.
D. D-globulin fraction.
E. prealbumin
804.
Chemical nature of immunoglobulins:
A. Lipoproteins
B. * Glykoproteins
C. Phosphoproteins
D. Chromoproteins
E. Nukleoproteins
805.
Choose the factor that is not a major metabolic source of hydrogen ions in the
body.
A. Anaerobic respiration of glucose
B. * Oxidation of amino acids that contain sulfur
C. Hydrolysis of phosphoproteins
D. Oxydation of fatty acid
E. Anaerobic respiration of glucose
806.
Choose the indexes of normal maintenance of hemoglobin in women:
A. 140-160 g/l
B. * 115-145 g/l
C. 125-160 g/l
D. 50-80 g/l
E. 70-100 g/l
807.
Choose the indexes of normal maintenance of hemoglobin in men:
A. 80-100 g/l
B. * 130-160 g/l
C. 115-145 g/l
D. 70-90 g/l
E. 100-120 g/l
808.
Circulating mature RBCs lack:
A. Ribosomes
B. * Mitochondria
C. Nuclei
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
809.
Colloid-osmotic pressure of blood is supported by:
A. * Albumins
B. B1- globulins
C. C- globulins
D. D- globulins
E. E- globulins
810.
Combination of haemoglobin with oxygen named:
A. Carboxyhemoglobin
B. Methemoglobin
C. Carbylaminhemoglobin
D. Carbhemoglobin
E. * Oxyhemoglobin
811.
Combination, that transported CO2 from tissues to lung named:
A. Methemoglobin
B. * Carbhemoglobin
C. Oxyhemoglobin
D. Carbylaminhemoglobin
E. Carboxyhemoglobin
812.
Connection of hemoglobin with CO is:
A. Oxyhemoglobin.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Carbhemoglobin.
* Carboxyhemoglobin.
Methemoglobin.
Cyancobalamine
813.
Contents of globulins in blood serum of healthy person:
A. 80-110 g/l
B. 50-60 g/l
C. 40-60 g/l
D. * 20-35 g/l
E. 100-120 g/l
814.
Crioglobulin – the protein of C-globulin fraction, which absent in blood plasma of
healthy people, appears at:
A. Diabetus Mellitus
B. Wilson disease
C. * С. Leykoses, mielom disease
D. Starvation
E. Lung emphysema
815.
Determination blood proteins fractions of patient is possible the method of
electrophoresis owing to following their property:
A. High optical activity
B. High dyspersity
C. S. High hydrophilicity
D. High viscidity
E. * Electric charge
816.
Detoxification function of blood is conditioned:
A. Gas transport (CO2 and O2)
B. Transport of nutritional substances
C. Exchange of heat between tissues and blood
D. * Detoxification toxic substanses by the enzymes of blood
E. Presents in blood of antibodies and by the phagocit function of leucocytes
817.
During RBC recycling, each heme unit is stripped of its iron and converted to:
A. Transferrin
B. Ferritin
C. * Biliverdin
D. Urobilin
E. None of the above
818.
Electrophoresis of blood proteins carry out at pH:
A. 5,5
B. 7,0
C. * 8,6
D. 4,7
E. 3,0
819.
Eosinophils are to granular white blood cells as ____ are to agranular white blood
cells.
A. Neutrophils
B. Basophils
C. * Monocytes
D. Stem cells
E. None of the above
820.
Erythropoietin
A. * Stimulates red blood cell synthesis
B. Stimulates white blood cell synthesis
C. Is released in response to a decrease in blood flow to the bone marrow
D. A and C
E. B and C
821.
Fibrinogen - is protein of blood which executes a function:
A. Transport
B. Strukture
C. * Protective
D. Regulation
E. Reduce
822.
Fibrinogen is a precussor of:
A. Protrombin
B. Haptoglobin
C. Fibronektin
D. * Fibrin
E. Fibroin
823.
For account of what fraction of proteins observe hypoproteinemia at the diseases
of liver:
A. A- globulins
B. Transferin
C. Gaptoglobin
D. Ceruloplazmin
E. * Albumins
824.
Formed elements in the blood are produced through the process of:
A. Diapedesis
B. Erythrocytosis
C. Hemolysis
D. * Hemopoiesis
E. None of the above
825.
From where do most of the plasma proteins come?
A. * Liver
B. Spleen
C. Red bone marrow
D. Progenitor cells that enlarge then rupture
E. Old erythrocytes that rupture
826.
General antyproteinase activity of blood serum of healthy man is determined the
followings inhibitors, except:
A. A1 -antitripsyn
B. B2-macroglobulin
C. С. Inter-I-ingibitor of trypsin
D. * Contrikal
E. Termoacidstability ingibitor
827.
Given that the liver synthesizes most of the plasma proteins, severe liver disorders
can be expected to cause
A. * Decreased osmotic pressure of the blood plasma
B. Less efficient transport of iron ions and lipids
C. Diminished clotting ability
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
828.
Haemoglobin A of erythrocytes in the adult include:
A. 22 – and 1 polypeptide chains
B. 11 – and 2 polypeptide chains
C. 4 4 - polypeptide chains
D. 4 - polypeptide chains
E. * 2 – and 2 - polypeptide chains
829.
Hemoglobin buffer system of blood consists:
A. * Oxihemoglobin and desoxyhemoglobin
B. Carbhemoglobin and carboxyhaemoglobin
C. Carboxyhemoglobin and oxyhemoglobin
D. Oxyhemoglobin and metHb
E. Methemoglobin and carbhemoglobin
830.
Hemoglobine of erythrocytes include:
A. * Hem and globin
B. Histones and hem
C. Protamines and hem
D. Globin and NAD
E. Iron, copper and protein
831.
How is it possible for the rate and depth of breathing to affect hydrogen ion
concentrations in body fluids?
A. During increased air exchange, more oxygen is exchanged with body cells,
binding hydrogen ions
B. * During increased air exchange, more carbon dioxide is given off, returning
hydrogen ion concentrations to normal
C. During increased respiration over the long term, more hemoglobin is produced,
thus increasing the buffering of the blood
D. The rate and depth of breathing does not alter hydrogen ion concentration in body
fluids
E. During decreased respiration over the long term, more oxyhemoglobin is
produced
832.
Immune status of organism is provided by:
A. * Leukocytes
B. Trombocytes
C. Erythrocytes
D. Hemoglobin
E. Bilirubin
833.
In addition to water and proteins, the plasma consists of:
A. Albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen
B. * Electrolytes, nutrients, and organic wastes
C. Erythrocytes, leukocytes, and platelets
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
834.
In formation of blood clot take part:
A. Fibronectin
B. Fibroin
C. * Fibrin
D. Haptoglobin
E. Hemoglobin
835.
In what combination present (Fe3+):
A. Carboxyhemoglobin
B. Oxyhemoglobin
C. * Met hemoglobin
D. Carbhemoglobin
E. Mioglobin
836.
Increase related to O2 in the perinatal period of child has:
A. HbS
B.
C.
D.
E.
* HbF
HbA
HbE
HbC
837.
Indicate proteins that not belong to fractions of globulins:
A. Ceruloplazmin
B. B1-antitrypsin
C. Transferin
D. Haptoglobin
E. * Fibrinogen
838.
Indicate the credible index of albumin-globulin coefficient in the case of kidney
disease:
A. 2,8
B. * 0,8
C. 1,5
D. 2,5
E. 2,0
839.
Indicate the maintenance of albumins in blood serum of healthy person?
A. 60-85 g/l
B. 40-60 g/l
C. * 35-50 g/l
D. 80-110 g/l
E. 100-120 g/l
840.
Indicate types of haemoglobins, that be found in the erythrocytes of healthy
people:
A. A2, F, С
B. M, A1, D
C. С, M, Е
D. * A1, A2, F
E. A2, S
841.
Ions of iron (Fe3+), which are absorbed in an intestine, deposited in the different
organs of organism in composition of:
A. Hemoglobin
B. Transferin
C. Haptoglobin
D. * Feritin
E. Ceruloplasmin
842.
Kinins of blood execute the followings functions, except:
A. Relax smooth muscles of blood vessels
B. Promote permeability of vascular walls
C. Lowering blood pressure
D. Broade vessels in the areas of inflammation
E. * Contract smooth muscles of blood vessels
843.
Leukocytes are divided into two classes based on the presence or absence of
microscopically visible structures called
A. Nuclei
B. * Granules
C. C. Ribosomes
D. Mitochondria
E. Golgi complexes
844.
Maintenances of acid-base balance of blood have the followings buffer systems,
except:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Bycarbonate
Phosphate
* Ammonia
Haemoglobin
Proteins
845.
Many animal contain an oxygen-carrying substance called:
A. * Hemoglobin
B. Chyme
C. Filtrate
D. Lymph
E. Gglobin
846.
Metabolic acidosis arise at all of the followings states, except:
A. Diabetus Mellitus
B. Starvation
C. * Delay hydrocarbonates under the influence of mineralcorticoids
D. Muscle hypoxia
E. Loss secrets of pancreas and intestine at diarrhea
847.
Most of the circulating leukocytes are
A. Basophils
B. Eosinophils
C. Leukocytes
D. Monocytes
E. * Neutrophils
848.
Name basic kinins which enters in the composition of the kallicrein-kinin system
of blood:
A. Macroglobulins, callydines
B. Callydin, protrombin
C. * Callydin, bradykinin
D. Antithrombins, bradykinin
E. Bradykinin, lipoproteins
849.
Name protein which appeared in a patient with leucosis in blood plasma:
A. Albumins
B. * Crioglobulin
C. Immunoglobulins
D. D1 - globulins
E. Fibrinogen
850.
Of the following, which are most active as phagocytes?
A. Erythrocytes
B. * Neutrophils
C. Platelets
D. Eosinophils
E. Monocites
851.
Of the following, which mechanisms are important in the death of erythrocytes in
human blood? Is it
A. Phagocytosis
B. Hemolysis
C. Mechanical damage
D. * All of the above
852.
Once the erythrocytes enter the blood in humans, i is estimated that they have an
average lifetime of how many days. Is it:
A. 10 days
B. * 120 days
C. 200 days
D. 360 days
E. 2 days
853.
One of the basic allocation of the kallikrein-kinin system of blood, it:
A. Supporting of blood oncotic pressure
B. * Regulation of vascular tone
C. Transport medical substances
D. Supportin acid - base balance
E. Blood clotting
854.
Osmoregulation is concerned with:
A. Excretion
B. Ionic regulation
C. * Control of the body's water content
D. Carbon dioxide regulation
E. Oxygen regulation
855.
Plasma contains all of the following EXCEPT
A. Glucose
B. Oxygen
C. * Hemoglobin
D. Electrolytes
E. Clotting factors
856.
Plasma is made up of water and _______________
A. Metabolites and wastes
B. Salts and ions
C. Proteins
D. * All of the above
E. None of the above
857.
preferentially with red-staining dyes?
A. Neutrophils
B. Basophils
C. * Eosinophils
D. Lymphocytes
E. Monocytes
858.
Proteins of the plasma that function in fighting infections are :
A. Albumins
B. Fibrinogen
C. * Gamma globulins
D. Alpha and beta globulins
E. Prothrombin
859.
Prothrombin and the procoagulants are involved in blood clotting and require
vitamin :
A. B12
B. E
C. * K
D. A
E. H
860.
Protrombin is to thrombin as _____ is/are to fibrin.
A. Prothrombin activator
B. Blood clot
C. * Fibrinogen
D. Platelets
E. Erythropoietin
861.
Red blood cells are destroyed in the :
A. Lungs
B. * Liver
C. Heart
D. Spleen
E. Kidney
862.
Select the fluid tissue that among other things transports dissolved gases,
distribute nutrients, stabilizes body temperature and aids in the defense against pathogens
and toxins
A. Lymph
B. Cerebrospinal fluid
C. Interstitial fluid
D. * Blood
E. Water
863.
Someone whose blood could not carry enough oxygen to the cells of the body
might have a deficiency of :
A. Estrogen
B. * Hemoglobin
C. Carbon dioxide
D. Lactose
E. Epinephryn
864.
Sources of protein in the diet are:
A. Fats, oils, butter, and margarine
B. Green pepper, cantaloupe, citrus fruits, and broccoli
C. Deep green and orange vegetables, and citrus fruits
D. * Meats, fish, legumes, nuts, dairy products, and eggs.
E. Onion, carrot, oils and apples
865.
Surplus red blood cells, needed to meet an emergency, are MAINLY stored in
what organ of the human body? Is it the:
A. Pancreas
B. * Spleen
C. Liver
D. Kidneys
E. Heard
866.
The basic event in the formation of a blood clot is the change of
A. * Fibrinogen to fibrin
B. Fibrin to fibrinogen
C. Thrombin to prothrombin
D. Vitamin K to prothrombin
E. Fibrin to thrombin
867.
The basic event in the formation of a blood clot is the change of
A. * Fibrinogen to fibrin
B. Fibrin to fibrinogen
C. Thrombin to prothrombin
D. Vitamin K to prothrombin
E. Rodopsyn to opsyn
868.
The basic function of erythrocytes in blood:
A. Promotes agregation of thrombocytes
B. * Transport of CО2 and O2
C. Syntheses of proteins of the contraction system (actine, myosine)
D. Provide immune status of organism
E. Take part in formation of active forms of oxygen
869.
The blood component responsible for clotting in injury is:
A. White blood cells
B. Erythrocytes
C. Platelets
D. Plasma
E. Serum
870.
The class of plasma proteins that produces antibodies is
A. Albumins
B. Alpha globulins
C. Beta globulins
D. * Gamma globulins
E. Fibrinogen
871.
The component of blood that is responsible for clotting is:
A. * Platelets
B. Erythrocytes
C. Neutrophils
D. Basophils
E. None of the above
872.
The concentration of fibrinogen in blood of pregnancy women consist 3,8 g/l.
Indicate the normal concentration of fibrinogen:
A. 1-3 g/l
B. 2-7 g/l
C. 9-11 g/l
D. 5-7 g/l
E. * 2-4 g/l
873.
The condition in which there is a DECREASE in the number of white blood cells
in humans is known as:
A. Leukocytosis
B. * Leukopenia
C. Leukemia
D. Leukohyperia
E. Anemia
874.
The degree of oxigenation of haemoglobin (synthesis of HbO2) depends on such
factors:
A. Parcial pressure of oxygen
B. pH
C. Concentration of CO
D. Concentration of 2,3 - diphosphoglycerat
E. * From all factors, resulted higher
875.
The extracellular buffering system for blood and tissue fluids is base on
A. Potassium hydroxide
B. * Bicarbonate
C. Carbonic anhydrase
D. Phosphate
E. Albumin
876.
The final reaction in the formation of a blood clot is
A. The formation of prothrombin activator
B. * That thrombin converts fibrinogen to fibrin
C. That prothrombin activator converts prothrombin to thrombin
D. Hageman factor activates prothrombin
E. Vitamin B12 ingibit formation of fibrinogen
877.
The fluid that does not form clots is :
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Blood
Plasma
Lymph
* Serum
Spinal-cord
878.
The formed elements of the blood consist of:
A. * Red and white blood cells and platelets
B. Electrolytes, nutrients, and organic wastes
C. Antibodies, metalloproteins, and lipoproteins
D. Albumins, globulins, and fibrinogen
E. None of the above
879.
The function of antibodies, basic effectors of humoral immunity, execute proteins:
A. Fibrinogen
B. Albumins
C. * C-globulins
D. D1-globulins
E. E-globulins
880.
The function of the lymphatic system is to:
A. Drain the blood of nutrients
B. * Returning proteins and water to the blood stream
C. Prevent blood loss by clotting the blood
D. Store energy reserves for the body
E. Synthesis of vitamins
881.
The functions of providing a gas exhange surface and moving air to and from the
exchange surface is performed by the _______________ system.
A. Cardiovasular
B. * Respiratory
C. Digestive
D. Lymphatic
E. Excretion
882.
The greatest concentration of antibodies is found in the fraction of the serum.
A. * Gamma globulin
B. Albumin
C. Beta globulin
D. Alpha globulin
E. Prealbumin
883.
The highest antyproteas activity of blood ( >90%) belongs:
A. * A -1-antytripsin
B. B-2-macroglobulin
C. Inter-I-ingibitor of trypsin
D. Termoacidstability inhibitor
E. E-1-antychimotripsin
884.
The hydrocarbonate buffer system of blood most effectively functions at рН that
equal:
A. 8,1
B. * 7,4
C. 6,8
D. 7,9
E. 7,0
885.
The increase permeability of vascular walls in the zone of inflammation and sense
of pain promote:
A. Contrikal
B.
C.
D.
E.
886.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
887.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
888.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
889.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
890.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
891.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
892.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
893.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Kinins
Renin
Angiotenzin
Gordox.
The liquid matrix of blood as it exists in the body is called:
Lymph
Stroma
Serum
* D Plasma
All of the above
The liquid portion of the blood is called :
Water
* Plasma
Serum
Sap
Cells
The lymphatic system
Is an open circulatory system
Contains one-way valves
Returns fluids to the bloodstream
* All of the above
None of the above
The lymphatic system is important because it:
Collects liquid lost from the circulatory system
Returns proteins to circulation
Transports fats
Carries bacteria to the lymph nodes for destruction
* Does all of the above
The lymphocyte that is responsible for cell-mediated immunity is the:
* T lymphocyte
NK cell
B lymphocyte
None of the above
All of the above
The main cells present in lymph are :
Red blood cells
Platelets
* Lymphocytes
Monocytes
Basophils
The maintenance of total protein in blood serum of healthy person?
50-60 g/l
80-110 g/l
* 65-85 g/l
100-120 g/l
40-60 g/l
The major component of plasma is:
* Water
Nutrients
Protein
Electrolytes
Vitamins
894.
the
The most important buffer system in the intracellular fluid compartment (ICF) is
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Phosphate buffer system
Protein buffer system
Bicarbonate buffer system
Sulfate buffer system
Chloride buffer system
895.
The most important buffer systems in body fluids include the bicarbonate buffer
system, the ______________ buffer system, and the protein buffer system.
A. Calcium
B. Sodium
C. Phosphate
D. * Hemoglobin
E. Chloride
896.
The most numerous white blood cell in normal blood is the:
A. * Neutrophil
B. Lymphoctye
C. Monocyte
D. Eosinophil
E. B lymphocyte
897.
The most powerful vesselsbroaden substance in an organism is:
A. Oxitocin
B. Histamin
C. Serotonin
D. Adrenalin
E. * Bradikinin
898.
The part of the hemoglobin molecule directly interacts with oxygen is:
A. The tertiary protein structure
B. The sodium ion
C. Globin
D. * The iron ion
E. None of the above
899.
The primary function of a mature red blood cell is:
A. Defense against toxins and pathogens
B. Delivery of enzymes to target tissues
C. Transport of respiratory gases
D. * All of the above
E. None of the above
900.
The process that halts bleeding is called:
A. Lymphopoiesis
B. Hematocrit
C. Hemangioma
D. * Hemostasis
E. None of the above
901.
The protein that consists of four protein subunits that each contain heme is:
A. Immunoglobulin
B. Myoglobin
C. * Hemoglobin
D. Myosin
E. Catalase
902.
The several types of white blood cells are sometime collectively referred to as:
A. Erythrocytes
B.
C.
D.
E.
903.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
904.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
905.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
906.
by:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Leukocytes
Erythroblasts
Thrombocytes
Monocytes
The shape of the red blood cell can best be described as a(n):
Ellipsoid
Sphere
* Biconcave disc
Donut
Circle
The sign deficit protein of blood plasma - haptoglobin is:
Hemolises
Lowering of plasma osmotic pressure
* Hemoglobinuria
Immunodeficit
Increase oncotic pressure
The smallest of the FORMED elements of the blood are the:
White cells
Red cells
* Platelets
Erythrocytes
Erythroblasts
The specific binding and transport of ions of copper in blood plasma is carried out
Interferon
Hemoglobin
Haptoglobin
Transferin
* Ceruloplasmin
907.
The strongest buffer system of blood, which compose 75% from all of the buffer
system of blood is:
A. Hydrocarbonate
B. * Hemoglobin
C. Phosphate
D. Proteins
E. Ammonium
908.
The sub-group of chromoproteins, which contain ironporphirine complex, take to:
A. Ceruloplasmin
B. Transferrin
C. Hemocianin
D. * Catalase
E. Xantinoxidase
909.
The three primary types of plasma proteins are:
A. Antibodies, metallo-proteins, lipoproteins
B. Serum, fibrin, fibrinogen
C. * Albumins, globulins, fibrinogen
D. Heme, iron, globin
E. None of the above
910.
The type of plasma protein that helps regulate osmotic pressure is:
A. * Albumin.
B. Globulin.
C. Fibrinogen.
D. Hemoglobin.
E. Oxyhemoglobin
911.
The ultimate source of all types of blood cells are the...
A. Thrombocytes
B. * Hemocytoblasts
C. Myeloid stem cells
D. Lymphoid stem cells
E. Granular leukocytes
912.
The white blood cell that is most like the mast cell is the:
A. * Basophil
B. Lymphocyte
C. Neutrophil
D. Eosinophil
E. Monocyte
913.
There is/are ____ heme group(s) in a molecule of hemoglobin.
A. Five
B. Four
C. Three
D. Two
E. One
914.
These cells have red granules when stained and two lobed nuclei.
A. Platelets
B. Lymphocytes
C. Basophils
D. * Eosinophils
E. none of the above
915.
Thick muscular walls are present in:
A. * Arteries
B. Arterioles
C. Veins
D. Venules
E. Aorta
916.
Thrombocytes is the other name of :
A. RBC
B. WBC
C. * Platelets
D. Lymphocytes
E. Monocytes
917.
Transport form of iron, which delivers the ions of iron (Fe3+), which enter in
blood after absorbtion in intestine to the places of depositing and using is:
A. Albumin
B. Hemoglobin
C. * Transferin
D. C-reactive protein
E. Ferritin
918.
Transport of drugs, fatty acids, pigments, ions of metals with blood to the
different organs and systems characteristic to albumins owing to their:
A. High dyspersity
B. Acid properties
C. High hydrophilic
D. * High adsorbtion
E. Small molecular mass
919.
Violation of acid-base balance of blood which is characterized the accumulation
of acid substances named:
A. Alcalosis
B. Anaciditas
C. Achilia
D. * Acidosis
E. Hyperaciditas
920.
Violation of acid-base balance of blood, which is characterized the accumulation
of base substances, named:
A. * Alkalosis
B. Achilia
C. Hyperaciditas
D. Acidosis
E. Anaciditas
921.
Vitamin K is needed for:
A. * Blood clotting
B. Prevention of sickle cell anemia
C. Hemoglobin synthesis
D. Prevention of hemolysis
E. None of the above
922.
What are the two major factors that regulate the movement of water and
electrolytes from one fluid compartment to the next?
A. Hydrostatic pressure and osmotic pressure
B. Sodium concentration and osmotic pressure
C. Hydrostatic pressure and potassium concentration
D. * Concentration of all electrolytes combined and water pressure
E. Osmotic and hydrostatic pressure
923.
What converts fibrinogen to fibrin?
A. * Thrombin
B. Thromboxane A2
C. Factor XIII
D. Tissue thrombopla
E. ADP
924.
What function of blood belong a concept “oncotic pressure of blood”?
A. Gas transport
B. Protective
C. Detoxification
D. Termoregulation
E. * Osmotic
925.
What is the difference between serum and plasma?
A. Plasma contains calcium; serum does not.
B. Plasma does not have blood cells; serum does.
C. * Plasma contains fibrinogen; serum does not.
D. Plasma contains albumin; serum does not.
E. Plasma contain zinc; serum does not.
926.
What is the most effective intracellular inorganic buffer?
A. Bicarbonate
B. * Phosphate
C. Hemoglobin
D. Lactate
E. Protein
927.
What is the organ that pumps blood all throughout the human body?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
The lungs
* The heart
The kidneys
The blood vessels and capillaries
The spleen
928.
What kinds of polypeptide chains are there in hemoglobin F?
A. 2222.
B. 222?.
C. * 2222.
D. 332?.
E. 1133.
929.
What metabolyt, that is present in erythrocytes, lower the related of haemoglobin
to oxygen?
A. 1,3-diphosphoglycerate
B. Laktat
C. * 2,3- diphosphoglycerate
D. Pyruvat
E. 3-phosphoglycerate aldehyde
930.
What method is it possible to distribute on separate fractions the proteins of blood
plasma?
A. Biuret
B. * Electrophoresis
C. Heller reaction
D. Polarimetric
E. Roberts-Stolnikov
931.
What part of the blood carries minerals, vitamins, sugar, and other foods to the
body's cells?
A. * Plasma
B. Platelets
C. Red corpuscles
D. Macrophage
E. Eosinophil
932.
What protein, assigned for transport, does hemoglobin bind ti in the
reticuloendotelial system of the liver?
A. Haptoglobin
B. Albumin
C. Ferritin
D. Transferrin
E. Ceruloplasmin
933.
When oxygen is carried by the blood, it is bonded to
A. Platelets.
B. Antibodies.
C. Plasma.
D. * Hemoglobin.
E. Water
934.
Which body system collects the fluid that is lost by the blood and returns it to the
body’s transport system?
A. Red blood cells
B. * Eosynophils
C. Platelets
D. Monocites
E. Lymphocites
F.
G.
H.
I.
J.
Circulatory
Lymphatic
Respiratory
Connection
Muscle
935.
Which cell count tends to be elevated when an individual has an allergy or
parasitic worms?
A. Red blood cells
B. Erythrocyte
C. * Esinophil
D. Platelet
E. Monocites
936.
Which element in the blood is round and colourless?
A. Plasma
B. Platelets
C. Red blood cells
D. * White blood cells
E. Globulins
937.
Which formed elements are most directly associated with the immune responses
that defend the body against pathogens?
A. Erythrocytes
B. * Leucocytes
C. Platelets
D. None of the above (the immune response is strictly a function of plasma)
E. All of the above
938.
?Which indexes be responsible for the normal volume of blood in adult?
A. 15 l
B. 25 l
C. * 5 l
D. 50 l
E. 2 l
939.
Which indexes of blood in men indicate hypohemoglobinemia?
A. * 100 g/l
B. 130 g/l
C. 145 g/l
D. 155 g/l
E. 160 g/l
940.
Which indexes of blood in women indicate hypohemoglobinemia?
A. 120 g/l
B. 130 g/l
C. 145 g/l
D. 115 g/l
E. * 80 g/l
941.
Which is the most common type of blood cell in a healthy human?
A. * Erythrocytes
B. Monocytes
C. Lymphocytes
D. Eosinophils
E. Basophils
942.
Which of the following does not occur as a result of a shift in the acid- base
balance of the body?
A. An alteration in the rate of enzyme-controlled metabolic reactions
B.
C.
D.
E.
943.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
944.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
945.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
946.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
947.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
948.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
949.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
950.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
An increase in metabolic efficiency within the cells
* A shift in the distribution of other ions
A modification in hormone actions
Hypovitaminosis
Which of the following is a function of the vertebrate circulatory system?
Temperature regulation
Transport metabolic wastes
Provide immune defense
Transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
* All of the above
Which of the following is a type of leukocyte?
Macrophage
Eosinophil
Monocyte
* All of the above
None of the above
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of red blood cells?
Biconcave disks
No nucleus
Some hormones
* All of the above
None of the above
Which of the following is NOT a component of blood plasma?
Carbon dioxide
* Hemoglobin
Oxygen
Ions
Hormones
Which of the following is NOT a type of blood vessel?
Artery
Vein
* Lymphatic cell
Aorta
Venules
Which of the following is NOT a type of granular white blood cell? ____
Monocytes
Neutrophils
* Eosinophils
Basophils
None of the above; all are granular
Which of the following is not found in blood?
Fibrinogen
Glucose
Urea
* Glycogen
Globulins
Which of the following is NOT needed for blood clotting?
* Vitamin A
Vitamin K
Calcium
Thrombin
Prothrombin
951.
Which of the following is the major form of hemoglobin produced in red blood
cells during normal adult life?
A. * Alpha2/beta2
B. Alpha2/gamma2
C. Zeta2/epsilon2
D. Alpha2/delta2
E. Alpha2/epsilon2
952.
Which of the following plasma proteins are not produced by the liver?
A. * Gamma globulin
B. Albumin
C. Beta globulins
D. Fibrinogen
E. Ceruloplasmin
953.
Which of the following statements about circulatory systems is true?
A. Hormones are transported in the blood.
B. All invertebrates have an open circulatory system.
C. Capillaries have thicker walls than veins do.
D. The systemic circulation carries blood to and from the lungs.
E. * All of the above are true.
954.
Which of the following statements concerning platelets is INCORRECT.
Platelets:
A. Contain DNA
B. Are roughly disk-shaped
C. Have little ability to synthesize proteins
D. Synthesis: actin, miosyn, troponin
E. * Take part in reactions: adgesion, agregation, secretion
955.
Which of the following would decrease blood pressure?
A. * An increase in the enzyme renin
B. An increase in blood volume
C. A decrease in Angiotensin II
D. An increase in hematocrit
E. A decrease of globulins
956.
Which of these is considered a secondary defense against changes in pH?
A. * Renal excretion of hydrogen ions
B. The bicarbonate buffer system
C. The phosphate buffer system
D. The protein buffer system
E. The hemoglobin buffer system
957.
Which one of the following has the greatest capacity to bind oxygen?
A. * Iron in heme portion of hemoglobin
B. Carbon in heme portion of hemoglobin
C. Hydrogen in heme portion of hemoglobin
D. Carbon in non-heme (protein) portion of hemoglobin
E. Nitrogen in non-heme (protein) portion of hemoglobin
958.
Which one of the following is not one of major classes of plasma protein?
A. Albumins
B. B-globulins
C. Fibrinogen
D. * Lipoproteins
E. E, ,-globulins
959.
Which plasma proteins help to regulate osmotic pressure and blood volume?
A. * Albumins
B.
C.
D.
E.
? - globulins
Fibrinogens
?- globulins
E - globulins
960.
Which plasma proteins help transport lipids in the bloodstream?
A. * Albumins
B. Alpha and beta globulins
C. Fibrinogen
D. Gamma globulins
E. Prealbumins
961.
Why is oxygen important to blood and to the cells?
A. Oxygen helps the blood to clot.
B. Oxygen brings food to the cells
C. * Oxygen is necessary for cell growth and energy.
D. Oxygen is not important - carbon dioxide is the most important substance to the
body.
E. Oxygen is not important – oxygen free radical is the most important
962.
С. С2-macroglobulin
A. C-reactive protein
B. Crioglobulin
C. Blood inhibitios of proteinas
D. Albumins
963.
At the electrophoretic research of patient blood plasma found interferon. In the
area of what fraction be found this protein?
A. Globulins
B. Albumins
C. C2 – Globulins
D. * Globulins
E. E - Globulins
964.
Ceruloplasmin is the protein of:
A. A-globulin fraction.
B. B1-globulin fraction.
C. * C2-globulin fraction.
D. D-globulin fraction.
E. prealbumin
965.
Electrophoresis of blood proteins carry out at pH:
A. 5,5
B. 7,0
C. * 8,6
D. 4,7
E. 3,0
966.
Red blood cells are destroyed in the :
A. Lungs
B. * Liver
C. Heart
D. Spleen
E. Kidney
967.
The plasma concentration of IgA is
A. 1–5 mg/dl
B. 40–200 mg/dl
C. * 60–500 mg/dl
D. 700–1,500 mg/dl
E. None of the above
968.
The transport of cholesterol from peripheral tissues to the liver takes place with
the help of such enzyme:
A. Lipoprotein lipase
B. * Lecithin cholesterol acyl transferase
C. Cholesterol esterase
D. Lecithinase
E. Acetyl choline esterase
969.
____________ is hydrolytically cleaved to directly yield urea in the urea cycle.
A. ornithine
B. glutamate
C. * arginine
D. carbamoyl phosphate
E. None of the above
970.
A deficiency in complement proteins or in their regulators can result in
A. blood in the urine from erythrocyte lysis.
B. decreased levels of certain complement proteins in the circulation.
C. immune complex disease.
D. increased numbers of infections.
E. * All of the above can result from complement deficiencies.
971.
A deficiency in complement proteins or in their regulators can result in
A. blood in the urine from erythrocyte lysis.
B. decreased levels of certain complement proteins in the circulation.
C. * immune complex disease.
D. increased numbers of infections.
E. All of the above can result from complement deficiencies.
972.
A Fab fragment:
A. * binds antigen.
B. is produced by pepsin digestion.
C. lacks light chains.
D. has no interchain disulfide bonds.
E. is all of the above.
973.
A reaction of cooperation of antibodies with an antigen is high-specific and takes
place due to the followings types of bonds, except:
A. Hydrogenic
B. Electrostatic
C. * Peptide
D. Vandervaal's
E. Hydrophobic
974.
Acidosis results in increasing levels of what ion?
A. Calcium
B. Chloride
C. Sodium
D. Phosphorus
E. * Hydrogen
975.
All of the following processes can be activated by complement except
A. inflammation
B. * antibody production
C. cytolysis
D. opsonization
E. none of the above
976.
Allergic reactions are mediated by
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
IgA
IgG
IgD
* IgE
All of the above
977.
Among transport forms of lipids distinguish LDH (beta-lipoproteins). What from
the below mentioned correlations of proteins, triacylglycerols, cholesterol and
phospholipids proper to the molecular form of beta – lipoproteins?
A. * 21 : 14 : 58: 8
B. 35 : 50 : 12 : 3
C. 10 : 5 : 60 : 25
D. 15 : 20 : 30 : 35
E. 2 : 85 : 5 : 7
978.
An antigen after incorporation into an organism contacts with the receptors of
lymphocytes, causes the transition of cells to a mitotic cycle. Transfer of the signal from
a membrane is carried out with the help of mediators. Which from them does not
participate in this process?
A. Inositol triphosphate
B. Diacylglycerol
C. Ions of Ca++
D. * UTP
E. cGМP
979.
An immunoglobulin found in exocrine secretions is
A. * IgA
B. IgG
C. IgM
D. IgE
E. All of these
980.
An immunoglobulin which can cross the placental barrier is
A. IgA
B. IgM
C. IgD
D. * IgG
E. None of these
981.
Antibodies are powerful weapons in the body's defense against microorganisms.
However, there are limits to what an antibody can actually do. Which of the following is
NOT an action that an antibody can actually accomplish?
A. cause an agglutination of antibodies and antigens, forming an antibody–antigen
complex
B. attach to a bacterial cell antigen, preventing the bacterium from attaching to
anything else
C. start a complement protein cascade
D. * poke microscopic "holes" in a bacterial cell membrane, causing it to die
E. Both A and D are correct
982.
Antibodies are produced as a reaction to the presence of :
A. Red blood cells
B. Haemoglobin
C. * Antigens
D. White blood cells
E. Platelets
983.
Antigen presenting cells are important in that they:
A. allow B-cells to recognize a viral invader
B.
C.
D.
E.
* allow helper T-cells to recognize a viral invader
allow cytotoxic T-cells to be suppressed
allow helper T-cells to fight a viral invader
all of the above
984.
As a result of development of kidney insufficiency a patient has a necessity for the
transplantation of a kidney. Which analysis must be done to avoid tearing away of
transplanted organ?
A. To define the amount of gamma-globulins in blood
B. To define the amount of lymphocytes in blood
C. * To define the proteins of main complex of histocompatability in leucocytes
D. To discover state of the system of complement in blood of recipient
E. To define A/G coefficient.
985.
As complement is activated by complexes of antibody-coated bacteria, bystander
lysis of nearby host cells is prevented by
A. a long-lived thioester bond on active complement proteins.
B. covalent attachment of all active complement proteins to the pathogen surface.
C. plasma proteins that inactivate the anaphylatoxins.
D. * proteins on host cell membranes that inhibit MAC formation.
E. the slow catalytic rates of complement proteases.
986.
As result of incorporation of antigen in an organism takes place a complex of
biochemical processes, directed on it neutralization and deletion. Choose from the below
mentioned an incorrect immune responses of organism:
A. Binding of antigen to the proteins-receptors of lymphocytes
B. * Activating of gluconeogenesis
C. Activating, prolipheration, differentiation of T-cell
D. Modification of B-lymphocytes in plasmatic cells and synthesis of antibodies
E. Activating of the system of complement, endocytosis and lysis of the antigen by
tissue macrophages
987.
B-cells do which of the following?
A. Proliferate and differentiate into plasma cells
B. Respond to antigens by making antibodies
C. Act as antigen-processing cells
D. * All of the above
E. None of the above
988.
Chemical nature of immunoglobulins:
A. Lipoproteins
B. * Glykoproteins
C. Phosphoproteins
D. Chromoproteins
E. Nukleoproteins
989.
Chylomicrones are formed in the ____________________ and their main function
is the __________________________________.
A. wall of intestine; transport of cholesterol;
B. liver; transport of triacylglycerols synthesized in liver;
C. * wall of intestine; transport of dietary triacylglycerols;
D. blood; transport of cholesterol.
E. all of the above.
990.
Complement activity is restricted by all of the following EXCEPT
A. dissociation of C3 and C5 convertases.
B. Gram positive cell walls that are resistant to MAC polymerization.
C. host cell plasma proteins that inactivate C3a, C4a, and C5a activity.
D. * LPS in the outer membrane of Gram negative bacteria that inactivates C3b.
E. proteolytic cleavage of complement proteins into smaller fragments.
991.
Complement factors C5b+C6+C7+C8 make up a membrane attack complex that
results in
A. enhanced phagocytosis
B. opsonization
C. * cytolysis
D. all of the above
E. none of the above
992.
Complement is
A. activated by binding to specific complement receptors.
B. antigen-specific.
C. a potent promoter of virus entry into host cells.
D. a series of intracellular proteins which work with antibody to eliminate
endogenous antigen
E. * present in the circulation in an inactive form.
993.
Complement is
A. activated by binding to specific complement receptors.
B. antigen-specific.
C. a potent promoter of virus entry into host cells.
D. a series of intracellular proteins which work with antibody to eliminate
endogenous antigen.
E. * present in the circulation in an inactive form.
994.
Complement is involved in all of the following except
A. attraction of neutrophils to an infection site.
B. increased presence of serum proteins in the infected tissues.
C. lysis of bacteria in the absence of specific antibodies.
D. opsonization of microorganisms for phagocytosis.
E. * sensitization of T cells to antigen
995.
Complement is involved in all of the following except
A. attraction of neutrophils to an infection site.
B. increased presence of serum proteins in the infected tissues.
C. lysis of bacteria in the absence of specific antibodies.
D. opsonization of microorganisms for phagocytosis.
E. sensitization of T cells to antigen
996.
Complement receptors (CR)
A. activate complement on the surface of pathogens.
B. bind only activated complement proteins.
C. inhibit complement activation on the surface of host cells.
D. * on erythrocytes remove immune complexes from the circulation.
E. on macrophages signal host cells to make opsonins.
997.
Complement system can be activated by binding of antigen to
A. IgA
B. IgD
C. IgE
D. * IgM
E. IgC
998.
Complement:
A. is a group of active proteolytic enzymes found in serum.
B. is secreted by macrophages and hepatocytes in response to antigen binding.
C. participates in both innate and adaptive immune responses.
D. couses lysis of cells.
E. * All of the above statements about complement are true.
999.
Components of the Fab fragment include:
A. an entire light chain.
B. the J chain.
C. the VH and CH1 domains.
D. the carboxyl terminal portion of the heavy chain.
E. * a and c are correct
1000.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is an example of which imbalance?
A. Respiratory acidosis
B. Respiratory alkalosis
C. Metabolic alkalosis
D. * Metabolic acidosis
E. Respiratory chain
1001.
Disulfide linkage between the heavy (H) and light (L) chains of most
immunoglobulins is between:
A. constant (C) L and CH1 segments.
B. variable (V) L and VH segments.
C. L chain joining (J) segments and H chain J segments.
D. CL and CH2 segments.
E. none of the above
1002.
Enzyme of capillary walls lipoprotein lipase named the factor of transparensy of
blood. What function does it execute?
A. Transformation of LDH into HDL
B. Hydrolysis of constitutional fats
C. * Mobilization of fat from chylomicrons
D. Mobilization of cholesterol from peripheral tissues
E. Mobilization of reserve fat
1003.
Essence of immune reaction of organism is formation of antibodies against
foreign factors. Choose what from below mentioned functions are not specific for the
antibodies:
A. Fastening and activating of complement
B. * Ability to change membrane potential of the antigen
C. Binding to the receptors on the cells surface of macrophages
D. Binding to the receptors of mast cell
E. Ability to penetrate the placenta barrier
1004.
From a liver neutral fats are transported as VLDL. What from the below
mentioned correlations of proteins, triacylglycerols, cholesterol and phospholipids proper
to the molecular form of VLDL?
A. 15 : 20 : 20 : 45
B. 45 : 8 : 38 : 10
C. 2 : 90 : 5 : 3
D. 21 : 14 : 58 : 8
E. * 8 : 60 : 20 : 15
1005.
HDL carry out a transport of:
A. Free fatty acids to the liver
B. Cholesterol from a liver in extra hepatic tissues
C. Cholesterol from tissues to the liver
D. Triacylglycerols from an intestine
E. Glycerol from adipose tissue to the liver
1006.
HDL carry out a transport of:
A. Free fatty acids to the liver
B. Cholesterol from a liver in extra hepatic tissues
C. Cholesterol from tissues to the liver
D. Triacylglycerols from an intestine
E. Glycerol from adipose tissue to the liver
1007.
HDL carry out a transport of:
A. Free fatty acids to the liver
B. Cholesterol from a liver in extra hepatic tissues
C. Cholesterol from tissues to the liver
D. Triacylglycerols from an intestine
E. Glycerol from adipose tissue to the liver
1008.
How is it a mother who is breast feeding positively affects her baby's immune
system?
A. she gives her baby permanent antibodies she has produced
B. she gives her baby antigens she has produced in her breast milk
C. * she gives her baby antibodies she has produced in her breast milk
D. she gives her baby immune cells to fight incoming invaders
E. Both C and B are correct.
1009.
Hyperuricemia is the increase of uric acid level more than:
A. * 0,5 mmol/l
B. 0,1 mmol/l
C. 10 mmol/l
D. 1 mmol/l
E. 2 mmol/l
1010.
Hyperuricemia is the increase of uric acid level more than:
A. * 0,5 mmol/l
B. 0,1 mmol/l
C. 10 mmol/l
D. 1 mmol/l
E. 2 mmol/l
1011.
If a person is born without C2 and C4,
A. C5 can still be cleaved by the classical pathway.
B. C3b will not be able to bind to bacteri
C. C9 will polymerize inappropriately and lyse host cells.
D. the classical pathway will be changed into the alternative pathway.
E. * the amount of C3b produced during bacterial infections will be reduced.
1012.
If a person is born without C2 and C4,
A. C5 can still be cleaved by the classical pathway.
B. C3b will not be able to bind to bacteria
C. C9 will polymerize inappropriately and lyse host cells.
D. * the classical pathway will be changed into the alternative pathway.
E. the amount of C3b produced during bacterial infections will be reduced.
1013.
If all of your cells are covered in antigens (and they are), why doesn't your
immune system kill/attack all cells?
A. because your immune system is dedicated to finding invaders
B. * because your immune system is very sophisticated
C. because your healthy cells are not "tagged" in any way
D. because your cells are "tagged" healthy by cell membrane protiens.
E. all of the above
1014.
If an amino acid is glucogenic, it will not be degraded to ______.
A. pyruvate
B. oxaloacetate
C. fumarate
D. * acetoacetate
E. malate
1015.
IgD
A. is the predominant antibody in colostrum,
B. * is present on the surface of all mature B cells,
C. has a molecular weight of 150,000,
D. mediates precipitation reactions,
E. is none of these.
1016.
IgE
A. * increases in individuals with parasitic infections,
B. is the major agglutinating antibody,
C. is a and b,
D. is none of these
E. all of these.
1017.
IgG is not
A. the major antibody that confers passive immunity on the fetus,
B. divided into five subclasses,
C. made up of two antigen-binding sites,
D. * all of these,
E. none of these.
1018.
IgM is
A. not involved in agglutination (clumping) reactions,
B. found as a pentamer on the B lymphocyte’s surface,
C. the predominant antibody in the serum,
D. * a pentamer in the blood,
E. none of these.
1019.
IgM possesses
A. Two light chains and two heavy chains
B. Four light chains and four heavy chains
C. Six light chains and six heavy chains
D. * Ten light chains and ten heavy chains
E. None of these
1020.
Immune complexes consist of
A. antibody plus complement
B. basophil plus complement
C. * antigen plus antibody
D. antigen plus complement
E. antigen plus basophil
1021.
Immune status of organism is provided by:
A. * Leukocytes
B. Trombocytes
C. Erythrocytes
D. Hemoglobin
E. Bilirubin
1022.
Immunoglobulins are classified on the basis of
A. Type of light chains
B. * Type of heavy chains
C. Types of light and heavy chains
D. Molecular weight
E. All of these
1023.
In blood of healthy man supported the constant concentration of hydrogen ions,
that put in arterial plasma:
A. 7,26± 0,04
B. 7,16± 0,04
C. 7,96± 0,04
D. * 7,36± 0,04
E. 7,46± 0,04
1024.
In the electrophoresis studies by Tiselius and Kabat, their conclusion was that
antibody molecules are:
A. alpha-globulins.
B. beta-globulins.
C. gamma-globulins.
D. albumins.
E. none of the above
1025.
In the membrane attack phase of the classical complement pathway, the role of
C5b is to
A. activate the C5 convertase activity.
B. attract neutrophils to lyse the pathogen.
C. * initiate formation of the MAC.
D. polymerize into a membrane-spanning channel.
E. All of these are activities of C5b.
1026.
In the membrane attack phase of the classical complement pathway, the role of
C5b is to
A. activate the C5 convertase activity.
B. attract neutrophils to lyse the pathogen.
C. initiate formation of the MAC.
D. polymerize into a membrane-spanning channel.
E. * All of these are activities of C5b.
1027.
In the presence of activated complement, neutrophils
A. are repelled
B. produce histamine
C. cause vasodilation
D. * degranulate and release enzymes that cause tissue damage
E. cause vasoconstriction
1028.
Indicate proteins that dont belong to fractions of globulins:
A. Ceruloplazmin
B. B1-antitrypsin
C. Transferin
D. Haptoglobin
E. * Fibrinogen
1029.
Intermediate size complexes
A. become basophils
B. * activate complement
C. are removed by phagocytosis
D. degranulate
E. all of the above
1030.
Isotypes refer to variations in the
A. light chain variable region
B. light chain constant region
C. heavy chain variable region
D. * heavy chain constant region
E. Any of the above
1031.
LDL are formed in the ____________________ and it is the major carrier of
_____________________________________________________.
A. wall of intestine; dietary triacylglycerols;
B. liver; triacylglycerols synthesized in liver;
C. * blood and liver; cholesterol (transport cholesterol to peripheral tissues);
D. blood and liver; cholesterol (transport cholesterol to liver from peripheral tissues).
E. all of the above.
1032.
Light chains of immunoglobulins are of following types:
A. Alpha and kappa
B. Alpha and gamma
C. Lambda and delta
D. * Kappa and lambda
E. All of these
1033.
Lipids are transported in blood with proteins, formed lipoprotein complexes. They
are determined with a method:
A. Chromatography
B. Salting-out
C. Spectral analysis
D. * Electrophoresis
E. Rephractometria
1034.
Lipids are transported in blood with proteins, formed lipoprotein complexes. They
are determined with a method:
A. Chromatography
B. Salting-out
C. Spectral analysis
D. * Electrophoresis
E. Rephractometria
1035.
Lipoproteinlipase – enzyme which is located ________________________ and
hydrolyses _____________________________________.
A. in the wall of intestine; triacylglycerols of chylomicrons;
B. * within capillaries of muscles and adipose tissue; triacylglycerols of
chylomicrons and VLDL;
C. within capillaries of muscles and adipose tissue; cholesterol esters of LDL;
D. in the blood; cholesterol esters of LDL.
E. all of the above.
1036.
Lipoproteins have a micellar structure. The nucleus of lipoproteins is made with
hydrophobic compounds; the membrane is formed with hydrophilic radicals. Choose
compounds of nucleus:
A. Free cholesterol
B. Free fatty acids
C. Ethers of cholesterol, triacylglycerols
D. Phospholipids, glycolipids
E. Glycerol, monoacylglycerols
1037.
Lipoproteins have a micellar structure. The nucleus of lipoproteins is made with
hydrophobic compounds; the membrane is formed with hydrophilic radicals. Choose
compounds of nucleus:
A. Free cholesterol
B. Free fatty acids
C. Ethers of cholesterol, triacylglycerols
D. Phospholipids, glycolipids
E. Glycerol, monoacylglycerols
1038.
Low density lipoproteins transport ________________ from __________ to
_________________.
A. triacylglycerols; intestine; liver
B. * cholesterol; liver; peripheral tissues;
C. cholesterol; peripheral tissues; liver
D. triacylglycerols; liver; adipose tissue and muscles
E. triacylglycerols; liver; muscles
1039.
Name glycogenic amino acids:
A. Valine, phenilalanine
B. Leucine, tryptophan
C. Glutamate, aspartate
D. Serine, isoleucine
E. * Methionine, valine
1040.
Name glycogenic amino acids:
A. Valine, phenilalanine
B. Leucine, tryptophan
C. Glutamate, aspartate
D. Serine, isoleucine
E. * Methionine, valine
1041.
Name glycogenic amino acids:
A. Valine, phenilalanine
B. Leucine, tryptophan
C. Glutamate, aspartate
D. Serine, isoleucine
E. * Methionine, valine
1042.
Neutral fats in blood are transported as chylomicrons. What from the below
mentioned correlations of proteins, triacylglycerols, cholesterol and phospholipids proper
to the molecular form of chylomicrons?
A. 15 : 20 : 30 : 35
B. 21 : 14 : 58 : 8
C. 10 : 5 : 60 : 25
D. * 2 : 90 : 5 : 3
E. 35 : 50 : 12 : 3
1043.
Nitric oxide is produced from which reaction?
A. * arginine to citrulline
B. glutamate to g-ketoglutarate
C. bicarbonate to carbamoyl phosphate
D. tryptophan to acetyl CoA
E. arginine to a-ketoglutarate
1044.
Normal level of uric acid in blood is:
A. * 0,12-0,46 mmol/l
B. 1,7-2,05 mmol/l
C. 20-40 grammes/л
D. 3,3-5,5 mmol/l
E. 3-8 mmol/l
1045.
? On the surface of lymphoid cells (B-lymphocytes) proteins -receptors which
recognize and specifically link antigens are placed. Which chemical nature of these
receptors?
A. Histons
B. Proteins
C. Krioglobulines
D. * Immunoglobulines
E. Globin
1046.
Once vaccinated, you have had a primary exposure to specific antigens. If you
ever encounter this antigen again, you will mount a rapid immune response due to:
A. cytotoxic T cells
B. antibodies
C. antigen presenting cells
D. * memory cells
E. all of the above
1047.
One of the transport forms of lipoproteins o blood there is HDL (alphalipoproteins). What from the below mentioned correlations of proteins, triacylglycerols,
cholesterol and phospholipids proper to the molecular form of alpha-lipoproteins?
A. 10 : 5 : 60 : 25
B. * 45 : 8 : 38 : 10
C. 25: 15 : 58: 2
D. 2 : 90 : 3 : 5
E. 15 : 20 : 30 : 35
1048.
Opsonization is
A. a membrane attack complex lysing a bacterium by making a hole in its membrane
B. when complement causes inflammation to occur
C. when the nine complement factors cascade in order
D. * coating of a bacterium with antibody to make it more susceptible to
phagocytosis
E. none of the above
1049.
Pollen often causes such allergic reactions as itch, edem Simultaneously in an
organism the enhanceable amount of histamine accompanies:
A. * Dilatation of blood vessels and increase their permeability
B. High blood pressure
C. Diminishing of the synthesis of immunoglobulins
D. Degradation of antibodies
E. Activation of a histidin decarboxylase
1050.
Proteins of main complex of histocompatability are the main proteins of
immunological individuality of organism. All below mentioned functions inherent them
EXEPT:
A. Participating is in cooperation between lymphoid cells
B. They are proteins of transplantation
C. * Execute a catalytic function
D. Participating in cooperating with an antigen on the cells surface
E. Send cytotoxic T-effectors to the infected „target”.
1051.
Recognition of antigen is the function of
A. Variable region of light chains
B. * Variable regions of light and heavy chains
C. Constant region of heavy chains
D. Constant regions of light and heavy chains
E. All of these
1052.
Recognition of foreign factors (antigens) in an organism carries out lymphocytes
with the help of proteins-receptors. How many molecules of immunoglobulin are placed
on the surface of lymphoid cell:
A. * About 105
B. 10-20 molecules
C. Near 1000 molecules
D. 1010
E. None of above
1053.
Reliability of implementation of protective function of organism is provided by
the numerous factors of the immune system. Immune function is inherent to all below
mentioned factors except:
A. Plenty of clones of B- lymphocytes
B. A high affinity of membranes immunoglobulins to the antigens
C. Cooperation of many clones of B- lymphocytes with antigen
D. Presence in the organism of activated B- lymphocytes as cells of „memory” to the
certain antigens
E. * Sufficient content of proteins in blood
1054.
Secretory component is present in
A. * IgA
B. IgG
C. IgM
D. All of these
E. None of these
1055.
Specific immunity can be acquired either naturally or artificially and involves
A. antigens
B. antibodies
C. the classical complement pathway.
D. * All of the above.
E. None of the above.
1056.
System of complement is important factor of defense of organism from infections.
Activating of the system takes place with:
A. Oxidation
B. hydroxylation
C. Conjugation
D. * Partial proteolysis
E. Association of subunits
1057.
Technogenic, ecological, social and other factors often result in the damage of the
immune system of organism, reduce resistance of human organism to the infections.
Immunological insufficiency can be result of such disorders except:
A. * Insufficient synthesis by the liver of gamma-globulins
B. Deficiency of stem cells of bony marrow
C. Disorders of activating of T-cells
D. Disorders of function B-lymphocytes and secretion of antibodies
E. Deficiency of the system of complement
1058.
The allergic reaction of organism is related to activating of complement by a
partial hydrolysis. Among the below named functions of the low-molecular peptides
choose correct:
A. Diminish the amount of eosinophils and basophiles
B. Weaken construction of smooth muscles
C. * Increase permeability of walls of capillaries
D. Diminish permeability of walls of capillaries
E. Strengthen the chemo taxis of leucocytes.
1059.
The alternative pathway of complement activation
A. causes tissue damage in the absence of C1INH.
B. occurs after the classic pathway is activated.
C. occurs only if the classical pathway is ineffective in pathogen clearance.
D. * requires C3
E. requires C4
1060.
The alternative pathway of complement activation
A. causes tissue damage in the absence of C1INH
B. occurs after the classic pathway is activated
C. occurs only if the classical pathway is ineffective in pathogen clearance.
D. * requires C3
E. requires C4
1061.
The amount of cholesterol in blood plasma is in normal state:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1062.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1063.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1064.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1065.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1066.
the
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* 3-7 mmol/l
10-15 mmol/l
20-25 mmol/l
1-3 mmol/l
5-7 mmol/l
The antigen-binding sites of an antibody molecule are located in the
C region of light chains,
V region of light chains,
C region of heavy chains,
V region of heavy chains,
* regions of both light and heavy chains,
The basic event in the formation of a blood clot is the change of
* Fibrinogen to fibrin
Fibrin to fibrinogen
Thrombin to prothrombin
Vitamin K to prothrombin
Fibrin to thrombin
The basic structural units of an immunoglobulin molecule include:
* two identical heavy and two identical light chains.
one constant and three variable regions.
identical kappa and lambda light chains.
a total of five domains.
all of the above
The class-specific antigenic determinants of immunoglobulins are associated with:
chains.
light chains.
disulfide bonds.
* heavy chains
variable regions
The class-specific antigenic determinants of immunoglobulins are associated with
light chain,
* heavy chain,
J chain,
secretory component,
none of these.
1067.
The component of blood that is responsible for clotting is:
A. * Platelets
B. Erythrocytes
C. Neutrophils
D. Basophils
E. None of the above
1068.
The concentration of urea in the blood of healthy adult is:
A. 10-12 mM/l
B. 12-20 mM/l
C. 1-2 mM/l
D. * 3-8 mM/l
E. 15-18 mM/l
1069.
The damage of the immune system reduces resisting of human organism to the
infections. Immune status of organism depends on the followings structures, except:
A. Bony marrow
B. Thymus
C. Tissue macrophages
D. Lymphatic nodes
E. * Hypophysis
1070.
The decrease of urea in blood is observed in some conditions, except:
A. Kidney diseases
B. * Diabetes Mellitus
C. Long starvation
D. Excessive proteins in food
E. Toxic goіter
1071.
The decrease of urea in blood is observed in some conditions, except:
A. Kidney diseases
B. * Diabetes Mellitus
C. Long starvation
D. Excessive proteins in food
E. Toxic goіter
1072.
The disease AIDS is caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). One of
the reasons why this disease has resisted a cure is because it attacks the body's immune
system, the very system that is designed to resist viral infections. Which of the immune
system cells does the AIDS virus specifically target for infection?
A. B cells
B. * Helper T cells
C. memory cells
D. natural killer cells
E. none of the above
1073.
The effector function of antibody is performed by
A. Variable region of light chains
B. Constant region of heavy chains
C. Variable regions of light and heavy chains
D. * Constant regions of light and heavy chains
E. Constant region of light chains
1074.
The following acute phase protein increase dramatically in concentration during
inflammation :
A. ceruloplasmin
B. haptoglobulin
C. C-reactive protein
D. fibrinogen
E. C3
1075.
The functions of HDL is a transport of:
A. Triacylglycerols from a liver
B. Cholesterol from an extra hepatic tissues to liver
C. Phospholipids from an intestine
D. Free fatty acids to the liver
E. * Cholesterol from a liver to extra hepatic tissues
1076.
The half-life of IgG is
A. 2–3 days
B. 5–6 days
C. 8–10 days
D. * 20–25 days
E. 5-6 hours
1077.
The hinge region of an IgG heavy chain is located:
A. between VH and CH1.
B. * between CH1 and CH2.
C. between CH2 and CH3.
D. between CH3 and CH4.
E. within the CH1 intrachain loops.
1078.
The idiotype of an antibody molecule is determined by the amino acid sequence of
the:
A. variable region of the light chain.
B. * variable regions of the heavy and light chains.
C. constant region of the light chain.
D. constant region of the heavy chain.
E. constant regions of the heavy and light chains.
1079.
The immunoglobulin having the longest half-life is
A. IgA
B. * IgG
C. IgM
D. IgE
E. IgD
1080.
The immunological response of organism for foreign factors is closely related to
the functions of proteins of main complex of histocompatability that initiate the lysis of
cells. The mechanism of their action includes the row of processes, except:
A. Proteins of main complex of histocompatability send cytotoxic T-effectors to the
antigen
B. Lymphocyte throws out on a membrane of the „target”-cells (antigen) protein
perphorin
C. Perphorin forms pores in the cellular membrane of „target” -cells
D. * Electrochemical potential changes on the membrane of „target” -cells
E. Through pores in a membrane water and electrolytes flow and cause lysis of
„target” -cells
1081.
The largest immunoglobulin is
A. IgA
B. IgG
C. * IgM
D. IgD
E. IgE
1082.
The largest lipoproteins are the __________.
A. * chylomicrons
B. VLDLs
C. LDLs
D. HDLs
E. none of the above.
1083.
The major amino acid that is released from muscle and converted to glucose in the
liver is:
A. * Alanine
B. Glutamine
C. Valine
D. Aspartate
E. Glutamate
1084.
The major amino acid that is released from muscle and converted to glucose in the
liver is:
A. * Alanine
B. Glutamine
C. Valine
D. Aspartate
E. Glutamate
1085.
The maturation of T cells and the production of particular T cell receptors occurs
in the
A. thyroid gland
B. * thymus gland
C. tonsils
D. testes
E. all of the above
1086.
The minimum number of polypeptide chains in an immunoglobulin is
A. Two
B. * Four
C. Five
D. Six
E. One
1087.
The molecular weight of heavy chains is
A. 20,000–25,000
B. 25,000–50,000
C. * 50,000–70,000
D. 70,000–1,00,000
E. None of these
1088.
The molecular weight of light chains is
A. 10,000–15,000
B. * 20,000–25,000
C. 25,000–50,000
D. 50,000–75,000
E. None of these
1089.
The most abundant immunoglobulin in plasma is
A. IgA
B. * IgG
C. IgM
D. IgD
E. IgE
1090.
The plasma and urine of patients with maple syrup urine disease contain elevated
levels of each of the following amino acid, except:
A. Valine
B. Leucine
C. * Lysine
D. Isoleucine
E. none of above
1091.
The possible reason of the increase of uric acid content in blood:
A. Action of ionizing radiation
B. * Kidney insufficiency
C. Leucosis
D. Burns
E. Malignant tumor
1092.
The protective functions of organism are closely related to the immunoglobulins.
What from below mentioned descriptions incorrect?
A. * Immunoglobulins are synthesed in a liver
B. Immunoglobulins belong to fraction of gamma-globulins
C. Antibodies neutralize bacterial toxins
D. Immune proteins take part in maturing and activating of lymphocytes
E. Immunoglobulins contact with bacteria and facilitate their absorption by
phagocytes
1093.
The ratio of cholesterol in the form of LDL to that in the form of HDL in healthy
person is __________ and the ______________ of this ratio is the prognostic symptom
of atherosclerosis development.
A. 3.5; decrease;
B. 0.5; decrease;
C. * 3.5; increase;
D. 0.5; increase
E. 1; increase
1094.
The surface of bacterial cells is covered with proteins that the human body can
recognize as belonging to a foreign, invading microorganism. These molecules are
collectively referred to as .
A. antibiotics
B. antiseptics
C. * antigens
D. antibodies
E. none of the above
1095.
The transport of cholesterol from peripheral tissues to the liver takes place with
the help of such enzyme:
A. Lipoprotein lipase
B. * Lecithin cholesterol acyl transferase
C. Cholesterol esterase
D. Lecithinase
E. Acetyl choline esterase
1096.
The variable region of heavy chains has
A. One hypervariable region
B. Two hypervariable regions
C. Three hypervariable regions
D. * Four hypervariable regions
E. None of the above
1097.
The variable region of light chains has
A. One hypervariable region
B. Two hypervariable regions
C. * Three hypervariable regions
D. Four hypervariable regions
E. All of the above
1098.
The variable region of light chains is the
A. N-terminal quarter
B. * N-terminal half
C. C-terminal quarter
D. C-terminal half
E. None of the above
1099.
The wide spectrum of immunological effects is related to the row of soluble
factors of protein nature, which produced by T-cell, mast cells, macrophages, fibroblasts.
All below named proteins belong to these factors, except:
A. * Liberines and statins
B. Cytokines, monokines
C. Lymphokines, lymphotoxins
D. Interleukins
E. Interferon
1100.
To the deficiency of which immune proteins AIDS related?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
B1- antitrypsin
* ? - globulins
С-reactive protein
Macroglobulin
Ceruloplazmin
1101.
Transplantation of organs and cells between persons, which are not relatives,
frequently leads to tearing away of transplanted organ. What proteins are unique for each
organism and serve as the markers of immunological individuality of organism?
A. Immunoglobulins of B- lymphocytes
B. Proteins-receptors of T-cell
C. Proteins of the system of complement
D. * Proteins of I class of main complex of histocompatability
E. Proteins of II class of main complex of histocompatability
1102.
Transport forms of blood lipids are different lipid-protein complexes. There are all
the followings compound in their composition, except:
A. * Free fatty acids
B. Proteins
C. Neutral fats
D. Phospholipids
E. Esters of cholesterol
1103.
Transport forms of blood lipids are different lipid-protein complexes. There are all
the followings compound in their composition, except:
A. * Free fatty acids
B. Proteins
C. Neutral fats
D. Phospholipids
E. Esters of cholesterol
1104.
Transport forms of blood lipids are different lipid-protein complexes. There are all
the followings compound in their composition, except:
A. * Free fatty acids
B. Proteins
C. Neutral fats
D. Phospholipids
E. Esters of cholesterol
1105.
What are the two types of immunity?
A. adaptive, innate
B. * active, adaptive
C. inactive, innate
D. acquired, inactive
E. inactive, active
1106.
What can be a cause of immunodeficiencies?
A. Genetic factors
B. Malnutrition
C. Both B and C
D. Drugs used to treat certain diseases
E. * All are correct
1107.
What is an allergy, in physiological terms?
A. an overreaction to antibodies
B. an overreaction to a pathogen
C. * an overreaction to antigens
D. a pathogen driven result
E. none of the above
1108.
What is the difference between serum and plasma?
A. Plasma contains calcium; serum does not.
B. Plasma does not have blood cells; serum does.
C. * Plasma contains fibrinogen; serum does not.
D. Plasma contains albumin; serum does not.
E. Plasma contain zinc; serum does not.
1109.
What is the source of control on the immune system?
A. cytotoxic T-cells
B. macrophages
C. B-cells
D. * suppressor T-cells
E. all of the above
1110.
What kind of cells produce antibodies?
A. T cells
B. * B cells
C. NK cells
D. Neutrophils
E. Basophils
1111.
Which amino acids are purely ketogenic?
A. arginine and lysine
B. leucine only
C. tryptophan only
D. * lysine and leucine
E. None of the above
1112.
Which class of antibody binds to poly-Ig receptor in order to cross into the lumen
of the gut?
A. * IgA
B. IgG
C. IgM
D. IgD
E. IgE
1113.
Which class of antibody crosses the placenta and provides the newborn with
passive immunity?
A. . IgA
B. * IgG
C. IgM
D. IgD
E. IgE
1114.
Which class of antibody is found in the highest concentration in the blood?
A. IgA
B. * IgG
C. IgM
D. IgD
E. IgE
1115.
Which class of antibody is secreted into breast milk where it is delivered to the
suckling neonate, and transported through the gut lumen into blood of the neonate?
A. * IgA
B. IgG
C. IgM
D. IgD
E. IgE
1116.
Which class of antibody is the first antibody produced in response to an antigen
challenge?
A. IgA
B. IgG
C. * IgM
D. IgD
E. IgE
1117.
Which class of antibody that is secreted is most likely of low affinity?
A. IgA
B. IgG
C. IgM
D. IgD
E. * IgE
1118.
Which do you expect to have the highest protein content by percent?
A. VLDLs
B. ILDs
C. * HDLs
D. All of the lipids above have about the same protein content.
E. none of the above.
1119.
Which does not provide long term immunity?
A. Naturally acquired active immunity
B. Artificially acquired active immunity
C. * Artificially acquired passive immunity
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
1120.
Which fraction of lipoproteins the less move during electrophoresis?
A. LDL
B. HDL
C. Chylomicrons
D. Albumins
E. VLDL
1121.
Which fraction of lipoproteins the less move during electrophoresis?
A. LDL
B. HDL
C. Chylomicrons
D. Albumins
E. VLDL
1122.
Which is an example of an autoimmune disease?
A. AIDS
B. Hepatitis
C. * Lupus
D. Mumps
E. All of these
1123.
Which is an example of an immunodeficiency disorder?
A. thyroiditis
B. rheumatic fever
C. systemic lupus erythematosus
D. * AIDS
E. All of the above
1124.
Which of the following are least sensitive to complement-mediated lysis?
A. Enveloped viruses
B. Erythrocytes
C. Gram negative bacteria
D. * Gram positive bacteria
E. Leukocytes
1125.
Which of the following is responsible for opening the calcium ion channel during
T-helper cell stimulation?
A. cAMP
B. cGMP
C. Tyrosine kinase
D. * Inositol trisphosphate
E. Protein kinase C
1126.
Which of the following plasma proteins are not produced by the liver?
A. * Gamma globulin
B. Albumin
C. Beta globulins
D. Fibrinogen
E. Ceruloplasmin
1127.
Which of these are the most abundant in circulation?
A. * neutrophils
B. mast cells
C. basophils
D. dendritic cells
E. no correct answer
1128.
Which of these is a professional antigen presenting cell (APC)?
A. erythrocytes
B. * dendritic cells
C. mast cells
D. eosinophils
E. basophils
1129.
Which of these is a secondary lymphoid organ?
A. * Spleen
B. Heart
C. Kidney
D. Brain
E. Liver
1130.
Which of these is an autoimmune disease?
A. Rheumatoid Arthritis
B. Graves Disease
C. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
D. * All of these
E. Both A and C
1131.
Which statement(s) apply to urea?
A. highly soluble in water
B. produced in the liver
C. compound used as a means of removing excess nitrogen
D. * all of the above
E. None of the above
1132.
Which type of antibody is MOST effective in activating complement?
A. IgE
B. IgG1
C. IgG2
D. IgG3
E. * IgM
1133.
Why is it important to have lymph nodes - immunologically?
A. to house the fluid in your blood
B. to house the mature B-cells and macrophages
C. to house the mature T-cells and macrophages
D. * Both B and C are correct.
E. Both A and B are correct.
1134.
Why is it important to have suppressor T-cells as part of your immune system?
A. to act as a feedback mechanism to gear up the immune system
B. * to act as a feedback mechanism to gear down the immune system
C. to lower the defences of the individual.
D. to lower the defences of the invaders.
E. to act as a global reactor cell to all invaders.
1135.
An immunoglobulin is a
A. protein
B. carbohydrate
C. * glycoprotein
D. fatty acid
E. nucleic acid
1136.
Cell-associated differentiation antigens (CDs) are functional cell surface proteins
or receptors that can be measured in situ.
A. In normal individuals the concentration of these molecules in serum is always
low.
B. * Detecting these soluble molecules may help in the management of disease
C. Thousands of CDs have been characterized
D. All of the above are true
E. None of the above are true
1137.
Which immunoglobulin is the least prevalent?
A. IgA
B. IgD
C. * IgE
D. IgG
E. IgM
1138.
Which of the following is the major immunoglobulin in human serum, accounting
for 80% of the immunoglobulin pool?
A. IgA
B. IgD
C. IgE
D. * IgG
E. IgM
1139.
Show on the possible sources formation of glucose-6-phosphate in the liver:
A. Glucose
B. Fructose
C. Galactose
D. Glycogen
E. * All title sources
1140.
The following are synthesized in the liver:
A. Anti-thrombin III
B. * C-reactive protein
C. Angiotensinogen.
D. Apolipoprotein B
E. Cholecystokinin
1141.
What is a result of conjugation of isoniazid via N-acetylation?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Detoxification of liver
Detoxification of kidneys
Detoxification of blood
Detoxification of urine
Hepatotoxicity
1142.
________ is/are produced in the liver by a complicated series of reactions
A. Amino acids
B. Nucleotides
C. Creatine phosphate
D. Ammonia
E. * Urea
1143.
A blood test found out the increase maintenance of residual nitrogen, part of urea
in residual nitrogen is considerably lowering. For the disease of what organ is
characteristic such analysis?
A. * Liver
B. Stomach
C. Intestine
D. Kidney
E. Heart
1144.
A child manifested yellowish skin and mucous membranes on the second day
after birth. The cause of such state is a temporal deficiency of:
A. Heme oxygenase
B. Sulfotransherase
C. Heme synthetase
D. * UDP-glucuronyltransferase
E. Biliverdin reductase
1145.
A concentration of general bilirubin in blood of healthy man is:
A. * 8-20 mkM/l
B. 15-30 mkM/l
C. 2-20 mM/l
D. 1-10 mM/l
E. 1-2 моль/l
1146.
A liver functioning improperly in an ill patient may cause the skin to become
A. Сyanotic and dry
B. * Jaundiced and warm
C. Blue and diaphorectic
D. None of the above
E. Pellagra
1147.
A liver provides other organs and tissues for all of substances, except:
A. Glucose
B. Proteins
C. Ketone bodies
D. Phospholipids
E. * Chylomicrons
1148.
A main supplier NH3 to the liver for the synthesis of urea is:
A. Glutamic acid
B. * Glutamin
C. Karbamoilfosfat
D. ammonium sulfate to the
E. Free NH3
1149.
A snakebite results of a hemolitic jaundice for a victim. Which index of blood
plasma for a victim does grow above all things?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Indirect bilirubin (unconjugated)
Direct bilirubin (conjugated)
Uric acid
Urea
Cholesterol
1150.
Acetyl-CoA in a liver experience the followings transformations, except:
A. Use on the synthesis of ketone bodies
B. On the synthesis of fatty acids
C. On the synthesis of cholesterol
D. * On the synthesis of amino acids
E. Oxidase to CO2 and H2O
1151.
Activity of which enzyme in hepatocytes is most activated at the terms of
carbohydrate starvation?
A. Hexokinase
B. Glycogensintase
C. * Glycogenphosphorilase
D. Phosphofructomutase
E. Al'dolase
1152.
Acute toxin induced liver necrosis can be due to
A. * Lipid peroxidation
B. Binding of toxin to cellular macromolecules
C. Mitochondrial damage
D. Disruption of cytoskeleton
E. All of the above
1153.
After starvation which resulted in general exhaustion of patient, in a liver and
kidney increases proceses:
A. Synthesis of creatin
B. Synthesis of bilirubin
C. * Gluconeogenesis
D. Formation of gipuric acid
E. Formation of uric acid
1154.
?All following functions are characteristic for liver, except:
A. Regulator-homoeostatic
B. Urea formation
C. Bile formation
D. Detoxification
E. * Urine formation
1155.
Although small quantities of lipids are normally stored in the liver, most of the
synthesized triglycerides are bound to:
A. * Hepatocytes in the liver
B. Transport proteins
C. Adipocytes
D. Glucose molecules
E. None of the above
1156.
Ammonia is formed in the process desamination of connections in a liver utillized
on the synthesis of such connections, except:
A. Glutamate
B. Glutamin
C. Urea
D. Nitric bases
E. * Nitric acid
1157.
An excrement contains sick plenty of the unsplit fat and has a white-grey color.
Name reason of this phenomenon:
A. * Obstruction of gall-bladder
B. Lack of pepsin and HCl
C. Hypovitaminoses
D. Inflammation of bowels
E. A lack of carbonhydratess in a meal
1158.
Are such functions of bile acids in an organism, except:
A. Activating of lipase in an intestine
B. Activating of phospholipase
C. Emulsification of fats in an intestine
D. Participating in absorbtion of fatty acids in enterocytes
E. * Participating in resynthesis of fats
1159.
At entering in organism big amount of toxic substances glucose-6-phosphate in a
liver including in:
A. Glycolysis
B. Glycogenogenesis
C. Glycolysis, Krebs cycle
D. * Pentosophosphate cycle
E. Gluconeogenesis
1160.
At research of blood plasma for a patient the decline level of proteins is set:
albumin, fibrinogen, protrombin, transferrin, ceruloplasmin. What does it testify?
A. * About decrease synthesis of proteins by a liver
B. About detoxification function of liver
C. About violation transformation of amino acids
D. About violation synthesis of urea and uric acid
E. About violation arrives of matters from liver into blood
1161.
At the condition of the limited utilisation of carbohydrates and strengthening
metabolism of fatty acids an acetyl-CoA little gets in the Krebs cycle and utillized in
ketolises. Which from factors does not promote ketolises:
A. Starvation
B. Diabets Mellitus
C. Kidney glucosuria
D. Hard physical work, combined with the consumption of alcohol
E. * All of above
1162.
At the sharp toxic defeats of liver the level of active forms of oxygen sharply
grows, that results in destruction of cellular membranes. For this prevention apply
antioxidants. The most strong natural antioxidant is:
A. * A-tocoferol
B. Uric acid
C. Creatinine
D. Transferrin
E. Bilirubin
1163.
Being poisoning with mushrooms a patient manifested yellow skin and scleras
coloring. The urine become dark. What pigment colored the patients urine with hemolytic
jaundice?
A. Biliverdin
B. Direct bilirubin
C. Indirect bilirubin
D. * Stercobilin
E. Verdohemoglobin
1164.
Bile facilitates digestion by causing the _____ of fats
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Hydrolysis
Digestion
Catalysis
* Emulsification
Synthesize
1165.
Bile is stored between meals in the:
A. Pyloris
B. * Gall bladder
C. Salivary glands
D. Jejunum
E. Stomac
1166.
Bile salts are produced by the
A. Stomach
B. * Liver
C. Pancreas
D. Gallbladder
E. Duodenum
1167.
Bile salts are produced by the
A. Stomach
B. * Liver
C. Pancreas
D. Gallbladder
E. Duodenum
1168.
Bile salts combine with fatty acids to form complexes called _____ that facilitate
absorption.
A. Chylomicrons
B. * Micelles
C. Globules
D. Lipoproteins
E. Globulins
1169.
Bilirubin is produced as the result of:
A. Digestion of salts
B. Digestion of carbohydrates
C. Digestion of phospholipid
D. * Digestion of hemoglobin
E. Absorbtion of carbohydrates
1170.
Biosynthesis of glycogen in liver is stimulated all indicated factors, except:
A. Insulin
B. * Glucagon
C. Hyperglycemia
D. ATP
E. Glycogensynthase, glicosyl-4,6-transferase
1171.
Blood test for a patient is discovered: the concentration of albumin makes 20 g/l,
increasing activity of lactatgehydrogenase (LDG5). The disease of what organ is
correspond to this index?
A. * Liver
B. Kidney
C. Heart
D. Pancreas
E. Lung
1172.
Brake oxidation of glucose and promote its converting into glycogen in a liver all
adopted components, except:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
ATP
NADH
Fatty acids
Amino acids, citrate
* Adrenalin, glucagon
1173.
By which ways pyruvat or lactat can transform on glucose-6-phosphate?
A. Glycolis
B. Crebs cycle
C. Condensation
D. Penthosophosphate cycle
E. * Gluconeogenesis
1174.
Chilomicrons enter the
A. Kidney
B. * Lymphatic capillaries
C. Liver
D. Blood capillaries
E. All of the above
1175.
Chilomicrons enter the
A. Kidney
B. * Lymphatic capillaries
C. Liver
D. Blood capillaries
E. All of the above
1176.
Cholesterol formed in many tissues and organs, but most in a liver. What function
is not inherent him from transferred?
A. Serves as basis for formation of bile acids
B. Steroid hormones appear from the cholesterol
C. In a skin appears from him the vitamin of D3
D. It is the structural component of cellular membranes
E. * Serves as energy source
1177.
Choose enzyme which carries out conjugation of toxic substances with glucuronic
acid:
A. Uridiltransferase
B. UDP-dehydrogenase
C. * UDP-glyucuroniltransferase
D. Acetyltransferase
E. Glucokinase
1178.
Choose peptid which is often utillized in conjugation of xenobiotics:
A. * Glutation
B. Anserin
C. Carnosine
D. Bradykinin
E. Kalidin
1179.
Cytochrome P450 induction (increased, amount of P450 enzyme protein) is often
associated with:
A. Increased enzyme synthesis rates
B. * Reduced enzyme degradation rates
C. Both
D. Neither
E. Only A and B
1180.
Damage at which of the following locations would most affect the goals of phase
II biotransformation?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Skin
Kidneys
Lungs
* Liver
GI Tract
1181.
Decomposition of liver’s glycogen.
A. * Glucose is generated
B. Electrons are passed along cytochromes
C. Carbon dioxide and hydrogen atoms are released, and two molecules of ATP form
D. Oxaloacetic acid is regenerated from coenzyme A
E. Lipids are generated
1182.
Detoxification of toxic substances takes a place in all of tissues and organs, but a
leading place belongs to the:
A. Kidney
B. Blood
C. Intestine
D. * Liver
E. Lung
1183.
Detoxification of xenobiotics (pharmaceutical drugs, epoxides,arenoxydes,
aldehydes, nitro derivates etc.) as well as endogenous metabolites (estradiol,
prostaglandins and leukotrienes take place in the liver by means of their conjugation
with:
A. Phosphoadenosine
B. Aspartate
C. Glycine
D. S-adenosylmethionine
E. * Glutathion
1184.
During glycogenolysis in liver - glycogen transforms into glucose-1-phosphate
under act of enzyme:
A. Glucokinase
B. Hexokinase
C. Phosphatase
D. * Phosphorylase
E. Phosphokinase
1185.
During the rest after hard physical work in a liver will be stimulated:
A. Glykolysis
B. Glycogenolysis
C. * Gluconeogenesis from lactat
D. Gluconeogenesis from amino acids
E. Biosynthesis of fatty acids
1186.
Factors affecting hepatic drug clearance:
A. * Drug delivery to liver elimination sites
B. Extent of plasma protein-bound drug
C. Blood flow
D. Carrier saturation
E. Wally and filtered in the glomerulus
1187.
Fats from liver are secreted to blood in composition of:
A. LDL
B. * VLDL
C. HDL
D. Chylomicronss
E. Triacylglicerol
1188.
Fatty acids and glycerol are released when _____ are broken down by liver or
muscle cells.
A. Micelles
B. Acteals
C. * Chylomicrons
D. Lipoproteins
E. Vitamins
1189.
Fatty acids in a liver are utillized in all directions, except:
A. On the synthesis of fats
B. On the synthesis of phospholipids
C. On formation of ethers of cholesterol
D. Oxidase to acetyl-CoA
E. * On the synthesis of amino acids
1190.
Fatty acids in a liver experience such transformations, except:
A. Formation of fats
B. Formation of phospholipids
C. Formation of ethers of cholesterol
D. Formation of ketone bodies
E. * Formation of cholesterol
1191.
Ferritin is a globular protein that transports and stores ______ in the liver and
blood
A. Glycogen
B. Lipids
C. Vitamin B12
D. * Iron
E. Cupper
1192.
Finished products metabolism of nitrogencontaining matters in a liver is:
A. Bile acids
B. * Urea
C. Purine basis
D. Karnitin
E. Ammonia
1193.
For a man the broken process synthesis of urea. To pathology of what organ does
it testify?
A. Urinary bladder
B. Kidney
C. * Liver
D. Muscles
E. Pancreas
1194.
For a patient with permanent hypoglycemia after introduction of adrenalin
maintenance of glucose did not almost change. About the change of what function of
liver can there be a language?
A. * Glycogendeponilic
B. Cholesterolformation
C. Ketogenic
D. Glycolitic
E. Excretory
1195.
For days with urine is selected in healthy people of urea in an amount:
A. 2-3 g
B. 10-15 g
C. * 20-30 g
D. 80-100g
E. 0,2-0,3 g
1196.
For determination of antitoxic function of liver to a pacient was appointed the
benzoate of sodium which in a liver convert into hypuric acid. Name connection X in a
reaction: benzoate of Na + X X hypuric acid:
A. * Glycine
B. Cystein
C. Methionine
D. PAPS
E. UDP-glucuronic acid
1197.
For microsomal oxidation as a donor of hydrogen atoms in main utillized
NADPH. Which metabolic way is the basic source of NADPH?
A. Glycolise
B. Crebs cycle
C. * Pentosophosphate cycle
D. Gluconeogenesis
E. Glycogenolysis
1198.
For the treatment of icterus, barbiturates that induce the synthesis of UDPglucuronyltransferase are prescribed. The curavite effect of barbiturates is conditioned by
the formation of:
A. * Direct (conjugation) bilirubin
B. Indirect (conjugation) bilirubin
C. Biliverdin
D. Protoporphyrin
E. Heme
1199.
Formation in liver from the glycogen glucose-1-phosphate experience subsequent
transformation:
A. In to galactose-1-phosphate
B. In to fructose-1-phosphate
C. Remains without changes
D. * In to glucose-6-phosphate
E. In to GAF and DOAF
1200.
From amino acids in a liver formed such substances, except:
A. Proteins
B. B-ketoacids
C. NH3, hem
D. Purine, pirimidine
E. * Fatty acids
1201.
Genetic deseases which is predefined the lack of glycogensynthetase in a liver, is
named aglycogenose. Thus there is observe all, except:
A. Considerable decrease of glycogen
B. Hypoglycemia is expressed in intervals between the consumption of meal
C. A hyperglycaemia lasted after the reception of meal
D. Delay of mental development
E. * Increase size of liver
1202.
Glucose in liver can experience such transformations, except:
A. Transformed into glucose-6-phosphate
B. Glicolytic oxidation
C. Oxidation in the penthosophosphate passways
D. Transformed into glycogen
E. * Transformed into the vitamin C
1203.
Glucose, that arrive with blood from an intestine to the liver, is utillized for all
functions, except:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Formation of glycogen
Oxidation to CO2 and H2O with selection of energy
Convert into fats for stocking of energy
Carried by blood to the brain as source of energy
* Use for detoxification of ammonia
1204.
Glycogenformation in a liver takes a place in a postabsorbtive period with
participation of enzymes, except:
A. Phosphoglucomutase
B. Glucose-1-phosphateurydiltransferase
C. Glycogensynthetase
D. Glycosil-4G6-transferase
E. * Glycogenphosphorilase
1205.
Glycogenolysis in a liver increases in such factors, except:
A. Glukagon
B. Proteinkinase
C. * Hyperglycemia
D. ADP
E. Phosphorylases A
1206.
Greater part of steroid hormones metabolised in liver by reduction to
tetrahydroderivatives (I stage). With wich matter do they contact (II stage), that results in
the loss of them biological action and excreted through kidney?
A. Amino acids
B. Glutation
C. * Glucuronic acid
D. Acetic acid
E. Acetyl-CoA
1207.
Harmless of toxic substanses in a cytoplasmic net passes in two phases. Indacate
2-nd phase:
A. Hydroxylating
B. * Conjugation
C. Phosphorylation
D. Dehydration
E. Dehydratation
1208.
Hepatic flow-dependent drug elimination refers to:
A. Changes in plasma protein concentration
B. Rate-limiting step is drug delivery to hepatic elimination sites
C. Number of functional hepatocytes
D. Carrier saturation
E. * Drug transfer rates across hepatic cell membrane
1209.
In a liver a major role belongs among all of detoxification enzymes systems:
A. Hydrolized system of cytoplasm
B. Lysosomal
C. Peroxidase
D. Sinthetase system with formation of conjugats
E. Monooxigenase system of cytoplasmic reticulum
1210.
In a liver between proteins, lipids and carbohydrates carried out interconversion.
In the following schemes indicate, which transformation is unreality:
A. Glucosesfats
B. Glucose Acetyl-CoA-cholesterol
C. Glucose Acetyl-CoA ketone bodies
D. Glucose pyruvatpCO2 and H2O
E. * Glucose nonsubstitution amino acidsnproteins
1211.
In a liver fatty acids transform in such directions, except:
A. Fatty acids tfats
B. Fatty acids tacytoacetate
C. Fatty acids iketone bodies
D. Fatty acids tAcetyl-CoA
E. * Fatty acids tglucose
1212.
In a liver xenobiotics enter in the reaction of conjugation (and detoxification) only
those which have certain functional groups or remains of molecules. Such groups are all,
except:
A. -ОН
B. -COOH
C. -NH2
D. * -CH3
E. -SH
1213.
In a patient which was in the area of radiation defeat, the concentration of malonic
dialdehyde, hydroperoxides was increased in blood. Reason of such changes could be:
A. * Increase in the organism of oxygen radicals and activating peroxidation of lipids
B. Increase of ketone bodies
C. Increase maintenance of lactic acid
D. Increase maintenance of cholesterol
E. Increase maintenance of proteins in blood
1214.
In afteroperation period in a patient periodically complication – bleeding comes
from a wound. With deficiency in blood of what substance, that is synthesized in a liver it
connected?
A. Haptoglobin
B. * Protrombin
C. Heparin
D. Creatin
E. Ceruloplasmin
1215.
In blood of patient found the increasing activity of LDG4,5, AlAT and ornithine
carbamoyltransferase. In wich organ is possible development of pathological process?
A. In a cardiac muscle (heart attack)
B. * In a liver (hepatitis)
C. In skeletal muscles
D. In kidney
E. In connective tissue
1216.
In blood plasma distinguish the stated below proteins. Which from them do not
appear in a liver?:
A. Albumins
B. B1-globulins
C. C2-globulins
D. D-globulins
E. * E-globulins
1217.
In humans, the liver _________.
A. Removes carbon dioxide from the body
B. Stores creatine phosphate
C. * Converts ammonia to urea
D. Regulates the body temperature
E. All of the above are liver functions
1218.
In the liver, when large amounts of acetyl-CoA are produced, some of the acetylCoA is used to form
A. Pyruvic acid
B.
C.
D.
E.
Citric acid
* Ketone bodies
Lactic acid
Urea
1219.
In the membranes of endoplasmatic reticulum of liver there are monooxigenase
reactions in which one atom of oxygen is utillized on oxidation of substrate, and second –
on formation of H2O. Reaction flows after such scheme: RH + O2 +reconstricte ROH +
H2O + oxidation reconstrict Choose what can not be a reconstrict (by the donor of
hydrogen) in these reactions:
A. NADPH
B. NADH
C. Cytochrom P-450
D. Cytochrom B5
E. * Vitamin H
1220.
In transition from the mixed ration to carbohydrate the biosynthesis of fats is
activated in a liver. Promotes this activating some enzymes, except:
A. Cytratshyntase
B. Acetyl-CоА-carboxilase
C. Palmitilshyntetase
D. Glucose-6-phosphatedehydrogenase
E. * Triacylglicerinlipase
1221.
In which of the following diseases will liver tissue be replaced by inactive fibrous
scar tissue?
A. Hemolytic jaundice
B. Obstructive jaundice
C. * Viral hepatitis
D. Cirrhosis
E. Lactose intolerance
1222.
Increased catabolism of nitrogencontain connections are accompanied
strengthening formation of urea and increase of its maintenance in blood and urine. All
belong to such matters, except :
A. Amino acids
B. Purins
C. Pirimidins
D. Biogenic аmins
E. * Nitric and nitrous acids
1223.
Indicate the basic functional differences of microsomal oxidation from
mithohondrial:
A. * Using of oxygen with «plastic» aims
B. Using of oxygen in bioenergetic processes
C. Using of energy in a appearance of ATP
D. Using of energy in a appearance of GTP
E. Using as substrates of FADH2 and FMNH2
1224.
Indicate, which bile acid is promote dissolution of cholesterol and gall-stones:
A. Cholic
B. Desoxycholic
C. * Chenodesoxycholic
D. Taurocholic
E. Litocholic
1225.
Investigation of blood serum rotined an increase activity of AlAT, LDG5 and globulin fractions of proteins. Name possible illness which stipulated these changes:
A. Cirrhosis of liver
B.
C.
D.
E.
Heart attack of myocardium
* Sharp toxic hepatitis
Pancreatitis
Sharp damage of muscles
1226.
Jaundice shows, when a concentration of bilirubin in blood is:
A. 20 – 30 mkM/l
B. * 35 mkM/l and higher
C. 10-15 mkM/l
D. 35-40 mM/l
E. 1-2 моль/l
1227.
Level of which metabolite in hepatocytes does brake the Krebs cycle, but
stimulates ketogenesis?
A. ADP
B. ATP
C. Acetyl-CoA
D. * Oxaloacetate
E. Fatty acids
1228.
Main appointmant formed in the liver glucose-1-phosphate – to serve as an energy
source for a brain after transformation in to glucose-6-phosphate and separation from him
residual of phosphoric acid. This action is executed by enzymes:
A. Phosphoglucomutase, phosphorylase
B. * Phosphoglucomutase, phosphatase
C. Phosphokinase, phosphoglucoepimerase
D. Proteinkinase, glucophosphattranspherase
E. Phosphotranskriptase, phosphatase
1229.
Mikrosomal oxidation system includes two short chains transport of electrons and
protons on oxygen: 1) monooxigenase, for which by the donor of protons and «е-» is
mainly NADPH and 2) reductase by the donor of protons and «е-» of NADH. Specify a
place, where can not be found this reductase system:
A. Microsoms membranes
B. Nuclear membrane
C. * Inner membrane of mithohondria
D. External membrane of mithohondria
E. Cellular membrane of erythrosites
1230.
Most of the nitrogen amount is excreted from the body in the form of urea. The
decrease of acrivity of what liver enzyme result in inhibiting of urea synthesis and
accumulation of ammonia in blood and tissues?
A. * Carbomoyl phosphate synthase
B. Aspartate aminotransferase
C. Urease
D. Amylase
E. Pepsin
1231.
Most proteins of blood plasma are synthesized in a liver. Wich from below
following proteins not synthesized in a liver?
A. Albumin
B. B-globulins
C. C-globulins
D. * D-globulins
E. Fibrinogen, protrombin
1232.
Name 2 products the first reaction of penthosophosphate cycle which flows in a
liver:
A. Glucose and phosphatidic acid
B.
C.
D.
E.
1233.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1234.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
NADH and pentose
Gluconic acid and ribulose
Glucose-1,6-diphosphate and NADPH
* 6-phosphogluconolactone and NADPH
Name enzyme in the ornitine cycle which conduces to the formation of urea:
Argininosuccinate lyase
Argininosuccinate synthetase
Malatdehydrogenase
* Arginase
Fumarathidratase
Name matters on which glucose-6-phosphate transforms in a liver:
Glucose
Piruvat
Pentosophosphate
Glicogen
* All substances together
Name substance which takes part in reaction formation active form of glucuronic
1235.
acid:
A. ATP
B. * UTP
C. c-AMP
D. TTP
E. CTP
1236.
Name the enzyme of urea cycle which results to formation of intermediate
metabolite argininosuccinate:
A. Argininosuccinate lyase
B. Succinatdehydrogenase
C. Succinatoxidase
D. Arginase
E. * Argininosuccinate synthetase
1237.
Nonbiological foreign chemicals are termed:
A. Antibiotics
B. Probiotics
C. Prebiotics
D. * Xenobiotics
E. Neurobiotics
1238.
Oxidation of ketone bodies takes place every where, except:
A. Myocardium
B. Skeletal muscles
C. Kidney
D. Brain
E. * Liver
1239.
Pentoses which appear from glucose-6-phosphate in the pentosophosphate cycle
can be utillized in such aims:
A. On the biosynthesis of nucleotides
B. On the construction of nucleic acids
C. On the construction of coenzymes
D. Transformation in to fructose-6-phosphate
E. * All adopted processes are correct
1240.
Pentosophosphate cycle oxidation of glucose provides reconstraction of NADPH
such processes:
A. Synthesis of fatty acids
B.
C.
D.
E.
Synthesis of cholesterol
Synthesis of bile acids from cholesterol
Inactivation of steroid hormones
* All adopted processes are correct
1241.
Red blood cells are broken down in abnormally large amounts in ____.
A. Hemolytic jaundice
B. Obstructive jaundice
C. Viral hepatitis
D. * Cirrhosis
E. Lactose intolerance
1242.
Red blood cells are broken down in abnormally large amounts in ____.
A. * Hemolytic jaundice
B. Obstructive jaundice
C. Viral hepatitis
D. Cirrhosis
E. Lactose intolerance
1243.
Some matters are harmless by formation of complex ethers with sulphuric acid.
Name substanse which help carried out sulfate conjugation:
A. Glucuronilsulphate
B. * Phosphoadeninphosphosulfate
C. Dimetilsulfate
D. S-adenosylmethyonin
E. Sulphuric acid
1244.
Strengthen oxidation glucose to pyruvat in a liver such regulators, except:
A. Insulin
B. ADP
C. AMP
D. Phosphofructokinase
E. * NADH
1245.
The buildup of bile pigment in tissues that can be caused by gallstones is _____.
A. Hyperbilirubinemia
B. * Obstructive jaundice
C. Hepatitis
D. Hepatocellular jaundice
E. None of the above
1246.
The contents of urea in blood of healthy:
A. 1-3 mM/l
B. 2-4 mM/l
C. * 3-7 mM/l
D. 10-12 mM/l
E. 20-30 mM/l
1247.
The decreasing synthesis of bile acids in a liver results in such violations, except:
A. Digestion of fats in an intestine
B. * Digestion of carbohydrates
C. Absorbtion of fatty acids
D. Absorbtion of vitamins A and K
E. Activation of lipasas
1248.
The digestive fluids that mix with chyme in the ____________ are secreted by
A. Stomach; the liver and pancreas
B. Biliary apparatus; the liver and gallbladder
C. * Duodenum; hepatocytes and cells of the pancreatic lobules and ducts
D. Hepatopancreatic ampulla; hepatocytes and cells of the pancreatic islets
E. None of the above
1249.
The fatty degeneration of liver and general obesity is prevented by lipotropic
factors. All belong to them, except:
A. Cholin, ethanolamine
B. Methionine, inositol
C. Serine
D. Vitamins B6, B10
E. * Alanin, leucine
1250.
The fatty degeneration of liver at the conditions of Diabetes Mellitus and
starvation is possible, because in hepatocytes:
A. Decrease oxidation of fatty acids
B. Decrease synthesis of triacylglicerol
C. Lowering formation ketone bodies from fatty acids
D. Lowering formation of HDL
E. * Increase arrive of fatty acids from adipose tissues
1251.
The first step in the utilization of proteins for energy is ________, which occurs in
the liver.
A. Beta oxidation
B. * Deamination
C. Hydrolysis
D. Amino acid synthesis
E. Decarboxilation
1252.
The function of bile salts is to:
A. Bind with simple sugars
B. * Emulsify fats
C. Digest proteins
D. Absorb water
E. Regulate water-salt metabolism
1253.
The functional state of liver, effectiveness of treatment and prognosis motion of
disease, estimate by such biochemical indexes of blood and urine, except:
A. AlAT
B. Gamma-glutamintranspeptidase
C. Alkaline phosphatase
D. Contents of albumins and globulins
E. * Diastase
1254.
The functions of the gall bladder involve:
A. Contraction and synthesis
B. * Absorption and digestion
C. Contraction and absorption
D. Synthesis and absorption
E. None of the above
1255.
The hepatic portal vein carries blood from the _______________ to the
A. * Small intestines, liver
B. Small intestines, heart
C. Liver, heart
D. Stomach, heart
E. Small intestines, colon
1256.
The hepatic portal vein carries blood from the _______________ to the
A. * Small intestines, liver
B. Small intestines, heart
C. Liver, heart
D. Stomach, heart
E. Small intestines, colon
1257.
The hormone that promotes the flow of bile and of pancreatic juice containing
enzymes is:
A. * Secretin
B. Gastrin
C. Enterogastrone
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
1258.
The increase maintenance of indican in urine of patient with disbacterios of
intestine testifies about:
A. Kidney disease
B. * Normal harmless function of liver
C. Strengthening fermentation of carbohydratess in an intestine
D. Strengthening hydrolysis of fats
E. Violetion functions of liver
1259.
The increase of total bilirubin content at the expense of indirect (free) fraction was
detected in the blood plasma of a patient suffering from icterus. There is also a high level
stercobilin in the feces and urine. The level of direct (linked) bilirubin in the blood
plasma is within the normal range. What type of icterus is observed in this case?
A. Machanical
B. Hepatic
C. * Hemolitic
D. Icterus of newborn
E. Gilbert disease
1260.
The key intermediate product of carbohydrate metabolism – glucose-6-phosphate
– can transformed in a liver by such ways, except:
A. From glucose-6-phosphate glycogen is synthesed
B. Glucose-6-phosphate under influence of specific phosphates split to free glucose
C. Spliting by glycolisis to pyruvate
D. Spliting to CO2 and H2O with selection energy of ATP
E. * Transforms in uracyl
1261.
The Kupffer cells are phagocytic cells found in the
A. Gallbladder
B. Pancreas
C. Intestine
D. * Liver
E. Kidney
1262.
The liver contains special blood channels termed _____.
A. Sinusoids
B. Central vein
C. Hepatic cells
D. * Portal veins
E. None of the above
1263.
The liver is often the target organ for many chemicals with diverse structures
because
A. First pass uptake of xenobiotics readily occurs due to the thinness of the
sinusoidal endothelial cells.
B. The liver contains many transport mechanism that concentrate and store
substances, including xenobiotics, intracellularly.
C. The liver contains mechanisms for storage of heavy metals that can mediate the
formation of ROS.
D. * The liver contains the highest concentration of biotransforming enzymes
compared to other organs.
E. All of the above.
1264.
The liver produces bile salts that aid in the digestion of:
A. * Fats
B. Proteins
C. Carbohydrates
D. Sugars
E. Vitamins
1265.
The liver stores ______ for energy.
A. Nucleic acids
B. Glycogen
C. * Glucose
D. Vitamins
E. Simple proins
1266.
The low level of what metabolite in hepatocytes does predetermine braking of
Krebs cycle and strengthens a ketogenesis?
A. ATP and CTP
B. ADP and AMP
C. Acetyl-KoA
D. * Oxaloacetate
E. Fatty acids
1267.
The main enzyme responsible for activation of xenobiotics is:
A. * Cytochrome P-450
B. Glutation S-transferase
C. NADH cytochrom P-450 resuctase
D. Glucuronil transferase
E. Pyruvatdehydrogenase
1268.
The organ(s) of excretion is/are _______.
A. Skin
B. Lungs
C. Liver
D. Kidneys
E. * EAll of the above
1269.
The perenchimatose defeat of liver is accompanied decreases maintenance in
blood plasma of proteins, except:
A. Albumins
B. B-globulins
C. Glycoproteins
D. Fibrinogen
E. * E-globulins
1270.
The primary function(s) of the liver is (are):
A. * Bile production
B. None of the above
C. Hematological regulation
D. All the above
E. Metabolic regulation
1271.
The primary function(s) of the liver is (are):
A. * Bile production
B. Metabolic regulation
C. Hematological regulation
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
1272.
The signs of jaundice appeared for a new-born child. Introduction small doses of
phenobarbital which induces the synthesis of UDP-glyukuroniltransferase resulted in the
improvement of the state of child. Which from the stated below processes is activated in
a liver under act of phenobarbital?
A. * Conugation
B. Microsomal oxidation
C. Respiratory chain
D. Gluconeogenesis
E. Synthesis of glycogen
1273.
There are different transformations of lipids in a liver, except:
A. Breaking up of complex lipids to the simple components
B. Synthesis of lipids, in particular - cholesterol
C. Oxidation of fatty acids
D. Synthesis of palmitic acid
E. * Synthesis of linolenic acid
1274.
Through 24 ours of starvation, maintenance of glycogen in a liver falls till about a
zero. For providing of necessities of organism glucose the process of gluconeogenesis
intensifies in a liver. A gluconeogenesis is carried out from all of matters, except:
A. Amino acids
B. Glycerol
C. PVA
D. * Fructose
E. Lactat
1275.
To the liver cholesterol come by such ways, after an exception:
A. With a meal
B. Synthesised in hepatocytes
C. Come from other tissues
D. From high density lipoproteins
E. * With chylomicrons
1276.
Typical biochemical features of serum in obstructive jaundice include
A. * Raised bilirubin
B. Increased acid phosphatase
C. Increased alkaline phosphatase
D. Increased amylase
E. Hepatitis B surface antigen
1277.
Ultrasound examination of a patient gave the possibility to establish an initial
diagnosis: cancer of the liver. What protein occurs in blood in this case?
A. A-globulin
B. Properdin
C. Paraproteins
D. C-reactive protein
E. * E-phetoprotein
1278.
Under stress circumstances increases breaking up of glycogen of muscles, one of
intermediate metabolites is - glucose-6-phosphate. Why can not he serve as the source of
glucose, like it takes a place at breaking up of glycogen in a liver?
A. * In muscles there is not an enzyme of glucose-6-phosphate phosphatase and the
last does not convert into glucose
B. In the muscles glucose-1-phosphate convert into lactat
C. Glucose-6-phosphate does not test changes
D. Transformed into amino acids
E. Transformation of glucose is characteristic only for a liver
1279.
Urea is synthesized in a liver from ammonia which appears in result of
desamination of such combinations, except:
A. Amino acids
B. Amins, аmids
C. Purine bases
D. Pirimidine bases
E. * Choline
1280.
Violation metabolism of copper is accompanied the deposit of it in a brain and
liver – develops Vilson disease. The concentration of protein which is synthesized in a
liver decrease in blood:
A. Transferrin
B. * Ceruloplasmin
C. Feritin
D. Xantinoxidase
E. Carbanhydrase
1281.
What coenzyme is needed for synthesis in the liver of cholesterol, higher fatty
acids, nucleic acids?
A. NADP
B. * NADPH
C. FMN
D. FAD
E. Tiamindiphosphate
1282.
What enzyme transform glucose of meal in liver on glucose-6-phosphate?
A. Phosphoglucomutase
B. Phosphatase
C. * Hexokinase
D. Fructokinase
E. Glucosisomerase
1283.
What is the goal of the P450 system (microsomes pinched off from endoplasmic
reticulum)?
A. Metabolism of substances
B. * Detoxification of substances
C. Increasing pH of compartments containing substances
D. Decreasing pH of compartments containing substances
E. A & B
1284.
What protein, assigned for transport, does hemoglobin bind to in the
reticuloendotelial system of the liver?
A. * Haptoglobin
B. Albumin
C. Ferritin
D. Transferrin
E. Ceruloplasmin
1285.
When liver glycogen levels are inadequate to supply glucose, especially to the
brain, amino acids and glycerol are used to produce ___________ in a process called
A. Glycogen; glycogenesis
B. * Glucose; gluconeogenesis
C. Lipids; lipogenesis
D. Glucose-6-phosphate; glycogenolysis
E. None of the above
1286.
Which amino acids does not take participating in the synthesis of urea in a liver?
A. * Alanin
B. Arginine
C. Aspartat
D. Ornitin
E. Citrulline
1287.
Which bile acids in most promote formation of gall-stones?
A. Cholic
B. * Litocholic
C. Glycocholic
D. Taurocholic
E. Desoxycholic
1288.
Which blood vessel will transport nutrient molecules that have been absorbed by
the small intestine to the liver?
A. Hepatic artery
B. Renal vein
C. Hepatic portal artery
D. * Hepatic portal vein
E. Inferior vena cava
1289.
Which component in bile helps to emulsify fat in the duodenum?
A. Bilirubin
B. Biliverdin
C. * Bile salts
D. Cholesterol
E. Ketone bodies
1290.
Which from the adopted substances are arrive gluconeogenesis in a liver?
A. Amino acids
B. Piruvat, lactat
C. Oxaloacetate
D. Glucocorticoids
E. * All taken together
1291.
Which from the adopted substances that are synthesized in liver do not „go to the
export”, that not utillized other tissues?
A. Glucose
B. * Hormonoids
C. Fats
D. Ketone bodies
E. Proteins of blood plasma
1292.
Which from the below matters is promotes in the supply of fatty acids to the liver?
A. Albumins
B. Tiroksin
C. Lipase of fatty tissues
D. Glucagon
E. * All adopted components
1293.
Which from the stated below processes does a major role belong in
desintoxification of toxic substances in a liver?
A. Demetilation
B. Pereamination
C. Desamination
D. * Hydroxylating
E. Decarboxilation
1294.
Which metabolic ways of carbohydrates are not stimulated during rest after hard
physical work?
A. Glycogenesis
B. Gluconeogenesis from lactat
C. * Glycolisis
D. Gluconeogenesis from amino acids
E. Transformation of carbohydrates on the fats
1295.
Which metabolic ways transformation of glucose-6-phosphate will prevail in a
liver at the condition strengthening of biosynthetic processes?
A. Gluconeogenesis
B. Glycolisis
C. Transformation of glucose-6-phosphate on free glucose and phosphate
D. * Pentosophosphate cycle
E. Glycogenesis
1296.
Which molecule represents the storage form of glucose in the liver?
A. * Glycogen
B. Glucagon
C. Disaccharide
D. Lactic acid
E. Pyruvate
1297.
Which of the following are liver waste products?
A. * Bilirubin
B. Bile salts
C. Cholesterol
D. Electrolytes
E. A and C
1298.
Which of the following comparisons is NOT correct?
A. * Constipation--hard and dry feces
B. Ulcer--open sore in the wall of the stomach
C. Peritonitis--inflammation of the cecum
D. Cirrhosis--liver first becomes fatty and then replaced by fibrous scar tissue
E. Jaundice--abnormally large amount of bilirubin in the skin and the whites of the
eyes
1299.
Which of the following has the most affinity for oxygen?
A. Hemoglobin F
B. Blood substitute
C. * Hemoglobin A
D. Hemoglobin S
E. Bens-Jonce protein
1300.
Which of the following is correct regarding hepatic failure?
A. The cardinal features are hepatic encephalopathy, coagulopathy, and jaundice.
B. Most cases following a sudden massive insult to a previous healthy liver.
C. * The activated partial thromoplastin time (APTT) serves as a good indicator of
the severity of hepatic failure.
D. Prognosis is generally good for recovery.
E. None of the above
1301.
Which of the following is correct regarding liver function tests?
A. An isolated rise in alkaline phosphatase level implies biliary disease
B. * Liver function tests are always deranged in patients with significant liver
disease
C. An isolated rise in A-glutamyltransferase (GGT) is often seen in alcoholics
D. Mild elevations of bilirubin, alanine aminotransferase, and aspartate
aminotransferase
E. All of the above
1302.
Which of the following is not a function of the adult liver?
A. Glycogen storage
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Detoxification
Synthesis of clotting proteins
Erythropoiesis
All of the above
1303.
Which of the following is NOT a function of the liver?
A. Converts hemoglobin from red blood cells to bile pigments that are excreted
along with bile salts in bile
B. * Detoxifies blood by removing poisonous substances
C. Produces urea from the breakdown of amino acids
D. Produces enzymes for digestion of food in the duodenum
E. Makes plasma proteins from amino acids
1304.
Which of the following is not a function of the liver?
A. Convert glucose to glycogen
B. Convert glycogen to glucose
C. Detoxify poisonous substances
D. Produce blood plasma proteins
E. * All of the above are functions of the liver
1305.
Which of the following is NOT a function of the liver?
A. Converts hemoglobin from red blood cells to bile pigments that are excreted
along with bile salts in bile
B. Detoxifies blood by removing poisonous substances
C. Produces urea from the breakdown of amino acids
D. * Produces enzymes for digestion of food in the duodenum
E. Makes plasma proteins from amino acids
1306.
Which of the following is NOT a phase II substrate?
A. Glucuronic acid
B. Sulfuric acid
C. Acetic acid
D. Amino acids
E. * Alcohol
1307.
Which of the following is true about jaundice?
A. * Pale stools and dark urine are characteristic of the jaundice of haemalytic
anaemia
B. Bilirubin is used by the liver in the synthesis of red blood cells
C. Itching may be a sign of obstructive jaundice
D. Putting a danger of infection sticker on blood samples from an intravenous drug
user with jaundice is optional
E. None of the above
1308.
Which of the following organs functions to remove poisonous substances and
works to keep the contents of blood constant?
A. Esophagus
B. Stomach
C. Duodenum
D. Pancreas
E. * Liver
1309.
Which of the following organs produces bile?
A. Gallbladder
B. * Liver
C. Duodenum
D. Stomach
E. Large intestine
1310.
Which of the following reactions is phase II and NOT phase I?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Oxidations
Reductions
* Conjugations
Deaminations
Hydrolyses
1311.
Which of the following statements is NOT correct about fat digestion?
A. Bile salts are needed to emulsify fat into fat droplets.
B. Lipase digests the fat droplets into glycerol and fatty acid molecules while
removing water molecules
C. Glycerol and fatty acids enter the cells of the villi.
D. * Glycerol and fatty acids, after entering the cells of the villi, rejoin and are
packaged as lipoprotein droplets
E. Lipoprotein droplets, which are formed in the cells of the villi, enter the lacteals
1312.
Which of the following vitamins is not stored in the liver?
A. * C
B. D
C. B12
D. A
E. E
1313.
Which organ has the most metabolically active cells?
A. Pancreas
B. * Liver
C. Stomach
D. Small intestine
E. Lung
1314.
Which substanses activate a gluconeogenesis?
A. Glucagon
B. Oxaloacetate
C. PVA
D. Glucockortikoids
E. * All answers are correct
1315.
Which transformation of glucose-6-phosphate will prevail in a liver at a reach in
the organism of toxic matters?
A. Glycolysis
B. Glycogenolysis
C. Gluconeogenesis
D. * Pentosophosphate cycle
E. Glykogenogenesis
1316.
Which way is real from the adopted ways the using of cholesterol in a liver?
A. Formation of bile acids
B. Secretion in a bile and leadingout from organism
C. * All of ways are use
D. Reducing membranes of hepatocytes
E. Transport to other tissues
1317.
Which way transformation galactose in a liver on glucose-6-phosphate?
A. By specific hecsoisomerase
B. Glicolitic to pyruvat, and farther – by gluconeogenesis
C. By glucomutase
D. By cytidiltransferase
E. * Galactose galactose-1-phosphatepglucose-1-phosphatepglucose-6-phosphate
1318.
ADH test is based on the measurement of
A. * Specific gravity of urine
B.
C.
D.
E.
1319.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1320.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1321.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1322.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1323.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1324.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1325.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1326.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Concentration of urea in urine
Concentration of urea in blood
Volume of urine in ml/minute
A and D
An early feature of renal disease is
* Impairment of the capacity of the tubule to perform osmotic work
Decrease in maximal tubular excretory capacity
Decrease in filtration factor
Decrease in renal plasma flow
All of the above
Fixation of specific gravity of urine to 1.010 is found in
Diabetes insipidus
Polydypsia
Cystinosis
* Chronic glomerulonephritis
None of the above
Polyuria can occur in
* Diabetes mellitus
Diarrhoea
Acute glomerulonephritis
High fever
All of the above
Specific gravity of urine is raised in all of the following except
Diabetes mellitus
* Diabetes insipidus
Dehydration
Acute glomerulonephritis
A and D
____________ is hydrolytically cleaved to directly yield urea in the urea cycle.
ornithine
glutamate
* arginine
carbamoyl phosphate
None of the above
A diuresis of a healthy adult is about:
* 1000 – 2000 ml daily
500 – 1000 ml daily
1000 –3000 ml daily
100 – 500 ml daily
3000 – 5000 ml daily
A diuresis of a healthy adult is about:
* 1000 – 2000 ml daily
500 – 1000 ml daily
1000 –3000 ml daily
100 – 500 ml daily
3000 – 5000 ml daily
A pH of urine in a norm is:
* 5,3 – 6,8
3,5 – 5
2,1 – 4,3
1,45 – 1,85
5,5 – 7,5
1327.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1328.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1329.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1330.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1331.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1332.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1333.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1334.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1335.
A.
B.
About the kidney insufficiency testify decrease of filtration to:
* 40 ml/min
50 ml/min
70 ml/min
60 ml/min
80 ml/min
About the kidney insufficiency testify decrease of filtration to:
* 40 ml/min
50 ml/min
70 ml/min
60 ml/min
80 ml/min
Acid-Base balance is important for:
Normal enzyme functions.
Normal metabolite solubility.
Normal membrane potentials.
A and C
* All of the above
Addis test is the measure of
* Impairment of the capacity of the tubule to perform osmotic work
Secretory function of liver
Excretory function of liver
Activity of parenchymal cells of liver
All of the above
ADH test is based on the measurement of
* Specific gravity of urine
Concentration of urea in urine
Concentration of urea in blood
Volume of urine in ml/minute
Both a and B
Albumin-globulin coefficient of blood plasma of healthy adult is:
3,0-4,0
1,0-1,5
5,0-6,5
8,0-10,0
* 1,5-2,0
All the following are true about phenylketonuria except
Deficiency of phenylalanine hydroxylase
Mental retardation
* Increased urinary excretion of hydroxyphenyl pyruvic acid
Decrease serotonin formation
C and D
All the following statements about phenylketonuria are correct except
Phenylalanine cannot be converted into tyrosine
Urinary excretion of phenylpyruvate and phenyllactate is increased
It can be controlled by giving a low phenylalanine diet
* It leads to decreased synthesis of thyroid hormones, catecholamines and
melanin
Both A and D
Amount of uric acid which excreted daily is:
Not excreted
10-12 g/day
C. 4-8 mg/day
D. * 270-600 mg/day
E. 2-5 g/day
1336.
An early feature of renal disease is
A. * Impairment of the capacity of the tubule to perform osmotic work
B. Decrease in maximal tubular excretory capacity
C. Decrease in filtration factor
D. Decrease in renal plasma flow
E. Both A and D
1337.
are correct except
A. It is completely non-toxic
B. It is completely filtered by glomeruli
C. It is not reabsorbed by tubular cells
D. * It is secreted by tubular cells
E. Both C and D
1338.
At a biochemical inspection of a patient were found a hyperglycemia, glucosuria,
high urine’s density, in blood found - enhanceable amount of glucocorticoids. At the
same time in blood and urine found excess of 17 – ketosteroids. What type of diabetes
developed:
A. * Steroid diabetes
B. Diabetes Mellitus, the I type
C. Diabetes Mellitus , the II type
D. Kidney diabetes
E. Hepatic diabetes
1339.
At what disease colour of urine is darkly – brown?
A. Pyelonephritis
B. Diabetes mellitus
C. * Hemolytic anemia
D. Acute nephritis
E. Diabetes insipidus
1340.
At what disease colour of urine is darkly – brown?
A. Pyelonephritis
B. Diabetes mellitus
C. * Hemolytic anemia
D. Acute nephritis
E. Diabetes insipidus
1341.
At what disease glomerular filtration is always decreased?
A. Acute nephritis
B. Chronic glomerulonephritis
C. Acute pyelonephritis
D. Amyloidosis of kidneys
E. * Acute kidney’s insufficiency
1342.
At what disease the excretions of calcium diminish with urine?
A. Icenko – Cushing disease
B. Osteomalacia
C. Addison disease
D. * Rickets
E. Aldosteronism
1343.
At what disease the excretions of calcium increase with urine?
A. Rickets
B. * Osteomalacia
C. Addison disease
D. Icenko – Cushing disease
E. Aldosteronism
1344.
Average creatinine clearance in an adult man is about
A. 54 ml/min
B. 75 ml/min
C. * 110 ml/min
D. 130 ml/min
E. None of above
1345.
Benedict’s test is less likely to give weakly positive results with concentrated
urine due to the action of
A. Urea
B. * Uric acid
C. Ammonium salts
D. Phosphates
E. All of these
1346.
Benzoic acid in the organism is transformed to hypuric acid (Quick's test). Name
the compound it connects with:
A. * glycine
B. glycocol
C. valine
D. alanine
E. threonine
1347.
By what method is conducted quantitative determination of glucose in urine?
A. Felling
B. Roberts - Stolnikov
C. Gmelin and Rosenbakh
D. * Altgauzen
E. Salkovskiy
1348.
By what test is conducted quantitative determination of proteins in urine?
A. Altgauzen
B. * Roberts – Stolnikov
C. Gmelin and Rosenbakh
D. Felling
E. Salkovskiy
1349.
Choose the normal level of relative density of urine.
A. * 1006 - 1020
B. 1015 - 1012
C. 1011 - 1013
D. 1004 - 1010
E. 1010 - 1016
1350.
Choose the substance of protein nature which is produced in kidneys:
A. Melatonin
B. * Eritropoetin
C. Epinephrine
D. Progesterone
E. Aldosterone
1351.
Choose the substance of protein nature which is produced in kidneys:
A. Melatonin
B. * Erythropoietin
C. Epinephrine
D. Progesterone
E. Aldosterone
1352.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1353.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1354.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1355.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1356.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1357.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1358.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1359.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1360.
A.
B.
C.
Chyluria can be detected by addition of the following to the urine:
Sulphosalicylic acid
Nitric acid
Acetic anhydride
* Chloroform
Ethanol
Creatinine coefficient for male is:
10-25
* 20-30
50-100
1-10
2-6
Cystinuria results from inability to
Metabolise cysteine
Convert cystine into cysteine
Incorporate cysteine into proteins
* Reabsorb cystine in renal tubules
Both C and D
Cystinuria results from inability to
Metabolise cysteine
Convert cystine into cysteine
Incorporate cysteine into proteins
* Reabsorb cystine in renal tubules
Only A and D
Daily excretion of creatinine with urine is:
3-5 g
4-6 g
8-10 g
7-9 g
* 1-2 g
Daily excretion of creatinine with urine is:
3-5 g
4-6 g
8-10 g
7-9 g
* 1-2 g
Daily excretion of urea with urine is:
20 – 35 g
20 – 35 g
20 – 35 g
* 20 – 35 g
20 – 35 g
Daily excretion of urea with urine is:
3-5 g
4-6 g
8-10 g
7-9 g
* 1-2 g
Daily excretion of uric acid with urine is:
* 0,6 – 1 g
0,5 – 1,5 g
2–3g
D. 1,5 – 3,5 g
E. 0,1 – 0,5 g
1361.
Determination of which products in urine is important for the estimation of
adrenal cortex function?
A. * 17-ketosteroids
B. Cholesterol
C. Cyclopentanoperhydrophenantren
D. Ketone bodies
E. Lanosterol
1362.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is an example of which imbalance?
A. Respiratory acidosis
B. Respiratory alkalosis
C. Metabolic alkalosis
D. * Metabolic acidosis
E. Respiratory chain
1363.
For a patient was found the increase of maintenance of urea and creatinine in
blood and diminishing in urine. What are possible reasons of such state?
A. Main reason of such state it is disorder of detoxification, transport and excretion
of ammonia with urine
B. Main reason is a disease of liver
C. Such state appears at the disease of muscles
D. * Diseases which result in insufficiency of kidneys
E. Such state appears as a result of disorder of acid-base balance in an organism
1364.
For diagnostic of acute inflammatory process in kidneys was conducted a specific
test - determination of such substance in urine:
A. Content of lactose
B. Activity of creatinkinase
C. Concentrations of creatin
D. Activity of pepsin
E. * Activity of alanine amino peptidase
1365.
For what disease is the most proper urine with low density?
A. Itchenko - Cushing
B. Addison disease
C. * Diabetes insipidus
D. Diabetes mellitus
E. Chronic pyelonephritis
1366.
For what disease is the most proper urine with low density?
A. Itchenko - Cushing
B. Addison disease
C. * Diabetes insipidus
D. Diabetes mellitus
E. Chronic pyelonephritis
1367.
Glomerular filtrate – it is a:
A. Whole blood
B. Blood plasma with a proteins
C. * Blood plasma without any proteins
D. Blood plasma without glucose
E. Blood plasma without glucose and proteins
1368.
Glomerular filtration mostly depends on
A. * Permeability of glomerular filter
B. Endothelia of capillaries
C. Level of filtration pressure
1369.
1370.
1371.
1372.
1373.
1374.
1375.
1376.
1377.
D. Hydrostatical pressure
E. Oncotic pressure
Glomerular filtration mostly depends on
A. * Permeability of glomerular filter
B. Endothelia of capillaries
C. Level of filtration pressure
D. Hydrostatical pressure
E. Oncotic pressure
Haematuria can occur in
A. Haemolytic anaemia
B. Mismatched blood transfusion
C. Yellow fever
D. * Stone in urinary tract
E. All of these
Haematuria can occur in all of the following except
A. Acute glomerulonephritis
B. Cancer of urinary tract
C. Stone in urinary tract
D. * Mismatched blood transfusion
E. Both C and D
Hormone associated with diuresis:
A. Oxytocine
B. * Vasopressin
C. Both oxytocine and vasopresin
D. Neither oxytocine nor vasopressin
E. ACTH
hours and, then, measure
A. Serum urea
B. Serum creatinine
C. Urine output in one hour
D. * Specific gravity of urine
E. Both C and D
How is diminishing of day's diuresis named?
A. Anuria
B. Polyuria
C. * Oliguria
D. Nicturia
E. Polakiuriya
How is diminishing of day's diuresis named?
A. Anuria
B. Poliuria
C. * Oliguria
D. Nicturia
E. Polakiuriya
How is frequent urination named?
A. * Polakiuria
B. Stranguria
C. Anuria
D. Nicturia
E. Polyuria
How is frequent urination named?
A. * Polakiuria
B.
C.
D.
E.
1378.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1379.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1380.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1381.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1382.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1383.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1384.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1385.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Stranguria
Anuria
Nicturia
Poliuria
How is the increase of acidity of urine named?
* Hyperaciduriya
Glucosuria
Ketonuria
Creatinuriya
Hyperacidity
How is the increase of acidity of urine named?
* Hyperaciduriya
Glucosuria
Ketonuria
Creatinuriya
Hyperacidity
How is the increase of day's diuresis named?
Anuria
Polakiuria
Oligouria
Ischuria
* Polyuria
How is the increase of day's diuresis named?
Anuria
Polakiuria
Oligouria
Ischuria
* Poliuria
How long do kidneys need for proceeding of imbalanced acid-base state?
30 sec. – 1 minutes
1 – 3 minutes
* 10 - 20 hours
5 – 10 minutes
1 - 2 hours
How many ascorbic acid in normal condition is excreted per day with urine:
* 20-30 mg
113,5-170,5 mg
10-28 g
80-100 mg
18-33 g
How many ascorbic acid in normal condition is excreted per day with urine:
* 20-30 mg
113,5-170,5 mg
10-28 g
80-100 mg
18-33 g
How many grammes of potassium are contained in daily urine of healthy adult?
*2–5g
0,5 – 1,5 g
2–3g
1,5 – 3,5 g
0,1 – 0,5 g
1386.
How many grammes of proteins can lose with urine patients with a
glomerulonephritis daily?
A. 100
B. 50
C. 60 -70
D. * 20 - 40
E. 120 - 150
1387.
How many litters of blood do flow daily through kidneys?
A. 200 – 300
B. 50 – 150
C. * 700 – 900
D. 15 – 35
E. 100 – 500
1388.
How much time do kidneys need for proceeding of imbalanced acid-base state?
A. 30 sec. – 1 minutes
B. 1 – 3 minutes
C. * 10 - 20 hours
D. 5 – 10 minutes
E. 1 - 2 hours
1389.
In a norm the clearance of endogenous creatinine is:
A. * 110 – 150 ml/min
B. 100 – 250 ml/min
C. 110 – 200 ml/min
D. 10 – 150 ml/min
E. 10 – 100 ml/min
1390.
In humans the sulphur of methionine and cysteine is excreted mainly as
A. Ethereal sulphate
B. * Inorganic sulphate
C. Sulphites
D. Thioorganic compound
E. All of these
1391.
In the urine of a patient with liver disease is absent urobilinogen. It is connected
with the affection of:
A. stercobilin formation
B. * direct bilirubin formation
C. kidneys function
D. transformation of bilirubin in the intestine
E. bile passage to the intestine
1392.
In what part of nephron does take place filtration of urine?
A. * In a glomerulus
B. In the loop of Henle
C. In a proksimal canaliculi
D. In a distal canaliculi
E. In the collective tubes
1393.
Is there what normal concentration of urea in blood?
A. 3 - 8 gramme/l
B. 1 - 3 mmol/l
C. * 3 - 8 mmol/l
D. 3 - 10 mmol/l
E. 10 - 15 mmol/l
1394.
Ketoacidosis refers to the metabolic acidosis caused by the overproduction of
ketoacids. The classic form of ketoacidosis is uncontrolled diabetes mellitus. All of the
following would occur in a patient suffering from a diabetes-induced metabolic acidosis
(diabetic ketoacidosis) EXCEPT:
A. Deep, rapid breathing causes a decrease in the partial pressure of carbon dioxide
(PaCO2) in the blood.
B. The removal of carbon dioxide through deep, rapid breathing results in a rise in
the blood pH
C. When endogenous acid production rises sharply, net acid excretion cannot keep
pace and the bicarbonate lost in buffering is not replaced causing plasma HCO3levels to fall
D. * Serum bicarbonate levels will decrease after the administration of an insulin
injection
E. The fall in insulin causes fat cells to liberate fatty acids, which flood the
hepatocytes
1395.
Laboratory test of a patient’s urine with intestines dysbacteriosis established the
increase of indican. It testifies:
A. kidney disease
B. * normal neutralization liver function
C. increased fat hydrolysis
D. liver malfunction
E. vitamins F hypovitaminosis
1396.
Maple syrup urine disease is the disorder of the:
A. tyrosine metabolism caused by the absence of homogentisate oxidase
B. phenylalanine metabolism caused by an absence or deficiency of phenylalanine
hydroxylase
C. * oxidative decarboxylation of o-ketoacids derived from valine, isoleucine, and
leucine caused by the defect of branched-chain dehydrogenase
D. glutamate metabolism caused by the defect of glutamate dehydrogenase
E. None of the above
1397.
Maple syrup urine diseases is an inborn error of metabolism of
A. Sulphur-containing amino acids
B. Aromatic amino acids
C. * Branched chain amino acids
D. Dicarboxylic amino acids
E. B and C
1398.
Maple syrup urine diseases is an inborn error of metabolism of
A. Sulphur-containing amino acids
B. Aromatic amino acids
C. * Branched chain amino acids
D. Dicarboxylic amino acids
E. None of the above
1399.
Maximum urea clearance is
A. 54 ml/min
B. * 75 ml/min
C. 110 ml/min
D. 130 ml/min
E. Both C and D
1400.
Mineralocorticoids increase the tubular reabsorption of
A. Sodium and calcium
B. Sodium and potassium
C. * Sodium and chloride
D. Potassium and chloride
E. Potassium and calcium
1401.
Mineralocorticoids increase the tubular secretion of
A. Sodium
B. * Potassium
C. Chloride
D. Bicarbonate
E. Calcium
1402.
Name the compound in the urine, which is a test of protein putrefaction processes
in the intestine:
A. A.Urates
B. B.Urea
C. Creatinine
D. * Indican
E. Lactic acid
1403.
Name the end product of protein’s metabolism, which is excreted with urine:
A. Uric acid
B. * Urea
C. Indican
D. Hyaluronic acid
E. Creatinine
1404.
Name the incretory function of kidneys
A. Adjusting of acid-base balance
B. Excretory function
C. Adjusting of water – salt exchange
D. * Adjusting of blood pressure, erythropoesis
E. Adjusting of electrolyte exchange
1405.
Name the incretpory function of kidneys
A. Adjusting of acid-base balance
B. Excretory function
C. Adjusting of water – salt exchange
D. * Adjusting of blood pressure, erythropoesis
E. Adjusting of electrolyte exchange
1406.
Name the matter in the urine, which is a test of intensivity of protein putrefaction
processes in the intestine:
A. Urates
B. Urea
C. Creatinine
D. * Indican
E. Lactic acid
1407.
pH of urine of healthy person is between:
A. 7-8
B. 8-10
C. 1.5-2.0
D. * 5.0-7.0
E. 4.0-5.0
1408.
Physiological glycosuria is met with in
A. Renal glycosuria
B. * Alimentary glycosuria
C. Diabetes Mellitus
D. Alloxan diabetes
E. All of these
1409.
Poliuriya of patients with diabetes insipidus appears as a result:
A. * Insufficient level of antidiuretic hormone in blood
1410.
1411.
1412.
1413.
1414.
1415.
B. Insufficient level of insulin in blood
C. Disorders of reabsorption of water in canaliculies as a result of high osmotic
pressure of urine
D. Excessive intake of liquid
E. Disorders of reabsorption of water in canaliculies as a result of low osmolality of
urine
Poliuriya of patients with diabetes mellitus appears as a result:
A. * Disorders of reabsorption of water in canaliculies as a result of high osmotic
pressure of urine
B. Insufficient level of glucagon in blood
C. Excessive intake of liquid
D. Insufficient level of antidiuretic hormone in blood
E. Disorders of reabsorption of water in canaliculies as a result of low osmolality of
urine
Principle of quantitative determination of proteins in urine method is based on:
A. * Empiric fixed fact, that at stratification of urine on an nitric acid appears a ring
on the margin of both liquids between 2th and 3th minutes at content of proteins
in urine 0,033g/l
B. Empiric fixed fact, that at stratification of urine on an acetic acid appears a ring
on the margin of both liquids between 2th and 3th minutes at content of proteins
in urine 0,033g/l
C. Empiric fixed fact, that at stratification of urine on an sulphosalicilic acid appears
a ring on the margin of both liquids between 2th and 3th minutes at content of
proteins in urine 0,033g/l
D. Empiric fixed fact, that at stratification of urine on an nitric acid appears a ring on
the margin of both liquids between 2th and 3th minutes at content of proteins in
urine 0,33g/l
E. Empiric fixed fact, that at stratification of urine on an nitric acid appears a ring on
the margin of both liquids between 2th and 3th minutes at content of proteins in
urine 0,0033g/l
Renal glycosuria occurs due to
A. Increased filtration of glucose in glomeruli
B. Increased secretion of glucose by renal tubular cells
C. Decreased reabsorption of glucose by renal tubular cells
D. * Increased conversion of glycogen into glucose in tubular cells
E. Both C and D
Renal threshold for bilirubinglucuronids is:
A. 60 ?mol/l
B. * 35 ?mol /l
C. 20 ?mol /l
D. 25 ?mol /l
E. 30 ?mol /l
Renal threshold for glucose is:
A. 8-10 ?mol l/l
B. 35 ?mol /l
C. * 8-10 mmol/l
D. 10-12 mmol/l
E. 10-12 ?mol /l
Small amount of urinary oxalates is contributed by the amino acid:
A. * Glycine
B. Tyrosine
C. Alanine
D. Serine
E. Both A and B
1416.
Specific gravity of urine increases in
A. * Diabetes mellitus
B. Chronic glomerulonephritis
C. Polydypsia
D. Hypercalcemia
E. All of the above
1417.
Standard urea clearance is
A. * 54 ml/min
B. 75 ml/min
C. 110 ml/min
D. 130 ml/min
E. None of above
1418.
Structural – functional unit of kidneys is:
A. Glomerulus
B. Kidney papilla
C. Capsule of Bowmen
D. Neuron
E. * Nephron
1419.
Syndrome of Lesch-Nyhan – hard hyperuricemia is the genetic deficiency of such
enzyme:
A. Xantine oxidase
B. Adenosine deaminase
C. Hypoxanthine oxidase
D. Phosphorylase
E. * Hypoxanthine – guanine phosphoribosyltransferase
1420.
The active form of vitamin D (1,25-dihydrocholecalciferol) maintain in an
organism a constant level of:
A. Potassium and phosphorus
B. * Calcium and phosphorus
C. S. Iron and calcium
D. Iron and magnesium
E. Magnesium and manganese
1421.
The amino acid which detoxicated benzoic acid to form hippuric acid is
A. * Glycine
B. Alanine
C. Serine
D. Glutamic acid
E. Tyrosine
1422.
The amount of urea in patient's urine is normal. Which of the listed indexes are
true in this case?
A. 10-15 g
B. 20-40 g
C. 10-35 g
D. * 25-30 g
E. 50-60 g
1423.
The concentration of what substance does increase in the blood at disorders of
excretory function of kidneys?
A. Uric acid and creatinine
B. * Creatinine and urea
C. Creatinine and creatin
D. Creatinine and indican
E. Uric acid and indican
1424.
The concentration of which substance is increased at an alkaptonuria?
A. Leukotrienes
B. Phenyl-pyruvic acid
C. Melatonin
D. * Gomogentisic acid
E. Erythropoietin
1425.
The constant increase of uric acid concentration in blood is named:
A. Uremia
B. Hyperazotemiya
C. Hyperacidaminemiya
D. Hyperlaktatemiya
E. Hyperuricemia
1426.
The excretion of chlorides with urine decreases at all of the followings states,
except:
A. Vomiting
B. Diabetes insipidus
C. Diarrhea
D. * Addison disease
E. Icenko – Cushing disease
1427.
The insufficient production of mineralocorticoids (Addison diseases, bronze
diseases) is accompanied with muscle weakness. This is explained by the excretion with
urine increased amount of ions of:
A. * Na+
B. K+
C. H+
D. Ca2+
E. Mg2+
1428.
The kidney threshold of glucose is:
A. * 8 – 9 mmol/l
B. 5 – 10 mmol/l
C. 1 – 5 mmol/l
D. 1 – 2 mmol/l
E. 10 – 15 mmol/l
1429.
The kidney threshold of glucose is:
A. * 8 – 10 mmol/l
B. 5 – 10 mmol/l
C. 1 – 5 mmol/l
D. 1 – 2 mmol/l
E. 10 – 15 mmol/l
1430.
The level of phenyl-pyruvic acid in urine increases at:
A. Osteomalacia
B. * Phenylketonuria
C. Addison disease
D. Icenko – Cushing disease
E. Aldosteronism
1431.
The main pigment of urine is:
A. Bilirubin
B. Uroeritrin
C. Uroporfirin
D. Urobilinoid
1432.
1433.
1434.
1435.
1436.
1437.
1438.
1439.
1440.
E. * Urochrome
The man's daily secretion of creatinine with urine is:
A. 3-5 g
B. 4-6 g
C. 8-10 g
D. 7-9 g
E. * 1-2 g
The most dangerous for life such effect of acute kidney insufficiency:
A. Overhydratation
B. Hypokaliemia
C. Hypermagniyemia
D. * Hyperkaliemia
E. Hyperkal'ciemia
The normal organic components of urine are all of the followings, except:
A. Urea
B. Hyaluronic acid
C. * Glucose
D. Uric acid
E. Creatinine
The pathological components of urine are all of the followings, except:
A. Ketone bodies
B. Blood
C. * Amino acid
D. Bile pigments
E. Glucose
The polysaccharide used in assessing the glomerular fittration rate (GFR) is
A. Glycogen
B. Agar
C. * Inulin
D. Hyaluronic acid
E. All of these
The possible reason of uric acid excretion decrease:
A. Action of ionizing an radiation
B. * Kidney insufficiency
C. Leucosis
D. Burns
E. Malignant tumor
The specific gravity of urine normally ranges from
A. 0.900–0.999
B. * 1.003–1.030
C. 1.000–1.001
D. 1.101–1.120
E. 1.999 – 2.111
The test of Reberg allows to define:
A. Transport of electrolytes
B. Concentration ability of kidneys
C. Plasma blood flow
D. * Glomerular filtration, reabsorption
E. Secretion
The test of Reberg allows to define:
A. Transport of electrolytes
B. Concentration ability of kidneys
C. Plasma blood flow
D. * Glomerular filtration, reabsorption
E. Secretion
1441.
Urine has a smell of rotten apples at presence in of:
A. Urea
B. Glucose
C. * Ketone bodies
D. Uric acid
E. Indican
1442.
Urine of patient after staying with oxygen becomes red. Biochemical research of
urine set the enhanceable excretion of protoporphyrin IX that is the marker of disorders
of synthesis:
A. Bilirubin
B. Purine nucleotides
C. Amino acids
D. * Hem
E. Pyrimidine nucleotides
1443.
What area of nephron does take part in the concentration of urine?
A. Glomerulus
B. * Henle’s loop
C. Distal canaliculi
D. Proksimal canaliculi
E. Collective tubes
1444.
What area of nephron does take part in the concentration of urine?
A. Glomerulus
B. * Henle’s loop
C. Distal canaliculi
D. Proksimal canaliculi
E. Collective tubes
1445.
What basic event in pathogenesis of chronic kidney’s insufficiency?
A. * All below transferred
B. Decline of glomerular filtration
C. Hyperazotemia
D. Disorders of water – electrolyte metabolism
E. Hyperkaliemia
1446.
What changes in urine can be a hyperglycemia accompanied?
A. * Appearance of glucose
B. Appearance of proteins
C. Appearance of bilirubin
D. Appearance of urobilin
E. Appearance of indican
1447.
What changes in urine can testify kidney insufficiency?
A. * Density less than 1,010
B. An acetone in urine
C. Absence of proteins in urine
D. Excess of urates
E. Bacterias in urine
1448.
What changes in urine can testify kidney insufficiency?
A. * Density less than 1,010
B. An acetone in urine
C. Absence of proteins in urine
D. Excess of urates
1449.
1450.
1451.
1452.
1453.
1454.
1455.
1456.
1457.
E. Bacteria in urine
What color of urine appears after its oxidation at alkaptonuria?
A. White
B. Yellow
C. Red
D. Brown
E. * Black
What content of mineral components is in daily urine of healthy adult?
A. * 15 – 25 g
B. 5 – 15 g
C. 20 – 30 g
D. 15 – 35 g
E. 1 – 5 g
What does hematuria mean?
A. Appearance of glucose in urine
B. * Appearance of blood in urine
C. Appearance of acetone in urine
D. Appearance of bile pigments in urine
E. Appearance of porphyrin in urine
What does hematuria mean?
A. Appearance of glucose in urine
B. * Appearance of blood in urine
C. Appearance of acetone in urine
D. Appearance of bile pigments in urine
E. Appearance of porphyrin in urine
What does prevent hyperuricemia:
A. Disorders of urinary acid excretion
B. Disintegration of DNK
C. Radiation defeat of cell
D. Toxemia of pregnancy
E. Application of structural analogue of hypoxanthine
What index of blood does represent the nitrogen excretory function of kidneys ?
A. Urea
B. Residual nitrogen
C. Uric acid
D. * Creatinine
E. Electrolytes
What index of blood does represent the nitrogen excretory function of kidneys ?
A. Urea
B. Residual nitrogen
C. Uric acid
D. * Creatinine
E. Electrolytes
What is average index of urine’s pH of healthy people at the mixed feed?
A. About 4,0
B. About 5,0
C. * About 6,0
D. About 3,0
E. About 2,0
What is average index of urine’s pH of healthy people at the mixed feed?
A. About 4,0
B. About 5,0
1458.
1459.
1460.
1461.
1462.
1463.
1464.
1465.
1466.
C. * About 6,0
D. About 3,0
E. About 2,0
What is the basic factor in pathogenesis of edema at an acute nephritis?
A. * Decline of glomerular filtration
B. Increase of permeability of capillaries
C. Decline of secretion of ADH
D. Decline of sodium excretion
E. Secondary hyperaldosteronism
What is the basic factor in pathogenesis of edema at an acute nephritis?
A. * Decline of glomerular filtration
B. Increase of permeability of capillaries
C. Decline of secretion of ADH
D. Decline of sodium excretion
E. Secondary hyperaldosteronism
What is the cause of primary enzymo-pathologies?
A. Liver diseases.
B. * Genetic disorders.
C. Trauma.
D. Ischemia.
E. All of these
What is the main reason of proteinuria?
A. * Increase of permeability of filtration barrier of kidney
B. Decline of permeability of filtration barrier of kidney
C. Increase of osmolality of primary urine
D. Increase of osmolality of the secondary urine
E. Decrease of osmolality of primary urine
What is the main reason of proteinuria?
A. * Increase of permeability of filtration barrier of kidney
B. Decline of permeability of filtration barrier of kidney
C. Increase of osmolality of primary urine
D. Increase of osmolality of the secondary urine
E. Decrease of osmolality of primary urine
What is the normal ratio between a day and night diuresis?
A. * 3 : 1
B. 1 : 1
C. 9 : 1
D. 6 : 1
E. 7 : 1
What is the simplest method for determination of urine pH:
A. * With the litmus paper
B. With biuret reaction
C. The Foll’s reaction
D. By the method of Altgauzen
E. With the ureometer
What is used for determination of urine’s density?
A. PhEC
B. Densitometer
C. * Urometer
D. Spectrophotometer
E. No any correct answer
What level of urine’s density at oliguriya?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1467.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1468.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1469.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1470.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1471.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1472.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1473.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1474.
A.
B.
C.
D.
Close to low
Low
Normal
* High
Close to normal
What level of urine’s density at oliguriya?
Close to low
Low
Normal
* High
Close to normal
What level of urine’s density at poliuriya?
Normal
High
* Low
Close to low
Close to normal
What level of urine’s density at polyuria?
Normal
High
* Low
Close to low
Close to normal
What method of research is characterized concentration property of kidneys?
Creatinine of blood
* Zimnitskiy’s test
Glomerular filtration
Electrolytes of blood
All of the above
?What pathology is developed in the absence of phenylalanine 4-monooxygenase?
* Phenylketonuria.
Alkaptonuria
Galactosemia.
Hyperglycemia.
Achilia
What substances are precursors of creatin?
Creatinine, glycine, arginine
Urinary acid, urea
Indican, organic acids
Hyaluronic acid, methionine
* Glycine, arginine, methionine
Which hormone increases sodium and water reabsorption by renal tubule cells:
A.Oxytocine
Aldosterone
Vasopressin
Prolactin
Cortisol
Which hormone intensify reabsorption of sodium in renal tubules?
glucagon
insulin
foliculin
* aldosterone
E. vasopressin
1475.
Which hormone intensify reabsorption of sodium in renal tubules?
A. glucagon
B. insulin
C. foliculin
D. * aldosterone
E. vasopressin
1476.
Which hormone intensify reabsorption of sodium in renal tubules?
A. glucagon
B. insulin
C. foliculin
D. * aldosterone
E. vasopressin
1477.
Which hormone intensify reabsorption of sodium in renal tubules?
A. glucagon
B. insulin
C. foliculin
D. * aldosterone
E. vasopressin
1478.
Which hormone regulates the excretion of chlorides with urine?
A. * Aldosterone
B. Insulin
C. Testosteron
D. Corticotropin
E. Cortisol
1479.
Which hormones take part in formation of urine:
A. * Aldosterone and ADH
B. Insulin and STH
C. Aldosterone and TTH
D. Adrenalin and FSH
E. Oxytocin and ADH
1480.
Which medicine is used to increase solubility of urates - salts of uric acid for
patients with gout:
A. Allopurinol
B. Chenodesoxycholic acid
C. Cholic acid and Allopyrinol
D. * Salts of lithium and anturan
E. Solutin of NaCl
1481.
Which of the buffer systems supports constant urine pH?
A. citrate
B. hemoglobin
C. * hydrocarbonate
D. protein
E. oxyhemoglobin
1482.
Which of the buffer systems majorily helps with the support of constant urine pH?
A. citrate
B. hemoglobin
C. * hydrocarbonate
D. protein
E. oxyhemoglobin
1483.
Which of the buffer systems supports constant urine pH?
A. citrate
B.
C.
D.
E.
hemoglobin
* hydrocarbonate
protein
oxyhemoglobin
1484.
Which of the following do you expect to see in a patient with metabolic acidosis
with no respiratory compensation?
A. Decrease of [H+] in blood
B. * Decrease of [HCO3-] in blood
C. Decrease of [H2CO3] in blood
D. Decrease of pCO2 in blood
E. Decrease of dissolved CO2 in blood
1485.
Which of these is considered a secondary defense against changes in pH?
A. * Renal excretion of hydrogen ions
B. The bicarbonate buffer system
C. The phosphate buffer system
D. The protein buffer system
E. The hemoglobin buffer system
1486.
Which statement(s) apply to urea?
A. highly soluble in water
B. produced in the liver
C. compound used as a means of removing excess nitrogen
D. * all of the above
E. None of the above
1487.
Which substance appears in urine by a secretion?
A. * Ammonia
B. Uric acid
C. Glucose
D. Ions of calcium
E. Proteins
1488.
Which substance appears in urine by a secretion?
A. * Ammonia
B. Uric acid
C. Glucose
D. Ions of calcium
E. Proteins
1489.
Which substance causes the decrease of level of uric acid in blood and urine:
A. Antimycin
B. Аminopterin
C. Barbiturates
D. * Allopurinol
E. AMP
1490.
Which test is used for the detection of blood in urine?
A. * Benzidine test
B. Ninhidrin reaction
C. Biuret reaction
D. Method of Al'thauzen
E. All of the above are correct
1491.
Which types of polyuria do you know?
A. Physiological and pathological
B. Real and unreal
C. * Renal and extra renal
D. Pancreatic and nonpancreatic
E. Primary and secondary
1492.
With urine of a healthy adult is excreted the following product of bilirubin
disintegration:
A. urobilin
B. stercobilin
C. mesobilin
D. biliverdin
1493.
verdoglobin 1. muscles is increased
A. After a resistance training session the rate of protein synthesis in the exercised
muscles is increased
B. After a resistance training session the rate of protein breakdown in the exercised
C. Both (a) and (b)
D. * Protein cannot be used as a fuel for exercise
E. Exercise increases the rate of secretion of growth hormone
1494.
A continuous supply of __________ is necessary for muscle contraction.
A. * ATP
B. Proteins
C. Cells
D. Water
E. Vitamins
1495.
A general characteristic of connective tissue is that it
A. * Consists of cells with much intercellular material between them
B. Has no blood supply to the tissue
C. Covers the outside of organs
D. Commonly is found lining body cavities
E. Consists of cells with smal extracellular material between them
1496.
A muscle fibre relaxes when:
A. * The nerve stimulus is removed
B. The nerve stimulus is too forceful
C. The actin binding sites are uncovered
D. The actin binding sites are saturated
E. All the ATP is used up
1497.
A muscle that is not consciously controlled and has a banded appearance would be
described as
A. Striated voluntary
B. * Striated involuntary
C. Nonstriated voluntary
D. Nonstriated involuntary
E. None of the above
1498.
A rheumaric arthritis is more frequent combined with disease?
A. Gald blader illness
B. Gout
C. * Rheumatism
D. Urolithiasis
E. Bronchial asthma
1499.
A tissue with collagen fibers, proteoglycans, and chondrocytes is
A. Adipose.
B. Blood.
C. Bone.
D. Cartilage.
E. * Dense connective tissue.
1500.
Actin and myosin filaments are found in ____ tissue.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Epithelial
* Connective
Muscle
Nervous
Blood
1501.
After calcium ions have been released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum they:
A. Initiate an action potential
B. Cause sodium channels to open in the sarcolemmal membrane
C. * Bind to troponin
D. Bind to actin
E. Cause oxygen to be released from myoglobin
1502.
After microscopic examination, an unknown tissue was found to have numerous
white and yellow fibers. What is your diagnosis as to this type of tissue?
A. Simple squamous epithelium
B. * Smooth muscle tissue
C. Elastic cartilage
D. Adipose tissue
E. Reticular fibers
1503.
After wound's recovery on its place scar appeared. What matter is the main
component of scar's connective tissue?
A. Keratan sulfate
B. Elastin
C. Hyaluronic acid
D. Chondroitin sulfate
E. * Collagene
1504.
Aggregates of mucin detained water which provides his viscesity and protective
action of mucin. It is possible because to the structure of mucin entered:
A. * Glucuronic acid and N-acetylgalactosamin
B. Cholesterol
C. Phospholipids
D. Pentoses
E. Nucleic acid
1505.
Aging affects connective tissues in which of the following ways?
A. * Loss of pliability and resiliency
B. Decreased efficiency in tissue repair and wound healing
C. Joint pains and brittle bones
D. All of the above
E. Increase pliability and resiliency
1506.
Amino acid remnants, most often met in collagene are:
A. Tryptophane, oxilysine, cysteine, valine
B. Tryptophane, cysteine, glycine, methionine
C. Lysine, arginine, cysteine, tryptophane
D. * Oxiproline, oxilysine, glycine, proline
E. Aminosuccinamic, glutamine, lysine
1507.
Ammonia is detoxificated in a liver by converting into urea. Transport of
ammonia from skeletal muscles into liver is carried out by:
A. * Alanine
B. Histidine
C. Glycine
D. Serine
E. Aspartat
1508.
An action potential arriving at the motor endplate causes release of:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Acetylcholine which traverses the neuromuscular junction
Sodium ions which binds to sodium receptors on the muscle membrane
Calcium ions which initiate an action potential along the muscle fibre
Noradrenaline which increases muscle metabolic activity
None of the above
1509.
are called:
A. * Actin and myosin
B. Progesterone and testosterone
C. Progesterone and estrogen
D. Albumins and globulins
E. Calmodulin and actin
1510.
As individuals age, epithelia become
A. Heavier
B. Thicker
C. * Thinner
D. None of the above
E. All of the above
1511.
At intensive manual labour quickly diminish supplies of carbonhydratess which
are stymulator of gluconeogenesis in liver. Which from noted amino acids synthesized in
muscles from pyruvic acid, enters liver and here utillized for the synthesis of glucose?
A. Valine
B. Isoleucine
C. * Alanin
D. Leucin
E. Cystein
1512.
At parodontose there is destruction of proteins and polysaccharides components of
connective tissue. Which from the resulted proteins does enter in the complement of
connective tissue?
A. Albumin
B. Transferrin
C. * Collagen
D. Ceruloplazmin
E. Antitrypsin
1513.
At the hyperfunction of adrenal glan there is thinning of skin and blood vessels,
osteoporosis. Reason of it can be:
A. Increase synthesis of glycosaminoglycans
B. Oppression synthesis of glycolipids
C. * Oppression synthesis of proteoglycans and collogen
D. Decrease synthesis of glycogen
E. Oppression synthesis of nucleoproteins
1514.
At the organ level, the term membrane generally refers to a thin lining or covering
composed of an epithelium that overlies a layer of ____.
A. * Smooth muscle
B. Skeletal muscle
C. Nerve
D. Loose connective tissue
E. Fibrous connective tissue
1515.
B Skull
A. * eart
B. Ribs
C. Bones
D. Lung
1516.
By cadaveric rigidity muscle rigidity appears, caused by the lack of energy in the
ATP form. What stage of elementary tractions acts is blocked by cadaveric rigidity?
A. Separation of myosin head from actin
B. * Joining of myosin head to actin
C. Joining of calcium to troponin
D. ATP hydrolysis in the actin center of myosin
E. Separation of troponin from actin
1517.
By myocardial ischemia the amount of ATP and creatine phosphate is rapidly
decreased as a result of oxidative phosphorylation affection. Among the first symptoms
of this state there is:
A. Membrane permeability affection
B. Contractible proteins synthesis
C. * Myoglobine synthesis
D. Ribosome malfunction
E. Fatty acids F-oxidation malfunction
1518.
Cardiac muscle is found in the wall of the
A. Stomach
B. Intestine
C. Urinary bladder
D. * Heart
E. Bone
1519.
Cardiac muscle tissue:
A. Is under voluntary control
B. All of the above
C. * Does not require nerve activity to stimulate a contraction
D. Will not contract unless stimulated by nerves
E. None of the above
1520.
Cardiac muscle tissue:
A. Is under voluntary control
B. All of the above
C. * Does not require nerve activity to stimulate a contraction
D. Will not contract unless stimulated by nerves
E. None of the above
1521.
Cartilage and bone are examples of what classification of connective tissue?
A. Supporting connective tissue
B. Connective tissue proper
C. Fluid connect tissues
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
1522.
Cartilage and bone are examples of what classification of connective tissue?
A. Fluid connect tissues
B. * Specialized connective tissue
C. Connective tissue proper
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
1523.
Cartilage tissues are likely to be slow in healing following an injury because
A. Cartilage cells cannot reproduce
B. They lack direct blood supplies
C. The intercellular material is missing
D. * Cartilage cells are surrounded by fluids
E. None of the above
1524.
Cell types likely to be seen in areolar connective tissue include all except:
________.
A. Fibroblasts
B. Macrophages
C. * Mast cells
D. Chondrocytes
E. Odontoblasts
1525.
Cells in which tissue type are specialized to transmit electrical impulses from one
body region to another?
A. Muscle
B. * Nervous
C. Connective
D. Epithelial
E. Blood
1526.
Changes concentration of which cytosol ion is biochemical regulator of including
of process of muscle reduction?
A. Mg+2
B. Ca+2
C. K+
D. Na+
E. Cl1527.
Characteristic for heart and liver troubles is an increase activity of LDG. What
additional research does need to be conducted for definition localization of pathological
process?
A. Determination activity of amylase
B. Determination activity of alkaline phosphatase
C. Determination isoenzymes of creatinkinase
D. Determination isoenzymes of LDG
E. Determination activity of aminotranaferase
1528.
Collagen, elastin, and reticular fibers in connective tissues are formed by
A. Phospholipids
B. Carbohydrates
C. Adipose tissue
D. * Proteins
E. Vitamins
1529.
Connective tissue cells that produce the extracellular matrix are called
A. Blast cells.
B. Cyte cells.
C. Clast cells.
D. * Macrophages.
E. Mast cells.
1530.
Dense irregular connective tissue that forms a supporting layer around cartilage is
called:
A. Perichondrium
B. * Periosteum
C. Dermis
D. Сapsule
E. Epidermis
1531.
Dense regular collagenous connective tissue would be found in
A. A nerve
B. The brain
C. A ligament
D. * Skull bone
E. Lung
1532.
?Destruction of thin myofilaments is observed during the research of a striated
muscle fiber after the action of hydrolytic enzymes. Which structures have been
damaged?
A. * Actin myofilaments
B. Collagen
C. T-systems
D. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
E. Myosin myofilaments
1533.
Disorder in the secretory activity of odontoblasts took place during mantle dentin
formation in a milk tooth. Formation of what fibers will be changed?
A. Elastic
B. Reticular
C. * Radial collagen fibers
D. Tangential collagen fibers
E. Nerve
1534.
During a race long-distance the skeletal musculature of the trained man utillizes
glucose with the purpose of receipt of energy ATP for muscular reduction. Specify the
basic process utilization of glucose in these conditions:
A. Glicogenesis
B. Anaerobic glicolysis
C. * Aerobic glicolysis
D. Gluconeogenesis
E. Glycogenolysis
1535.
During the biosynthesis of collagen, in posttranslation modification of proteins
with formation of mature collagen, namely hydroxylating of proline and lysine take part
ascorbatdepending hydroxilase. For what ascorbic acid is needed?
A. * Regenerations of the reconstract form of iron
B. Oxidation of iron
C. Diminishing concentration reconstract form iron
D. Increase maintenance active forms of oxygen
E. Influences on apoenzyme of hydroxilase
1536.
Embryonic connective tissues include
A. * Mesenchyme
B. Wharton's jelly
C. Both of the above
D. Neither of the above
E. Basofills
1537.
Endocrine and exocrine glands are formed from what type of tissue?
A. Connective
B. Blood
C. Muscle
D. Nerve
E. * Epithelial
1538.
Endurance training increases the muscle’s capacity to:
A. Contract faster
B. Breakdown phosphocreatine
C. * Burn fat and carbohydrate
D. Generate energy anaerobically
E. Produce more blood cells
1539.
Extracellular liquid matrix in blood is
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Adipose
* Plasma
Fibroblast
Calcium salt
All of the above
1540.
Extracellular matrix in bone is formed by
A. Mineral salts
B. * Reticular fibers
C. Collagen and elastin
D. Lipids
E. All of the above
1541.
Fast-twitch fibres contain:
A. A relatively large number of mitochondria and low ATPase activity
B. A relatively small number of mitochondria and low ATPase activity
C. * A relatively small number of mitochondria and high ATPase activity
D. A relatively large number of mitochondria and high ATPase activity
E. No mitochondria and high ATPase activity
1542.
Feeding must contain calcium, which is necessary for traction triggering by
connecting it to the:
A. * ATP-ase center of myosin
B. Molecules of globular actin
C. One of troponin subunits
D. Tropomyosin
E. Calmodulin
1543.
Fetal skeleton in early stages is formed by
A. * Hyaline cartilage
B. Elastic cartilage
C. Bone
D. Muscular tissue
E. Tendon
1544.
For bottled fruit of blood apply various anticoagulants, in a that number
policacharides of natural origin, namely:
A. * Heparinum
B. Hyaluronic acid
C. Dermatan sulfate
D. Chondroitin sulfates
E. Dextrane
1545.
For maintenance of normal elasticity and regeneration of skin and its appendages
is needed the sufficient amount of vitamin:
A. * A
B. C
C. B12
D. K
E. B1
1546.
For the function of muscles important significance has creatinphosphate which
appears from a creatin and ATP. Name amino acids which are needed for the synthesis of
creatin:
A. Glycine, proline, cystein
B. Methionine, leucine, phenilalanin
C. * Glycine, arginine, methionine
D. Arginine, tryptophane, lisyne
E. Valine, leucine, isoleucine
1547.
For very high force muscle contractions lasting 1-2 seconds, the initial energy
source is from:
A. glycolysis
B. Creatine phosphorylation
C. Phosphocreatine stores
D. * ATP stores
E. None of the above
1548.
For what rheumatic disease characteristic rentgenologic sign of osteoartroses?
A. * Gout
B. Rheumatic arthritis
C. Rheumatism
D. Disease of Shegrena
E. Pellagra
1549.
From what albumins built filaments of muscles?
A. Albumins and globulins
B. * Actin and miosin
C. Albumins and histons
D. Tubulins and actin
E. Calmodulin and tropomiosine
1550.
Hemopoietic tissue is found in
A. Adipose tissue
B. Cartilage
C. The dermis of the skin
D. * Red marrow
E. Yellow marrow
1551.
Heparinum synthesized fat cells and enters to blood where he executes a main
function:
A. Procoagulant
B. Antitripsin
C. Oxidant
D. Antioxidant
E. * Anticoagulant
1552.
Hipovitaminoses C is accompanied by violations of connective tissue, namely to
the synthesis of collogen. What role in here take part vitamin C?
A. * Activates prolinhydroxilase
B. Activates hyaluronidase
C. Activates creatinphosphokinase
D. Activates glutation
E. Activates amylase
1553.
Hyaline cartilage is classified as ____ tissue.
A. Nervous
B. Muscle
C. * Connective
D. Epithelial
E. All of the abvove
1554.
Hyaline cartilage is different from elastic or fibrocartilage because ________.
A. It is more vascularized
B. It contains more nuclei
C. * It has more elastic fibers
D. Fibers are not normally visible
E. Fibers are normally visible
1555.
Important function in the processes of bone mineralisation is executed by
glycosaminoglycans, except:
A. Chondroitin 4-sulfate
B. Hyaluronic acid
C. Dermatan sulfate
D. Keratan Sulfates
E. * Heparin
1556.
In the complement of connective tissue of saliva, teeth enter complex connections
of proteins and carbohydrates as glycosaminoglycans. Violation metabolism of these
substances is one of reasons development of caries. Specify on these connections:
A. Hyaluronic acid
B. Chondroitin sulfates
C. * Proteoglikans
D. Heparin
E. Dermatan sulfate
1557.
In the process of get olding there is diminishing of elasticity of skin, blood
vessels, resiliently elastic properties of cartilages are worsened, reparative ability of
connecting tissue goes down. Reason of it can be:
A. * Decline amount of proteoglycans
B. Maintenance of collogen fibres grows
C. Increase degree hydratation of proteoglycans
D. Diminishing maintenance of hepatin in muscles
E. Increase of amount of elastin
1558.
In the process of get olding there is diminishing of elasticity of skin, blood
vessels, resiliently elastic properties of cartilages are worsened, reparative ability of
connecting tissue goes down. Reason of it can be:
A. * Decline amount of proteoglycans
B. Maintenance of collogen fibres grows
C. Increase degree hydratation of proteoglycans
D. Diminishing maintenance of hepatin in muscles
E. Increase of amount of elastin
1559.
In the process of organism's ageing is decreased bonding of water by connective
tissue. This is tied with the decrease of concentration of:
A. Glycosaminoglycan
B. * Collagene
C. Phospholipids
D. Hyaluronic acid
E. Chondroitin sulphuric acid
1560.
In tissues of organism during the update of proteoglycans there is their
disintegration in lysosomes by breaking up cathepsins and glycosidases. There is a
decline of activity of lysosomal glycosidases at mucopolysaccharidoses. Which products
disintegration of proteoglycans will appear in big amounts in urine?
A. Glucose-6-phosphate
B. Glucose
C. * Chondroitin sulfates
D. Fructose-6- phosphate
E. Glucosamine
1561.
In tissues of organism during the update of proteoglycans there is their
disintegration in lysosomes by breaking up cathepsins and glycosidases. There is a
decline of activity of lysosomal glycosidases at mucopolysaccharidoses. Which products
disintegration of proteoglycans will appear in big amounts in urine?
A. Glucose-6-phosphate
B.
C.
D.
E.
Glucose
* Chondroitin sulfates
Fructose-6- phosphate
Glucosamine
1562.
In what kinds of tissue would you find gap junctions?
A. * Heart and smooth muscle tissue
B. Cells lining the digestive tract
C. Layers of the skin
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
1563.
In which of the following ways does cardiac muscle tissue differ from skeletal
muscle tissue?
A. Cardiac muscle fibers are relatively short and branched or bifurcated
B. Neighboring cardiac muscle fibers are connected by intercalated discs
C. Each cardiac muscle cell has only one or two centrally located nuclei
D. * All of the above
E. Cardiac muscle, like other muscles, can contract, but it can also carry an action
potential
1564.
In which of these locations is dense irregular collagenous connective tissue found?
A. Walls of large arteries
B. * Tendons
C. Nuchal ligament
D. Dermis of the skin
E. Reticular tissue
1565.
It is known that a sinovial liquid diminishes the friction of arthral surfaces. At
rheumatism or arthritis its viscidity goes down as a result of depolamirisation of such
substance:
A. Glycogen
B. Collagen
C. Heparin
D. Albumin
E. * Hyaluronic acid
1566.
Large arteries stretch during systole and return to the start state during diastole to
provide bloodstream stability. Which structural components of vessels wall explain this?
A. * Elastic fibers
B. Muscle fibers
C. Reticular fibers
D. Collsgen fibers
E. Numerous fibriblasts
1567.
Ligaments connect
A. * Cartilage to bone.
B. Bone to muscle.
C. Muscle to muscle.
D. Bone to bone.
E. All of the above
1568.
Lisocim provides death of bacterial cells, because have action on the cellular
membrane of bacteria, splitting:
A. Lipids
B. * Carbohydrate components
C. Proteins
D. Nucleic acids
E. Cholesterol
1569.
Lizocim is antybacterial factor, for mechanism of action there is muraminidase.
To which class of enzymes does he belong, if splits glycosidic bonds in to the
polisacharide chain of muramine?
A. * Hidrolyse
B. Transferase
C. Oxidoreductase
D. Lyases
E. Izomerase
1570.
Loose connective tissue contains
A. Collagen and elastin fibers
B. Myosin and actin fibers
C. Plasma
D. * All of the above
E. Blood serum
1571.
Major proteins of connecive tissue are:
A. Fibroin and keratin
B. Albumins and globulins
C. * Collagene and elastin
D. Myosin and actin
E. Protamines and histons
1572.
Microfilaments bunch together to form myofibrils in:
A. * Cardiac muscle
B. Skeletal muscle
C. Smooth muscle
D. A and B
E. A and C
1573.
Mineralization of organic matrixe of bone tissue is related to the big energy
outlay, mainly due to the breaking up of:
A. Ketone bodies
B. Fatty acids
C. * Glycogen
D. Proteins
E. Amino acids
1574.
Movement of food through the digestive tract results from the action of
A. Cardiac muscle
B. * Smooth muscle
C. Skeletal muscle
D. Undifferentiated muscle
E. Tendon
1575.
Mucin – one of the basic components of saliva, for chemical nature is complex
protein, namely:
A. Metalloprotein
B. Nukleoprotein
C. Phosphoprotein
D. Lipoprotein
E. * Glycoprotein
1576.
Muscle fatigue can result from:
A. Depletion of ATP
B. Depletion of Ca+
C. Depletion of acetylcholine
D. * Both (A) and (B)
E. A combination of both (A) & (C).
1577.
Muscle tissue cells are contractile, which means they
A. Are responsible for the production and secretion of enzymes
B. * Are specialized in contraction and relaxation
C. Help in the movement of involuntary organs only
D. All of the above statements are true.
E. None of the above
1578.
Muscles are made of
A. Silica
B. Polyester threads
C. Calcium and phosphorous
D. * Groups of cells called fibres
E. All of the above
1579.
Muscles of the pectoral girdle and upper limbs are organized into all of the
following groups except
A. * Muscles that move the pectoral girdle
B. Muscles that move the glenohumeral joint
C. Intrinsic muscles of the forearm
D. Intrinsic muscles of the hand
E. All of the folliwing
1580.
Muscular endurance is defined as:
A. * Peak ability of a muscle to generate force.
B. An ability you are born with and cannot train.
C. The ability of a muscle or muscle group to generate force repeatedly
D. he ability of the heart to provide oxygen rich blood to the muscles.
E. All of above
1581.
Muscular endurance is:
A. * A muscle's ability to exert force repeatedly without fatiguing
B. A force exerted by a muscle that is less than or equal to the resistance
C. A withering of muscle tissue that can result from injury or disease
D. The length of time a particular movement can be sustained by a muscle or muscle
group
E. All of the above
1582.
Muscular endurance is:
A. * A muscle's ability to exert force repeatedly without fatiguing
B. A force exerted by a muscle that is less than or equal to the resistance
C. A withering of muscle tissue that can result from injury or disease
D. The length of time a particular movement can be sustained by a muscle or muscle
group
E. All of the above
1583.
Myosin and actin make up
A. Osteoblasts
B. * Myofibrils
C. Collagen
D. Red marrow
E. Elastin
1584.
Myosin and actin make up:
A. Osteoblasts
B. Collagen
C. * Myofibrils
D. Red marrow
E. Desmosoms
1585.
Name enzyme determination of which in blood is most informing at first hour
after the origin of heart attack of myocardium:
A. Aspartataminotransferase
B. Alaninaminotransferase
C. Laktatdehidrogenase
D. * Creatinphosfokinase MB
E. Glutamatdehidrogenase
1586.
Nitric oxide mediates this effect on vascular smooth muscle:
A. * Smooth muscle relaxation
B. B. Smooth muscle contraction
C. No effect
D. Provide production of energy
E. Smooth muscle protection
1587.
One of the important differences between skeletal muscle tissue and cardiac
muscle tissue is that cardiac muscle tissue is
A. Multinucleated
B. * Striated involuntary muscle
C. Striated voluntary muscle
D. Comprised of unusually large cells
E. None of the above
1588.
One of the important differences between skeletal muscle tissue and cardiac
muscle tissue is that cardiac muscle tissue is:
A. Multinucleated
B. * Striated involuntary muscle
C. Comprised of unusually large cells
D. Striated voluntary muscle
E. None of the above
1589.
One of the rules of surgery is performing sections along the so-called lines of skin
tension. What tissue forms the reticular layer of derma?
A. Reticular connective tissue
B. * Dense irregulat connective tissue
C. Loose connective tissue
D. Epithelial tissue
E. Dense regular connective tissue
1590.
One of the sources of formation of ATP in muscles is the reaction 2
ADP?ATP+adenosine monophosphate. By what enzyme is it catalyzed?
A. Hexokinase
B. Aldolase
C. Adenylate kinase
D. * Adenylate cyclase
E. ATP-ase
1591.
Select the correct statement regarding adipose tissue.
A. Mature adipose cells are highly mitotic
B. Most of the cell volume is occupied by the nucleus
C. * Its primary function is nutrient storage
D. It is composed mostly of extracellular matrix
E. All of the above
1592.
Select the correct statement regarding the cells of connective tissue.
A. * Chondroblasts are the main cell type of connective tissue proper
B. Connective tissue cells are nondividing
C. Connective tissue does not contain cells
D. "Blast" cells are undifferentiated, actively dividing cells
E. Connective tissue contain all type of cells
1593.
Skeletal muscle is
A. Striated and voluntary
B. Nonstriated and involuntary
C. * Striated and involuntary
D. Nonstriated and voluntary
E. All of above
1594.
Skeletal muscle is irritated with a series of electropulses in an experiment. Every
next impulse is in the period of the shortening of a single muscular contraction. What
type of muscular contraction will arise?
A. * Smooth tetanus
B. Skeletal tetanus
C. Asynchronous tetanus
D. A series of single contraction
E. Muscle contracture
1595.
Skeletal muscle is irritated with a series of electropulses in an experiment. Every
next impulse is in the period of the shortening of a single muscular contraction. What
type of muscular contraction will arise?
A. * Smooth tetanus
B. Skeletal tetanus
C. Asynchronous tetanus
D. A series of single contraction
E. Muscle contracture
1596.
Smooth muscles occur in
A. Uterus
B. Artery
C. Vein
D. * All the above
E. Bronchi
1597.
Striated muscle is also called
A. ardiac muscle
B. mooth muscle
C. * keletal muscle
D. nvoluntary muscle
E. None of the above
1598.
Tendons and ligaments are composed primarily of
A. Adipose tissue
B. * Fibrous connective tissue
C. Muscle tissue
D. Loose connective tissue
E. Elastic connective tissue
1599.
Tendons and ligaments contain the protein
A. Keratin
B. Fibrin
C. Lignin
D. * Collagen
E. Elastin
1600.
The "all or nothing" law in muscle contraction refers to .
A. The muscle action potential of the motor neuron
B. The contraction of the entire muscle
C. * Only the contraction of individual muscle fibers
D. The myoneural junction generator potential
E. The release of Ca+
1601.
The advantage of strength training is that it:
A. Helps reduce body weight.
B. Improves cardiovascular fitness
C. Gives the body a trim muscular appearance
D. All of the above
E. Produce force and cause motion
1602.
The affection of collagenic fibers structure by the lack of vitamin C in the
organism is caused by enzymes activity malfunction:
A. Glycosyltransferase
B. Lysine hydroxylase and lysine oxidase
C. * Lysine hydroxylase and proline hydroxylase
D. Procolagenpeptidase
E. Colagenase
1603.
The amount of sialic acids in patient's blood is 1060 mg/l. From the probable
diagnosis should be removed the following:
A. Atherosclerosis
B. Tuberculosis
C. Malignant growth
D. * Rheumatism
E. Cardiac infarction
1604.
The basic mechanism of action of glucocorticoids consists in the following:
A. Cooperate with receptors on the plasmatic membranes of cells
B. Provide disintegration of glycogen in liver
C. * Repress inflammatory reaction, related to the hypersensitiveness
D. Find out greater ability to retain sodium, than mineralkorticoids
E. Provide the mechanism activating of glucose
1605.
The cells that act to guard and protect the body are:
A. * Connective cells
B. Nervous cells
C. Endocrine cells
D. Epithelial cells
E. Muscle cells
1606.
The concentration of creatinine in patient's blood is normal. What figures
correspond this state?
A. 1-2 g/l
B. 50-70 mkmol/l
C. 20-35 g/l
D. 100-150 mlmol/l
E. * 70-100 mkmol/l
1607.
The connective tissue that forms "packing" around organs and attaches the skin to
underlying structures is
A. * Loose (areolar).
B. Dense regular collagenous.
C. Dense regular elastic.
D. Dense irregular collagenous.
E. Dense irregular elastic.
1608.
The dangerous skin cancer that has a dark pigmented spot is ____.
A. * Melanoma
B. Basal cell carcinoma
C. Squamous cell carcinoma
D. Prostatic cancer
E. Ovarian cancer
1609.
The decrease of ATP synthesis by ischemia causes irreversible cells affections
mainly as a result of amount growth in the cell of:
A. * Lactate
B. Sodium ions
C. Adenosine monophosphate
D. Ketone bodies
E. Pyruvate
1610.
The end nitrogenated metabolism product of creatine is:
A. Ammonia
B. Indican
C. Hypuric acid
D. * Creatinine
E. Urea
1611.
The energy for all forms of muscle contraction is provided by:
A. * ATP
B. ADP
C. Phosphocreatine
D. Oxidative phosphorylation
E. Generated in the mitochondria of the cell
1612.
The enzyme of hyaluronidase decompose hyaluronic acid, in result increase the
intercellular penetrating. Which vitamin does repress activity of hyaluronidase and
promote strengthening walls of vessels?
A. * Vitamin P
B. Vitamin A
C. Vitamin B1
D. Vitamin B2
E. Vitamin D
1613.
The gel of the extracellular matrix is composed mostly of water and
A. * Proteoglycans
B. Collagen
C. Keratin
D. Reticular fibers
E. None of the above
1614.
The general term for any pain that occurs below the knee and above the ankle is:
A. Muscle cramps
B. * Muscle strain
C. Shin splints
D. Tendonitis
E. Muscle dystrophy
1615.
The major functions of loose connective tissue include
A. * Occupying spaces between organs and supporting epithelia
B. Supporting and surrounding blood vessels and nerves
C. Cushioning organs, storing lipids, and facilitating diffusion
D. All of the above
E. None of the folloving
1616.
The major tissue types in the body are
A. * Epithelial, connective, muscle and neural
B. Mesothelilum, endothelium, adiocytes and desmosomes
C. Stylohyoid, digastric, thyrohyoid and zygomatic
D. Squamous, simple cuboidal, columnar and stratified cuboidal
E. All of the above
1617.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1618.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1619.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1620.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1621.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1622.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1623.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1624.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1625.
A.
B.
C.
The major types of muscles cells are:
* Skeletal, cardiac, smooth
Superficial, subserous, abtruse
Appositional, osseous, elastic
All of the above
None of the above
The man's daily secretion of creatinine with urine is:
3-5 g
4-6 g
8-10 g
7-9 g
* 1-2 g
The maximal ability of a muscle to generate force is:
* Muscular endurance
Optimal health.
Strength training.
Muscular strength.
All of the above
The menisci of the knee are made of
Fibrocartilage.
Hyaline cartilage.
* Dense connective tissue similar to ligaments and tendons
Elastic connective tissue.
all of the above
The most important function of the skin is
* Protection
Sweating
Storing fat
Insulation
Produced energy
The muscle tissue that can be consciously controlled is
Smooth
* Skeletal
Intercalated
Cardiac
All of the above
The only type of cell seen in a tendon is
Muscle fibers
Reticular cells
Collagenous cells
* Fibroblasts
Elastin
The only type of muscle with multinucleated fibers is
* Skeletal muscle
Cardiac muscle
Smooth muscle
Visceral muscle
All of the above
The oxidative deamination of the amino acid alanine in muscle produces:
* One molecule of pyruvic acid and a molecule of ammonia
One molecule of pyruvic acid and a molecule of carbon dioxide
One molecule of pyruvic acid and another amino acid
D. One molecule of pyruvic acid and a molecule of water
E. One molecule of pyruvic acid and a molecule of urea
1626.
The patient has vessel penetration malfunction. Name the connective tissue
protein, which synthesis is affected:
A. Tropomyosin
B. Myoglobine
C. * Albumin
D. Collagene
E. Ceruloplasmin
1627.
The perichondrium is a layer of fibroconnective tissue surrounding
A. A bone
B. * Most cartilage
C. A blood vessel
D. The pericardial cavity
E. All of the above
1628.
The process of mineralisation is provided the structure of collagen which give
possibility to join:
A. N2O
B. N+
C. NH3+
D. Lipids
E. * Ca2+
1629.
The remnants of desmosine and isodesmosine in elastin are formed from
aminoacid radicals of the following amino acids:
A. * Lysine
B. Glycine
C. Proline
D. Ornithine
E. Hydrooxilysine
1630.
The sarcoplasmic reticulum in muscle cells acts as a:
A. Store of digestive enzymes
B. Store of sodium ions
C. Store of lipid
D. * Store of calcium ions
E. Buffer of hydrogen ions
1631.
The secretory cells of a gland are supported by a connective tissue framework
called the
A. Serosa
B. * Stroma
C. Parenchyma
D. Trabecula
E. Plasma
1632.
The shape of a person's ear is due mainly to
A. Dense regular connective tissue
B. Dense irregular connective tissue
C. * Elastic cartilage
D. Fibrocartilage
E. Adipose tissue
1633.
The shape of the external ear is maintained by ________.
A. Adipose tissue
B. Fibrocartilage
C. * Elastic cartilage
D. Hyaline cartilage
E. None of the above
1634.
The start of traction is connected with the usage as a donor of muscle energy rich
bonds energy:
A. Guanosine triphosphate
B. Adenosine triphosphate
C. 1.3-diphosphoglycerate
D. Adenosine diphosphate
E. * Creatine phosphate
1635.
The three basic components of all connective tissues are:
A. * Specialized cells, extracellular protein fibers, ground substance
B. Fluid matrix, cartilage, osteocytes
C. Free exposed surface, exocrine secretions, endocrine secretions
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
1636.
The three main components of connective tissue are ________.
A. Alveoli, fibrous capsule, and secretory cells
B. Ground substance, fibers, and cells
C. * Collagen, elastin, and reticular fibers
D. Fibroblasts, chondroblasts, and osteoblasts
E. Only B and D
1637.
The tissue found under the skin to insulate the body with cells that contain a lot of
fat is ___.
A. Loose connective tissue
B. * Adipose tissue
C. Fibrous connective tissue
D. Hyaline cartilage
E. Stratified squamous epithelium
1638.
The toxin of stupor causes tonic tension of skeletal muscles and vessels because
represses secretion from nervous completions of neurotransmitter:
A. * GABA
B. Noradrenalin
C. Acetylcholin
D. Glycine
E. Glutamate
1639.
The trigger to initiate the contractile process in skeletal muscle is:
A. Potassium binding to myosin
B. Calcium binding to tropomyosin
C. ATP binding to the myosin cross bridges
D. * Calcium binding to troponin
E. ATP breakdown by actin
1640.
The two principal contractile proteins found in skeletal muscle are:
A. Actin and troponin
B. * Actin and myosin
C. Troponin and tropomyosin
D. Myosin and tropomyosin
E. Actin and tropomyosin
1641.
The type of Connective Tissues are
A. * Connective tissue proper
B. Fluid connect tissues
C. Supporting connective tissue
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
1642.
The type of muscle found in the walls of blood vessels is
A. Cardiac
B. * Smooth
C. Striated
D. Voluntary
E. Sceletal
1643.
The type of muscle that makes up the walls of blood vessels is:
A. Cardiac muscle
B. Seletal muscle
C. * Smooth muscle
D. A and b
E. A and c
1644.
The type of tissue that has specialized cells, extracellular protein fibers and
ground substance are:
A. * Connective
B. Neural
C. Muscle
D. Epithelial
E. All of the above
1645.
The types of Connective Tissues are:
A. Fluid connect tissues
B. Connective tissue proper
C. Supporting connective tissue
D. * All of the above
E. None of the above
1646.
The volume of oxygen consumed by muscles during exercise is:
A. * Aerobic capacity
B. Maximum oxygen capacity
C. Flexibility
D. Muscle endurance
E. Muscle strain
1647.
The volume of oxygen consumed by muscles during exercise is:
A. * Aerobic capacity
B. Flexibility
C. Muscle endurance
D. Maximum oxygen capacity
E. Anaerobic oxidation
1648.
These two proteins are called:
A. * Actin and myosin
B. Progesterone and testosterone
C. Progesterone and estrogen
D. Albumins and globulins
E. Collogen and ekastin
1649.
Triggering signal for the processse of tracion is the growth of concentration of
calcium ions in sarcoplasma. Which of the mentioned factors is necessary for muscles
weakening?
A. * ATP
B. Reducted NADP
C. Sodium ions
D. Creatine
E. Creatinine
1650.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1651.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
1652.
by:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Tropocolagene fibres in colagenic fibre are interconnected by:
Aldol bonds
Hydrophobic bonds
Disulfide bonds
Hydrogen bonds
* Peptide bonds
Type I muscle fibres have the following characteristics:
White, glycolytic, slow contracting
White, oxidative, slow contracting
Red, oxidative, fast contracting
Red, glycolytic, slow contracting
* Red, oxidative, slow contracting
Viscoelastic features of major matter of connective tissue are conditioned mainly
Glycosaminoglycans
* Elastin
ATP
Collagene
Keratin
1653.
Vitamin P used in treatment of diseases which have a place violation of
permeability of vascular walls. Medical effect is related to his participating in:
A. Processes of ripening of collagen
B. * Ingibition of hyaluronidase
C. Activation of hyaluronidase
D. Synthesis of elastin
E. Synthesis of proteoglycans
1654.
What are the three basic components of connective tissue?
A. Ground substance, cells, and basement membrane
B. Cartilage, intercellular matrix, and serum
C. Cells, protein fibers, and ground substance
D. * Collagen, elastin, and reticular fibers
E. Protein fibers, cells
1655.
What enzyme is needed for converting of procollagen into collagen by
hydroxylating of residues of proline to 4 – hydroxyproline?
A. Mn2+-ascorbatdepending prolinhydroxilase
B. Mg2+-ascorbatdepending prolinhydroxilase
C. Cu2+-ascorbatdepending prolinhydroxilase
D. * Fe2+ -ascorbatdepending prolinhydroxilase
E. Ca2+ -ascorbatdepending prolinhydroxilase
1656.
What enzyme used for a sclerodermia?
A. Trypsin
B. Amylase
C. Catalase
D. * Hyaluronidase
E. Pepsin
1657.
What happens when the thin filaments in a muscle fiber slide over the thick
filaments?
A. Muscle contracts.
B. Muscle relaxes.
C. * A muscle both contracts and relaxes.
D. A muscle neither contracts nor relaxes.
E. All of above
1658.
What happens when the thin filaments in a muscle fiber slide over the thick
filaments?
A. * Amuscle contracts.
B. A muscle relaxes.
C. A muscle both contracts and relaxes.
D. A muscle neither contracts nor relaxes.
E. All of the above
1659.
What hydrocarboxylic acid, intermediate product of tricarboxilic acids cycle, does
take part in regulation and transportation of blood calcium?
A. Isocitric acid (isocitrate)
B. Oxalo-acetic acid (oxaloacetate)
C. * Citric acid (citrate)
D. Succinate acid (succinate)
E. ?-ketoglutaric acid (?-ketoglutarate )
1660.
What indexes discover in the sharp phase of rheumatism?
A. Seromucoid
B. AsAT, AlAT
C. * C- reactive protein
D. Fibrinogen
E. Creatinine
1661.
What is the difference between cartilage and bone?
A. Bone is rubbery, and cartilage is firm.
B. * Cartilage is rubbery, and bone is firm.
C. Bone is a more primitive tissue than cartilage.
D. Bone is inside the body, and cartilage is outside
E. Only C
1662.
What is the function of a tendon?
A. To link bones to bones
B. To link muscles to bones
C. To link muscles to ligaments
D. * To bind the cells in compact bone closer together
E. None of the above
1663.
What joins the epithelium to the underlying connective tissue?
A. Tight junction
B. Desmosome
C. * Gap junction
D. Microvilli
E. Basement membrane
1664.
What matter in composition of saliva is synthesized in salivary glands and pose by
them and gives saliva thick mucus character?
A. Phosphates
B. Sulfates
C. * Mucin
D. Amylase
E. Maltase
1665.
What neuromediators take part in a nerve-muscle transmission?
A. * Acetylcholin
B. Histamin
C. Adrenalin
D. -aminobutiric acid
E. Serotonin
1666.
What polysacharide (glycosaminoglycan) is the base of connective tissue
intercellular matter, vitreous humor, synovial fluid, umbilical cord?
A. Chondroitin sulphuric acid
B. * Hyaluronic acid
C. Keratan sulfate
D. Heparin
E. Heparan sulfate
1667.
What tough connective tissue joins skeletal muscles to bones?
A. Joints
B. Periosteum
C. * Ligaments
D. Tendons
E. Osteoblasts
1668.
When a muscle fiber contracts, what actually shortens?
A. Actin and myosin filaments
B. A bands and zones of overlap
C. * Sarcomeres, H bands, and I bands
D. Both b and c
E. All of the above
1669.
When cardiac muscle cells are damaged by a heart attack, they are usually
replaced by
A. Connective tissue cells
B. New smooth muscle cells
C. * New cardiac muscle cells
D. Epithelial cells
E. Extracellular matrix
1670.
Where is cardiac muscle tissue located in the body?
A. * Heart
B. Skull
C. Ribs
D. Bones
E. Cartilage
1671.
Which from amino acids does prevail in the molecule of collogen?
A. Tryptophane
B. Asparagin
C. Glycine
D. Alanin
E. * Hydroxyproline
1672.
Which age human skin undergoes changes, which may declare themselves by
reduction of skin elasticity. What structure of connective tissue provide skin elasticity
most of all?
A. Cells of epidermis
B. Ground substance
C. * Collagen and elastic fibers
D. Connective tissue cells
E. Reticular fibers
1673.
Which changes from the side of the isolated heart of frog is it possible to expect
after introduction to perfunic solution of surplus amount of calcium chloride?
A. Stop of heart
B. Increase frequency of reductions
C. * Increase frequency and force of reductions
D. Increase force of reductions
E. Decrease force of reductions
1674.
Which diagnostic test does represent the degree of muscular destruction at
inflammations?
A. Uric acid
B. Diastase
C. Transaminase
D. Indican
E. * Creatine phosphokinase
1675.
Which from amino acids does prevail in the molecule of collagen?
A. Triptofan
B. Asparagin
C. Glycine
D. Alanin
E. * Hydroxyproline
1676.
Which is true concerning muscle tissue?
A. Is a single-celled tissue
B. Cuboidal shape enhances function
C. Highly cellular and well vascularized
D. * Contains contractile units made of collagen
E. A force exerted by a muscle that is less than or equal to the resistance
1677.
Which of the following are elements of skeletal muscle contraction?
A. Cross-bridges binding
B. Myofibrils shortening
C. * Actin filaments sliding past myosin
D. All of the above
E. In the presence of ATP, the myosin head detaches from F-actin.
1678.
Which of the following characteristics is NOT correct about cardiac muscle?
A. Found only in the wall of the heart
B. Has striations
C. Single, centrally placed nucleus; cells branch
D. Cells bound end to end at intercalated disks
E. * Under voluntary control
1679.
Which of the following characteristics of skeletal cartilage limits its thickness?
A. It has a girdle of perichondrium that resists outward expansion when it is
compressed.
B. It is primarily composed of water.
C. It is avascular and receives most of its nourishment from the perichondrium that
surrounds it
D. * It is resilient.
E. All of the above
1680.
Which of the following factors does not influence success in sport?
A. Ability to tolerate heavy training without succumbing to illness or injury
B. Tactics
C. The diet
D. Skill
E. * Ingestion of carnitine during exercise
1681.
Which of the following is NOT correctly paired?
A. Columnar epithelium--lining of intestine
B. Fibrous connective tissue--tendons
C. * Elastic cartilage--end of long bones
D. Smooth muscles--walls of intestine
E. Neurons—brain
1682.
Which of the following is true?
A. Increasing the protein intake above 3 grams per kg body mass per day will
stimulate
B. * muscle growth and increase strength
C. Creatine supplements can increase muscle strength and power
D. Amino acid supplements can increase muscle strength and power
E. Muscle damage is induced by shortening contractions
F. There is an inverse relationship between dietary protein intake and total energy
intake
1683.
Which of the following organs protect underlying parts from physical trauma,
microbes, and water loss and help regulate body temperature?
A. Muscle
B. * Skin
C. Kidney
D. Small intestine
E. Lungs
1684.
Which of the following provides support for the body, attachment sites for
muscles, and protection for internal organs?
A. Skin
B. * Skeleton
C. Spinal cord
D. Joints
E. Blood
1685.
Which of the following statements best describes interstitial growth of cartilage?
A. Cartilage forming cells divide and secrete new matrix on the external surface of
the cartilage
B. It grows from the outside.
C. Cells in the perichondrium differentiate into chondroblasts.
D. * Chondrocytes divide and secrete new matrix from within the cartilage.
E. All of the above
1686.
Which of the following statements is true of connective tissue?
A. Elastin fibers are sometimes called white fibers
B. Reticular fibers form thick, ropelike structures
C. * Collagen fibers provide high tensile strength
D. When connective tissue is stretched, collagen gives it the ability to snap back
E. All of the above
1687.
Which of the following structures is made of elastic cartilage?
A. The epiglottis
B. The costal cartilage
C. The larynx
D. * Articular cartilage
E. None of the above
1688.
Which of the following tissues is attached by tendons to bone and has cells with
multiple nuclei and striations?
A. Tendons
B. Ligaments
C. Cardiac muscle
D. Smooth muscle
E. * Skeletal muscle
1689.
Which of the following types of connective tissue is MISMATCHED with its
matrix?
A. * Areolar—loosely packed matrix of protein fibers
B.
C.
D.
E.
Bone—mineralized matrix
Cartilage—highly vascular matrix
Blood—liquid matrix
None of the above
1690.
Which of these is NOT a connective tissue?
A. Blood
B. * Muscle
C. Cartilage
D. Areolar tissue
E. Skin
1691.
Which of these is not considered connective tissue?
A. Blood
B. * Muscle
C. Cartilage
D. Adipose
E. Bone
1692.
Which of these is NOT found in connective tissue?
A. Hyaluronic acid
B. * Basement membrane
C. Collagen fibers
D. Fluid
E. Reticular fibers
1693.
Which of these substances gives cartilage the ability to spring back after being
compressed?
A. Reticular fibers
B. Collagen fibers
C. Elastic fibers
D. * Proteoglycan aggregates
E. Adipocytes
1694.
Which of these tissue types does NOT contain collagen fibers?
A. Areolar connective tissue
B. Dense regular connective tissue
C. Skeletal muscle
D. Cartilage
E. * Bone
1695.
Which of these tissues has cells located in lacunae?
A. Adipose
B. Blood
C. Bone
D. * Cartilage
E. Both C and D
1696.
Which one among the following statement about smooth muscle is TRUE?
A. * The smooth muscles are responsible for the movements of the internal organs.
B. The cells in the smooth muscles have actin, but no striations.
C. The muscular cells in the smooth muscles are shorter than the skeletal muscles.
D. All of the above statements are true about the smooth muscle.
E. All of the above statements are incorrect about the smooth muscle.
1697.
Which one of the following is not a type of storage or transport connective tissue?
A. * Lymphocytes
B. Adipose tissue
C. Erythrocytes
D. All of the above are types of storage or transport connective tissue.
E. None of the above are types of storage or transport connective tissue.
1698.
Which one of the following is not a type of tissue?
A. Epithelial
B. Nervous
C. Connective
D. Muscle
E. * Endocrine
1699.
Which statement best describes connective tissue?
A. Usually lines a body cavity
B. Usually contains a large amount of matrix
C. Primarily concerned with secretion
D. * Always arranged in a single layer of cells
E. None of the above
1700.
Which term describes a band of dense regular connective tissue that attaches two
bones?
A. Aponeurosis
B. * Tendon
C. Ligament
D. Capsule
E. Vessels
1701.
Which two classes of cells are found in connective tissue proper?
A. Resident cells and wandering cells
B. * Mast cells and fibroblasts
C. Adipocytes and leukocytes
D. Macrophages and mesenchyme cells
E. Neitrofills and basofils
1702.
Which type of connective tissue has a matrix that has a white translucent (milk
glass) appearance and is found in the nose and at the ends of long bones?
A. Fibrocartilage
B. Elastic cartilage
C. * Hyaline cartilage
D. Spongy bone
E. Compact bone
1703.
Which type of connective tissue is found in tendons?
A. Loose connective tissue
B. * Fibrous connective tissue
C. Hyaline cartilage tissue
D. Elastic cartilage tissue
E. Compact bone tissue
1704.
Which type of tissue facilitates movement of the skeleton or organ walls?
A. Epithelial
B. * Muscular
C. Connective
D. Nervous
E. Blood
1705.
Which type of tissue has a rigid matrix of calcium salts deposited around protein
fibers, has lacunae containing osteocytes arranged in concentric circles, and is found
along the shaft of a long bone?
A. * Hyaline cartilage
B. Elastic cartilage
C. Fibrocartilage
D. Compact bone
E. Spongy bone
1706.
Which type of tissue will be found immediately below the skin and most epithelial
layers?
A. * Loose connective tissue
B. Adipose tissue
C. Fibrous connective tissue
D. Hyaline cartilage
E. Bone
1707.
Which types of junction will be found in heart and smooth muscle to ensure
synchronized contraction?
A. Tight junctions
B. Adhesion junctions (desmosomes)
C. * Gap junctions
D. Canaliculi
E. Basement membrane
1708.
With age of man in cartilaginous tissue goes down speed update of proteoglycans,
that results in diminishing degree hydratation of them and loss of resiliency in tissue.
Activity of which enzymes of lysosomes does rise here?
A. Deaminase, decarboxilase
B. Isomerase, dehydrogenase
C. Proteases, lipases
D. * Cathepsins, glicosydase
E. Oxidoreductase, phosphatases
1709.
Your heart is a muscle that is made up of highly specialized _______.
A. Cartilage
B. * Tissue
C. Ligaments
D. Red blood cells
E. Bone
1710.
Your skeletal muscles are also called
A. Smooth muscle
B. * Striated muscle
C. Better teeth
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
Real life situation questions
1. Conversion of deoxyuridine monophosphate to thymidine monophosphate is catalysed by
the enzyme:
A. Ribonucleotide reductase
B. * Thymidylate synthetase
C. CTP synthetase
D. Orotidylic acid decarboxylase
E. Thymidylate phosphatase
2. Conversion of uridine diphosphate into deoxyuridine diphosphate requires all the
following except
A. Ribonucleotide reductase
B. Thioredoxin
C. * Tetrahydrobiopterin
D. NADPH
E. Both C and D
3. CTP synthetase forms CTP from
A. CDP and inorganic phosphate
B. CDP and ATP
C. * UTP and glutamine
D. UTP and glutamate
E. UTP and ammonia
4. Cytosolic carbamoyl phosphate synthetase is activated by
A. Glutamine
B. * PRPP
C. ATP
D. Aspartate
E. Glutamate
5. Cytosolic carbamoyl phosphate synthetase is inhibited by
A. * UTP
B. CTP
C. PRPP
D. TMP
E. All of these
6. d-UMP is converted to TMP by
A. * Methylation
B. Decarboxylation
C. Reduction
D. Deamination
E. Oxidation
7. De novo synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides is regulated by
A. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase
B. Aspartate transcarbamoylase
C. * Both (A) and (B)
D. Arginase
E. None of these
8. Deoxycytidine kinase can salvage
A. Adenosine
B. Adenosine and deoxyadenosine
C. Adenosine and guanosine
D. * Adenine and adenosine
E. All of these
9. Deoxyribonucleotides are formed by reduction of
A. Ribonucleosides
B. Ribonucleoside monophosphates
C. * Ribonucleoside diphosphates
D. Ribonucleoside triphosphates
E. All of these
10. DNA does not contain
A. Thymine
B. Adenine
C. * Uracil
D. Deoxyribose
E. Both C and D
11. DNA is
A. Usually present in tissues as a nucleo protein nd cannot be separated from its
protein component
B. * A long chain polymer in which the internucleotide linkages are of the diester
type between C-3’ and C-5’
C. Different from RNA since in the latter the internucleotide linkages are between C2’ and C-5’
D. Hydrolyzed by weal alkali (pH9 to 100°C)
E. Both a and B
12. DNA rich in A-T pairs have
A. 1 Hydrogen bond
B. * 2 Hydrogen bonds
C. 3 Hydrogen bonds
D. 4 Hydrogen bonds
E. None of the above
13. DNA rich in G-C pairs have
A. 1 Hydrogen bond
B. 2 Hydrogen bonds
C. * 3 Hydrogen bonds
D. 4 Hydrogen bonds
E. None of the above
14. During de novo synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides, the first ring compound to be
formed is
A. Carbamoyl aspartic acid
B. * Dihydro-orotic acid
C. Orotic acid
D. Orotidine monophosphate
E. Aspartic acid
15. For de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides, aspartate provides
A. * Nitrogen 1
B. Nitrogen 3
C. Nitrogen 7
D. Nitrogen 9
E. Both A and B
16. For synthesis of CTP and UTP, the amino group comes from
A. Amide group of Asparagine
B. * Amide group of glutamine
C. ?-Amino group of glutamine
D. ?-Amino group of glutamate
E. Ammonia
17. For the synthesis of TMP from dump, a coenzyme is required which is
A. N10- Formyl tetrahydrofolate
B. N5- Methyl tetrahydrofolate
C. * N5, N10- Methylene tetrahydrofolate
D. N5- Formimino tetrahydrofolate
E. None of these
18. Free ammonia is liberated during the catabolism of
A. Cytosine
B. Uracil
C. Thymine
D. * All of these
E. None of these
19. Genetic information flows from
A. DNA to DNA
B. * DNA to RNA
C. RNA to cellular proteins
D. DNA to cellular proteins
E. RNA to RNA
20. Genetic information in human beings is stored in
A. * DNA
B. RNA
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. ATP
E. None of these
21. Gout is a metabolic disorder of catabolism of
A. Pyrimidine
B. * Purine
C. Alanine
D. Phenylalanine
E. Both A and B
22. Hypouricaemia can occur in
A. * Xanthine oxidase deficiency
B. Psoriasis
C. Leukaemia
D. All of these
E. None of these
23. In DNA molecule
A. Guanine content does not equal cytosine content
B. Adenine content does not equal thymine content
C. Adenine content equals uracil content
D. * Guanine content equals cytosine content
E. A and D are correct
24. In humans purine are catabolised to uric acid due to lack of the enzyme:
A. Urease
B. * Uricase
C. Xanthine oxidase
D. Guanase
E. Both A and B
25. In purine biosynthesis carbon atoms at 4 and 5 position and N at 7 position are
contributed by
A. * Glycine
B. Glutamine
C. Alanine
D. Threonine
E. THFA
26. In purine nucleus nitrogen atom at 1 position is derived from
A. * Aspartate
B. Glutamate
C. Glycine
D. Alanine
E. THFA
27. In the biosynthesis of purine nucleotides the AMP feed back regulates
A. Adenylosuccinase
B. * Adenylosuccinate synthetase
C. IMP dehydrogenase
D. HGPR Tase
E. Both B and C
28. Increased urinary excretion of orotic acid can occur in deficiency of
A. Orotate phosphoribosyl transferase
B. OMP decarboxylase
C. Mitochondrial ornithine transcarbamoylase
D. * Any of the above
E. Both A and B
29. Infantile convulsions due to lesser formation of gamma amino butyric acid from glutamic
acid is seen in the deficiency of
A. Glutamate-dehydrogenase
B. * Pyridoxine
C. Folic acid
D. Thiamin
E. Cobalamine
30. Inherited deficiency of adenosine deaminase causes
A. Hyperuricaemia and gout
B. Mental retardation
C. * Immunodeficiency
D. Dwarfism
E. Goiter
31. Inherited deficiency of purine nucleoside phosphorylase causes
A. Dwarfism
B. Mental retardation
C. * Immunodeficiency
D. Gout
E. All of these
32. Intestinal nucleosidases act on nucleosides and produce
A. Purine base only
B. Phosphate only
C. Sugar only
D. * Purine or pyrimidine bases and sugars
E. All of the above
33. Mammals other than higher primates do not suffer from gout because they
A. Lack xanthine oxidase
B. Lack adenosine deaminase
C. Lack purine nucleoside phosphorylase
D. * Possess uricase
E. Both c and D
34. Orotic aciduria can be controlled by
A. Oral administration of orotic acid
B. Decreasing the dietary intake of orotic acid
C. Decreasing the dietary intake of pyrimidines
D. * Oral administration of uridine
E. Both B and D
35. Progressive transmethylation of ethanolamine gives
A. Creatinine
B. Choline
C. * Methionine
D. N-methyl nicotinamide
E. Adenine
36. PRPP glutamyl amidotransferase, the first enzyme uniquely committed to purine
synthesis is feed back inhibited by
A. * AMP
B. IMP
C. XMP
D. CMP
E. All of these
37. Purine biosynthesis is inhibited by
A. * Aminopterin
B. Tetracyclin
C. Methotrexate
D. Chloramphenicol
E. Both B and C
38. Pyrimidine and purine nucleoside biosynthesis share a common precursor:
A. * PRPP
B. Glycine
C. Fumarate
D. Alanine
E. IMP
39. Ring closure of formimidoimidazole carboxamide ribosyl-5-phosphate yields the first
purine nucleotide:
A. AMP
B. * IMP
C. XMP
D. GMP
E. ATP
40. RNA does not contain
A. adenine
B. * OH methyl cytosine
C. d-ribose
D. Uracil
E. Both A and B
41. Tetrahydrofolate is required as a coenzyme for the synthesis of
A. UMP
B. CMP
C. * TMP
D. All of these
E. None of these
42. The cofactors required for synthesis of adenylosuccinate are
A. ATP, Mg++
B. ADP
C. * GTP, Mg++
D. GDP
E. AMP
43. The first pyrimidine nucleotide to be formed in de novo synthesis pathway is
A. * UMP
B. CMP
C. CTP
D. TMP
E. IMP
44. The following cannot be salvaged in human beings:
A. Cytidine
B. Deoxycytidine
C. * Cytosine
D. Thymidine
E. Both A and B
45. The mean intracellular concentration of ATP in mammalian cell is about
A. * 1 mM
B. 2 mM
C. 0.1 mM
D. 0.2 mM
E. 10 mM
46. The sugar moiety present in DNA is
A. * Deoxyribose
B. Ribose
C. Lyxose
D. Ribulose
E. Glucose
47. Transcription is the formation of
A. DNA from a parent DNA
B. mRNA from a parent mRNA
C. * pre mRNA from DNA
D. protein through mRNA
E. protein through DNA
48. Translation is the formation of
A. DNA from DNA
B. mRNA from DNA
C. * Protein through mRNA
D. mRNA from pre mRNA
E. Protein through DNA
49. UDP and UTP are formed by phosphorylation from
A. AMP
B. ADP
C. * ATP
D. GTP
E. All of these
50. UTP is converted to CTP by
A. Methylation
B. Isomerisation
C. * Amination
D. Reduction
E. Oxidation
51. Whcih of the following compound is present in RNA but absent from DNA?
A. Thymine
B. Cytosine
C. * Uracil
D. Guanine
E. Both A and B
52. Which of the following contains a deoxy sugar?
A. RNA
B. * DNA
C. ATP
D. UTP
E. AMP
53. Which of the following statements is correct?
A. a nucleo protein usually contain deoxy sugars of the hexose type
B. Nucleoproteins are usually absent from the cytoplasm
C. Nucleoproteins usually are present in the nucleus only
D. * Nucleoproteins usually occur in the nucleus and cytoplasm
E. Both B and D
54. 5-Phosphoribosyl-1-pyrophosphate is required for the synthesis of
A. Purine nucleotides
B. Pyrimidine nucleotides
C. * Both (A) and (B)
D. Uric acid
E. None of these
55. A drug which prevents uric acid synthesis by inhibiting the enzyme Xanthine oxidase is
A. Aspirin
B. * Allopurinal
C. Colchicine
D. Phenyl benzoate
E. All of these
56. A nitrogenous base that does not occur in mRNA is
A. * Cytosine
B. Thymine
C. Uracil
D. Both A and C
E. All of these
57. A purine nucleotide is
A. * AMP
B. UMP
C. CMP
D. TMP
E. Both A and B
58. A pyrimidine nucleotide is
A. GMP
B. AMP
C. CMP
D. IMP
E. C and D are correct
59. A synthetic nucleotide analogue, 4-hydroxypyrazolopyrimidine is used in the treatment
of
A. Acute nephritis
B. * Gout
C. Cystic fibrosis of lung
D. Multiple myeloma
E. Goiter
60. Acid hydrolysis of ribonucleic acid would yield the following major products:
A. d- deoxyribose, cytosine, adenine
B. d-ribose, thymine, Guanine
C. d-ribose, cytosine, uracil, thymine
D. * d-ribose, uracil, adenine, guanine, cytosine
E. Both B and D
61. Adenosine kinase can salvage
A. Adenosine
B. * Adenosine and deoxyadenosine
C. Adenosine and guanosine
D. Adenine and adenosine
E. All of these
62. Adjusting of purine nucleotides biosynthesis is carried out:
A. with c-AMP
B. with c-GMP and Ca2+
C. through a hypothalamus
D. with ATP
E. * with principle of feed back regulation with the usage of inhibitors such as IMP, AMP, GMP
63. Alanine is formed from catabolism of
A. Thymine
B. Thymine and cytosine
C. Thymine and uracil
D. * Cytosine and uracil
E. Adenine
64. Alimentary hyperuricemia, which can appear due to functioning of „salvage pathway” in
which excess of hypoxanthine transforms into:
A. Xanthine
B. Inosine
C. Uric acid
D. * Guanine
E. Uracil
65. Alkalis cannot hydrolyse
A. mRNA
B. tRNA
C. rRNA
D. * DNA
E. Both C and D
66. All below mentioned substances are components of pyrimidine nucleotides except:
A. Uracil
B. Thymine
C. Cytosine
D. Phosphoric acid
E. * Adenine
67. All of the following statements about uric acid are true except
A. It is a catabolite of purines
B. It is excreted by the kidneys
C. * It is undissociated at pH above 5.8
D. It is less soluble than sodium urate
E. Both C and D
68. All of the following statements about uric acid are true except
A. * It can be formed from allantoin
B. Formation of uric acid stones in kidneys can be decreased by alkalinisation of
urine
C. Uric acid begins to dissociate at pH above 5.8
D. It is present in plasma mainly as monosodium Urate
E. Both A and B
69. All the following statements about primary gout are true except
A. Its inheritance is X-linked recessive
B. It can be due to increased activity of PRPP synthetase
C. * It can be due to increased activity of hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl
transferase
D. De novo synthesis of purines is increased in it
E. Both C and D
70. Amount of uric acid which excreted daily is:
A. Not excreted
B. 10-12 g/day
C. 4-8 mg/day
D. * 270-600 mg/day
E. 2-5 g/day
71. AMP is an allosteric inhibitor of
A. PRPP synthetase
B. Adenylosucciante synthetase
C. * Both (A) and (B)
D. IMP dehydrogenase
E. None of these
72. An allosteric inhibitor of adenylosuccinate synthetase is
A. * AMP
B. ADP
C. GMP
D. GDP
E. All of these
73. An allosteric inhibitor of IMP dehydrogenase is
A. AMP
B. ADP
C. * GMP
D. GDP
E. ATP
74. An allosteric inhibitor of PRPP glutamyl amido transferase is
A. AMP
B. ADP
C. * GMP
D. All of these
E. None of these
75. An alternate substrate for orotate phosphoribosyl transferase is
A. Allopurinol
B. Xanthine
C. Hypoxanthine
D. * Adenine
E. None of these
76. An enzyme common to de novo synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides and urea is
A. Urease
B. * Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase
C. Aspartate transcarbamoylase
D. Argininosuccinase
E. None of these
77. An enzyme of pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis sensitive to allosteric regulation is
A. * Aspartate transcarbamoylase
B. Dihydroorotase
C. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
D. Orotidylic acid decarboxylase
E. A and B
78. An enzyme which acts as allosteric regulator and sensitive to both phosphate
concentration and to the purine nucleotides is
A. * PRPP synthetase
B. PRPP glutamyl midotransferase
C. HGPR Tase
D. Formyl transferase
E. PRPP transferase
79. At the initial stages of degradation the pyrimidine bases transform into:
A. ?-amino acids
B. * ?-amino acid
C. Acetic acid
D. Keto-acids
E. Biogenic amines
80. Biochemical index, which characterizes the genetic disorder of UMP biosynthesis is
following:
A. Aspartataciduria
B. * Orotaciduria
C. Gomogentisinuria
D. Uraciluria
E. Cytosinuria
81. Carbamoyl phosphate reacts with aspartate with formation:
A. Dihydroorotic acid
B. Orotic acid
C. Orotidine-5-phosphate
D. * Carbamoyl aspartate
E. UDP
82. Choose enzyme which catalyses the first reaction of pyrimidine nucleotides biosynthesis:
A. * Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase
B. Phosphoribosil transferase
C. Ornitine carbamoyl phosphattransferase
D. Aspartate aminotransferase
E. Alanine aminotransferase
83. Choose from following regulative enzyme of deoxyribonucleotides synthesis:
A. * Ribonucleotidreductase
B. Deoxyribonukleotidreductase
C. Nucleosidmonophosphatkinase
D. Nucleosidphosphorilase
E. ATP-ase
84. Choose precursor of pyrimidine nucleotide – uridine monophosphate:
A. * Orotidine-5-phosphate
B. Ribose-5-phosphate
C. Dihydroorotic acid
D. Uracil
E. Uridine
85. Choose substance which does not take part in formation of pyrimidine ring:
A. Carbamoyl phosphate
B. NH3
C. SO2
D. Aspartic acid
E. * Alanine
86. Choose substrates and products of the third reaction of biosynthesis of purine:
A. Ribosephosphateamine + ATP glycineamineribonucleotide
B. Ribosephosphateamine + ADP + pp ribosephosphate -aminodiphosphate
C. Ribosephosphateamine + ATP + glycine glycineamineribonucleotide
D. Glycine + glutamate + ATP glycineamineribonucleotide
E. Ribose-5-phosphate + ATP phosphoribosepyrophosphate
87. Choose the substance which gives the most atoms for purine ring:
A. aspartate
B. * glycine
C. glutamine
D. formyl -THF
E. CO2
88. Conversion of formylglycinamide ribosyl-5-phosphate to formyl-glycinamide ribosyl-5phosphate is inhibited by
A. * Azaserine
B. Diazonorleucine
C. 6-Mercaptopurine
D. Mycophenolic acid
E. Both A and B
89. Conversion of inosine monophosphate to xanthine monophosphate is catalysed by
A. * IMP dehydrogenase
B. Formyl transferase
C. Xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferase
D. Adenine phosphoribosyl transferase
E. Xanthine oxydase
90. Cyclic AMP can be formed from
A. AMP
B. ADP
C. * ATP
D. GTP
E. All of these
91. Daily uric acid excretion in adult men is
A. 2–6 mg
B. 20–40 mg
C. 150–250 mg
D. * 40–600 mg
E. 2-6 g
92. De novo synthesis of purine nucleotide occurs in
A. Mitochondria
B. * Cytosol
C. Microsmes
D. Ribosomes
E. Nucleus
93. De novo synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides occurs in
A. Mitochondria
B. * Cytosol
C. Microsomes
D. Ribosomes
E. Nucleus
94. Decarboxilation of which substance results in formation of uridylic acid?
A. * Orotidilic acid
B. Dihydroorotic acid
C. Orotic acid
D. Carbamoyl aspartate
E. Carbamoyl phosphate
95. Deficiency of all the followings substances causes disorders of pyrimidine nucleotides
synthesis except:
A. Glutamine
B. Aspartate
C. CO2
D. * FAD
E. Ribose-5-phosphate
96. Deficiency of which of below mentioned enzyme causes orotaciduria?
A. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase ІІ
B. Aspartate carbamoyl transferase
C. * Orotate phosphoribosyl transferase
D. Orotate carboxylase
E. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
97. Deposition of uric acid crystals in joints results in development of such desease:
A. Pellagra
B. Diabetes mellitus
C. Xanthinuria
D. * Gout
E. Alkaptonuria
98. Dietary purines are catabolised in
A. Liver
B. Kidneys
C. * Intesitnal mucosa
D. Brain
E. All of these
99. Difference of synthesis of purine nucleotides „De novo” from the salvage pathway of
biosynthesis:
A. a salvage pathway takes place in the liver
B. a synthesis „De novo” is in the extrahepatic tissues
C. * a salvage pathway converts free purine bases (hypoxantine, guanine) to IMP
and GMP
D. a salvage pathway is longer
E. a salvage pathway is not regulated
100.
Disintegration of nucleic acids in small intestine requires such enzymes:
A. Lipase
B. * DNA and RNA-аse
C. Amylase
D. Glucose-6-phosphatese
E. Alcoholdehydrogenase
101.
Disintegration of pyrimidine bases via some intermediate transformations leads to
synthesis of:
A. Pyruvic acid, glycine.
B. * Urea, acetic acid, CO2
C. NH3, CO2
D. Uric acid, NH3.
E. NH3, urea.
102.
Disorders of pyrimidine nucleotides biosynthesis inhibit all process except:
A. Biosynthesis of DNA
B. Biosynthesis of m-RNA
C. * Transport of amino acid through cell’s membranes
D. Transport of amino acid from a cytoplasm to ribosomes
E. Biosynthesis of proteins
103.
Disorders of pyrimidine nucleotides synthesis take place at blocking of primary
synthesis one of them. Choose this nucleotide:
A. * UMP
B. CMP
C. TMP
D. AMP
E. GMP
104.
Double helical structure model of the DNA was proposed by
A. Pauling and Corey
B. Peter Mitchell
C. * Watson and Crick
D. King and Wooten
E. Horbachevsky
105.
dАТP, dGТP, dТТP, dCТP are used for the DNA synthesis. Choose precursors of
these substanses:
A. * Ribonucleotides
B. Products of nucleic acids degradation
C. Purines and pyrimidines, deoxyribose and phosphoric acid
D. Products of absorption in the intestine
E. Ribose at its reduction in composition of DNK
106.
For de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides, glycine provides
A. One nitrogen atom
B. One nitrogen and one carbon atom
C. Two carbon atoms
D. * One nitrogen and two carbon atoms
E. Three carbon atoms
107.
For DNA biosynthesis are used dАТP, dGТP, dТТP, dCТP. Which enzyme
catalyses their synthesis from nucleosidmonophosphates?
A. Phosphorylase
B. * Kinase
C. Phosphatase
D. Phosphodiesterase
E. Phosphoglucomutase
108.
For modification of inosine monophosphate into guanosine monophosphate is
necessary:
A. aspartate
B. glycine
C. * glutamine
D. urea
E. uric acid
109.
For the synthesis of DNA followings nucleosidphosphates is used except:
A. dАТP
B. * dUТP
C. dGТP
D. dCТP
E. dТТP
110.
For the synthesis of pyrimidine bases used all substanses except:
A. NH3
B. CO2
C. ATP
D. N2O
E. * H2SO4
111.
For transformation of inosine monophosphate to adenylate NH2 is needed. The
donor of it is:
A. glycine
B. * aspartate
C. glutamine
D. serine
E. methionine
112.
Formation of deoxyribonucleotides takes place with reduction of OH-group C-2
ribose with coenzyme:
A. * NADPH
B. NADH
C. FADH2
D. TPP
E. HSCoA
113.
Four atoms of nitrogen are in purine ring. Which amino acid gives a nitrogen atom
for purine synthesis?
A. alanine
B. methionine
C. * aspartate
D. glutamate
E. serine
114.
Free purine bases which can be salvaged are
A. Adenine and guanine
B. Adenine and hypoxanthine
C. Guanine and hypoxanthine
D. * Adenine, guanine and hypoxanthine
E. Hypoxanthine
115.
Genetic information originates from
A. * Cistron of DNA
B. Codons of mRNA
C. Anticodons of tRNA
D. Histones of nucleoproteins
E. All of these
116.
GMP is an allosteric inhibitor of all the following except
A. PRPP synthetase
B. PRPP glutamyl amido synthetase
C. IMP dehydrogenase
D. * Adenylosuccinate synthetase
E. Both C and D
117.
Gout is characterized by increased plasma levels of
A. Urea
B. * Uric acid
C. Creatine
D. Creatinine
E. Ammonia
118.
high energy intermediate is
A. ATP
B. UTP
C. * UDPG
D. CMP
E. AMP
119.
How uric acid excretes from an organism?
A. With saliva
B. With feces
C. With sweat
D. * With urine
E. With hepato-enteral circulation
120.
If the amino group and a carboxylic group of the amino acid are attached to same
carbon atom, the amino acid is called as
A. * Alpha
B. Beta
C. Gamma
D. Epsilon
E. Delta
121.
In DNA, the complementary base of adenine is
A. Guanine
B. Cytosine
C. Uracil
D. * Thymine
E. Adenine
122.
In humans end product of purine catabolism is
A. * Uric acid
B. Urea
C. Allantoin
D. Xanthine
E. Ammonia
123.
In inherited deficiency of hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase
A. De novo synthesis of purine nucleotides is decreased
B. * Salvage of purines is decreased
C. Salvage of purines is increased
D. Synthesis of uric acid is decreased
E. All of these
124.
In mammals other than higher primates uric acid is converted by
A. * Oxidation to allantoin
B. Reduction to ammonia
C. Hydrolysis to ammonia
D. Hydrolysis to allantoin
E. None of the above
125.
In nucleotides, phosphate is attached to sugar by
A. Salt bond
B. Hydrogen bond
C. * Ester bond
D. Glycosidic bond
E. Peptide bond
126.
In purine biosynthesis ring closure in the molecule formyl glycinamide ribosyl-5phosphate requires the cofactors:
A. ADP
B. NAD
C. FAD
D. * ATP and Mg++
E. AMP
127.
In the pathway of de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides, all the following are
allosteric enzymes except
A. PRPP glutamyl amido transferase
B. Adenylosuccinate synthetase
C. IMP dehydrogenase
D. * Adenylosuccinase
E. Both A and D
128.
In the purine nucleus, carbon 6 is contributed by
A. Glycine
B. * CO2
C. Aspartate
D. Glutamine
E. THFA
129.
In which process mononucleotides does not take part?
A. Synthesis of nucleic acids
B. Formation of nucleotide coenzymes
C. Realization of genetic information
D. Form the products of nitrogenous (nucleic) metabolism
E. Treatment of gout
130.
Inheritance of primary gout is
A. Autosomal recessive
B. Autosomal dominant
C. * X-linked recessive
D. X-linked dominant
E. None of these
131.
Inhibitors of deoxyribonucleotides synthesis are the followings factors:
A. dАТP
B. Structural analogues of pyrimidines
C. Structural analogues of purines
D. Structural analogues of folic acid
E. * All above named
132.
Inosine monophophate is an intermediate during the de novo synthesis of
A. * AMP and GMP
B. CMP and UMP
C. CMP and TMP
D. ATP and AMP
E. All of these
133.
Intermediate products of disintegration of purine nucleotides – xanthine and
hypoxanthine are products of metabolism:
A. TMP and ADP
B. * AMP and GMP
C. CTP and ATP
D. CTP and GTP
E. CTP and TMP
134.
Last reaction of uric acid synthesis catalyses such enzyme:
A. 5-nucleotides
B. Adenosine deaminase
C. * Xantine oxidase
D. Guanine deaminase
E. Phosphorylase
135.
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome, the sex linked recessive disorder is due to the lack of the
enzyme:
A. * Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyl transferse
B. Xanthine oxidase
C. Adenine phosphoribosyl transferase
D. Adenosine deaminase
E. Both A and B
136.
Medicine, which is used for treatment of gout is the structural analogue of
hypoxanthine, it:
A. Salts of lithium
B. Anturan
C. * Allopyrinol
D. Uridine
E. Acetilisoniazid
137.
Methotrexate blocks the synthesis of thymidine monophosphate by inhibiting the
activity of the enzyme:
A. * Dihydrofolate reductase
B. Orotate phosphoribosyl transferase
C. Ribonucleotide reductase
D. Dihydroorotase
E. Orotate reductase
138.
N10-formyl and N5N10-methenyl tetrahydrofolate contributes purine carbon
atoms at position
A. 4 and 6
B. 4 and 5
C. 5 and 6
D. * 2 and 8
E. 2 and 3
139.
Name a coenzyme which takes part in transformation of dihydroorotic acid to
orotic acid:
A. FAD
B. FMN
C. * NAD
D. PLP
E. TDPK
140.
Name an enzyme which catalyzes oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and
xanthine to uric acid:
A. Phosphorylase
B. Isocitratdehydrogenase
C. Succcinatdehydrogenase
D. Cytochromoxidase
E. Xanthineoksidase
141.
Name nitrogen bases that enter into the structure of DNA:
A. Guanine, uracil, thymine
B.
C.
D.
E.
Cytosine, uracil, thymine
Uracil, adenine, guanine
* Adenine, thymine, guanine
Thymine, adenine, uracil
142.
Name nitrogenous bases included into the structure of RNA:
A. Guanine, uracil, thymine
B. Cytosine, adenine, thymine
C. * Uracil, adenine, guanine
D. Adenine, thymine, guanine
E. Thymine, adenine, uracil
143.
Name products of nucleoproteins digesting:
A. Carbohydrates and lipids
B. Lipids and nucleic acids
C. Proteins and nucleic acids
D. Lipids and proteins
E. Carbohydrates and proteins
144.
Name substances, necessary for formation of substrate for synthesis of pyrimidine
bases - carbamoyl phosphate:
A. Urea, ATP
B. ?-alanine, SO2
C. Phosphoribosilpyrophosphate, orotic acid
D. * CO2, Ammonia, ATP
E. Aspartic acid, CO2
145.
Name the first reaction of biosynthesis of purine nucleotides:
A. Reaction of ribose-5-phosphate with glycine
B. * Reaction of ribose-5-phosphate with ATP
C. Reaction of aspartate and THFA
D. Condensation of pyrimidine and diazole rings with formation of purine
E. Reaction of AMF with ribose-5-phosphate
146.
Name the structural monomers of DNA molecule:
A. * Mononucleotides
B. Nucleosides
C. Nitric bases
D. Polynucleotides
E. Peptides
147.
Name the substrate for synthesis of pyrimidine bases:
A. Cytosine
B. Ornithine
C. * Carbamoyl phosphate
D. Citrate
E. Fumarate
148.
Nitrogen at position 1 of pyrimidine nucleus comes from
A. Glutamine
B. Glutamate
C. Glycine
D. * Aspartate
E. Asparagine
149.
Nitrogen at position 3 of pyrimidine nucleus comes from
A. * Glutamine
B. Glutamate
C. Glycine
D. Aspartate
150.
151.
152.
153.
154.
155.
156.
157.
158.
E. Ammonia
Nitrogenous bases are used for the synthesis of such substances as?
A. Cholesterol
B. Carbohydrates
C. Catecholamines
D. * Nucleic acids
E. Fatty acids
Normal level of uric acid in blood is:
A. * 0,12-0,46 mmol/l
B. 1,7-2,05 mmol/l
C. 20-40 grammes/л
D. 3,3-5,5 mmol/l
E. 3-8 mmol/l
Nucleic acids are:
A. Mononucleotides
B. Nucleosides
C. Nucleoproteins
D. * Polynucleotides
E. Dinucleotides
Nucleotides required for the synthesis of nucleic acids can be obtained from
A. Dietary nucleic acids and nucleotides
B. De novo synthesis
C. Salvage of pre-existing bases and nucleosides
D. * De novo synthesis and salvage
E. Both A and B
Orotaciduriya is accompanied the followings symptoms:
A. Dermatitis of the opened areas of body
B. Bleeding, disorders of growth
C. Disorders of mental development, galactosemia
D. * Disorders of physical and mental development, megaloblastic anemia
E. Diarrhea, dermatitis, demention
Orotic aciduria type II reflects the deficiency of the enzyme:
A. Orotate phosphoribosyl transferase
B. * Orotidylate decarboxylase
C. Dihydroorotase
D. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
E. Both B and C
Phosphodiesterases of intestinal mucous are able to split nucleic acids to:
A. Dipeptides
B. Phosphoric acid, pentoses and nitrogenous bases
C. Riboses and desoxyriboses
D. * Mononucleotides
E. Amino acid and phosphoric acid
Phosphorylation of adenosine to AMP is catalysed by
A. * Adenosine kinase
B. Deoxycytidine kinase
C. Adenylosuccinase
D. Adenylosuccinate synthetase
E. Adenosine phosphorylase
presence of
A. NAD
B. FMN
C. HS-CoA
D. * B6-PO4
E. FAD
159.
Protein part of nucleoproteins disintegrates to:
A. Enzymes
B. Pentoses
C. Phosphoric acid
D. Nitrogenous bases
E. Amino acids
160.
PRPP synthetase is allosterically inhibited by
A. AMP
B. ADP
C. GMP
D. * All of these
E. None of these
161.
Purin consists of the condensed rings of two heterocycles – pyrimidine and
imidazole. Which substance gives nitrogen atoms simultaneously for pyrimidine and
imidazole rings:
A. aspartate
B. formyl
C. methenil -THF
D. glycine
E. * glutamine
162.
Pyrimidine biosynthesis begins with the formation from glutamine, ATP and
CO2, of
A. Carbamoyl aspartate
B. Orotate
C. * Carbamoyl phosphate
D. Dihydroorotate
E. Both A and C
163.
Reaction of reduction of C-2 ribose OH-group in biosynthesis of
deoxyribonucleotides catalyses an enzyme:
A. Glutatione reductase
B. CоQ-cytochrom в-reductase
C. * Ribonucleotide reductase
D. Folatreductase
E. Deoxyribonucleotid-reductase
164.
Reduction of ribonucleotide diphosphates (NDPs) to their corresponding
deoxyribonucleotide diphosphates (dNDPs) involves
A. FMN
B. FAD
C. NAD
D. * NADPH
E. PLP
165.
Salvage of purine bases is regulated by
A. Adenosine phosphoribosyl transferase
B. Hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase
C. * Availability of PRPP
D. All of these
E. None of these
166.
Synthesis of purine nucleotides requires low-molecular precursors, products of
metabolism:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Lipids and proteins
* Carbohydrates and proteins
Enzymes and vitamins
Lipids and carbohydrates
Lipids and vitamins
167.
Synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides is inhibited with the following substanse:
A. GMP
B. AMP
C. cАМP
D. * UMP
E. ATP
168.
The ‘transforming factor’ discovered by Avery, McLeod and McCarty was later
found to be
A. mRNA
B. tRNA
C. * DNA
D. Nucleotide
E. None of these
169.
The atoms of what connections do not enter in the complement of pyrimidine,
condensed into purine:
A. glutamine
B. * methenil THF
C. glycine
D. CO2
E. Formyl-THF
170.
The available PRPP is used preferentially for
A. De novo synthesis of purine nucleotides
B. De novo synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides
C. * Salvage of purine bases
D. Salvage of pyrimidine bases
E. Both C and D
171.
The carbon atom at position 2 of pyrimidine nucleus is contributed by
A. * CO2
B. Glycine
C. Aspartate
D. Glutamine
E. None of these
172.
The carbon atoms of pyrimidine nucleus are provided by
A. Glycine and aspartate
B. * CO2 and aspartate
C. CO2 and glutamate
D. CO2 and glutamine
E. Aspartate
173.
The carbon of the pentose in ester linkage with the phosphate in a nucleotide
structure is
A. C1
B. C3
C. C4
D. * C5
E. C2
174.
The chemical name of guanine is
A. 2,4-Dioxy-5-methylpyrimidine
B.
C.
D.
E.
175.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
176.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
177.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
178.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
179.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
180.
by
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
181.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
182.
A.
B.
C.
D.
* 2-Amino-6-oxypurine
2-Oxy-4-aminopyrimidine
2, 4-Dioxypyrimidine
None of the above
The coenzyme of uracildehydrogenase is:
FAD
PLP
Coenzyme A
* NAD
FMN
The constant increase of uric acid concentration in blood is named:
Uremia
Hyperazotemiya
Hyperacidaminemiya
Hyperlaktatemiya
Hyperuricemia
The correct sequence of the reactions of catabolism of adenosine to uric acid is
Adenosine>hypoxanthine>xanthine>uricacid
Adenosine>xanthine>inosine>uric acid
* Adenosine>inosine>hypoxanthine>?xanthine>uric acid
Adenosine>xanthine>inosine>hypoxanthine>uric acid
Adenosine>inosine>>uric acid
The degradation of RNA by pancreatic ribonuclease produces
Nucleoside 2-Phosphates
Nucleoside 5-phosphates
Oligonucleosides
* Nucleoside 3-phosphate and oligonucleotide
Both C and D
The end product of purine catabolism in man is
Inosine
Hypoxanthine
Xanthine
* Uric acid
Urea
The enzyme aspartate transcarbamoylase of pyrimidine biosynthesis is inhibited
ATP
ADP
AMP
* CTP
GMP
The enzyme common to catabolism of all the purines is
Adenosine deaminase
* Purine nucleoside phosphorylase
Guanase
All of these
None of these
The enzyme required for salvage of free purine bases is
Adenine phosphoribosyl transferase
Hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase
* Both (A) and (B)
PRPP synthetase
E. None of these
183.
The fact that DNA bears the genetic information of an organism implies that
A. Base composition should be identical from species to species
B. DNA base composition should charge with age
C. * DNA from different tissues in the same organism should usually have the same
base composition
D. DNA base composition is altered with nutritional state of an organism
E. Both a and C
184.
The first reaction unique to purine nucleotide synthesis is catalysed by
A. PRPP synthetase
B. * PRPP glutamyl amido transferase
C. Phosphoribosyl glycinamide synthetase
D. Formyl transferase
E. None of these
185.
The first true pyrimidine ribonucleotide synthesized is
A. UMP
B. UDP
C. TMP
D. CTP
E. AMP
186.
The following abnormality in PRPP synthetase can cause primary gout:
A. High Vmax
B. Low Km
C. Resistance to allosteric inihbition.
D. * All of these
E. None of these
187.
The following coenzyme is required for catabolism of pyrimidine bases:
A. NADH
B. * NADPH
C. FADH2
D. PLP
E. None of these
188.
The following compounds are formed in complete hydrolysis of nucleic acids,
except:
A. Phosphoric acid
B. Pentoses
C. Purine bases
D. * Acetic acid
E. Adenine
189.
The four nitrogen atoms of purines are derived from
A. Urea and NH3
B. NH3, Glycine and Glutamate
C. NH3, Asparate and Glutamate
D. * Aspartate, Glutamine and Glycine
E. Ammonia and Glutamine
190.
The genetic disorder of UMP synthesis often blocks such process:
A. Formation of carbamoylphospate
B. Reaction of carbamoylphospate with aspartate
C. Oxidation of dihydroorotic acid
D. * Formation of orotidilyc acid from orotic
E. Decarboxilation of orotidilyc acid
191.
The key substance in the synthesis of purine, phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate is
formed by
A. * D-ribose 5-phosphate
B. 5-phospho -ribosylamine
C. D-ribose
D. Deoxyribose
E. D-ribose 3-phosphate
192.
The major catabolic product of pyrimidines in human is
A. * Alanine
B. Urea
C. Uric acid
D. Guanine
E. All of these
193.
The major determinant of the overall rate of denovo purine nucleotide
biosynthesis is the concentration of
A. * 5-phosphoribosyl 1-pyrophosphate
B. 5-phospho D-ribosylamine
C. Glycinamide ribosyl-5-phosphate
D. Formylglycinamide ribosyl-5-phosphate
E. Glucose
194.
The nitrogen atoms for de novo synthesis of purine nucleotides are provided by
A. Aspartate and glutamate
B. Aspartate and glycine
C. * Aspartate, glutamine and glycine
D. Aspartate, glutamate and Glycine
E. THFA
195.
The nitrogen atoms of pyrimidine nucleus are provided by
A. Glutamate
B. Glutamate and aspartate
C. Glutamine
D. * Glutamine and aspartate
E. Ammonia
196.
The possible reason of uric acid excretion decrease:
A. Action of ionizing an radiation
B. * Kidney insufficiency
C. Leucosis
D. Burns
E. Malignant tumor
197.
The precursor of ?-alanine in the reactions of pyrimidine bases disintegration is:
A. Dihydrouracil
B. Uracil
C. * ? -ureidpropionic acid
D. Thymine
E. Cytosine
198.
The product of disintegration of thymine is:
A. ?–alanine
B. Dihydrouracil
C. * ? -aminoisobutyrate
D. Uredoisobutyrate
E. Ant acid
199.
The products of pyrimidine nucleotides disintegration are:
A. * ?-alanine, SO2, NH3, ?-aminoisobutyrate.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Ribose, SO2.
Urinary acid, N2O.
Hypoxanthine, FADH2
? -ureidpropionic acid
200.
The reactions of uric acid synthesis take place mainly in:
A. * Cytoplasm of hepatocytes
B. Mitochondria of myocytes
C. Nucleus of hepatocytes
D. Cytoplasm of kidney’s cells
E. Lysosomes of adrenal’s cells
201.
?The structural monomers of nucleic acids are:
A. * Mononucleotides
B. Oligonucleotides
C. Dinukleotides
D. Threenucleotides
E. c-AMP
202.
The two nitrogen of the pyrimidine ring are contributed by
A. Ammonia and glycine
B. * Asparate and carbamoyl phosphate
C. Glutamine and ammonia
D. Aspartate and ammonia
E. Ammonia and ammonia
203.
Thymidine nucleotide is a structural component of DNA, which formed from
dUМP with:
A. Hydroxylating
B. Amination
C. Phosphorylating
D. * Metilation
E. Hydrolysis
204.
Thymidine nucleotide is a structural component of DNA, which formed from
dUМP with metilation of uracil. What is the source of methyl group in this process?
A. Methionine
B. Valine
C. Creatine
D. * Methylentetrahydrofolic acid
E. Methylcyanocobalamin
205.
Thymine is present in
A. * tRNA
B. Ribosomal RNA
C. Mammalian mRNA
D. Prokaryotic mRNA
E. All of these
206.
Uracil and ribose form
A. * Uridine
B. Cytidine
C. Guanosine
D. Adenosine
E. Uric acid
207.
Uracil is formed in reaction of such substance decarboxilation :
A. * Orotic acid
B. Aspartic acid
C. Serine
D. Glutamine
E. Histidine
208.
Which of the following is not an essential attribute that a biological molecule
would need to be a useful genetic material?
A. * It must carry all of the information needed to direct the specific organization
and metabolic activities of the cell
B. It must replicate accurately so that the information it contains is precisely
inherited by the daughter cells
C. It must be capable of undergoing occasional mutations, such that the information
it carries is altered in a heritable way
D. It must have highly repetitive DNA sequences.
E. All are essential attributes of useful genetic material.
209.
____ regulate which genes or subsets of genes are transcribed in a particular cell
type.
A. * Transcription factors
B. Chaperone proteins
C. RNA polymerases
D. Transcription is not regulated
E. All of the above
210.
_______________ join DNA fragments to the lagging strand.
A. A.Telomeres
B. Centromeres
C. Helicase
D. * Ligases
E. Antiparallel strands
211.
A DNA strand with the sequence AACGTAACG is transcribed. What is the
sequence of the mRNA molecule synthesized?
A. AACGTAACG
B. UUGCAUUGC
C. AACGUAACG
D. * TTGCATTGC
E. None of the above
212.
A molecule of DNA is a polymer composed of
A. Glucose
B. Amino acids
C. Fatty acids
D. * Nucleotides
E. Vitamins
213.
A reaction of the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids in the process
of translation is catalyzed by:
A. * Peptydyltransferase
B. Aminoacylsynthetase
C. Peptidylligase
D. Peptidase
E. Peptydylhydrolase
214.
According to Chargaff's rule, the following proportion exists in DNA
A. * C=G
B. C»T
C. C»G
D. C=T
E. None of the above
215.
All of the below mentioned are the components of the protein synthesis system,
except:
A. Ribosomes
B. m-RNA
C. t-RNA
D. Regulatory proteins
E. * DNA
216.
Amino acid during synthesis of proteins bounds to the:
A. * 33-end of t-RNA
B. Anticodon
C. Codon
D. 55-end of t-RNA
E. 33-end of m-RNA
217.
Areas of a eukaryotic gene that are represented in the final protein product are
termed __________.
A. Introns
B. Mutons
C. Recons
D. * Exons
E. Cistrons
218.
Binding of RNA-polymerase to DNA-matrix takes place in specific areas of
genome. What is the name of these areas?
A. Active centers
B. Contact areas
C. * Promotors
D. Catalytic areas
E. There is not correct answer
219.
Biosynthesis of proteins is related to the following organelles:
A. Mitochondria
B. Lysosomes
C. Microsomes
D. Endoplasmic reticulum
E. * Ribosomes and nucleus
220.
By convention, the sequence of bases in a nucleic acid is usually expressed in the
_________ direction
A. 3' to 1'
B. 3' to 5'
C. 1' to 3'
D. * 5' to 3'
E. Clockwise
221.
By which mechanism the synthesis of RNA is inhibited by actinomycin D?
A. * Penetration inside the double strand of DNA between G-C with local
deformation of DNA matrix
B. Inhibition of RNA synthesis initiation
C. Associates with A-subunit
D. Ingibition of elongation process of RNA synthesis
E. Oppression of synthesis of matrix RNA
222.
Clusters of highly repetitive DNA located near the centromeres and telomeres are
called
A. * Nucleosomes
B. Euchromatin
C. Chromatids
D. Heterochromatin
E. 30 nm chromatin
223.
Codons are composed of:
A. * Triplet sequences of nucleotide bases in mRNA
B. Triplet sequences of nucleotide bases in DNA
C. Triplet sequences of amino acids in polypeptide chains
D. Triplet sequences of deoxyribose sugars in DNA
E. None of the above
224.
Common mechanisms of action of tetracyclin, streptomycin and levomycitin:
A. All these antibiotics ingibit replication
B. All these antibiotics ingibit transcription
C. * All these antibiotics ingibit translation
D. All these antibiotics stimulate the synthesis of protein
E. All these antibiotics ingibit posttraslation modifications of protein
225.
Conformity of A-T, G-C in the DNA molecule is defined as a rule of:
A. Watson
B. Crick
C. * Chargaphe
D. Jakob
E. Starling
226.
Decide whether each statement is true (T) or false (F). Place your answer in the
blank space given. A. A-T is a possible base pair in a DNA molecule.
A. * A-C is a possible base pair in a DNA molecule
B. C-A is a possible base pair in a DNA molecule.
C. A-G is a possible base pair in a DNA molecule.
D. G-A is a possible base pair in a DNA molecule.
227.
DNA is made up of a phosphate group, an organic base, and:
A. A protein
B. * A sugar
C. A molecule of ATP
D. A fat
E. None of the above
228.
DNA replication is called semiconservative because _______________ of the
original duplex appears in the duplex formed in replication.
A. * None
B. Most
C. Half
D. Hardly any
E. All
229.
DNA–polymerase can show except polymerase activity:
A. * Exonuclease activity
B. Endonuclease activity
C. Intranuclease activity
D. Glyconuclease activity
E. Liponuclease activity
230.
Each individual zone of a chromosome replicates as a discrete section called
A. Telomere
B. Euchromatin
C. * Okazaki fragment
D. Replication unit
E. Linker DNA
231.
Each unit of a nucleic acid consisting of a sugar, attached phosphate group, and
base is a
A. Nucleolus
B. * Nucleotide
C. Nucleosome
D. Histone
E. Genetisome
232.
Enzyme which catalyses replication of both chains in eukaryotes:
A. DNA – polymerase 4
B. * DNA – polymerase A
C. DNA – polymerase D
D. DNA – polymerase D
E. DNA – ligase
233.
First stage of proteins biosynthesis – activation of amino acids is catalyzed by:
A. Aminoacyl-kinase
B. Aminoacyl- transferases
C. Aminoacyl-t-RNA- hydrolases
D. * Aminoacyl-t-RNA- synthetases
E. Аміноаcyl-t-RNA- lyases
234.
For the activation of amino acids in the first stage of proteins biosynthesis the
following ion is needed:
A. Ca2+
B. Na+
C. K+
D. ClE. * Mg2+
235.
For the process of transcription the followings components are needed, except:
A. DNA-matrix
B. DNA-depending-RNA-polymerase
C. Nucleoside triphosphates
D. Ions of Mg2+
E. * Ions of Zn2+
236.
Genetic code is informative only when it is read in direction:
A. 55 – 3
B. From right to left
C. Direction is not important
D. 33 – 4
E. * 33 – 5
237.
Give the definition of transcription term:
A. * A biosynthesis of RNA on DNA-matrix
B. Synthesis of daughter molecules of DNA
C. Synthesis of proteins, the amino acid sequence of which is determined by the
nucleotide sequence of mRNA
D. Enzymatic deleting and repeating synthesis of areas of DNA
E. Moving of gene or groups of genes
238.
How does protein synthesis begin?
A. * The cell divides
B. Multiple cells join
C. The DNA unzips
D. The DNA zips up
E. Nothing happens
239.
How many combinations of DNA nitrogen bases are possible in a DNA triplet
code?
A. * 20
B. 32
C. 64
D. 128
E. 19
240.
How many molecules of histons does a nucleus of every nucleosome have?
A. 2
B. 4
C. 6
D. * 8
E. 10
241.
If one side of a DNA molecule contains the following sequence of nucleotides,
AGTCCG, the complementary sequence on the other side would be:
A. GCCTGA
B. AGTCCG
C. * TCAGGC
D. CTGAAT
E. None of the above
242.
In a double stranded molecule of DNA, the ratio of purines : pyrimidines is:
A. Variable
B. Determined by the base sequence in RNA
C. Genetically determined
D. * Always 1:1
E. Determined by the number of purines in the sense strand of the DNA
243.
In DNA guanine always pairs with
A. Adenine
B. Cytosine
C. Guanine
D. * Thymine
E. Uracil
244.
In DNA, thymine always pairs with
A. * Adenine
B. Cytosine
C. Guanine
D. Thymine
E. Uracil
245.
In nucleic acids, the free hydroxyl group is attached to the _______________
carbon of the sugar.
A. 5'
B. 4'
C. * 3'
D. 2'
E. 1'
246.
In nucleic acids, the phosphate group is attached to the ___ carbon of the sugar.
A. * 5'
B. 4'
C. 3'
D. 2'
E. 1'
247.
In replication of DNA, the helix is opened and untwisted by
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Ribase
Ligase
Deoxase
* Helicase
Polymerase
248.
In the DNA molecule:
A. * Adenine pairs with thymine
B. Guanine pairs with thymine
C. Cytosine pairs with thymine
D. Adenine pairs with cytosine
E. All of the above are possible.
249.
In the process of elongation there is untwisting of the double-helical DNA areas
with formation of the bonds in polyribonucleotide chain. What bonds are formed?
A. 1,6-glycosidic
B. B-1,4- glycosidic
C. * 3'-5'- phosphodiester
D. Disulfide
E. Ionic
250.
Indicate the difference between RNA transcription and DNA replication:
A. * In RNA transcription as a matrix only 1 chain of DNA is used
B. In RNA transcription as a matrix 2 chains of DNA are used
C. In RNA transcription ions of Zn2+ are necessary
D. In RNA transcription the factors of replisome are necessary
E. In RNA transcription the whole DNA molecule is transcribed
251.
Initiation aminoacyl-t-RNA in eukaryotes is:
A. Alanine-t-RNA
B. Histidine –t-RNA
C. * Methionine –t-RNA
D. Glycine- t-RNA
E. Cysteine- t-RNA
252.
lustersWhat is the percentage of thymine in the DNA molecule, if the content of
cytosine is 22%?
A. 38
B. * 28
C. 22
D. 44
E. 11
253.
Main enzyme which catalyzes the reaction of synthesis of both chains of DNA in
prokaryotes:
A. DNA - ligase
B. DNA – polymerase D
C. DNA - synthetase
D. * DNA - polymerase 3
E. DNA - ligase 5
254.
Name nitrogen bases that enter to the structure of DNA:
A. Guanine, uracil, thymine
B. Cytosine, uracil, thymine
C. Uracil, adenine, guanine
D. * Adenine, thymine, guanine
E. Thymine, adenine, uracil
255.
Name nitrogenous bases included into the structure of RNA:
A. Guanine, uracil, thymine
B.
C.
D.
E.
256.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
257.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
258.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
259.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
260.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
261.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
262.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
263.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Cytosine, adenine, thymine
* Uracil, adenine, guanine
Adenine, thymine, guanine
Thymine, adenine, uracil
Name process which is catalyzed by aminoacyl-t-RNA synthetases?
* Recognition and joining of amino acids to t-RNA
Initiation of translation
Elongation of polypeptide chain
Termination of translation
Synthesis of t-RNA
Name proteins that take part in the regulation of transcription in eukaryotes?
Albumins
Globulins
Immunoglobulins
* Histons
Cathepsins
Name the mechanism of DNA replication:
* Semiconservative
Conservative
Depressive
Repressive
Replicative
Named the structural monomers of DNA molecule:
* Mononucleotides
Nucleosides
Nitric bases
Polynucleotides
Peptides
Normal self-termination of transcription occurs due to the presence of
Stem-loop sequences in mRNA
Termination proteins
* Multiple RNA polymerase molecules
Polyribosome formation
All of the above
?Nucleic acids are:
Mononucleotides
Nucleosides
Nucleoproteins
* Polynucleotides
Dinucleotides
Nutritional mutants
Grow on minimal medium
* Lack an essential metabolic protein
Are also called prototrophs
Are the same as carbon-source mutants
Are usually antibiotic resistant
Okazaki fragments are used to elongate
The leading strand toward the replication fork
The lagging strand toward the replication fork
Both strands in both directions
* The leading strand away from the replication fork
The lagging strand away from the replication fork
264.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
265.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
266.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
267.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
268.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
269.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
270.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
271.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
272.
A.
B.
C.
On which of the following molecules would you find a codon?
* Messenger RNA
Ribosomal RNA
Transfer RNA
Small nuclear RNA
Big nuclear RNA
On which of the following molecules would you find an anticodon?
Messenger RNA
Ribosomal RNA
* Transfer RNA
Small nuclear RNA
Big nuclear RNA
Polymerase III is actually a complex containing
* Сatalytic subunits
Proofreading subunits
"Sliding clamp" subunits
All of the above
None of the above
Polysomes - are structures which are formed during translation from:
tRNA and one ribosome
* One molecule of mRNA and several ribosomes
A few molecules of mRNA and a few ribosomes
A few molecules of mRNA and one ribosome
A few molecules of tRNA, mRNA and few ribosomes
Primer is synthesized by specific:
* Primase
DNA – ligase
RNA – ligase
RNA - polymerase
None of above
Properties of genetic code are all below, except:
Universality
* Interruption
Nonoverlapping
Degeneration
Specificity
Proteins are made from amino acids by the process of
* Hydrolysis
Pinocytosis
Active transport
Dehydration synthesis
All of the above
Proteins that block the passage of RNA polymerase are called:
Operons
Activators
* Repressors
Enhancers
Promoters
Regulatory domains of most activators interact with
The transcription factor complex
* RNA polymerase
Repressors
D. The regulatory factor complex
E. The DNA binding domain
273.
Regulatory proteins of the protein synthesis system on ribosomes are all below,
except:
A. Factors of initiation
B. * Factors of polymerization
C. Releasing-factors
D. Factors of elongation
E. Factors of termination
274.
Replication fork has configuration like:
A. W
B. R
C. C
D. * V
E. T
275.
Represors of proteins synthesis on the level of transcription are:
A. Protamines
B. Glutelins
C. * Prolamines
D. Scleroproteins
E. Histons
276.
Reverse transcriptase (revertase or RNA-depending-DNA-polymerase) catalyzes:
A. * Synthesis of і-RNA on the DNA
B. Synthesis of DNA on the DNA
C. Synthesis of tRNA on the DNA
D. Synthesis of DNA on the RNA matrix
E. Synthesis of DNA on the ribosome
277.
RNA contains which bases?
A. Adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine, uracil
B. Adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine
C. Thymine, guanine, cytosine, uracil
D. * Adenine, guanine, cytosine, uracil
E. None of the above
278.
RNA synthesis on a DNA template is called __________.
A. Transformation
B. Translation
C. Transduction
D. * Transcription
E. Transfection
279.
Since the first nucleotides cannot be linked in a newly synthesized strand in DNA
replication, ___________ is required
A. A DNA primer
B. * DNA polymerase
C. Ligase
D. An RNA primer
E. Helicase
280.
Synthesis of daughter molecules of DNA, identical to maternal DNA, is named:
A. Reverse transcription
B. Transcription
C. Replication of RNA
D. * Replication of DNA
E. Translation
281.
The acceptor region of t-RNA contains such terminal sequence of nucleotides:
A. * CCA
B. CAC
C. CCU
D. GCA
E. CGA
282.
The actual synthesis of DNA in E. coli is the function of
A. * Polymerase I
B. Primase
C. Polymerase III
D. DNA ligase
E. Hirase
283.
The amino acid sequence of a polypeptide chain comprises the ____ structure of
the protein.
A. * Primary
B. Secondary
C. Tertiary
D. Quaternary
E. Presecondary
284.
The amino acids are transported to the place of synthesis of proteins in the cells
by:
A. Proteins-carryer
B. r-RNA
C. * t-RNA
D. Lipoproteins
E. m-RNA
285.
The base thymine is always paired with ___.
A. * Adenine
B. Guanine
C. Cytosine
D. Thymine
E. Uracil
286.
The component of the protein synthesis system on ribosomes is:
A. Nucleus
B. * mRNA
C. RNA- primer
D. DNA- primer
E. DNA
287.
The double strand model of DNA was proposed by:
A. Mitchel
B. Krebs
C. * Watson – Crick
D. Knoop
E. Nirenberg
288.
The effort to decipher the genetic code was led by ____ who was awarded a Nobel
Prize for his work.
A. * Nirenberg
B. Lederberg
C. Watson
D. Crick
E. Van-Helmont
289.
The first mRNA codon to specify an amino acid is always
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
TAC
* UAA
UAG
AUG
UGA
The following compounds are formed in complete hydrolysis of nucleic acids,
290.
except:
A. Phosphoric acid
B. Pentoses
C. Purine bases
D. * Acetic acid
E. Adenine
291.
The four ribonucleotide triphosphates incorporated into mRNA are
A. Inosine, Guanine, Uracil, Thymine
B. Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, Thymine
C. * Cytosine, Uracil, Adenine, Guanine
D. Thymine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine
E. Inosine, Guanine, Adenine, Cytosine
292.
The genetic code is considered "degenerate" because __________.
A. The code originated from bacterial genomes
B. DNA is unstable
C. Degenerate is the name of the person who deciphered the code
D. * More than one nucleotide triplet codes for the same amino acid
E. None of the above
293.
The initiation of synthesis of RNA is started from the including of first nucleotide
into the chain. What nucleotide does begin this process in pro- and in eukaryotes?
A. Pyrimidine nucleosidtriphosphate
B. Urydinmonophosphate
C. Desoxyribonucleosidtriphosphate
D. * Purine nucleosydtriphosphate
E. Cytidyltriphosphate
294.
The mode of action of a steroid hormone involves:
A. * Binding to a cell membrane receptor
B. Activation of protein kinases
C. Binding to calmodulin
D. Covalent modification of enzyme activity
E. Modifaing gene transcription
295.
The Okazaki fragment is synthesized in direction:
A. Along the movement of replication fork
B. 3'-5'
C. * Oppositely to the movement of replication fork
D. Antiparallely to the daughter chain
E. Proportionally to the movement of new synthesized daughter chain
296.
The operon that controls tryptophan producing genes in E. coli consists of
_______________ .
A. Only one gene
B. * Two genes
C. Three genes
D. Four genes
E. Five genes
297.
The presence of DNA is important for cellular metabolic activities because DNA
A. Directs the production of enzymes
B.
C.
D.
E.
Is a structural component of cell walls
Directly increases the solubility of nutrients
* Is the major component of cytoplasm
Nonproduction f enzymes
298.
The process of copying a gene's DNA sequence into a sequence of RNA is called
A. Replication
B. * Transcription
C. Translation
D. PCR
E. Posttranslation modification
299.
The process of DNA synthesis, the nucleotides sequence of which is
complementary to the sequence of RNA, is named:
A. * Reverse transcription
B. Transcription
C. Replication of RNA
D. Replication of DNA
E. Translation
300.
The process of producing a RNA polymer from a DNA template is called __.
A. Replication
B. * Transcription
C. Translation
D. Duplication
E. Iniciation
301.
The process of producing an amino acid polymer (polypeptide) from a RNA
template is called _.
A. Replication
B. * Transcription
C. Translation
D. Duplication
E. Transreplication
302.
The process of the exchange of genetic materials between the different DNA
molecules is named:
A. Replication of RNA
B. Reverse transcription
C. * Recombination
D. Reparation
E. Transposition
303.
The process of translation requires the presence of:
A. * mRNA, tRNA and ribosomes
B. mRNA, ribosomes and RNA polymerase
C. DNA, mRNA and RNA polymerase
D. Chromatin, DNA and amino acids
E. Free nucleotide bases, amino acids and ribosomes
304.
The stages of replication include:
A. Recognition of the point of replication beginning
B. Untwisting of double spiral of matrix DNA
C. Formation of fragments for the imitation synthesis of daughter's chains
D. Elongation of synthesis and termination
E. * All of the above
305.
The synthesis of new chains during replication takes place in such direction:
A. 4' – 5'
B. 7' - 8'
C. * 5' - 3'
D. 2' - 6'
E. 9' - 4'
306.
The synthesis of Okazaki fragments begins from:
A. Homonucleotide
B. Mononucleotide
C. Heteronucleotide
D. Polynucleotide
E. * Primer
307.
The synthesis of primer - fragment of RNA - takes a place in:
A. Transcription
B. Recognition
C. Reparation
D. * Replication
E. Translation
308.
The total length of all DNA of human cell is:
A. 20 sm
B. * 2
C. 2 sm
D. 0,2 sm
E. 20 m
309.
The transcribing enzyme is
A. Ligase.
B. DNA polymerase.
C. * RNA polymerase.
D. Amino-acyl transferase.
E. Hydrolases
310.
The transcription of DNA to a molecule of messenger RNA occurs:
A. * On the ribosomes
B. In the cytosol
C. In the nucleus
D. Only during cell division
E. When amino acids are made available by transfer RNA
311.
Theory of induction-repression of genes activity or theory of operon was
developed by:
A. Crick and Watson
B. Mitchel and Knoop
C. * Jakob and Monod
D. Krebs and Knoop
E. Gorbachevsky and Parnass
312.
There is the dynamic equilibrium between subunits and full ribosomes in the cells.
Full ribosomes are formed mainly in period of:
A. Transcription
B. Activation of amino acids
C. * Translation
D. Posttranslation modifications
E. Posttranslation modification of RNA
313.
Three types of RNA involved in comprising the structural and functional core for
protein synthesis, serving as a template for translation, and transporting amino acid,
respectively, are:
A. * mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
B. rRNA, tRNA, mRNA
C. tRNA, mRNA, rRNA
D. tRNA, rRNA, mRNA
E. rRNA, mRNA ,tRNA
314.
To describe the genetic code as degenerate indicates that
A. mRNA is rapidly degraded
B. The code is not universal among organisms
C. * Some amino acids have more than one codon
D. Frameshift mutations are tolerated
E. Stop codons may have corresponding tRNA molecules
315.
To which of the following does guanine form hydrogen bonds in DNA?
A. Adenine
B. Thymine
C. * Cytosine
D. Guanine
E. Uracyl
316.
Transcription factors appear to be unable to bind to a nucleosome because
A. Activators are inhibited by the configuration
B. * Of inhibition of RNA polymerase
C. Of histones positioned over promoters
D. Nucleosomes are especially vulnerable to repressors
E. Operators are placed in an inaccessible position
317.
Transcription is:
A. Activation of amino acids
B. * Rewriting of information to RNA on the matrix DNA
C. Process of formation of functional ribosome
D. Process of elongation of polypeptide chain
E. Processing of m-RNA
318.
Transcription occurs along a ____ template forming an mRNA in the ____
direction.
A. 5' to 3'; 5' to 3'
B. * 5' to 3'; 3' to 5'
C. 3' to 5'; 5' to 3'
D. 3' to 5'; 3' to 5'
E. None of the above
319.
Transfer RNA's bind during translation by the
A. Codon
B. * Anticodon
C. Template
D. Operon
E. None of the above
320.
Translation repressor proteins may shut down translation of processed mRNA
transcripts by
A. * Binding with the poly-A tail
B. Resetting the reading frame
C. Reinserting introns into the transcript
D. Excising a short sequence of nucleotides
E. Excising a short sequence of nucleosides
321.
What amino acid is coded by the triplet of bases UAU?
A. * Phenylalanine
B. Serine
C. Tyrosine
D. Cysteine
322.
323.
324.
325.
326.
327.
328.
329.
E. Lusine
What are the two processes of protein synthesis in order?
A. Meiosis, Translation
B. Translation, Transcription
C. Replication, Mitosis
D. * D.Transcription, Translation
E. Protein, Synthesis
What does a ribosome do?
A. Calls the xRNA with no codons
B. * Helps create the mRNA
C. Nothing
D. Calls the tRNA with the appropriate codon
E. Explodes
What does the speed of initiation process depend of?
A. * Structures of promotors sequences
B. Nucleotide sequences
C. Amount of RNA-depending-DNA-polymerase
D. The presence of 3'-5'-phosphodiester bonds
E. The structure of coplement dNМP in the coding chain of DNA
What form of DNA is a left-handed spiral?
A. B
B. С
C. Т
D. A
E. * Z
What function of gene-operator in the structure of operon?
A. On the gene-operator mRNA is transcribed that serves as a matrix for the
synthesis of protein-repressor
B. * Regulates (turns on) transcription on the structural genes
C. On the gene-operator mRNA is transcribed that serves as a matrix for the
synthesis of proteins which are necessary for cell
D. On the gene-operator mRNA is transcribed that serves as a matrix for the
synthesis of protein-inductor
E. On the gene-operator rRNA transcribed
What happens in Transcription?
A. The xRNA is destroyed
B. The rRNA is destroyed
C. * The mRNA is synthesized
D. The mRNA is destroyed
E. The xRNA is made
What happens in Translation?
A. The xRNA is destroyed
B. Translation doesn't exist
C. The tRNA is called and the protein is made
D. * The mRNA creates amino acids
E. Amino Acids cause a nuclear reaction
What is a polypeptide?
A. A strand of DNA
B. * An incomplete strand of protein (amino acids and enzymes)
C. A strand of mRNA
D. An RNA molecule
E. It doesn't exist
330.
What is operon?
A. Area of mRNA which codes the synthesis of one protein
B. Area of DNA in which the information about the synthesis of one protein is coded
C. * Area of DNA which consists of gene-operator and a few structural genes
D. Area of DNA which consists of gene-regulator and promoter
E. Area of DNA which consists of gene-regulator and structural genes
331.
What is protein made up of?
A. Enzymes and DNA
B. Happiness and Sadness
C. Meat
D. * Enzymes and Amino Acids
E. Amino Acids and Hydroclorich
332.
What is the function of gene-regulator in accordance with the theory of Jakob and
Monod?
A. * On the gene-regulator mRNA is transcribed that serves as a matrix for the
synthesis of protein-repressor
B. Directly regulates (turns on) transcription on structural genes
C. On the gene-regulator mRNA is transcribed that serves as a matrix for the
synthesis of necessary for cell proteins
D. On the gene-regulator mRNA is transcribed that serves as a matrix for the
synthesis of protein-inductor
E. On the gene-regulator rRNA transcribed
333.
What is the function of tRNA?
A. * Transport of amino acids
B. Transferring of genetic information
C. Formation of ribosomes
D. Storage of genetic information
E. Transport of mononucleotides
334.
What is the polysome?
A. Conglomerate containing few ribosomes
B. A few mRNA, that combined with one ribosome
C. * Many ribosomes that accommodate on one matrix RNA
D. A few tRNA transporting one amino acid to ribosome
E. A few amino acids which are transported by one tRNA to ribosome
335.
What is the terminal signal in the synthesis of polypeptide chain on ribosome?
A. Deficit of ATP energy in a cell
B. * Meeting of A-center of ribosome with terminal codon of mRNA
C. Dissociation of large and small subunits of ribosome
D. Decreasing of the amount of elongation factors in the cell
E. Placing methionine of tRNA in the P-center of ribosome
336.
What methods of DNA replication do you know?
A. * Conservative and semiconservative
B. Complete and incomplete
C. Completed and uncompleted
D. Determined and nondetermined
E. Temporal and permanent
337.
What of the following changes have relation to posttranslation modification of
proteins?
A. Formation of disulfide bonds between residues of cystein
B. Adding of cofactors or prosthetic groups
C. Formation of oligomers from a few polypeptide chains
D. Phosphorylation of some amino acids residues
E. * All of the above
338.
What role does messenger RNA play in the synthesis of proteins?
A. It catalyses the process.
B. It provides the genetic blueprint for the protein.
C. * It translates the genetic code to a specific amino acid.
D. It modifies messenger RNA molecules prior to protein synthesis.
E. None of the above
339.
What role does mRNA play in protein synthesis?
A. It explodes
B. It blows up
C. It helps form ribosomes
D. Nothing
E. * It is what the tRNA matches up to in order to form protein
340.
What role does small nuclear RNA play in the synthesis of proteins?
A. It catalyses the process.
B. * It provides the genetic blueprint for the protein
C. It translates the genetic code to a specific amino acid.
D. It modifies messenger RNA molecules prior to protein synthesis.
E. None of the above
341.
What role does the rRNA play in protein synthesis?
A. It is part of a ribosome that calles the tRNA molecules
B. It forms the mRNA
C. It creates DNA
D. It is a harmful molecule that is associated with protein synthesis
E. * Play role as adaptor
342.
What sequence on the template strand of DNA corresponds to the first amino acid
inserted into a protein?
A. TAC
B. UAA
C. UAG
D. * AUG
E. UUA
343.
What term is used to describe the process by which a segment of DNA is copied
to produce a molecule of messenger RNA?
A. Reproduction
B. Replication
C. Translation
D. * Transcription
E. Recombination
344.
What term is used to describe the process by which proteins are synthesised from
a genetic code?
A. Reproduction
B. Replication
C. * Translation
D. Transcription
E. Recombination
345.
What type of DNA, except nuclear, are in the eukaryotic cells:
A. * Mitochondrial
B. Lisosomal
C. Endoplasmic
D. Ribosomal
E. Mesosomal
346.
What type of enzyme is used in recombinant DNA technology to split a specific
sugar phosphate bond in each strand of a DNA double helix?
A. * Esterase
B. Restriction enzyme
C. Lipase
D. Ligase
E. Transferase
347.
Which enzyme catalyzes transcription of RNA on DNA matrix?
A. * DNA-depending-RNA-polymerase
B. DNA-polymerase II
C. DNA-polymerase III
D. DNA-ligase
E. RNA-depending-DNA-polymerase
348.
Which ions are needed for DNA replication?
A. Ca2+ and Na+
B. Mg2+ and Mn2+
C. Zn2+ and K+
D. Na+ and Ca2+
E. * Mg2+ and Zn2+
349.
Which is not part of the lac operon?
A. * Repressor
B. Activator protein
C. Operator
D. Promotor
E. Structural gene
350.
Which mode of information transfer usually does not occur?
A. DNA to DNA
B. DNA to RNA
C. * DNA to protein
D. All occur in a working cell
E. None of the above
351.
Which molecule contains the genetic code?
A. DNA
B. * mRNA
C. tRNA
D. rRNA
E. dRNA
352.
Which nitrogenous bases make up DNA nucleotides?
A. * Adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine
B. Adenine, uracil, guanine and cytosine
C. Adenine, thymine, uracil, and cytosine
D. Adenine, thymine, guanine, and uracil
E. Adenine, thymine, uracil, guanine
353.
Which nucleic acids contain the lowest number of nucleotides?
A. DNA
B. * t-RNA
C. m-RNA
D. r-RNA
E. і-RNA
354.
Which of the following are not matched correctly?
A. Exon splicing-occurs in nucleus
B. Post-translational modifications-phosphorylation
C. SnRNA-splice out exons from transcript
D. Activated enhancers-trigger transcription
E. * All are matched correctly
355.
Which of the following does NOT involve introns?
A. Alternative splicing
B. * Ribozymes
C. Intervening sequences
D. Heteroduplexes
E. Antisense oligonucleotides
356.
Which of the following features is common to both DNA replication and
transcription?
A. Nucleotides are added to the 5' end of the newly synthesized strand
B. * A sugar-phosphate bond is formed between the 3' hydroxyl and the 5' phosphate
C. Deoxyribonucleotides are incorporated into the growing sequence
D. Both RNA and DNA polymerase require oligonucleotide priming
E. Both RNA and DNA polymerase initiate at promoter sequences
357.
Which of the following is an example of the degeneracy of the genetic code?
A. * A given amino acid has more than one codon
B. Each codon specifies more than one amino acid
C. The first two bases specify the amino acid
D. The genetic code is not degenerate
E. None of the above
358.
Which of the following is part of an operon?
A. Structural genes
B. An operator
C. A promoter
D. A CAP binding site
E. * All of the above
359.
Which of the following is true regarding RNA processing?
A. Spliceosomes are present in organelles and nuclei
B. Involves removal of exons
C. Involves removal of one or more introns.
D. Occurs in prokaryotes
E. * None of the above
360.
Which of the following is true regarding the machinery of translation?
A. * Initiation usually begins at an AUG codon
B. Eukaryotes have nuclear ribosomes
C. Polycistronic mRNA usually has a single ribosome binding site
D. tRNAs released from the ribosome are degraded
E. Termination is at inverted repeats
361.
Which of the following is unique to eukaryotic mRNA synthesis?
A. Polycistronic mRNA
B. * Coupled transcription-translation
C. Removal of introns
D. Polysomes
E. All of the above
362.
Which of the following is unique to prokaryotic mRNA synthesis?
A. Coupled transcription-translation
B. Exon processing
C. 3' polyadenylation
D. mRNA capping
E. * Promoter sequences
363.
Which of the following molecules does not form part of DNA?
A. Purine
B. Pyrimidine
C. Deoxyribose
D. * Amino acid
E. Phosphate
364.
Which of the following nucleotide bases is not found in RNA?
A. * Thymine
B. Adenine
C. Uracil
D. Guanine
E. Cytosine
365.
Which of the following statements is true regarding introns?
A. * Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated.
B. Introns have no function.
C. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms
D. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling.
E. None of the above
366.
Which of the following statements is true regarding transposons?
A. * They are sequences of mRNA that can move around in the genome
B. They exist in corn, but are not found in the human genome
C. They are the most abundant type of repeat in the genome
D. All of the above are true regarding transposons
E. None of the above
367.
Which of the statements below is false?
A. The genetic code is overlapping
B. The genetic code is universal
C. Degenerate codons specify the same amino acids
D. * The genetic code is triplet
E. None of the above
368.
Which process is the first stage of biosynthesis of proteins?
A. * Activation of amino acids
B. Elongation
C. Termination
D. Transcription
E. Translation
369.
Which statement about the elongation of the lagging strand during DNA
replication is correct?
A. * It is synthesized in a 3' --> 5' direction.
B. It progresses (grows) toward the replication fork.
C. It requires a short RNA primer to proceed.
D. It is synthesized by DNA ligase.
E. It is synthesized continuously.
370.
Which subunits do ribosomes of eukaryotes reversibly dissociate to?
A. * 60s and 40s
B. 60s and 80s
C. 40s and 45s
D. 40s and 40s
E. 60s and 20s
371.
With few exceptions, all nucleic of eukaryotes contain
A. Genes to specify the portion of the organism in which they are found
B. All the information needed for growing the whole organism
C. All of the chromosomes except sex chromosomes which are restricted to sex
organs
D. * Single stranded DNA
E. Only euchromatin except in the case of the Y-chromosome
372.
All of the following help to explain the mechanism for releasing insulin from
beta-cells in response to the concentration of blood glucose - EXCEPT
A. The important regulator of glycolysis in beta cells is the concentration of glucose
reacting with glucokinase
B. ATP is made in proportion to the rate of glycolysis
C. The rate of K+ leaving the cell through a potassium channel is a major
determinant of the polarization of the cell membrane
D. ATP inhibits the K+-channel, the more ATP, the less K+ leaving the cell, and the
less polarized (more depolarized) the cell membrane
E. * Depolarization causes Ca++ to exit the cell and insulin leaves the cell through
the insulin transporter
373.
During an overnight fast, the major source of blood glucose is
A. Dietary glucose from the intestine
B. * Hepatic glycogenolysis
C. Gluconeogenesis
D. Muscle glycogenolysis
E. Glycerol from lipolysis
374.
Inhibitory factors of hypothalamus are:
A. somatostatin, melanostatin, folliclestatin
B. * somatostatin, melanostatin, prolactostatin
C. A. somatostatin, prolactostatin, folliclestatin
D. prolactostatin, folliclestatin, luteostatin
E. melanostatin, folliclestatin, thyrostatin
375.
The absorption of glucose from the gut into intestinal mucosal cells is coupled to
Na?,K?-ATPase. In contrast, the movement of glucose from the intestinal epithelial cells
into the submucosal bloodstream occurs through passive transport. Given these facts,
which of the following statements can be true at one time or another?
A. Cytosolic levels of glucose in intestinal mucosal cells are regulated by levels of
glucose in skeletal muscle cells
B. Free glucose levels in the lumen of the intestine can never be higher than levels in
intestinal cells
C. Plasma glucose levels are much higher than intestinal cell cytosolic levels of
glucose
D. Levels of glucose in the intestinal lumen are always higher than those in the
cytosol of intestinal epithelial cells
E. * Levels of plasma glucose are approximately equal to levels in the cytosol of
intestinal epithelial cells
376.
A 62 yaears old woman has cataract (lenticular opacity) by diabetes mellitus.
Which process increase by diabetes is the reason for lenticular opacity?
A. ketogenesis
B. lipolysis
C. protein proteolysis
D. * protein glycosylation
E. gluconeogenesis
377.
A dysfunction of Langergans islets results in the decline of such hormones:
A. * Glucagon and insulin
B. Thyroxin and calcitonin
C. Insulin and epinephrine
D. Callicrein and angiotensin
E. Parathormone and cortisol
378.
A hormone that secreted in the pancreatic duct is
A. Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Somatostatin
D. * Lipocain
E. Cortisol
379.
A man after 1,5 litres blood loss has suddenly reduced diuresis. The increased
secretion of what hormone caused such diuresis alteration?
A. Corticotropin
B. Natriuretic
C. Parathormone
D. Cortisol
E. * Vasopressin
380.
A patient has such sympthoms as hyperglycaemia, glucosuria, increased urine
density, thirst, acidosis. What from below mentioned disorders can result in such state?
A. * Insufficiency of insulin
B. Hyperproduction of insulin
C. Insufficiency of vasopressin
D. Hyperproduction of glucocorticoids
E. Insufficiency of glucagon
381.
A patient has such sympthoms as polyuria, decreased urine density, thirst. What
from below mentioned disorders can result in such state?
A. Insufficiency of insulin
B. Hyperproduction of insulin
C. * Insufficiency of vasopressin
D. Hyperproduction of glucocorticoids
E. Insufficiency of glucagon
382.
A patient, which visited a doctor, has increased level of glucose in blood and
urine. Diabetes mellitus is suspected. What changes in lipid metabolism causes this
disease?
A. hyperketonemia
B. hypercholesterolemia
C. * hypoketonemia, ketonuria
D. hyperphospholipidemia, hyperketonemia
E. hypophospholipidemia , hypoketonemia
383.
A typical symptom of cholera is a body water loss and sodium ions loss. The
biochemical mechanisms of choleric toxin action is:
A. Activation of synthesis of atrial natriuretic factor
B. * Activation of adenylate cyclase in small intestine
C. Decrease of synthesis of antidiuretic hormone in a hypothalamus
D. D. Activation of secretion renin by the cells of yukstaglomerular aparatus
E. Oxydation of aldosterone in the adrenal cortex
384.
ACTH- hormone of the adenohypophysis. Per oral introduction of ACTH as
medical preparation ineffective because this hormone is:
A. * Decomposed with the proteolytic enzymes
B. Does not absorbed in the intestine
C. Inactivated in the cells of intestinal wall
D. Inactivated in a liver
E. Does not transferred with blood
385.
After meal an alimentary hyperglycemia stimulates the secretion of such
hormone:
A. Cortisol
B. Glucagon
C. Epinephrine
D. Norepinephrine
E. * Insulin
386.
Alfa-cells of pancreas synthesize the glucagon, which participates in the
metabolism of carbohydrates. Which process in a liver it effects.
A. Inhibits glycogenolysis
B. Activates glycolysis
C. * Activates a glycogenolysis
D. Ingibits glycolysis
E. Activates lipogenesis
387.
All other things being constant, an increase in stress hormones would result in an
increase in:
A. Fatty acid synthesis in adipose tissue
B. * Blood amino acids for gluconeogenesis
C. Malonyl CoA concentrations in liver
D. Protein synthesis in muscle
E. Glycogen synthesis in muscle
388.
All the following are important in the glucagon second messenger cascade
EXCEPT
A. Glucagon binds causing the dissociation of GDP from and the association of GTP
with the G-protein
B. Adenylate cyclase catalyzes the conversion of ATP to cAMP
C. Phosphodiesterase catalyzes the conversion of cAMP to AMP
D. * The receptor for glucagon undergoes an autophosphorylation which activates
adenylate cyclase
E. The cAMP binds to Protein Kinase A regulatory subunits, releasing catalytic
subunits
389.
All the following statements about serotonin are true except
A. * It causes vasolidatation
B. It causes bronchoconstriction
C. It is metabolized by monoamine oxidase
D. Its metabolite is 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid
E. Both A and B
390.
Alpha – cells of pancreas produse such hormon as:
A. Insulin
B. * Glucagon
C. Somatostatin
D. Lipocain
E. Cortisol
391.
As a medical preparations derivates of amino acids are widely used. Which from
the below mentioned hormones is derivative of amino acid?
A. * Thyroid hormones
B. Glucocorticoids
C. Androgens
D. Hormones of hypophysis
E. Estrogens
392.
As a result of insulin binding to the insulin receptor, the GRB protein binds to the
IRS. The binding of the GRB adaptor protein occurs because the IRS contains
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* A phosphorylated tyrosyl residue
A phosphorylated seryl residue
A src homology binding domain (SH2 domain)
Bound inositol trisphosphate
An alpha-1 receptor
393.
At emotional stress in adipocytes hormone sensitive threeacylglycerollipase is
activated. What second mediator does take part in this process?
A. * cАМP
B. cGМP
C. AMP
D. Diacylglycerol
E. Ions of Ca2+
394.
At pheochromocytoma (adrenal glands medullary substance tumour) epinephrine
synthesis is increased. Which of the mentioned changes is observed in such conditions?
A. hard hypoglycemia
B. * hyperglycemia
C. normal glucose amount
D. hyperproteinemia
E. hypercholesterolemia
395.
Ca2+ ions - are an evolutional oldest secondary messenger in cells. They are the
activators of glycogenolysis, if cooperate with:
A. Calcitonin
B. * Calmodulin
C. Calciferol
D. Kinase of light chains of myosin
E. Phosphorylase C
396.
Chemical nature of ACTH:
A. simple protein
B. derivative of amino acid
C. derivative of unsaturated fatty acid
D. * hormone of peptide structure
E. steroid hormone
397.
Chemical nature of glucagon is:
A. * Peptide
B. Protein
C. Steroid
D. Derivative of amino acid
E. Derivative of arachidonic acid
398.
Chemical nature of growth hormone:
A. * simple protein
B. derivatives of amino acid
C. derivatives of unsaturated fatty acid
D. hormone of peptide structure
E. steroid hormone
399.
Chemical nature of insulin is:
A. * Protein
B. Derivative of amino acid of thyrosin
C. To the derivates of arachidonic acid
D. Oligopeptide
E. Steroid
400.
Choose a stimulus for rennin formation
A. * Diminishing of kidney blood flowing
B.
C.
D.
E.
Increase of kidney blood flowing
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Aldosterone
Hypoglycemia
401.
Choose a substance which carries out the role of the secondary mediator at the
membrane-intracellular mechanism of action of hormones:
A. UMP
B. GTP
C. Oleic acid
D. Arachidonic acid
E. * Cyclic АМP
402.
Choose from below mentioned compouds statins of hypothalamus:
A. Thyrostatin, prolactostatin, melanostatin
B. Somatostatin, thyrostatin, melanostatin
C. Somatostatin, prolactostatin, thyrostatin
D. Thyrostatin, lipostatin, melanostatin
E. * Somatostatin, prolactostatin, melanostatin
403.
Choose from the below mentioned effects of insulin:
A. Represses oxidization of glucose in glycolysis, represses a PPP, activates
glycogen synthase (synthesis of glycogen)
B. Activates oxidization of glucose in glycolysis, represses a PPP, represses
glycogen synthase (synthesis of glycogen)
C. Represses oxidization of glucose in glycolysis, activates a PPP, represses
glycogen synthase (synthesis of glycogen)
D. * Activates oxidization of glucose in glycolysis, activates a PPP, activates
glycogen synthase (synthesis of glycogen)
E. Represses oxidization of glucose in glycolysis, inhibites PPP, represses glycogen
synthase (synthesis of glycogen)
404.
Choose, which biogenic аmines are the derivates of tryptophane:
A. Serotonin and dopamine
B. Dopamine and melatonin
C. * Serotonin and melatonin
D. Dopamine and histamine
E. Serotonin and histamine
405.
Cooperating of catecholamines with the beta - adrenoreceptors increases the level
of cАМP in the cells. Which enzyme catalyses the reaction of cАМP formation:
A. * Adenylatecyclase
B. Phosphodiesterase
C. Phosphatase
D. Guanilatciclase
E. Creatinkinase
406.
Cooperating of catecholamines with the beta - adrenoreceptors promotes the level
of cАМP in the cells. Name an enzyme which catalyzes the reaction of cАМP formation:
A. Creatinkinase
B. Phosphodiesterase
C. Phosphatase
D. Guanilatcyklase
E. * Adenylatecyclase
407.
Cyclic nucleotides (cАМP and cGМP) is the secondary mediators at transfer of
information. Witch their role as a regulators?
A. * Activating of specific proteincinases.
B. Phosphorylating of histons.
C. Activating of neiromediators.
D. Stimulation of CNS
E. Stimulation of transcription and translation.
408.
Delta cells of pancreas produse such hormon as:
A. Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. * Somatostatin
D. Lipocain
E. Cortisol
409.
Dopamine is biogenic amine which is intermediate in a synthesis:
A. * Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
B. Serotonin
C. Serotonin and melatonin
D. Insulin
E. All of above correct
410.
During stress there takes place a rapid output of glucose into blood with the
purpose of providing of organism energy. It takes a place due to:
A. * Increased secrection epinephrine which splits a glycogen in a liver and muscles
B. Increased secrection of thyroxine, which promotes absorption of glucose in an
intestine
C. Increased secrection of glucocorticoids which activate formation of glucose from
noncarbohydrate components
D. Increased secrection of epinephrine which activates a gluconeogenesis
E. To the increased secrection of epinephrine which promotes absorption of glucose
in an intestine
411.
During the series of events following an increase in insulin, all of the following
occur EXCEPT:
A. Insulin binds its receptor, causing the autophosphorylation of receptor subunits
B. Active protein kinases can cause the induction/repression of genes
C. Glucagon-stimulated phosphorylation is reversed by the effects of insulin
D. Phosphorylation results in more glucose transporters in adipose tissue cells
E. * Phosphorylation inhibits 3', 5'-phosphodiesterase
412.
Effect of epinephrine on a lipid metabolism is:
A. Inhibits a tissue lipase and mobilization of fat from a depot;
B. * Activates a tissue lipase and mobilization of fat from a depot;
C. Inhibits lipids oxidation
D. Stimulates converting of fats into carbohydrates
E. Stimulates transformation of fats into proteins
413.
Effect of insulin on a carbohydrate metabolism is:
A. * Activates transfer of glucose through the cells membranes
B. Activates glucokinase
C. Activates glycogensynthase
D. Activates a gluconeogenesis
E. Inhibits transfer of glucose through the cells membranes
414.
Effect of insulin on a lipid metabolism is:
A. * Activates the synthesis of fatty acids
B. Inhibits the synthesis of fatty acids
C. Activates converting of fatty acids into carbohydrates
D. Inhibits convention of fatty acids into carbohydrates
E. Stimulates transformation of lipids into proteins
415.
Effect of insulin on a proteins metabolism is:
A. * Activation of the synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids
B.
C.
D.
E.
Repression of the synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids
Reducing of permeability of cells membranes for amino acids
Activation of conversion of amino acids into glucose
Activation of conversion of amino acids into lipids
416.
Effect of somatotropic hormone on a proteins metabolism:
A. Represses entering of amino acids into cells
B. Represses the biosynthesis of proteins, DNA, RNA
C. Activates conversion of amino acids into fats
D. Stimulates conversion of amino acids into glucose
E. * Activates the biosynthesis of proteins, DNA, RNA
417.
Epinephrine increases the glucose level in the blood by activation of:
A. * glycogenolysis
B. glycolysis
C. ketolysis
D. gluconeogenesis
E. glycogenesis
418.
Epinephrine increases the glucose level in the blood by activation of:
A. * glycogenolysis
B. glycolysis
C. ketolysis
D. gluconeogenesis
E. glycogenesis
419.
Epinephrine stimulates a glycogenolysis by:
A. * Activation of glycogenphosphorylase
B. Inhibition of glycogenphosphorylase
C. Activation of glycogensynthase
D. Activation of hexokinase
E. Inhibition of hexokinase
420.
Epinephrine stimulation of lipolysis in adipocytes is thought to differ from
epinephrine stimulation of glycogenolysis in the liver in which way?
A. Glucagon, not epinephrine, stimulates lipolysis in adipocytes
B. The mechanism of hormone-receptor interaction is thought to be fundamentally
different in each tissue
C. Phosphorylase kinase is activated directly by a second messenger in adipocytes,
but not in the liver
D. Adenosine 3?,5?-cyclic monophosphate (cyclic AMP) is the second messenger in
adipocytes, but not in the liver
E. * Only protein kinase is interposed as an amplification factor between the second
messenger and the physiologically important enzymes in adipocytes
421.
Excess accumulation of which biogenic аmine in the areas of inflammation and
areas of cooperation an antigen-antibody is one of mechanisms of development of
allergic reactions:
A. Serotonin
B. Dopamine
C. * Histamine
D. Melatonin
E. Epinephrine
422.
Following release of norepinephrine by sympathetic nerves and epinephrine by
the adrenal medulla, which of the following metabolic processes is decreased?
A. * Glycolysis
B. Lipolysis
C. Gluconeogenesis
D. Glycogenolysis
E. Ketogenesis
423.
For what from the following hormones are specific such effects as activation of
decomposition of glycogen in a liver, activation of lipolysis, stimulation of
gluconeogenesis.
A. Insulin
B. * Glucagon
C. Epinephrine
D. Cortisol
E. Testosteron
424.
For what glycolysis enzyme the activator is insulin?
A. * hexokinase
B. B.glucose-6-phosphatase, phosphoglucom
C. C.glucose-6-phosphate-isomerase, aldolase
D. aldolase, lactate dehydrogenase
E. phosphoglucomutase, aldolase
425.
Formation of insulin is increased at:
A. During starvation
B. During the physical loading
C. At emotional stress
D. * After meal
E. At a flu
426.
Glucocorticoids increase the level of glucose in the blood by activation of:
A. glycogenogenesis
B. glycogenolysis
C. * gluconeogenesis
D. ketogenesis
E. glycolysis
427.
Histamine responsible for all of physiological effects, except:
A. * Narrowing of peripheral vessels
B. Dilatation of peripheral vessels
C. Stimulation of secretion of HCl in a stomach
D. Narrowing of bronchus
E. Participating is in immunological reactions.
428.
Hormone, which increase the activity of lipolysis in fatty tissue:
A. * epinephrine
B. parathyroid hormone
C. insulin
D. B. vasopressin
E. prostaglandins
429.
Hormones regulate the numeral processes of metabolism. Which from the below
mentioned hormones has аnabolic action:
A. * Insulin
B. Epinephrine
C. Vasopresin
D. Glukagon
E. Oxytocin
430.
How can be diabetic tendency detected?
A. Determinating the level of 17-ketosteroids in blood .
B. * By the glucose-tolerance test.
C. Determinating the glucose level in blood.
D. Determinating the glucose level in urine
431.
432.
433.
434.
435.
436.
437.
438.
E. Determinating the level of cholesterol in blood
How could be an inactive kininogens converted into an active kinins?
A. Under the action of rennin
B. Under the action of angiotensin
C. Under the action of prostaglandins
D. Under the action of somatotropin
E. * Under the action of kallikreins
How do catecholamins influence on a carbohydrate metabolism?
A. Activate decomposition of glycogen in a liver
B. * Activate decomposition of glycogen in a liver and muscles
C. Activate a gluconeogenesis
D. Activate suction of glucose in an intestine
E. Activate the synthesis of glycogen
How do catecholamins influence on a lipids metabolism?
A. * Activate mobilization and oxidization of fats
B. Activate lipogenesis
C. Activate synthesis of phospholipids in a liver
D. Activate formation of transport forms of lipids in a liver
E. Promote formation of chylomicrons in the wall of intestine
How do catecholamins influence on a protein metabolism?
A. Promote synthesis of proteins
B. Promote synthesis of proteins in a liver and activate its decomposition in
connective tissue
C. * Promote in a proteins catabolism
D. Activate convertion of proteins into carbohydrates
E. Activate transformation of carbohydrates into a proteins
How does glucagon influence on a carbohydrate metabolism?
A. Activates the synthesis of glycogen in a liver
B. Activates the synthesis of glycogen in a liver and muscles
C. Activates decomposition of glycogen in a liver and muscles
D. * Activates decomposition of glycogen in a liver
E. Activates the transport of glucose across cellular membranes
How does insulin influence on a lipid metabolism?
A. Represses synthesis of fats, activates a gluconeogenesis
B. * Activates synthesis of fats, represses a gluconeogenesis
C. Activates synthesis of fats, activates a gluconeogenesis
D. Represses synthesis of fats, represses a gluconeogenesis
E. Participates in converting of lipids into carbohydrates, activates oxidization of
fatty acids
How does insulin influence on a mineral metabolism?
A. Regulates calcium-phosphate metabolism
B. * Activates a transport of potassium into a cells, and sodium from the cells
C. Activates insertionof iron into hemoglobin
D. Regulates metabolism of copper in an organism
E. Instrumental in insertion of iodine in tyrosine
How does insulin influence on a protein metabolism?
A. * Promotes permeability of membranes for amino acid, activates the synthesis of
proteins and nucleic acids, represses a gluconeogenesis
B. Reduces permeability of membranes for amino acid, represses the synthesis of
proteins and nucleic acids, represses a gluconeogenesis
C. Reduces permeability of membranes for amino acid, represses the synthesis of
proteins and nucleic acids, activates a gluconeogenesis
D. Promotes permeability of membranes for amino acid, represses the synthesis of
proteins and nucleic acids, activates a gluconeogenesis
E. Promotes permeability of membranes for amino acid, activates the synthesis of
proteins and nucleic acids, activates a gluconeogenesis
439.
How is active insulin formed in a pancreas?
A. From the protein - precursor by phosphorylation
B. From the protein - precursor by acetylation
C. * From the protein - precursor by partial proteolysis
D. From the protein - precursor by the methylation
E. It formed in an active form
440.
How is insulin catabolised after its action?
A. Excreted from an organism in an unchanging form with urine
B. Excreted from an organism in an unchanging form with a bile
C. Excreted from an organism with a bile after oxidization in a liver
D. * By the enzyme of insulinase to amino acids
E. By lysosomal enzymes in all of rissues
441.
How is regulated intensity of insulin secretion?
A. By insulinotropin - a hormone of hypophysis
B. By insulinoliberin of hypothalamus
C. * By the concentration of glucose in blood
D. By the somatic nervous system
E. By the concentration of calcium and phosphorus in blood
442.
How many gramms of glucose is it necessary to eat for a patient half-starving to
perform a method of sugary loading aiming to reveal the hidden form of diabetes
mellitus?
A. * 1 g per 1 kg of weight
B. 100 g
C. 20 g
D. 50 g
E. 10 g
443.
Impairment in the synthesis of dopamine by the brain is a major causative factor
for the disorder:
A. * Parkinson’s disease
B. Addison’s disease
C. Cushing’s syndrome
D. Goiter
E. Insulin-dependent diabetes
444.
In stress the level of glucose increases in blood. Which hormone does result in it
with the activating of glycogenolysis?
A. Parathyroid hormone
B. Aldosterone
C. * Epinephrine
D. Vasopressin
E. Progesterone
445.
In diabetes mellitus the tissues of organism have heavy deficit of oxidative
substratum, as they can not assimilate glucose. Gluconeogenesis increases and ketone
bodies become the main substratum for oxidation. What is one of the reasons for
ketonuria by diabetes mellitus?
A. lack of HS-CoA
B. lactate excess
C. * lack of oxaloacetate
D. glucose formation
E. polyuria
446.
In emotional stress threeacylglycerollipase is activated in adipocytes.
Concentration of which secondary messenger increases?
A. * cАМP
B. cGМP
C. AMP
D. Diacylglycerol
E. Ca2+
447.
In liver and muscle, glycogen degradation is characterized by all of the following
EXCEPT:
A. * The activation by insulin of glycogen phosphorylase
B. The yielding of glucose-1-phosphate residues by the enzyme glycogen
phosphorylase
C. The activity of a 4: 4- transferase to ensure the debranching
D. The activity of a specific alpha-1, 6- glucosidase that yields free glucose residues
E. The use of inorganic phosphate by glycogen phosphorylase
448.
In pheochromocytoma (adrenal glands medullary substance tumour) increase
epinephrine synthesis. Which of the mentioned changes is observed by such conditions?
A. hard hypoglycemia
B. * hyperglycemia
C. normal glucose amount
D. hyperproteinemia
E. hypercholesterolemia
449.
In the blood of the patient the amount of glucose half-starving is 5,6 mmol/l, in an
hour after sugary loading – 13,8 mmol/l, in two hours – 9,2 mmol/l. Such figures are
typical for:
A. healthy man
B. patient with thyrotoxicosis
C. * patient with hidden form of diabetes mellitus
D. patient with Cushing's syndrome
E. patient with acromegaly
450.
In the synthesis of Insulin, which of the following is NOT TRUE?
A. * The alpha-cells of the pancreas are centered such that blood flow carries new
glucagon over the beta-cells explaining the inhibitory effect of glucagon on
insulin release
B. Glucose is a major regulator of insulin release
C. Cleavage of proinsulin to insulin yields a C-Peptide
D. The chains of insulin are held together and in active conformation by disulfide
bridges
E. The A chain of insulin is shorter than the B chain
451.
Increace of insulin secretion takes place in a pancreas after the carbohydrate meal.
Activity of which enzymes of glycolisis regulates insulin:
A. * Glucokinase, phоsphоfructokinase, pyruvatkinase
B. Aldolase, LDH, enolase
C. Phosphoglyceromutase, LDH, phosphoglucomutase
D. Enolase, аldolase, hexokinase
E. Phosphoglycerokinase, pyruvatkinase, enolase
452.
Increased blood insulin specifically plays a major role in all of the following
EXCEPT:
A. Glucose storage as glycogen in liver and muscle
B. * Conversion of glucose to triacylglycerols in liver
C. Amino acid uptake and protein synthesis in skeletal muscle
D. Promotion of the sparing of glucose utilized for energy in the brain during a fast
E. Stimulation of transport of glucose into muscle and adipose tissue
453.
Increased reabsorption of water from the kidney is the major consequence of
which of the following hormones?
A. Cortisol
B. Insulin
C. * Vasopressin
D. Glucagon
E. Aldosterone
454.
Insulin decreases the level blood glucose by means of:
A. gluconeogenesis activation
B. gluconeogenesis oppression
C. * glucose phosphorylation oppression
D. glucose with urine excretion
E. adrenalin excretion decrease
455.
Insulin effects on the metabolism of carbohydrates, stimulates the transport of
glucose from extracellulary space through cellular membranes inside the cells. Which
cells are the target – cells for insulin?
A. * Myocytes, adipocytes
B. Neurons, myocytes
C. Neurons, red blood cells
D. Hepatocytes, neurons
E. Lymphocytes, red blood cells
456.
Insulin has many direct effects on various cell types from such tissues as muscle,
fat, liver, and skin. Which of the following cellular activities is decreased following
exposure to physiologic concentrations of insulin?
A. Plasma membrane transfer of glucose
B. Glucose oxidation
C. * Gluconeogenesis
D. Lipogenesis
E. Formation of ATP, DNA, and RNA
457.
Insulin is secreted by the B-cells of the pancreas into the hepatic portal vein.
Which of the following regarding insulin synthesis is FALSE:
A. The active form of insulin is composed of two polypeptide chains linked by two
interchain disulfide bonds
B. The A-Chain has an intrachain disulfide bond
C. Insulin is synthesized as a preprohormone which is converted to proinsulin
D. * Stimulation of A-cells by glucose causes exocytosis of the insulin storage
vesicles
E. Cleavage of proinsulin to insulin yields a C-peptide
458.
Introduction of epinephrine to the organism increases the level of glucose in
blood. What process is activated mainly?
A. * Disintegration of glycogen
B. Synthesis of glycogen
C. Cycle of Krebs
D. Pentosophosphate cycle
E. Alcoholic fermentation
459.
Introduction of epinephrine to the organism results in the increase of glucose level
in blood. Which process is activates mainly?
A. Alcoholic fermentation
B. Synthesis of glycogen
C. Cycle of Krebs
D. Pentose phosphate cycle
E. * Disintegration of glycogen
460.
Melatonin responsible for all of physiological effects, except:
A. Synchronization of endogenous biorhythms in an organism
B. Adjusting of “sleep-wake” activity
C. * Activation of immune reactions
D. Inhibition of secretion somatotropic and gonadotropic hormones
E. Inhibition of free radical oxidization reactions
461.
Name the hormone, predominantly produced in response to fight, fright and flight:
A. Thyroxine
B. * Epinephrine
C. Aldosterone
D. ADH
E. Insulin
462.
One of the following hormones is an amino acid derivate:
A. Epinephrine
B. Norepinephrine
C. Thyroxine
D. * All of them
E. Insulin
463.
One of the ways of glucose oxidation is pentose-phosphate cycle. What is the
main destination of this process?
A. * formation of NADPH2 and pentose
B. formation of NADPH2 and gluconic acid
C. glycogen synthesis in the liver
D. acetyl CoA formation
E. formation of NADH2
464.
Oversecretion of which hormone causes higher growth, unproportionally large
hands?
A. * Somatotropic hormone
B. Epinephrine
C. Thyroxin
D. Antidiuretic hormone
E. Melanocytostimulation hormone
465.
Patient is in condition of constant stress, what caused the violation of lipid
metabolism. Characteristic for this condition are the following features, but:
A. hyperglycemia
B. hyperketonemia
C. decrease of total lipids in blood
D. organism emaciation
E. * fatty liver degeneration
466.
Prostaglandins are inactivated by
A. * 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase
B. Cyclo-oxygenase
C. Lipo-oxygenase
D. None of these
E. Both B and C
467.
Prostaglandins have a common structure based on prostanoic acid which contains
carbon atoms:
A. 12
B. 16
C. 18
D. * 20
E. 32
468.
Specify chemical nature of hormones of a neurohypophysis:
A. * Cyclic peptides
B. Simple proteins
C. Derivates of tyrosine
D. Derivates of fatty acids
E. Glycoproteins
469.
The B-cells of endocrine portion of pancreas are selectively damaged by alloxan
poisoning. How will it be reflected in blood plasma?
A. The content of fibrinogen decrease
B. The content of albumins decreases
C. * The content of sugar increases
D. The content of globulins decreases
E. The level of sugar decreases
470.
The cause of insulin dependent diabetes (type II) is:
A. * malfunction of structure and insulin receptors function
B. decreased insulin synthesis
C. increased insulin synthesis
D. increased epinephrine synthesis
E. decreased epinephrine synthesis
471.
The cause of insulin-dependent diabetes (type I) is:
A. * decreased insulin synthesis
B. increased insulin synthesis
C. increased glucocorticoids synthesis
D. increased glucagon synthesis
E. decreased glucagon synthesis
472.
The chemical nature of tropic hormones of adenohypophysis is:
A. Simple proteins
B. * Glycoproteins
C. Lipoproteins
D. Derivates of fatty acids
E. Derivates of amino acid
473.
The feature of tyrosine metabolism is its including in the process of hormones
synthesis. Choose one of them that synthesizes in the adrenal medulla.
A. Thyroxin
B. Glucagon
C. * Epinephrine
D. Histamine
E. Serotonin
474.
The following are all effects of insulin EXCEPT
A. Stimulation of acetyl CoA carboxylase
B. * Stimulation of the lipolytic activity of hormone sensitive lipase (HSL)
C. Stimulates adipose cells to synthesize and secrete LPL (lipoprotein lipase)
D. Stimulates the enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
E. Increase in the number of glucose transporters in adipose cell membranes
475.
The hormone, that depresses lipolysis in fatty tissue:
A. * insulin
B. epinephrine
C. glucagon
D. thyroxine
E. adrenocorticotropin
476.
The hormones of protein – peptide nature regulate biochemical processes with
activating of adenylatecyclase. Choose the substance which appears as a result of this
enzyme action.
A. cCМP
B. cGМP
C. * cАМP
D. cТМP
E. cUМP
477.
The hypersecretion of which hormone causes development of hyperglycemia?
A. * Glucagon
B. Insulin
C. Somatomedine
D. Melanotropin
E. Vasopressin
478.
The level of glucose in blood of a patient increases. Excess of which hormone
could results such effect?
A. * Epinephrine
B. Insulin
C. Testosteron
D. Norepinephrine
E. Oxytocin
479.
The level of glucose in blood of a patient increased. Excess of which hormone
could result in such effect?
A. Oxytocin
B. Insulin
C. Testosterone
D. Norepinephrine
E. * Epinephrine
480.
The patient complains for undue fatiguability after working day, constant thirst. A
doctor suspected diabetes mellitus. Choose the blood plasma glucose concentration,
which proves the diagnosis:
A. * 8,5 mmol/l
B. 2 mmol/l
C. 4,5 mmol/l
D. 5 mmol/l
E. 3,3 mmol/l
481.
The patient complains of polyuria. The pathological components in urine are not
detected. The deficiency of what hormone can result in such state?
A. Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Epinephrine
D. * Vasopressin
E. Cortisol
482.
The patient with diabetes mellitus has hypoglycemic coma. The reasons for this
can be:
A. * overdosage of insulin
B. starvation
C. dehydration of the organism
D. pancreatic islet adenoma
E. Addison's disease
483.
The patient with diabetes mellitus has hypoglycemic coma. The reasons for this
can be:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* overdosage of insulin
starvation
dehydration of the organism
pancreatic islet ?-cells adenoma
Addison's disease
484.
The precursor of what bioactive substanse is thyrosine?
A. Bensoic acid
B. Androsteron
C. Insulin
D. * Epinephrine
E. Bilirubin
485.
The products of hydrolysis and modification of some proteins are biologically
active substances – hormones. Which from the below mentioned proteins is precursor for
lipotropin, corticotropin, melanotropin and endorphin?
A. * Proopiomelanocortin (POMC).
B. Neuroalbumin
C. Neurostromin
D. Neuroglobulin
E. Thyreoglobulin
486.
The prostaglandins are synthesized from
A. * Arachidonic acid
B. Oleic acid
C. Linoleic acid
D. Linolenic acid
E. Both C and D
487.
The secondary mediator in the mechanism of action of epinephrine is:
A. cCMP
B. cGMP
C. cUMP
D. cTMP
E. * cAMP
488.
The secondary mediator in the mechanism of epinephrine action is:
A. cGМP
B. * cАМP
C. cUМP
D. cТМP
E. cCМP
489.
The secondary messenger in the mechanism of ACTH action is:
A. cТМP
B. cGМP
C. cUМP
D. * cАМP
E. cCМP
490.
The secretion of glucagon is increased at:
A. In a postabsorptive period (after meal)
B. * At starvation
C. At the use of plenty of carbonhydratess
D. At the use of plenty of lipids
E. At stress
491.
The usage of glucose takes a place with its transport from intracellular space
across cell membrane inside cells. This process stimulates such hormone:
A. * Insulin
B.
C.
D.
E.
Glucagon
Thyroxin
Aldosterone
Epinephrine
492.
There is only one hormone among the neurohormones which refers to the
derivatives of amino acids according to classification. Point it out:
A. Oxytocin
B. * Melatonin
C. Vasopressin
D. Thyroliberin
E. Somatotropin
493.
These compounds relax a smooth muscles of blood vessels and reduce a blood
pressure, promote permeability of capillaries and take part in development of
inflammatory reactions. Choose this hormones (hormonoids)?
A. Renin and angiotensin
B. * Kinins
C. Prostaglandins
D. Glucocorticoids
E. Corticosteroids
494.
This hormone narrows vessels and promotes a blood pressure, increases a pulse,
relaxes a smooth muscles of bronches and intestine. Choose this hormone:
A. Thyroxine
B. Somatotropic hormone
C. Cortisol
D. Testosteron
E. * Epinephrine
495.
Transfer of information from the hormones of peptide nature on intracellular
secondary messenger takes place with participation of adenylatecyclase. Which reaction
is catalyzed with adenylatecyclase?
A. * Breaking up of ATP with formation of cАМP and pyrophosphate.
B. Breaking up ATP with formation ADF and phosphorus inorganic.
C. Synthesis ATP from AMF and pyrophosphate.
D. Breaking up of ADP with formation of AMF and inorganic phosphate.
E. Breaking up ATP with formation of AMP and pyrophosphate.
496.
?Tryptophan could be considered as precursor of
A. * Melanotonin
B. Thyroid hormones
C. Melanin
D. Epinephrine
E. Both A and B
497.
Tumor of adenohypophysis caused disorders of tropic hormones synthesis.
Choose, high level of which hormone causes acromegalia?
A. Melanocytostimulating
B. CTH
C. Luteinizing
D. * Somatotropic
E. Folikulostimulating
498.
Tumors of endocrine glands enhance amounts of hormones in blood as a rule.
What biochemical changes in blood can be at a tumor of adenohypophysis?
A. Hypoglycemia
B. * Hyperglycemia
C. Hypercholesterolemia
D. Ketoacidosis
E. Acetonuria
499.
Vasopressin has a strong antidiuretic action, stimulates the reabsorbtion of water
through the membranes of kidney canaliculies. What is its chemical nature?
A. * Peptide
B. Carbohydrate
C. Steroid
D. Lipid
E. Derivate of amino acid
500.
What from below mentioned hormones is antagonist of insulin?
A. Somatotropic hormone
B. Thyrotropic hormone
C. Calcitonin
D. * Glucagon
E. Parathormone
501.
What amino acid is a precursos for epinephrine and norepinephrine synthesis?
A. Lysin
B. * Tyrosine
C. Alanine
D. Glutamic acid
E. Aspartic acid
502.
What are effects of the kallikrein-kinin system action?
A. * Relaxion of the smooth muscles of blood vessels, reducing of blood pressure,
promotes permeability of capillaries, takes part in development of inflammatory
reactions
B. Inhibits lipase activity, regulates calcium metabolism, inhibits a gastric secretion,
stimulates a lipogenesis
C. Narrows vessels, increases a blood pressure, stimulates a secretion of aldosteron
D. Promotes glucosemia, activates a gluconeogenesis, stimulates glycogenolysis in a
liver
E. Rises a blood pressure, a pulse, promotes contractive activity of myocardium.
503.
What are effects of the rennin-angiotensin system action?
A. Vasoconstriction, oppression of secretion of aldosteron
B. * Vasoconstriction, stimulation of secretion of aldosteron
C. Relaxion of vessels, oppression of secretion of aldosteron
D. Relaxionof vessels, stimulation of secretion of aldosteron
E. Stimulation of reabsorption of sodium and potassium in kidney tubulis
504.
What biochemical symptoms are specific for diabetes insipidus?
A. Hyperglycemia, glucosuria, polyuria, decreased density of urine
B. Hypoglycemia, glucosuria, polyuria, increased density of urine
C. Normoglycemia, glucosuria, normal density of urine
D. Normoglycemia, polyuria, decreased density of urine, acidosis
E. * Normoglycemia, polyuria, decreased density of urine
505.
What biochemical symptoms are specific for diabetes mellitus?
A. Hyperglycemia, glucosuria, decreased urine density
B. Hypoglycemia, glucosuria, increased urine density, acidosis
C. Hypoglycemia, glucosuria, normal urine density
D. Hyperglycemia, glucosuria, decreased urine density, acidosis
E. * Hyperglycemia, glucosuria, increased urine density, acidosis
506.
What changes in lipid metabolism may be caused by insufficiency of
somatotropin excretion?
A. emaciation
B.
C.
D.
E.
fatty liver degeneration
atherosclerosis
* obesity
ketonemia
507.
What from below mentioned effects are specific for insulin?
A. Increases permeability of cellular membranes for glucose, activates enzymes of
Krebs cycle, activates a gluconeogenesis
B. Increases permeability of cellular membranes for glucose, represses the Krebs
cycle, inhibites a gluconeogenesis
C. * Increases permeability of cellular membranes for glucose, activates enzymes of
Krebs cycle, inhibites a gluconeogenesis
D. Diminishes permeability of cellular membranes for glucose, activates enzymes of
of Krebs cycle, inhibites a gluconeogenesis
E. Diminishes permeability of cellular membranes for glucose, inhibites enzymes of
of Krebs cycle, activates a gluconeogenesis
508.
What from next hormones has anabolic effects?
A. * Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Epinephrine
D. Thyroxine in high concentrations
E. Norepinephrine
509.
What from the below mentioned hormones are catecholamins?
A. Cortisol, hydrocortisol
B. Thyroxine
C. Estriol, estradiol
D. * Epinephrine, Norepinephrine
E. Insulin, glucagon
510.
What from the below mentioned functions specific for lipocain?
A. Activates lipogenesis, inhibits lipolysis and mobilization of fats from a depot
B. Activates oxidization of fatty acids, promotes converting of carbohydrates into
lipids
C. * Activates formation of phosphotids in a liver, stimulates the action of lipotropic
food’s factors
D. Inhibits formation of phospholipids in a liver, assists in the fatty degeneration of
liver
E. Stimulates formation of triacylglycerols in the wall of intestine, activates the
synthesis of chylomicrons in an intestine
511.
What from the below mentioned hormones activate formation of phospholipids in
a liver?
A. Somatostatin
B. Insulin
C. Lipotropnic hormone
D. Thyroxine
E. * Lipocain
512.
What from the below mentioned hormones are catabolics?
A. Thyroxine
B. * Catecholamins
C. Glucocorticoids
D. Sex hormones
E. Insulin and glucagon
513.
What from the below mentioned hormones does reduce speed of lipolysis in fatty
tisuues?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
514.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
515.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
516.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
517.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
518.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
519.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
520.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Hydrocortison
Epinephrine
* Insulin
Somatotropin
Norepinephrine
What from the below mentioned hormones is not produced in adenohypophysis?
Somatotropic.
Adrenocorticotropic.
* Melanotropin.
Thyrotropnin.
Prolactin.
What from the transferred hormones is not secreted by a pancreas?
Somatostatin;
Glucagon;
* Somatomedin;
Insulin;
Lipocain.
What hormone promotes glycogen synthesis?
Glucagon
Epinephrine
Thyroxine
* Insulin
Parathormone
What hormone promotes lipogenesis?
Epinephrine
Thyroxine
Parathormone
Glucagon
* Insulin
What hormones are prodused in a pancreas?
Insulin, glucagon, somatomedins, lipotropic hormones
Insulin, glucagon, melanocytostimulation hormone, lipocain
Insulin, glucagon, liberines and statines
* Insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, lipocain
Insulin, glucagon, lipotropic hormone, oxytocin
What is a reason of acidosis development at I type of diabetes mellitus ?
Insufficiency of insulin results in the increased formation of pyruvate, which
transforms into acetyl CoA, which is utillized for the synthesis of ketone bodies
* Insufficiency of insulin results in oppression of formation of pyruvate which
determines insufficiency of oxaloacetate
Insufficiency of insulin results in activation of glycolysis and the synthesis of
ketone bodies is activated as a result
Insufficiency of insulin results in oppression of PPP and as a result to the
increased formation of ketone bodies
Insufficiency of insulin results in increasing of glucose in blood and it
transformation on ketone bodies
What is the chemical nature of catecholamins?
Proteins
Peptids
* Derivatives of amino acid
Steroids
Derivatives of arachidonic acid
521.
What is the chemical nature of insulin?
A. Nucleotide
B. * Protein
C. Steroid
D. Carbohydrate
E. Lipid
522.
What metal is needed for functioning of insulin?
A. Iron
B. Copper
C. Cobalt
D. Calcium
E. * Zinc
523.
What substance is a precursor in the synthesis of prostaglandins in the organism?
A. Linolic acid
B. Palmitic acid
C. Linolenic acid
D. Oleic acid
E. * Arachidonic acid
524.
What types of metabolism does insulin influence on?
A. Only on carbohydrate
B. On carbohydrate and lipid
C. On carbohydrate and albumen
D. On carbohydrate, lipid and protein
E. * On carbohydrate, lipid, protein and mineral
525.
When epinephrine binds to alpha-1 receptors, one result is
A. The receptor binds to the IRS-protein
B. The receptor inhibits phospholipase-C
C. * The endoplasmic reticulum releases calcium ions
D. There is a reduction in the diacylglycerol concentration
E. Calmodulin dissociates from all the proteins to which it normally binds
526.
When the blood concentration of insulin is increases, less glucagon is produced
and there is a(n)
A. Increases in the activity of adenylate cyclase
B. * Increase in the activity of cAMP phosphodiesterase (3’, 5’-phosphodiesterase)
C. Increase in binding of cAMP to the inhibitory subunits of protein kinase A
D. Increase in cAMP
E. Increase in protein kinase A activity
527.
Where are catecholamins secrected?
A. In a thyroid gland
B. In a parathyroid glands
C. In the cortex of a suprarenal gland
D. * In the medulla of a suprarenal gland
E. In the islets of Langerhans of pancreas
528.
Where is insulin synthesized?
A. In alfa-cells of Langergans ilets
B. * In the beta-cells of Langergans ilets
C. In the delta-cells of Langergansa ilets
D. In the endothelial cells of conclusion channels of pancreas
E. In стромі of pancreas
529.
Where is rennin synthesized?
A. In a liver
B. In a pancreas
530.
531.
532.
533.
534.
535.
536.
537.
538.
C. In a thyroid gland
D. * In kidneys
E. In a hypophysis
Which from below mentioned hormones is a complex protein?
A. ACTH.
B. * Follicle stimulating hormone
C. Oxytocin
D. Glucagon
E. Somatostatin
Which from below mentioned hormones is a derivate of amino acid?
A. Calcitonin
B. Adrencorticotropic hormone
C. Insulin
D. Vasopressin
E. * Epinephrine
Which hormone does stimulate lipolysis in fatty tissue?
A. Oxytocin
B. * Epinephrine
C. Foliculotropin
D. Melanotropin
E. Calcitonin
Which hormone does stimulate lipolysis in fatty tissue?
A. Folikulotropin
B. Oxytocin
C. * Epinephrine
D. Melanotropin
E. Kalcitonin
Which hormones effect on the cells genetic apparatus?
A. Protein nature
B. Peptide nature
C. Hormones - derivates of amino acids
D. * Steroid hormones
E. All of above
Which of the following action is improper for insulin?
A. Increases the permeability of cell membranes for glucose.
B. * Inhibits the first enzyme of glycolysis – glucokinase.
C. Activates some enzymes of Krebs cycle.
D. Activates the pentose phosphate cycle;
E. Activates some enzymes of glycolysis
Which of the following effect of insulin is correct?
A. Activates the oxidation of fatty acids.
B. Activates the lipolysis.
C. Inhibits the synthesis of lipids.
D. * Enhances the synthesis of lipids.
E. All of the above
Which of the following hormone acts on the cell genetic apparatus?
A. Insulin.
B. * Testosteron.
C. Thyroxin.
D. Epinephrine.
E. Glucagon
Which of the following hormone acts on the cell genetic apparatus?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Insulin.
* Testosteron.
Glucagon
Epinephrine.
Vasopressin
539.
Which of the following hormone acts through the activation of adenilate cyclase?
A. * Epinephrine.
B. Estrol.
C. Testosteron.
D. Cortisol.
E. Aldosteron
540.
Which of the following hormone acts through the activation of adenilate cyclase?
A. * Epinephrine.
B. Estrol.
C. Testosteron.
D. Cortisol.
E. Aldosteron
541.
Which of the following hormones promotes hypoglycemia?
A. Epinephrine
B. Norepinephrine
C. * Insulin
D. Glucagon
E. Glucocorticoids
542.
Which of the following is NOT a result of insulin binding to its receptor on a
muscle cell?
A. The receptor undergoes a change in conformation
B. The receptor autophosphorylates tyrosyl residues
C. Phosphorylation of the insulin receptor substrate (IRS) is increased
D. More glucose transporters are inserted into the membrane
E. * G-protein and adenylate cyclase are activated
543.
Which of the following is not true?
A. Glucagon causes the breakdown of glycogen in liver to yield glucose to the blood
B. Insulin inhibits glycogenolysis in the liver
C. Epinephrine causes the glycogen in liver to be degraded to yield glucose to the
blood
D. Insulin causes the transport of glucose into muscle cells
E. * Epinephrine inhibits glycolysis of glucose in muscle cells
544.
Which of the following proteins is responsible for secretion of pancreatic juice
into the intestine?
A. Cholecystokinin
B. Gastrin
C. Insulin
D. Intrinsic factor
E. * Secretin
545.
Which of the following rules is correct for epinephrine?
A. Epinephrine promotes synthesis of proteins.
B. * Epinephrine promotes decomposition of proteins.
C. Epinephrine promotes synthesis of lipids.
D. Epinephrine promotes synthesis of glycogen.
E. Epinephrine promotes decomposition of glucose
546.
Which of the following rules is correct for epinephrine?
A. Epinephrine promotes synthesis of proteins.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Epinephrine promotes decomposition of proteins.
Epinephrine promotes synthesis of lipids.
Epinephrine promotes synthesis of glycogen.
All correct
547.
Which of the following statements about prostaglandins is true?
A. They are precursors to arachidonic acid
B. They release arachidonic acid from membranes through the action of
phospholipase A
C. * They were first observed to cause uterine contraction and lowering of blood
pressure
D. Although found in many organs, they are synthesized only in the prostate and
seminal vesicles
E. They may be converted to leukotrienes by lipoxygenase
548.
Which of the following statements accurately describes sex hormones?
A. They bind specific membrane receptors
B. They interact with DNA directly
C. They cause release of a proteinaceous second messenger from the cell membrane
D. * They enhance transcription when bound to receptors
E. They inhibit translation through specific cytoplasmic proteins
549.
Which of the following statements correctly describes insulin?
A. It is an anabolic signal to cells that glucose is scarce
B. It is converted from proinsulin to insulin primarily following secretion from ?cells
C. It does not have a prohormone form
D. It is a small polypeptide composed of a single chain bridged by disulfide groups
E. * Its action is antagonistic to that of glucagon
550.
Which of the following tissues is capable of contributing to blood glucose?
A. Brain
B. Adipose tissues
C. Cardiac muscle
D. * Duodenal epithelium
E. Cartilage
551.
With the purpose of analgesia a substance, which imitates the effects of morphine,
but produced in CNS, can be used. Choose it.
A. Somatoliberin
B. Oxytocin
C. Vasopressin
D. Calcitonin
E. * Endorphin
552.
________ is a process in which hormones are made less active or are eliminated
by attaching water-soluble molecules such as sulfate or glucuronic acid groups to them in
the liver.
A. Active transport
B. * Conjugation
C. Excretion
D. Metabolism
E. Structural protection
553.
A dietary deficiency of iodine can:
A. Directly affect the synthesis of thyroglobulin on ribosomes
B. * Result in increased secretion of thyroid stimulating hormone
C. Result in decreased production of thyrotropin releasing hormone
D. Result in increased heat production
E. Result in decreased heat production
554.
A hormone that increases sodium loss and lowers blood pressure is
A. Aldosterone
B. * Atrial natriuretic peptide
C. Antidiuretic hormone
D. Calcitonin
E. Glucagon
555.
A key intermediate for the synthesis of both testosterone and cortisol from
cholesterol is:
A. 7-hydroxycholesterol
B. * Pregnenolone
C. Aldosteron
D. Retinoic acid
E. 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
556.
Action of parathormone is tightly connected with vitamin:
A. A. С
B. B. A
C. * C. D
D. D. Е
E. E. K
557.
Adrenaline is...
A. Produced by the adrenal cortex
B. * Also called epinephrine
C. Released when the parasympathetic nervous system is stimulated
D. None of the above
E. All of the above
558.
An example of a mineralocorticoid is:
A. Glucagon
B. Cortisol
C. * Aldosterone
D. Testosterone
E. Insulin
559.
Associated with increased TBG (thyroxine-binding globulin):
A. Androgens
B. Colestipol
C. * Interleukin 2
D. Amiodarone
E. Estrogens
560.
Biochemical manifestation of excessive secretion of calcitonin:
A. A. Hypercalciemia
B. * B. Hypocalciemia
C. C. Hyperphosphatemia
D. D. Hypophosphaturia
E. E. Hypernatriemia
561.
Chemical nature of calcitonin:
A. * A. Peptide
B. B. Steroid
C. C. Derivative of amino acid
D. D. Derivative of аrachidonic acid
E. E. Glycoprotein
562.
Chemical nature of parathormone:
A. * A. Protein
B.
C.
D.
E.
B. Steroid
C. Derivate of amino acid
D. Lipid
E. Derivate of arachidonic acid
563.
Chemical nature of sex hormones
A. A. Proteins
B. B. Peptides
C. * C. Steroids
D. D. Derivates of the unsaturated fatty acids
E. E. Derivates of amino acids
564.
Choose a male sex hormone:
A. A. Estradiole
B. * B. Testosterone
C. C. Cortizon
D. D. Progesterone
E. E. Cortikosterone
565.
Choose the correct name of the state of hyperglycemia and glucosuria that appears
in hypercorticism?
A. A. Diabetes mellitus
B. B. Diabetes insipidus
C. * C. Steroid diabetes
D. D. Kidney diabetes
E. E. Adrenal diabetes
566.
Choose the pair of hormones that have agonistic effects on blood sugar levels:
A. A. Calcitonin and PTH
B. * B. Adrenalin and Glucagon
C. C. Glucagon and Glucose
D. D. ADH and Aldosterone
E. E. Only A
567.
Choose the statement about steroid hormones that is incorrect
A. Steroids are lipids with complex ring structures.
B. * Steroids can pass through their target cell membrane and interact with receptors
in the nucleus.
C. Steroids employ first and second messengers that amplify the cellular response.
D. The estrogens and testosterone are examples of steroid hormones.
E. All of the above
568.
Chose the effects that are caused by parathormone?
A. A. Hypocalciemia, hypophosphatemia, hyperphosphaturia
B. * B. Hypercalciemia, hypophosphatemia, hyperphosphaturia
C. C. Hypocalciemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperphosphaturia
D. D. Hypercalciemia, hypophosphatemia, hypophosphaturia
E. E. Hypercalciemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypophosphaturia
569.
Competitive inhibition of iodide uptake by the thyroid:
A. Perchlorate
B. Pertechnetate
C. * Thiocyanate
D. A & C
E. A, B & C
570.
Cortisol is produced by the:
A. * Adrenal cortex
B. Adrenal medulla
C. Pancreas
D. Thyroid gland
E. Salivary gland
571.
Cyclic AMP functions as a(n) _______________ for _______________
hormones.
A. Binding site; nonsteroid
B. Membrane receptor; steroid
C. Activity site; G protein
D. * Second messenger; nonsteroid
E. All of the above
572.
Diabetes insipidus results from a lack of:
A. Glucagon
B. Aldosterone
C. Calcitonin
D. * Antidiuretic hormone
E. Insulin
573.
Displacement of thyroid hormones (thyroxine, triiodothyronine) from TBG; may
cause hyperthyroxinemia:
A. * Methadone
B. Sucralfate
C. Lithium
D. Furosemide
E. None of the above
574.
Down-regulation occurs because
A. * Both hormone and receptor are taken into the cell by phagocytosis
B. Receptor molecules are degraded more quickly
C. There is a decrease in the rate of receptor synthesis
D. All of these
E. None of thes
575.
During emergencies, the "fight-or-flight" response
A. Decrease the heartrate
B. * Is caused by hormone secretions in the adrenal medulla
C. Is stimulated by cortisol
D. Is the result of aldosterone causing faster blood flow
E. Is ingibitad by cortisol
576.
Effective hyperthyroidism on thyroxine (T4) metabolic clearance:
A. * Increased
B. Decreased
C. No change
D. C and B
E. Only B
577.
Epinephrine, norepinephrine, and thyroid hormones are examples of
A. Proteins.
B. Glycoproteins
C. Polypeptides.
D. * Amino acid derivatives.
E. Steroids.
578.
Estrogen, progesterone, testosterone, and glucocorticoids are all examples of
A. Proteins
B. Glycoproteins
C. Polypeptides
D. Amino acid derivatives
E. * Steroids
579.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
580.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
581.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
582.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
583.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
584.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
585.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
586.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
587.
A.
B.
C.
Excessive production of thyroid hormones by the thyroid gland
Is called hypothyroidism
* Can cause nervousness, irregular heartbeat, and weight loss
Can cause stunted growth and retardation in children
Can cause a goiter
Can cause riskets
Functions of parathormone:
A. Promotes deposition of calcium in bones and decreases Ca in blood
* B. Promotes resorption of calcium from bones and increases in blood
C. Stimulates reabsorption of phosphorus in kidney
D. Stimulates reabsorbtion of sodium in kidney
E. Inhibits reabsorption of sodium in kidney
Functions of prostaglandins:
A. Regulate activity of dehydrogenase in liver
B. Regulate reabsorption of water in kidney
C. Regulate the functions of nervous system
* D. Regulate gastric secretion
E. Regulate activity of hydrolase in cells
Glands in the endocrine system
Produce hormones that are secreted into the digestive tract
* Release hormones into the bloodstream or the fluid around cells
Release hormones as rapidly as nerve impulses are transmitted
None of the above
All of the above
Hormon, that binds to receptors on Leydig cells:
* Luteinizing hormone
Prolactin
Thyroid stimulating hormone
Growth hormone
Follicle stimulating hormone
Hormone associated with diuresis:
Oxytocin
* Vasopressin
Both oxytocine and vasopresine
Neither oxytocine nor vasopressin
ACTH
Hormone associated with induction of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase:
* Cortisol
Aldosteron
Both cortisol and aldosteron
Neither cortisol nor aldosterone
Prolactin
Hormone found associated with neurophysin in secretory granules:
Oxytocin
Vasopressin
* Both oxytocine and vasopresine
Neither oxytocine nor vasopressin
Melanotonin
Hormone produced by anterior pituitary:
Oxytocin
Vasopressin
Both oxytocine and vasopresine
D. * Neither oxytocine nor vasopressin
E. Melanotonin
588.
Hormone secreted in response to angiotensin II
A. Cortisol
B. * Aldosteron
C. Both cortisol and aldosteron
D. Neither cortisol nor aldosterone
E. Prolactin
589.
Hormone that binds to intracellular receptor:
A. Cortisol
B. Aldosteron
C. * Both cortisol and aldosteron
D. Neither cortisol nor aldosterone
E. Prolactin
590.
Hormone that is incoded by the propiomelanocortin gene:
A. Luteinizing hormone
B. Follicle stimylating hormone
C. Growth hormone
D. * Melanocyte stimulating hormone
E. Thyroid hormones
591.
Hormone that mediates its action by the second messenger:
A. Cortisol
B. Aldosteron
C. Both cortisol and aldosteron
D. * Neither cortisol nor aldosterone
E. Testosterone
592.
Hormone that stimulates testosterone production:
A. * Luteinizing hormone
B. Follicle stimylating hormone
C. Growth hormone
D. Melanocitostimulating hormone
E. Thyroid hormones
593.
Hormone that stimulates the production of estradiol by the immature ovarian
follicle:
A. Luteinizing hormone
B. Prolactin
C. Thyroid stimulating hormone
D. Growth hormone
E. * Follicle stimulating hormone
594.
Hormone that stimulates the production of progesterone by the corpus luteum:
A. * Luteinizing hormone
B. Prolactin
C. Thyroid stimulating hormone
D. Growth hormone
E. Follicle stimulating hormone
595.
Hormones can be any of these types of molecules EXCEPT
A. Proteins
B. Glycoproteins
C. Polypeptides
D. * Glycolipids
E. Steroids
596.
Hormones released by nerve cells of the _______ regulate hormones secreted by
the ____________.
A. Hypothalamus, anterior pituitary
B. * Hypothalamus, posterior pituitary
C. Anterior pituitary, hypothalamus
D. Cerebellum, posterior pituitary
E. Posterior pituitary, anterior pituitary
597.
Hormones that bind to plasma proteins
A. Bind reversibly
B. Establish an equilibrium between free hormones and bound hormones
C. Must be free hormones to diffuse through the capillary walls.
D. * Usually bind only to specific types of plasma proteins.
E. All of these
598.
Hormones with a short half-life regulate activities that have a __________ onset
with a __________ duration.
A. Rapid, long
B. Rapid, short
C. Slow, long
D. * Slow, short
E. Only C
599.
Hormones'
A. Are not secreted at a constant rate
B. Function to regulate the rates of many activities in the body
C. Secretion rate is controlled by negative feedback mechanisms
D. Help maintain homeostasis
E. * All of these
600.
How glucocorticoids affect carbohydrate metabolism?
A. A. Repress gluconeogenesis
B. * B. Activate gluconeogenesis
C. C. Activate glycolisis
D. D. Stimulate the transport of glucose into cells
E. E. Stimulate pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
601.
How glucocorticoids affect lipid metabolism?
A. * A. Activate lypolysis and transformation of fats into carbohydrates
B. B. Inhibit lypolysis and transformation of fats into carbohydrates
C. C. Activate the synthesis of phospholipids and cholesterol in liver
D. D. Stimulate the synthesis of triacylglycerols and chylomicrones in the walls of
intestine
E. E. Activate oxidation of fatty acids and formation of ketone bodies
602.
How glucocorticoids affect protein metabolism?
A. A. Promote the synthesis of proteins in all organs
B. * B. Promote the synthesis of proteins in liver and activate their decomposition in
connective and muscle tissues
C. C. Promote the proteolysis in all organs
D. D. Stimulate the transport of amino acids in cells
E. E. Activate the transformation of carbohydrates to proteins
603.
How iodine containing hormones are transported in blood?
A. A. In the free state
B. * B. Connected with albumins
C. C. Connected with w-globulins
D. D. Connected with C-globulins
E. E. Connected with C-globulins
604.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
605.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
606.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
607.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
608.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
609.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
610.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
611.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
How many carbon atoms the molecules of euicosanoids contain?
A. 15
B. 18
* C. 20
D. 22
E. 24
How sex hormones affect the protein metabolism?
A. Stimulate disintegration of proteins
B. Activate conversion of proteins into carbohydrates
* C. Stimulate the synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids
D. Activate transaminases of amino acids
E. Activate the synthesis of urea
How thyroid hormones affect lipid metabolism?
A. Stimulate the synthesis of triacylglycerols
B. Stimulate lipogenesis and synthesis of cholesterol in liver
C. Activate formation of chylomicrones in intestine and VLDL in liver
* D. Activate mobilization of fats and their oxidation
E. Activate the synthesis of phospholipids in liver
How thyroid hormones affect protein metabolism?
* A. In normal concentration stimulate the synthesis of proteins, in increased –
decomposition.
B. In a small concentration stimulate decomposition of proteins, in increased their
synthesis
C. Stimulate the decomposition of proteins and their transformation into
carbohydrates
D. In certain organs stimulate the synthesis of proteins, in other - decomposition
E. Repress desamination and transamination of aminoacids
Hypersecretion of Thyroxin would be caused by an increase in the release of:
FSH or LH
STHRH or STH
TSH or ACTH
* TRH or TSH
All of the above
Hypofunction of thyroid gland in adults results in:
A. Cretinism
B. Dwarfing
C. Toxic goiter
* D. Mixedema
E. Acromegalia
Hypofunction of thyroid gland in children results in:
A. Gigantism
B. Graves disease
C. Toxic goiter
D. Dwarfing
* E. Cretinism
If there is a decrease in the specific plasma protein to which a hormone binds
More free hormone occurs
Less hormone binds to target cells
* Blood levels of the hormone increase
All of these
None of above
612.
In excess of this hormone uncoupling of the tissue respiration and oxidative
phosphorylation takes place. Decrease of ATP formation and increase of heat formation
occur. What hormone is it?
A. A. Cortizol
B. * B. Thyroxine
C. C. Progesteron
D. D. Parathormone
E. E. Glucagon
613.
In the "second messenger" theory, which is the first messenger?
A. cAMP
B. Hormone
C. Enzyme
D. * Receptor
E. All of the above
614.
In the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland is controlled by hormones made where?
A. * In the Hypothalamus
B. In the Adrenal Gland
C. In the Pancreas
D. In the Parathyroid
E. In the Anterior pituitary
615.
Increased blood glucose causes increased insulin secretion from the pancreas. This
is an example of
A. * Hormonal regulation of hormone secretion.
B. Neural regulation of hormone secretion.
C. Nonhormonal regulation of hormone secretion.
D. All of the above
E. None of the above
616.
Inhibition of thyroid hormone synthesis or release:
A. Amiodarone
B. * Lithium
C. Minoglutethimide
D. Iodides
E. E. All of the above
617.
Inhibits iodide transport into thyroid gland:
A. Ipodate
B. * Thiocyanate
C. Thioamides
D. A & C
E. A, B & C
618.
Intracellular hormone receptors are located
A. * Floating freely in the cytoplasm of target cells.
B. In the nucleus.
C. In the mitochondria.
D. In the endoplasmic reticulum.
E. Both a and b
619.
Lipid-soluble hormones
A. * Can bind to plasma proteins
B. Attach to intracellular receptors in target cells
C. Tend to have slower onset and longer duration
D. Include steroids
E. All of these
620.
More potent thyroid hormone:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
621.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
622.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
623.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
624.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
625.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
626.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
627.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
628.
A.
B.
C.
D.
T4
* T3
Equal potent
Vasopressin
Prolactin
Name a biological active compound which is the derivative of arachidonic acid:
* A. Prostaglandin
B. Thyroxine
C. Noradrenaline
D. Cholin
E. Ethanolamine
Name female sex hormones?
* A. Estradiol, estrione, estrole, progesterone
B. Testosterone, estrione, estrole
C. Cortisone, progesterone, estrione, estrole
D. Progesterone, corticosterone, estrione, estrole
E. Testosterone, estrole, corticosterone, estrione
Name hormone that is synthesized from cholesterol by cells of the adrenal cortex:
Cortisol
Aldosteron
* Both cortisol and aldosteron
Neither cortisol nor aldosterone
Prolactin
Name hormone that stimulates production of insulin-like growth factor:
Luteinizing hormone
Prolactin
Thyroid stimulating hormone
* Growth hormone
Follicle stimulating hormone
Name hormone that stimulates the synthesis of milk proteins:
Luteinizing hormone
* Prolactin
Thyroid stimulating hormone
Growth hormone
Follicle stimulating hormone
Name hormone which release is inhibited by thyroxine:
Luteinizing hormone
Prolactin
* Thyroid stimulating hormone
Growth hormone
Follicle stimulating hormone
Parathyroid hormone stimulates the formation of active form of vitamin D:
A. In liver
B. In blood
C. In brain
D. In intestine
* E. In kidneys
Parathyroid hormone stimulates the formation of active form of vitamin D:
A. In liver
B. In blood
C. In brain
D. In intestine
629.
630.
631.
632.
633.
634.
635.
636.
637.
E. * E. In kidneys
Preparation of choice for thyroid replacement.
A. * Dessicated thyroid
B. Liothyronine
C. Levothyroxine
D. Propylthiouracil
E. Methimazole
Prostaglandins are ___________ substances that regulate neighboring cells.
A. Endocrine
B. * Paracrine
C. Eccrine
D. Glycoprotein
E. Lipoprotein
Prostaglandins are synthesized from:
A. Cholesterol
B. Amino Acids
C. Carbohydrates
D. * Fatty Acids
E. Vitamins
Sex hormones are secreted by ________________.
A. All endocrine tissues of the body
B. The inner cortex of the adrenal medulla
C. The inner cortex of the adrenal medulla and the gonads
D. * The gonads
E. Pancreas
Steroid hormones are synthesized from:
A. A. Fatty acids
B. * B. Cholesterol
C. C. Glucose
D. D. Phospholipids
E. E. Amino acids
Target organs for specific hormones are determined by
A. Whether the hormone is water-soluble or lipid-soluble
B. How close the target organ is to the endocrine gland that secretes that hormone
C. * The type of receptors on that organ
D. How much hormone is secreted
E. The blood supply to the specific organ
The body's normal metabolic rate is regulated by
A. * Thyroid hormones
B. Epinephrine
C. Metaboloxin
D. Prolactin
E. Vasopressin
The derivatives of which amino acid are iodthyronines?
A. A. Tryptophane
B. B. Histidine
C. C. Glutamic acid
D. D. Serine
E. * E. Tyrosine
The effect of thyroxine on carbohydrate metabolism:
A. * A. Activates decomposition of glycogen
B. B. Represses absorption of carbohydrates in intestine
C. C. Represses decomposition of glycogen
D. D. Represses gluconeogenesis
E. E. Activates the synthesis of glycogen
638.
The following compound is a precursor for the synthesis of prostaglandins:
A. A. Tyrosine
B. B. Cholesterol
C. C. Acetyl-CoA
D. D. Glycerol
E. * E. Arachidonic acid
639.
The followings hormones are synthesized in thyroid glands:
A. A. Parathormone and iodthyronines
B. * B. Calcitonin and iodthyronines
C. C. Thyrotropic hormone and iodthyronines
D. D. Thyrotropic hormone and calcitonin
E. E. Thyrotropic hormone and parathormone
640.
The hormone _____ causes the contractions of labor.
A. Prolactin
B. Estrogen
C. * Oxytocin
D. Progesterone
E. Thyroid hormon
641.
The hormone Progesterone causes what to occur in women?
A. Follicle Development
B. Development of the Uterine Lining
C. Spermatogenesis
D. * Female Secondary Sex Characteristics
E. Only A
642.
The hypothalamus has a dual function in that it
A. * Sends nerve impulses and also makes hormones
B. Is both a nervous and olfactory organ
C. Belongs to both the nervous and circulatory systems
D. Is found connected to both kidneys
E. All of the above
643.
The insufficient production of mineralocorticoids (Addison diseases, bronze
diseases) is accompanied with muscle weakness. This is explained by the excretion with
urine increased amount of ions of:
A. * A. Na+
B. B. K+
C. C. H+
D. D. Ca2+
E. E. Mg2+
644.
The islets of Langerhans are found in the:
A. Kidney
B. Adrenal gland
C. * Pancreas
D. Pituitary gland
E. Liver
645.
The large gland located on either side of the larynx is the:
A. Parathyroid gland
B. Pituitary gland
C. * Thyroid gland
D. Adrenal gland
E. Pancreas
646.
The largest number of hormones binds to
A. Membrane-bound receptors and control ion channels.
B. Membrane-bound receptors and activate G proteins.
C. Membrane-bound receptors that phosphorylate intracellular proteins.
D. * Intracellular receptors.
E. Only C
647.
The lipid hormones are either __________ or derivatives of fatty acids.
A. Glycolipids
B. Phospholipids
C. * Steroids
D. Triglycerides
E. Glycerols
648.
The Pancreas produces which 2 hormones:
A. Epinephrine and Insulin
B. Melatonin and Glucagon
C. * Insulin and Glucagon
D. Glucagon and Norepinephrine
E. Glucagon and vasopressin
649.
The pineal gland has been implicated in the disorder
A. Diabetes mellitus
B. Hypothyroidism
C. * Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) syndrome
D. None of the above
E. Scurvy
650.
The pituitary gland is controlled by the:
A. A. Anterior LobeB.
B. * B. Hypothalamus
C. C. Posterior Lobe
D. D. Frontal Cortex
E. E. All of thq above
651.
The stalk connecting the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland is called the:
A. * Pituitary cortex
B. Infundibulum
C. Anterior lobe
D. Hypophysis
E. Neurohypophysis
652.
The synthesis of sex hormones is controlled by:
A. A. Central nervous system
B. B. Neurophysin
C. C. Hormones of hypothalamus
D. D. Aldosterone
E. * E. Gonadotropic hormones of hypophysis
653.
The target of the hormone Erythropoietin is:
A. White Blood Cells
B. The Kidneys
C. * Bone Marrow
D. Right Atrium of the Heart
E. All of the above
654.
This hormone in a normal concentration stimulates the synthesis of proteins and
nucleic acids, in increased concentration – activates catalytic processes. What hormone is
it?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
A. Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Somatotropic hormone
D. Testosteron
* E. Thyroxine
655.
This hormone promotes the transition of calcium from bones to blood, inhibits
reabsorption of phosphorus in kidneys and stimulates absorption of calcium in intestine.
Which hormone is it?
A. A. Calcitonin
B. B. Thyroxine
C. C. Triiodthyronine
D. * D. Parathormone
E. E. Thyrotropin
656.
This hormone promotes the transition of calcium from bones to blood, inhibits
reabsorption of phosphorus in kidneys and stimulates absorption of calcium in intestine.
Which hormone is it?
A. A. Calcitonin
B. B. Thyroxine
C. C. Triiodthyronine
D. * D. Parathormone
E. E. Thyrotropin
657.
This hormone stimulates the formation of 1,25- dihydroxycholecalciferol in
kidneys. What hormone is it?
A. A. Calcitonin
B. B. Thyroxine
C. C. Triiodthyronine
D. * D. Parathormone
E. E. Thyrotropin
658.
This hormone stimulates the formation of 1,25- dihydroxycholecalciferol in
kidneys. What hormone is it?
A. A. Calcitonin
B. B. Thyroxine
C. C. Triiodthyronine
D. * D. Parathormone
E. E. Thyrotropin
659.
Thyroid hormone more to be completely absorbed following oral administration
A. Thyroxine
B. Triiodothyronine
C. Both equally absorbed
D. * Neither absorbed orally, requires parenteral administration
E. Vasopressin
660.
Water-soluble hormones
A. Have a long half-life.
B. Have a short half-life.
C. * Bind to intracellular receptors.
D. Both a and c
E. Only A
661.
Water-soluble hormones, such as proteins, glycoproteins, epinephrine and
norepinephrine
A. Have relatively long half-lives.
B. * Are degraded rapidly by enzymes.
C. Have half-lives that increase and decrease slowly.
662.
663.
664.
665.
666.
667.
668.
D. Regulate activities that have a long duration
E. A, c, and d
What is a precursor for the synthesis of corticosteroids?
A. A. Tyrosine
B. B. Arachidonic acid
C. C. Phenylalanine
D. * D. Cholesterol
E. E. Glycerol
What is another name for thyroxine?
A. * Tetraiodothyronine
B. Thyroid
C. Thymus
D. Triiodothyronine
E. Lipotropic hormon
What is the function of aldosterone?
A. A. Represses reabsorption of sodium, activates reabsorption of water
B. * B. Activates reabsorption of sodium, activates reabsorption of water
C. C. Represses reabsorption of sodium, represses reabsorption of water
D. D. Represses the excretion of potassium ions from organism, activates
reabsorption of sodium
E. E. Represses the excretion of potassium ions from organism, represses
reabsorption of sodium
What is the function of calcitonin?
A. A. Promotes the transition of calcium from bones to blood, inhibits reabsorption
of phosphorus in kidney
B. B. Promotes the transition of calcium from blood to bones, stimulates
reabsorption of phosphorus in kidney
C. * C. Promotes the transition of calcium from blood to bones, inhibits reabsorbtion
of phosphorus in kidney
D. D. Promotes the transition of calcium from bones to blood, stimulates
reabsorption of phosphorus in kidney
E. E. Inhibits the exit of calcium from bones, activates reabsorption of phosphorus in
kidney
What is the function of insulin?
A. Antagonistic to glucagon
B. Decreases glycogen storage in liver and muscle
C. Reduces hyperglycemia
D. * All of the above
E. None of the above
What is the function of parathormone?
A. * Promotes transition of calcium from bones to blood, inhibits reabsorbtion of
phosphorus in kidney
B. Promotes transition of calcium from blood to bones, stimulates reabsorption of
phosphorus in kidney
C. Promotes transition of calcium from blood to bones, inhibits reabsorbtion of
phosphorus in kidney
D. Promotes transition of calcium from bones to blood, stimulates reabsorption of
phosphorus in kidney
E. Inhibits the exit of calcium from bones, inhibits reabsorption of phosphorus in
kidney
What is the half-life time of iodine containing hormones?
A. A. 20 min
B.
C.
D.
E.
669.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
670.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
671.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
672.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
673.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
674.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
675.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* B. 1 week
C. 20 sec
D. 60 min
E. 1 month
What is the name of disease that is developed in hyperfunction of thyroid glands:
A. Cretinism
B. Mixedema
C. Gigantism
* D. Graves disease
E. Dwarfism
What is the nature of iodthyronines?
A. Proteins
B. Peptids
* C. Derivatives of amino acid
D. Derivates of fatty acids
E. Steroids
What is the target of ACTH?
Most cells
Thyroid gland
Mammary glands
* Adrenal cortex
Adrenal medulla
What is the ultimate purpose of hormones?
To maintain growth
To keep the brain functioning
* To stimulate metabolism
None of the above
All of the above
Where is hormone calcitonin synthesized?
A. In parathyroid glands
B. In a hypophyses
* C. In a thyroid gland
D. In a pancreas
E. In adrenal glands
Where progesterone is formed?
A. In follicles of ovaries
B. In adrenal cortex
C. In testicules
* D. By a yellow body and placenta
E. By follicles, adrenal cortex, testicules
Which effects are specific for the thyroid hormones?
A. Stimulate the synthesis of glycogen, stimulate decomposition of proteins,
stimulate the synthesis of lipids
B. Stimulate lipogenesis, promotes the formation of ATP in mithochondria, at
large concentrations stimulate the synthesis of proteins
C. Activate lipolysis, activate the synthesis of cholesterol, activate a
gluconeogenesis
D. Activate decomposition of proteins and stimulate a basic metabolism, repress
decomposition of fats, stimulate the synthesis of glycogen in muscles and liver
* E. Activate breaking up of glycogen and absorbtion of carbohydrates in
intestine, activate lipolysis and oxidation of fatty acids, in an increased
concentration stimulate the decomposition of proteins
676.
Which fatty acid is a precursor in the synthesis of such important compounds as
prostaglandins, leucotrienes and thromboxanes?
A. * A. Arachidonic
B. B. Linolic
C. C. Oleic
D. D. Stearic
E. E. Palmitooleic
677.
Which hormone directly affects blood pressure?
A. * ADH
B. Insulin
C. PTH
D. ACTH
E. Glucagon
678.
Which hormone has steroid nature?
A. A. Calcitonine
B. B. Parathormone
C. C. Norepinephrine
D. D. Epinephrine
E. * E. Estron
679.
Which hormone has the greatest effect on metabolism?
A. GH
B. * Thyroxine
C. TSH
D. ACTH
E. FSH
680.
Which hormone has the greatest influence on the ability to secrete milk?
A. Oxytocin
B. Estrogen
C. * Prolactin
D. Progesterone
E. Vasopressin
681.
Which hormone is mineralocorticoid?
A. A. Corticosteron
B. B. Cortison
C. C. Hydrocortisone
D. * D. Aldosterone
E. E. Progesteron
682.
Which hormone is produced in the Beta cells of the islets of Langerhans:
A. Melatonin
B. Glucagon
C. * Insulin
D. Calcitonin
E. Vasopressin
683.
Which hormone is the derivative of the unsaturated fatty acids?
A. A. Estradiol
B. B. Progesterone
C. C. Noradrenaline
D. D. Testosterone
E. * E. Prostaglandins
684.
Which hormone opposes the effects of parathyroid hormone?
A. * Calcitonin
B. Glucagon
685.
686.
687.
688.
689.
690.
691.
692.
693.
C. Growth hormone
D. Prolactin
E. Vasopressin
Which hormone stimulates the synthesis of W-lactalbumin:
A. A.Oxytocin
B. Aldosterone
C. Vasopressin
D. * Prolactin
E. Cortisol
Which hormone stimulates the uterine contraction:
A. * A.Oxytocin
B. Aldosterone
C. Vasopressin
D. Prolactin
E. Cortisol
Which hormone works antagonistically to parathormone:
A. Triiodothyronine
B. Insulin
C. Estrogen
D. * Calcitonin
E. Vasopressin
Which hormones act on the genetic apparatus of cell?
A. A. Protein nature
B. B. Peptide nature
C. C. Hormones - derivates of amino acids
D. * D. Steroid nature
E. E. Polipeptide nature
Which hormones are the derivates of cholesterol?
A. * A. Adrenal cortex, sex hormones
B. B. Tropic hormones of hypophysis
C. C. Vasopressine and oxytocine
D. D. Thyroid gland hormones
E. E. Glucagon and insulin
Which hormones belong to glucocorticoids?
A. A. Cortison, hydrocortisone, aldosterone
B. * B. Cortison, hydrocortisone, corticosterone
C. C. Hydrocortisone, corticosterone, aldosterone
D. D. Estriole, corticosterone, aldosterone
E. E. Corticosterone, estradiol, corticosterone
Which hormones regulate the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus?
A. A. Liberins and statins
B. * B. Parathormone and calcitonin
C. C. Thyroid hormones and glucagon
D. D. Calcitonin and somatostatin
E. E. Calcitonin and glucagon
? Which iodthyronines do you know?
A. A. Тriiodthyronine, diiodthyronine
B. * B. Tetraiodthyronine, triiodthyronine
C. C. Thyroxine, calcitonin
D. D. Calcitonin, parathormone
E. E. Thyroxine, diiodthyronine
Which is not a function of the hypothalamus?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Affect heart rate
Control temperature
Affect water balance
Secrete FSH
None of the above
694.
Which microelement is needed for the synthesis of hormones of thyroid glands?
A. A. Iron
B. B. Fluorine
C. * C. Iodine
D. D. Cobalt
E. E. Zinc
695.
Which of the following compounds increases the release of Ca2+ from the
endoplasmatic reticulum?
A. Diacylglycerol
B. * Inositol tryphosphate
C. Parathyroid hormone
D. 1,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
E. Retinol
696.
Which of the following effects are caused by calcitonin?
A. * A. Hypocalciemia, hypophosphatemia, hyperphosphaturia
B. B. Hypercalciemia, hypophosphatemia, hyperphosphaturia
C. C. Hypocalciemia, hyperphosphatemia, hyperphosphaturia
D. D. Hypercalciemia, hypophosphatemia, hypophosphaturia
E. E. Hypercalciemia, hyperphosphatemia, hypophosphaturia
697.
Which of the following hormones is synthesized in the posterior pituitary?
A. * Antidiuretic hormone
B. Melatonin
C. Growth hormone
D. None of the above
E. Somatotropic hormon
698.
Which of the following is MISMATCHED?
A. Oxytocin – hypothalamus
B. Insulin – pancreas
C. Glucagon – pancrease
D. * Thyroid hormone -- pituitary gland
E. Vasopressin – posterior pitutery gland
699.
Which of the following is NOT a product of the adrenal gland?
A. Cortisol
B. * Aldosterone
C. Progesterone
D. Epinephrine
E. Insulin
700.
Which of the following is true of epinephrine?
A. Acts only throught the phosphatidylinositol biphosphate system
B. * Is synthesized from tyrosine
C. Decreases the level of cAMP in liver cells
D. Functions like a steroid hormone
E. Is produced from estradiol
701.
Which of the following is true of testosterone?
A. * May be converted to a more active androgen in its target cells
B. Acts by binding to receptors on the cell surface
C. Is produced from estradiol
D. Stimulates the synthesis of gonadotropin releasing hormone by the hypothalamus
E. Stimulates the synthesis of epinephrine
702.
Which of these does not directly stimulate the gonads?
A. FSH
B. * TTH
C. LH
D. ACTH
E. All of the above
703.
Which of these hormone types bind to intracellular receptors?
A. * Proteins
B. Glycoproteins
C. Polypeptides
D. Epinephrine
E. Steroids
704.
Which of these hormones is made by the posterior pituitary?
A. FSH
B. LH
C. ACTH
D. * ADH
E. Prolactin
705.
Which of these hormones is secreted in the liver?
A. Renin
B. * Somatomedin
C. Erythropoietin
D. Estrogen
E. Insulin
706.
Which of these is an example of positive-feedback regulation in the endocrine
system?
A. * An increase in blood glucose causes an increase in insulin secretion; insulin
moves glucose into cells.
B. An increase in TSH causes an increase in thyroid hormone secretion; thyroid
hormones inhibit TSH secretion.
C. Before ovulation, an increase in LH causes an increase in estrogen, which causes
an increase in LH.
D. An increase in TRH causes an increase in TSH secretion; thyroid hormone
inhibits TRH secretion.
E. An increase in blood calcium causes an increase in calcitonin secretion; calcitonin
moves calcium into the blood.
707.
Which of these is not an endocrine gland?
A. Pancreas
B. Testes
C. * Salivary gland
D. Parathyroid
E. All of the above
708.
Which statement is false?
A. The endocrine system is composed of ductless glands
B. Contents of the endocrine system are released into the bloodstream
C. * The mammory gland is part of the endocrine system
D. Exocrine glands are not part of the endocrine system
E. Non of the above
709.
Which symptoms are typical for hypofunction of thyroid gland?
A. A. Increase of body temperature, exophthalmia, loss of weight
B.
C.
D.
E.
B. Sweat, increased body temperature
* C. Lowering of basic metabolism, lowering of body temperature, and swelling.
D. Loss of weight, increase sweating, mucosa edema.
E. Hyperpigmentation, obesity
710.
Which two groups of hormones are synthesized by adrenal cortex?
A. A. Corticosteroids and mineralocorticoids
B. B. Corticosteroids and glucocorticoids
C. * C. Glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids
D. D. Catecholamines and corticosteroids
E. E. Catecholamines and glucocorticoids
711.
Which two hormones are released from the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland?
A. ADH and GH
B. ACTH and TSH
C. * ADH and oxytocin
D. TRH and CRH
E. Insulin and glucagon
712.
Disorders of the nervous system which can be observed at hypovitaminosis of B6
is related to insufficient formation of biogenic amine which is the inhibitor of CNS
activity of. Choose this biogenic amine:
A. Gamma-amino-butyric acid
B. Histamine
C. Serotonin
D. Dopamine
E. Thriptamine
713.
For a patient megaloblastic anaemia ( Addison-birmer disease). The expedient
setting of treatment the vitamin of B12 is in combination with the following preparation:
A. Nicotinic acid
B. Lipoic acid
C. Ascorbic acid
D. * Folic acid
E. Pangamic acid
714.
A doctor-dietitian advises to a patient with perinecious anaemia to use a half raw
liver in the diet. The presence of which vitamin in this product does stimulate the process
of hemopoesis?
A. Vitamin B2
B. Vitamin B1
C. * Vitamin. B12
D. Vitamin C
E. Vitamin H
715.
A patient complains about a general weakness and bleeding of gums.
Insufficiency of which vitamin can be reason of such state?
A. * Vitamin C
B. Vitamin E
C. Vitamin A
D. Vitamin H
E. Vitamin D
716.
A patient complains about absence of appetite, nausea, pain of stomach, diarrhea,
head ache, disorders of memory. There is dermatitis in the area of the neck and face.
Insufficiency of which vitamin does cause such symptoms?
A. * Vitamin B5
B. Vitamin B1
C. Vitamin B3
D. Vitamin B2
E. Vitamin B6
717.
A patient complains about loss of weight, general weakness, pain in the area of
heart, petehial hemorrhages, bleeding of gums, loss of teeth. The lack of which vitamin
does cause such symptoms?
A. Vitamin K
B. Vitamin PP
C. * Vitamin B1
D. Vitamin C
E. Vitamin B2
718.
A patient was diagnosed with beri-beri disease. Activity of which enzyme is
inhibited in an organism of the patient?
A. Fumarase
B. Citrate synthase
C. Malate dehydrogenase
D. Succinate dehydrogenase
E. * Pyruvate dehydrogenase
719.
Activation of peroxide oxidation of lipids takes place due to lack of vitamin E.
Vitamin of Е is a powerful and main antioxidant. What from the mentioned function does
not confirm it?
A. Participating in the transport of electrons and protons in a respiratory chain
B. Stimulation of ubikhinon synthesis
C. Serves as a trap for „free radicals”
D. * Stimulates mobilization of Ca from bones
E. Prevents peroxide oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids in composition of cells
membranes
720.
At bleeding the synthetic analogue of vitamin K was used. Choose it
A. Dikumarol
B. * Vikasol
C. Phylokhinon
D. Galascorbin
E. Ubikhinon
721.
Biochemical research of patient with complaints about pain in a stomach,
diminishing of secretory function of stomach which accompanied anaemia was
established. Choose vitamin, which has an antianaemic action:
A. * Coballamin
B. Thiamine
C. Retinol
D. Nicotinic acid
E. Tocopherol
722.
Biotin deficiency has been found in patient. He consumes large amounts of:
A. Meat
B. * Raw eggs.
C. Milk
D. Potato
E. Liver
723.
Concentration of Ca in blood of a patient is increased. Tubular reabsorption of
calcium is increased by
A. Cholecalciferol
B. 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol
C. * Calcitriol
D. Both B and C
E. All of these
724.
Concentration of pyruvic acid and lactic acid in blood of a patient with
sympthoms of beri beriis is increased due to deficiency of the vitamin:
A. * Thiamin
B. Riboflavin
C. Niacin
D. Pantothenic acid
E. Ascorbic acid
725.
Determination of activity of alanine aminotransferases (ALT) and aspartate
aminotransferases (AST) widely used in medical practice with the purpose of diagnostics
of internal organs damages. The coenzyme form of what vitamin is a prostetic group of
these enzymes?
A. Vitamin B5
B. * Vitamin B6
C. Vitamin B1
D. Vitamin C
E. Vitamin P
726.
For the patient with decreased immunity and frequent cold diseases was
recommend to use ascorutin as more effective preparation than ascorbic acid. Which
component in this preparation does strengthen the action of vitamin of C?
A. * Vitamin P
B. Vitamin A
C. Glucose
D. Lactose
E. Vitamin D
727.
For treatment of dermatitises, wounds and ulcers which heal badly are used
coenzyme preparations of flavin mononucleotide and flavinate. The active forms of
which vitamin are they?
A. B1
B. * B2
C. B5
D. B3
E. C
728.
For treatment of heart diseases apply preparation cocarboxylase. The coenzyme
form of which vitamin is this preparation?
A. Vitamin B1
B. Vitamin B6
C. Vitamin B12
D. Vitamin C
E. Vitamin P
729.
Formation of collagen in the organism needs hydroxylating of proline which takes
a place with participation of proline hydroxylase. Which vitamin activates this process:
A. NAD
B. Biotin
C. * Ascorbic acid
D. FAD
E. Pyridoxine phosphate
730.
Hyaluronidase splits hyaluronic acid, intercellular permeability rises as a result.
Which vitamin does inhibit activity of hyaluronidase, assist in strengthening of walls of
vessels?
A. * Vitamin P
B. Vitamin A
C. Vitamin B1
D. Vitamin B2
E. Vitamin D
731.
Insufficiency of ascorbic acid results in development of scurvy. Synthesis of
which protein is diminished?
A. * Collagen
B. Protrombin
C. Fibrinogen
D. Albumin
E. Ceruloplasmin
732.
It was established disorders of hydroxylation of proline and lysine in composition
a collagen of a patient with scurvy. Inhibition of which biochemical process does result in
this disorders?
A. * Microsomal oxidation
B. Peroxidation of lipids
C. Tissue respiration
D. Peroxidase oxidation
E. Phosphorylation
733.
It was established of POL. Activation of peroxide oxidation of lipids (POL) and
biopolymers is one of basic mechanisms of damage of structure and function of cellular
membranes. Reason of such effect is:
A. * Formation of free radicals of oxygen and suppression of anti-oxidant system
B. Hypovitaminosis B1
C. Hypervitaminosis B1
D. Hypovitaminosis B12
E. Hypervitaminosis B9
734.
Laboratory diagnosis of vitamin B12 deficiency can be made by measuring the
urinary excretion of
A. Xanthurenic acid
B. Formiminoglutamic acid
C. * Methylmalonic acid
D. Homogentisic acid
E. Both A and C
735.
Magenta tongue of a patient is found at the deficiency of the vitamin:
A. * Riboflavin
B. Thiamin
C. Nicotinic acid
D. Pyridoxine
E. Ascorbic acid
736.
Maintenance of vitamin C in an patient’s organism is normal. How much ascorbic
acid in normal condition is excreted per day with urine:
A. * 20-30 mg
B. 113,5-170,5 mg
C. 10-28 g
D. 80-100 mg
E. 18-33 g
737.
Patien with pancreatitis has hypovitaminisis of vitamin A. Vitamin A play a
general role in the folowing biochemical processes, except:
A. * The transport of Ca2+ across certain membranes
B. Processes of growth and cell differentiation
C. Inhibits the oxidation of hemoglobin
D. Processes of glycoproteins formation
E. Reduces the disulfide bonds to sulfhydril bonds
738.
Patien with pancreatitis has hypovitaminisis of vitamin A. The deficiency of
tocopherol causes many other symptoms, except:
A. Infertility in male and female
B. Degeneration of the kidneys
C. Necrosis of the liver
D. * Mental retardation
E. Dystrophy of skeletal muscles
739.
Patient complains for dry lips, cracks and “crusts” in the mouth corners, bright red
tongue, dermatitis of nasolabial folds, photophobia and conjunctivitis. To the lack of
which vitamin is it related?
A. * Riboflavin
B. Cholecalciferol
C. Pyridoxin
D. Coballamin
E. Ascorbic acid
740.
Patient suffers from redness of oral mucous, crack of mouth corners, shelling of
skin, dryness of face, inflammation of conjunctiva, vascularisation of a cornea. Possible
reason of this pathology is lack of:
A. Vitamin D
B. Vitamin C
C. Antioxidants
D. Vitamin K
E. * Vitamin B2
741.
Patient after resection of stomach. For absorption of which vitamin the Castle’s
factor is need (glycoprotein which produced by the cells of stomach)?
A. Vitamin B6
B. Vitamin E
C. Vitamin C
D. Vitamin B5
E. * Vitamin B12
742.
Patient has prolonged dark adaptation time. Prosthetic group in cone cell
photoreceptors is:
A. Iodine
B. Opsin
C. * 11-cis-retinal
D. all-trans-retinal
E. Both C and D
743.
Patient has prolonged dark adaptation time. Which from the below mentioned
enzymes does take part in the vision?
A. Glucose-6-phosphatase
B. * Alcohol dehydrogenase
C. Lactate dehydrogenase
D. Malonyl transferase
E. Alanine aminotransferase
744.
Patient has sympthoms of beri beri (lack of B1). B1 formes coenzyme TPP which
is involved in:
A. * Oxidative decarboxylation
B. Hydroxylation
C. Transamination
D. Carboxylation
E. Oxidation
745.
Patient has sympthoms of beri beri. Both Wernicke’s disease and beri beri can be
reversed by administrating:
A. Retinol
B. * Thiamin
C. Pyridoxine
D. Vitamin B12
E. Cholecalciferol
746.
Patient has sympthoms of lack of vitamin A. An early effect of vitamin A
deficiency is
A. Xerophthalmia
B. Keratomalacia
C. * Prolonged dark adaptation time
D. Follicular hyperkeratosis
E. All of these
747.
Patient has sympthoms of pellagra. In pellagra, dermatitis usually affects:
A. * Exposed parts of body
B. Covered parts of body
C. Trunk only
D. All parts of the body
E. Both (A) and (C)
748.
Patient suffers from disoders of lipids metabolism and hypovitaminosis. For
normal absorption of lipid soluble vitamins are needed:
A. Lipase
B. Phospholipase A2
C. * Bile acids and fats
D. Chylomicrones
E. Beta-lipoproteins
749.
Patient suffers from disoders of lipids metabolism and hypovitaminosis. Vitamin
F is necessary for the normal vital functions of human organism. Which from the
transferred functions are not inherent him?
A. Necessary for normal growth and regeneration of a skin epithelium
B. Decrease of cholesterol level in blood
C. Necessary for the biosynthesis of prostoglandins
D. Participating in the synthesis of phopho- and glycolipids
E. * Takes part in hydroxylation of proline and lysine
750.
Patient suffers from disoders of lipids metabolism. In the human organism
vitamins are transformed. Which vitamin does take part in formation of the coenzyme of
acylation (CoASH)?
A. Vitamin D3
B. Vitamin D
C. Vitamin C
D. Vitamin A
E. * Vitamin B3
751.
Patient suffers from disoders of proteins metabolism. Determination of activity of
some transaminases is widely used in medical practice with a purpose of diagnostics of
internal organs damages. The coenzyme of these enzymes is an active form of such
vitamin:
A. * B6
B. B1
C. B12
D. B2
E. PP
752.
Patient suffers from disoders of proteins metabolism. Avitaminosis of which
vitamin can decrease activity of transaminases of blood?
A. * B6 (pyridoxine)
B. B1 (Thiaminum)
C. B2 (riboflavin)
D. B5 (nicotine amide)
E. B10 (folic acid)
753.
Patient suffers from hypovitaminosis and disoders of lipids metabolism. Lipid
soluble vitamins execute numerous functions in an organism except:
A. * They are components of enzymes
B. Modulators of cell membranes
C. Antioxidants
D. They have provitamins
E. Cause hypervitaminosis
754.
Patient suffers from lack of vitamin K. All the following conditions cause a real or
functional deficiency of vitamin K except:
A. Prolonged oral, broad spectrum antibiotic therapy
B. * Total lack of red meat in the diet
C. The total lack of green leafy vegetables inthe diet
D. Being a new born infant
E. A and D
755.
Patient suffers from lack of vitamin K. Vitamin K is involved in posttranslational
modification of the blood clotting factors by acting as cofactor for the enzyme:
A. * Carboxylase
B. Decarboxylase
C. Hydroxylase
D. Oxidase
E. Dehydrogenase
756.
Patient suffers from scurvy. Below named are the main clinical symptoms of
scurvy, except:
A. Gums bleeding
B. Pain in heart
C. Tachycardia
D. * Xeroftalmia
E. Petechias
757.
Patient’s wounds heal badly. For treatment of dermatitises, wounds and ulcers are
used coenzymes preparations of flavin mononucleotide and flavinate. The active forms of
what vitamin are they?
A. * B2
B. B1
C. B5
D. B3
E. C
758.
People consuming polished rice as their staple food are prone to
A. * Beriberi
B. Pellagra
C. Both (A) and (B)
D. Scurvy
E. None of these
759.
?Pernicious anemia was developed in patient suffering from atrophic gastritis.
What cause of this state?
A. Increasing of HCI in gastric juice
B.
C.
D.
E.
Increasing of amylase action in urine
Increasing of pepsin secretion
* The lack of a intrinsic factor in gastric juice
All of above
760.
Proline and lysine was founded in composition of collagen fibres of a patient with
the frequent bleeding from internal organs and mucous membranes. Lack of which
vitamin does cause disorders of hydroxylation?
A. Vitamin E
B. Vitamin K
C. Vitamin A
D. Thiamin
E. * Vitamin C
761.
Pyridoxine deficiency can be diagnosed by measuring the urinary excretion of
xanthurenic acid following a test dose of
A. Glycine
B. Histidine
C. * Tryptophan
D. Pyridoxine
E. All of these
762.
Sulfanilamides of bacteriostatic action repress the synthesis of nucleotides,
nucleic acids and proteins in microorganisms cells, however in pharmacological doses
don’t change the synthesis of these compounds in the human organism because
eukaryotic cells:
A. * Don’t synthesize folic acid
B. Don’t synthesize paraaminobenzoic acid
C. Don’t synthesize nucleotides
D. Impermeable for Sulphanilamide
E. Very quickly іnactivate Sulphanilamide
763.
Sulphanilamide was prescribed to the patient with tonsillitis. The antimicrobial
action of this preparation is caused with disorders of folic acid synthesis. With which
compound does sulphanilamide compete for a active site of enzyme?
A. Glutamic acid
B. Citric acid
C. Succinate
D. Ubikhinon
E. * Para amino benzoic acid
764.
The accumulation of pyruvate in blood, decrease of activity of red blood cells
transketolase takes place of a 36 years patient, which suffers with chronic alcoholism.
Insufficiency of coenzyme form of which vitamin causes such changes?
A. * Thiamine diphosphate
B. Carboxybiotin
C. Metylcobalamin
D. Phosphopyridoxal
E. Tetrahydrofolate
765.
The lack of vitamin D in the organism of children causes a rickets. All below
mentioned are reasons of this disease except:
A. Disorders of Ca and Р metabolism
B. Disorders of mineralisation
C. * Lower activity of alkaline phosphatase
D. Lack of ultraviolet
766.
The level of hemoglobin is substantially mionectic in blood of patient. A deficit of
what vitamin is more frequent all reason of origin of anaemia?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
B2
A
E
* B12
PP
767.
The vitamin which would most likely become deficient in an individual who
develop a completely carnivorous life style is
A. Thiamin
B. Niacin
C. * Vitamin C
D. Cobalamin
E. Cholecalciferol
768.
To the patient with the heavy form of diarrhea, dermatitis and dementia was
prescribed vitamin PP. What is its role in metabolism?
A. * Participating in oxidation-reduction processes
B. Participating in the transport of oxygen
C. Participating in the hydrolysis of peptide bonds
D. Participating is in the reactions of isomerization
E. Participating is in formation of peptide bonds
769.
Vitamins are the essential components of the human diet. What from below
mentioned vitamins is used for a prophylaxis and treatment of pellagra?
A. * Vitamin B5
B. Vitamin C
C. Vitamin A
D. Vitamin B1
E. Vitamin D
770.
Woman which long time ingest the polished rice was diagnosed with polyneuritis
(beri-beri disease). Absence of which vitamin in a meal does result in development of this
disease?
A. Folic acid
B. Ascorbic acid
C. Pyridoxal
D. * Thiamin
E. E Riboflavin
771.
Appearance of what protein of fraction of A1-globulins in blood plasma,
determined by method of electrophoresis, is confirmation of diagnosis the „Primary
cancer of liver”?
A. * A-fetoprotein
B. Transferin
C. Haptoglobin
D. Ceruloplasmin
E. Interferon
772.
Appearance of what protein of fraction of A1-globulins in blood plasma,
determined by method of electrophoresis, is confirmation of diagnosis the „Primary
cancer of liver”?
A. * A-fetoprotein
B. Transferin
C. Haptoglobin
D. Ceruloplasmin
E. Interferon
773.
At the electrophoretic research of patient blood plasma found interferon. In the
area of what fraction be found this protein?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
A - Globulins
Albumins
C2 – Globulins
* D - Globulins
E - Globulins
774.
Biochemical blood test of patient B. in 70 years indicate hyperproteinemia. Which
indexes be responsible such state?
A. 40-60 g/l
B. 20-40 g/l
C. * 100-120 g/l
D. 50-60 g/l
E. 60-85 g/l
775.
Boy С., 16 years, from babyhood is sick by emphysema of lung which probably
are result of born insufficiency:
A. Fyibronektyin
B. Ceruloplazmin
C. Haptoglobin
D. * D1-antitrypsin
E. Transferin
776.
Clinico-biochemical research of patient K., 52 years, found hypoproteinemia, on
what specifies such index?
A. * 40 g/l
B. 70 g/l
C. 100 g/l
D. 85 g/l
E. 120 g/l
777.
Contents of C- globulins in blood plasma consist 30 gr/l. It can meet at all of the
followings states, except:
A. Chronic inflammatory processes
B. Infection diseases
C. Polyartrites
D. * Lung emfizema
E. Inflammatory of lung
778.
Courtmedexamination for identification of haemoglobin and manifestation of
poisoning of CO or methemoglobinformations used method:
A. Photoelectrocolorimetryc
B. Polarimetryc
C. * Spektral analysis
D. Oxyidometryc
E. Rentgenstructure analysis
779.
Exit of ions of copper from a vascular river-bed and his accumulation of
proteoglicans of connective tissue, which shows up pathological changes in a liver, brain
(hepatocerebralic degeneration), cornea, probably is the result of lowering of
maintenance in blood plasma:
A. Feritin
B. * Ceruloplasmin
C. Transferin
D. Fibronektyn
E. Haptoglobin
780.
For diagnostics of rheumatism in a patient was appointed analisis of blood on the
С-reactiv-protein. In the zone of what fraction of proteins does this protein appear on the
electrophoregrame?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Albumins
B1-globulins
С. С2- globulins
D- globulins
* E-globulins
781.
Genetic deases which arise in result of violation formation G - and -polypeptide
chains in equal amounts in the molecule of haemoglobin named:
A. Adisson-Birmer oncotic anaemia
B. Beri-beri deases
C. Porphirinuria
D. Sickle cell anaemia
E. * Talasemia
782.
In a pacient С. 38 years is uncompensated form of Diabetus Mellitus. What type
of hemoglobin does appear in erythrocytes at these terms?
A. Fetal haemoglobin (HbF)
B. Mutant haemoglobin (HbS)
C. * Glycosilic haemoglobin (HbA1c)
D. Anomalic haemoglobin G
E. Metgemoglobin (MetHb)
783.
In a patient during operation arise a stop of respiration. What consequences of this
state are observed in blood:
A. * Increase parcial pressure of CO2 and decline рН of blood
B. Lowering of parcial pressure of CO2 in blood
C. Increase рН of blood
D. Lowering рН of blood
E. Respiratory alkalosis
784.
In a patient observe hypoalbuminemia, which can be accompanied:
A. Hyperglicemia
B. * Hypocalciemia
C. Hypochloremia
D. Hypercholesterolemia
E. Hyperketonemia
785.
In a patient which appealed to the doctor, found out the method of electrophoresis
the increase of 1 – globulin fraction of blood, which is possible mainly for an account:
A. Haptoglobin
B. Ceruloplasmin
C. * C1-fetoprotein
D. Ferritin
E. Transferin
786.
In biochemical laboratory by the method of electrophoreses is conduct
fractionating of hemolysate of new-born child. It is set that correlation of haemoglobin A
the adult (HbA) and haemoglobin F (HbF) new-born is within the limits of norm and
makes:
A. HbA- 50% ; HbF- 50%
B. HbA- 40% ; HbF- 60%
C. * HbA- 80% ; HbF- 20%
D. HbA- 5% ; HbF- 95%
E. HbA- 20% ; HbF- 80%
787.
In blood of healthy man supported the constant concentration of hydrogen ions,
that put in arterial plasma:
A. 7,26± 0,04
B. 7,16± 0,04
C. 7,96± 0,04
D. * 7,36± 0,04
E. 7,46± 0,04
788.
In hospital brought an ambulance a patient L., 28 years, with the signs of the sharp
poisoning. A biochemical investigation of blood indicate high maintenance in it
methemoglobin. Which from the substances can reduce to such state?
A. Lead solts
B. Alcaloids
C. Radionuklyds
D. * Cianids
E. Carbon monoxide CO
789.
In man 30 years, that have kidney disease, which accompanied with proteinuria,
appeared the signs of violation of rolling up to blood. One of the credible causes is:
A. * Hypoalbuminemia and lowering maintenance of Ca
B. Lowering maintenance of globulins
C. Glucosuria
D. Lowering maintenance of transdoerine
E. Hypoproteinemia and increase maintenance of Ca
790.
In sick B. 41 years, is diagnosed - myelomatosis. Except for clinical signs,
characteristic for this disease, pay aattention to hypoproteinemia (180 g/l), main causes of
which is increase maintenance of:
A. Albumins
B. B1- globulins
C. C2- globulins
D. * Bens-Jonson protein
E. Ceruloplazmin
791.
In sick M. 30 years diagnosed hepatitis, main cause - violation transporting by
blood:
A. Glucose
B. Renin
C. * Calcium
D. Amino acids
E. Silfur
792.
In the patient - cirrhosis of liver. What changes on the electrophoregramme of
proteins of blood plasma can be here?
A. * Decrease fractions of albumins and D- globulins
B. Increases fractions of s- and - globulins
C. Increases fractions of albumins and lowering of I- and - globulins
D. Increase fractions of albumins and lowering of I- globulins
E. Changes are not observed
793.
In the patient M., 30 years, that during a few years suffers chronic hepatitis,
decline decreases of oncotic pressure of blood plasma which characterized the rise of
edemata. What situations can corresponding to this case?
A. Increase concentrations of albumins
B. Elevation maintenance of E - globulins
C. Decrease maintenance of D - globulins
D. * Decrease concentrations of albumins
E. Decrease maintenance of D - globulins
794.
Influence of toxic exogenous matters on the organism of man cause formation of
additional fraction of proteins in blood plasma, that discovered the method of
electrophoresis. It is:
A. Albumins
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Prealbumins
C1- globulins
D2-globulins
E-globulins
795.
Influence of toxic exogenous matters on the organism of man cause formation of
additional fraction of proteins in blood plasma, that discovered the method of
electrophoresis. It is:
A. Albumins
B. * Prealbumins
C. C1- globulins
D. D2-globulins
E. E-globulins
796.
Lowering of oncotic pressure of blood and, as result the exit of water from blood
at tissues which is accompanied edemata, comes at decreasing of albumins in blood
plasma below:
A. 60 g/l
B. 80 g/l
C. 50 g/l
D. * 30 g/l
E. 40 g/l
797.
On sharpening of rheumatic process in the patients, specifies the increase of
maintenance of all the followings indexes of blood, except:
A. С-reactive protein
B. B1 - antitrypsin
C. Sialic acids
D. Haptoglobin
E. * Albumins
798.
Patient A., 58 years, that suffers a chronic pyelonephritis (kidney disease), found
out research proteins of blood plasma by method of electrophoresis additional fraction
which confirms this diagnosis:
A. * Prealbumin
B. B2-globulin
C. Albumin
D. D1- globulin
E. Bens-Jonson protein
799.
Patient A., 58 years, that suffers a chronic pyelonephritis (kidney disease), found
out research proteins of blood plasma by method of electrophoresis additional fraction
which confirms this diagnosis:
A. * Prealbumin
B. B2-globulin
C. Albumin
D. D1- globulin
E. Bens-Jonson protein
800.
Relative hyperproteinemia takes place at all of the below states, except:
A. Diarrhea
B. Burns
C. Violetion of hemodynamics
D. Vomiting
E. * Mielomnic disease
801.
Sick women, 50 years, it is hospitalized concerning sharpening of rhematoid
process. The presence high maintenance of what protein of „acute phase of
inflammation” in blood plasma will probably confirm this diagnosis? :
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Transferin
* C-reactive protein
Albumin
Ceruloplasmin
E-fetoprotein
802.
Sick women, 50 years, it is hospitalized concerning sharpening of rhematoid
process. The presence high maintenance of what protein of „acute phase of
inflammation” in blood plasma will probably confirm this diagnosis? :
A. Transferin
B. * C-reactive protein
C. Albumin
D. Ceruloplasmin
E. E-fetoprotein
803.
The degree of oxygenation of haemoglobin (formation of HbO2) depends from
the followings factors, except:
A. Parcial pressure of blood
B. Lowering рН
C. Concentration of carbon dioxide
D. * Concentration of 1,3-dyphosphoglicerate
E. Concentration of 2,3- dyphosphoglicerate
804.
The most credible clinical-biochemical sign of sickle cell anaemia is:
A. Uremia
B. Hemoragy
C. Hyperglicemia
D. * Anemia
E. Glukosuria
805.
The people-transmitters of gene of HbS have replacement in position 6 of T-chain
of hemoglobin glutamic acid on:
A. Phenilalanin
B. Serin
C. Aspartat
D. * Valin
E. Methionin
806.
The people-transmitters of gene of HbS have replacement in position 6 of t-chain
of hemoglobin on a valine:
A. Methionine
B. * Glutamic acid
C. Serine
D. Cysteine
E. Tryptophan
807.
The people-transmitters of gene of HbS have an origin and development of
desease:
A. Talasemia
B. Hemoglobinose С
C. * Sickle cell anaemia
D. Hemoglobinose F
E. Hemoglobinose D
808.
To the doctor appealed a patient with complaints about a general weakness,
enhanceable fatigueability, mionectic capacity, turn attention on itself the blue color of
scleroticas is enhanceable. In anamnesis - disease of Konovalov-Vilson is diagnosed in
family of patient. What diagnostic test of blood plasma confirm or eliminate this disease
for a patient?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Contents of ceruloplasmin
Aktivity of A-amilase
Aktivity of trypsin
Contents of properdin
Contents of macroglobulin
809.
What fractions of proteins discover the method of electrophoresis in blood plasma
of healthy people:
A. Prealbumins, P1-, ,2- globulins
B. B1-, ,2-, , -, ,-globulins, protein of Bens-jonson
C. * Albumins, A1-, ,2-, ,-, ,-globulins
D. Prealbumins, P1-, ,2-, ,-, ,-globulins
E. Albumins, prealbumins, A1-, ,2-, ,- globulins
810.
What protein of blood absent in blood plasma of healthy man?
A. Ceruloplasmin
B. Transferin
C. Haptoglobin
D. D2-macroglobulin
E. * C-reactive protein
811.
A 3- month child has development asevere form of hypoxia manifested by
dyspnea and cyanosis. What way of hemoglobin formation is broken?
A. Replacement of hemoglobin F with hemoglobin M
B. Replacemenr of hemoglobin F woth hemoglobin S
C. Replacement of hemoglobin F with glycosylated hemoglobin
D. Replacement of hemoglobin F with methemoglobin
E. Replacement of hemoglobin F with hemoglobin A
812.
A 38-year-old women suffers from rheumatism in its active phase. The
determination of which of the following laboratory indexes is essential for diagnostics in
case of the pathology?
A. Urea
B. Uric acid
C. C-reactive protein
D. Creatinine
E. Transferrin
813.
A 70-year-old man has an intensified blood clotting, caused, first and foremost, by
the decrease of the level of ……. In the blood plasma
A. Vitamin D.
B. Albumin
C. Immunoglobulin A
D. Calcium
E. Antithrombin
814.
A considerable rise activities of MB-form of creatine kinase amf LDH1 is
revealed in the blood of a pscient. Name the most probable pathology.
A. Hepatitis
B. Myocardial infarction
C. Reumatism
D. Pancreatitis
E. Cholectstitis
815.
A disease of newborns caused by maternal antibodies attacking fetal blood cells is
A. Hemophilia
B. Erythryblastosis fetalis
C. Pernicious anemia
D. Erythropoietin
E. Chronic leukemia
816.
A man in the state of rest purposely makes himself breathe frequently and deeply
for 3 or 4 minutes. How does this exercise influence the acid-baseic balance of the
organism?
A. Metabolic alkalosis appears
B. Respiratory acidosis appears
C. Respiratory alkalosis appears
D. Metabolic acidosis appears
E. Acid-base balance does not change
817.
A patient has sicle-cell anemia diagnosed. Replacement of which amino acid in
the hemoglobin polypeptide chains with valine result in this disease?
A. Glutamate
B. Aspartate
C. Leucine
D. Arginine.
E. Threonine
818.
A patient shows rapid development of edemata. The decrease of which serum
blood proteins is responsible for edemata appearance?
A. A1-globulins
B. Albumins
C. C2-globulins
D. D-globulins
E. Fibrinogen
819.
A patient with alkalosis would experience
A. Hyperventilation
B. Hypoventilation
C. * Increased acid secretion at kidney
D. Higher blood pressures
E. Increased sodium retention
820.
A six month-old child has manifestations of frequent and axpressed hypodermic
hemorrhages.The administration of synthetic analogue of vitamin K (vikasol) proved to
have a favorable effect. In the reaction of i-carboxylation of glutamate of what blood
coagulation system proteins does this this vitamin take pert?
A. Fibrinogen
B. Prothrombin
C. Hademan factor
D. Antihemophilic globulin A
E. Rosenthal factor
821.
After repairing a car ion a garage, a car driver was brought to a clinic with
symptoms of poisoning with exhaust fumes. The concentration of what type of
hemoglobin is ncreased in his blood?
A. Carboxyhemoglobin
B. Methemoglobin
C. Carbhemoglobin
D. Oxyhemoglobin
E. Glycosylated hemoglobin
822.
Among the types of haemoglobin, indicate type of Hb of healthy person:
A. HbE
B. HbD
C. С. HbN
D. * HbA
E. Е. HbS
823.
An emergency doctor stated the sign of poisoning by carbon monoxide. What
compound became the reason for in?
A. Carboxyhemoglobin
B. Carbhemoglobin
C. Methemoglobin
D. Deoxyhemoglobin
E. * Oxyhemoglobin
824.
As a result of poisoning with carbon monoxide a person has got a head-ache, short
breath, vertigo. The decline of the content of what compound in blood resulted in this?
A. * Oxyhemoglobin
B. Carboxyhemoglobin
C. Carbhemoglobin
D. Methemoglobin
E. Deoxyhemoglobin
825.
?Basic amount of energy necessary for the transport systems through membranes
and for maintenance of integrity of cellular membrane, erythrocyte get for an account:
A. A-oxidation of higher fatty acids
B. Krebs cycle
C. * Anaerobic glycolysis
D. Aerobic glycolysis
E. Penthosophosphate pathways
826.
Currently, many states perform capital punishment (execution) using potassium
chloride injection. Why would this kind of an injection cause death?
A. Increased K+ results in disruption of the electric potential of cardiac tissue
B. Hypokalemia causes dehydration
C. Potassium chloride is an adrenergic receptor mimic
D. Hyperkalemia results in acidosis which is lethal
E. * Increased K+ causes hyperpolarization of membranes
827.
Diabetic ketoacidosis is an example of which imbalance?
A. Respiratory acidosis
B. Respiratory alkalosis
C. Metabolic alkalosis
D. * Metabolic acidosis
E. Respiratory chain
828.
Hemoglobin catabolism is accompanied by the release of iron which enters bone
marrow in composition with special transport protein and there after is repetedly used for
the synthesis of hemoglobin. The transport protein for iron is:
A. * Transferrin (siderifilin)
B. Transcobalamin
C. Haptoglobin
D. Ceruloplasmin
E. Albumin
829.
If a patient's pH is 7.3, PCO2 is 50 mmHg and bicarbonate level is higher than
normal, she is in
A. * Metabolic acidosis compensated
B. Respiratory acidosis compensated
C. Respiratory acidosis uncompensated
D. Metabolic alkalosis compensated
E. Metabolic acidosis uncompensated
830.
In the hospital of first-aid brought the patient M. which was poisoned carbon
monoxide (CO). The spectral analysis of blood of patient confirmed a presence in it:
A. * Carboxyhemoglobin
B.
C.
D.
E.
Methemoglobin
Carbhemoglobin
Oxyhemoglobin
Carbylaminhemoglobin
831.
Intoxicationcan occuer as a result of the increase of carbon monoxide
concentration in the air. Thus, transport of oxygen from the lungd to tissues realized by
hemoglobin breaks. What hemoglobin derivative appers in this case?
A. Methemoglobin
B. Oxyhemoglobin
C. Carboxyhemoglobin
D. Carbhemoglobin
E. Hemochromogen
832.
lymphatic vessels are blocked because of injury or disease?
A. Hemophilia
B. * Stroke
C. Edema
D. Acidosis
E. Alcalosis
833.
many weeks for the body RESERVE of red corpuscles to be replaced? Is it:
A. 1 week
B. 3 weeks
C. * 7 weeks
D. 21 weeks
E. 12 days
834.
Normal arterial blood pH is
A. Highly acidic
B. 6.45
C. Neutral
D. Strongly alkaline
E. * Between 7.35 and 7.45
835.
Once CO2 enters the blood stream in the tissues it is transported to the lungs
A. As a dissolved gas in the blood plasma.
B. In red blood cell cytoplasm
C. Bound to hemoglobin.
D. * As HCO3 - ion in the blood plasma
E. As HCO3 - ion in the red blood cell cytoplasm
836.
Patient С., 24 years have anaemia during few years. Hospitalized concerning great
pains in the area of stomach and joints. Laboratory information: erythrocytes – 3200000,
leucocytes – 14000, thrombocytes – 537000. During electrophoresis of hemolysate HbS
was found and 3,2% HbF. Most credible diagnose:
A. Hemoglobinose F
B. Hemoglobinose C
C. Talasemia
D. * Sickle cell anaemia
E. Hemoglobinose D
837.
The molecular analysis of hemoglobin of a patient suffering from anemia showed
replacement of 6Glu with 6Val in rWhat is the molecular mechanism of this pathology?
A. Gene mutation
B. Chromosome mutation
C. Genomic mutation
D. Amplification of genes
E. Transduction of genes
838.
The right side of the heart deals with :
A. Oxygenated blood
B. * Deoxygenated blood
C. Mixture of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
D. Either a or b at a time
E. All above
839.
The threads formed during clotting are made up of :
A. Thrombin
B. Prothrombin
C. Fibrinogen
D. * Fibrin
E. Fibronectin
840.
Under normal circumstances, _________ is probably the greatest source of H+.
A. Сarbon dioxide
B. Lactic acid
C. Oxidation of fatty acids
D. * Hydrolysis reactions
E. Salts
841.
Under the action of oxidants (hydrogen peroxide, nitrogen axides atc/),Fe2+containing hemoglobin is converted into the substance that includes Fe3+ and is not able
to transport oxygen. What substabce is it?
A. Carbhemoglobin
B. Carboxyhemoglobin
C. Methemoglobin
D. Oxyhemoglobin
E. Glycosylated hemoglobin
842.
Water, nutrients,.wastes, and gases are to the plasma as ____ is/are to the red
blood cells.
A. Carbon dioxide
B. * Oxygen
C. Gamma globulins
D. Bicarbonate
E. Hemoglobin
843.
What compound of hemoglobin will have the inhabitans of the house, where the
flue was blocked untimely?
A. Deoxyhemoglobin
B. Carbhemoglobin
C. * Carboxyhemoglobin
D. Methemoglobin
E. Oxyhemoglobin
844.
Which of the following is a treatment for leukemia?
A. Radiation
B. Chemotherapy
C. Vitamin B12 shots
D. Both a and b
E. * A, B, and C
845.
Which of the following is not likely to cause acidosis?
A. * Lung cancer
B. Hipoxia
C. Ketonemia
D. Diarrhea
E. Diabets mellitus
846.
Which of the following is the cause of sickle cell anemia:
A. A deletion of the beta globin gene promoter
B. The increased production of the alpha globin gene due to a duplication.
C. The increased production of the beta globin gene due to a duplication
D. * A missense mutation in the coding region of the beta globin gene.
E. A nonsense mutation in the coding region of the beta globin gene
847.
Which of these is not a consequence of vomiting?
A. Dehydration
B. * Metabolic acidosis
C. Respiratory alkalosis
D. Metabolic alkalosis
E. Deleytion of hydrocarbonates in organism
848.
С-thalassemia of a patient is diagnosed. What disturbances concerning
hemoglobin synthesis are observed in case of this disease?
A. Inhibition of I-chains synthesis
B. Inhibition of I-chains synthesis
C. Inhibition of I-chains synthesis
D. Inhibition of I- and --chains synthesis
E. Inhibition of I- and --chains synthesis
849.
A patient was diagnosed with the hereditary deficiency of lipoprotein lipase.
Which biochemical changes in the blood serum of this patient are possible?
A. * An increase of chylomicrons and VLDL
B. Increase of amount of chylomicrons and free fatty acids
C. Increase of amount of LDH
D. Increase of amount of chylomicrons and LDH
E. Increase of amount of HDL
850.
The plasma and urine of patients with maple syrup urine disease contain elevated
levels of each of the following amino acid, except :
A. Valine
B. Leucine
C. * Lysine
D. D.Isoleucine
E. none of above
851.
. In the patient M., 30 years, that during a few years suffers chronic hepatitis,
decline decreases of oncotic pressure of blood plasma which characterized the rise of
edema. What situations can corresponding to this case?
A. Increase concentrations of albumins
B. Elevation maintenance of E - globulins
C. Decrease maintenance of r - globulins
D. * Decrease concentrations of albumins
E. Decrease maintenance of D - globulins
852.
A 38-year-old women suffers from rheumatism in its active phase. The
determination of which of the following laboratory indexes is essential for diagnostics in
case of the pathology?
A. Urea
B. Uric acid
C. C-reactive protein
D. Creatinine
E. Transferrin
853.
A 45 years old women after long starvation has hyperketonemia. Where the
synthesis of ketone bodies takes place:
A. * mitochondria of hepatocytes
B.
C.
D.
E.
cytoplasm of hepatocytes
mitochindria of cardiomyocytes
nucleus of cardiomyocytes
cytoplasm of adipocytes
854.
A 5 years old child intestinal worms discovered. Which changes in a blood test do
testify the allergic state of organism of child?
A. Increase of amount of red blood cells
B. Worsening of blood clotting
C. * Increase of amount of eosinophils, basophiles
D. Diminishing of lymphocytes and thrombocytes
E. A blood test is in a norm
855.
A 5 years old child suffers from xanthomatos, increase of liver. Table of contents
of general lipids in blood 16 g/l, the cholesterol 9 mmol/l. After centrifugation of blood a
white layer appears. The increase of maintenance of what transport forms of lipids in
blood does take a place in this case and to the defect of what enzyme it is related?
A. Alpha-lipoproteins, LCHAT
B. Beta- lipoproteins, cholesterol estherase
C. Chylomicrons , lipoprotein lipase
D. VLDL, lipoprotein lipase
E. Chylomicrons, tissue lipase
856.
A 70-year-old man has an intensified blood clotting, caused, first and foremost, by
the decrease of the level of ________in the blood plasma
A. Vitamin D.
B. Albumin
C. Immunoglobulin A
D. Calcium
E. Antithrombin
857.
A patient has increased content of chylomicrons on an empty stomach, the
concentration of fats is extraordinarily enhanced in blood after meal, there are depositions
of fat in a skin (xanthoma). The possible reason of such state is:
A. Excess usage of animal fats
B. Hyperactivity of tissue lipase
C. Disorders of fats oxidation
D. * Insufficient activity of lipoprotein lipase in endothelium of vessels
E. The organism don’t need energy of fats oxidation
858.
A patient has increased content of chylomicrons on an empty stomach, the
concentration of fats is extraordinarily enhanced in blood after meal, there are depositions
of fat in a skin (xanthoma). The possible reason of such state is:
A. Excess usage of animal fats
B. Hyperactivity of tissue lipase
C. Disorders of fats oxidation
D. * Insufficient activity of lipoprotein lipase in endothelium of vessels
E. The organism don’t need energy of fats oxidation
859.
A patient is found to have a high concentration of cholesterol in the blood and
deposits of cholesterol under the skin. The patient is diagnosed with familial
hypercholesterolemia. What is the likely cause of this condition?
A. A deficiency in insulin production by the pancreas.
B. Insufficient chylomicron concentration in the blood.
C. Overproduction of lysosomal lipases.
D. * Lack of LDL receptors on the surfaces of nonhepatic cells.
E. all of the above.
860.
A patient suffers from obesity, atherosclerosis, in blood was established the
increase of atherogenic lipoproteins. What from the below mentioned is not reason of
such state?
A. Genetic inclination
B. Hormonal disorders
C. A lack of carbohydrates in a diet
D. Excess of carbohydrates in a diet
E. Hypodynamia
861.
A patient was diagnosed with the hereditary deficiency of lipoprotein lipase.
Which biochemical changes in the blood serum of this patient are possible?
A. * An increase of chylomicrons and VLDL
B. Increase of amount of chylomicrons and free fatty acids
C. Increase of amount of LDH
D. Increase of amount of chylomicrons and LDH
E. Increase of amount of HDL
862.
A reaction of cooperation of antibodies with an antigen is high-specific and takes
place due to the followings types of bonds, except:
A. Hydrogenic
B. Electrostatic
C. * Peptide
D. Vandervaal's
E. Hydrophobic
863.
A reaction of cooperation of antibodies with an antigen is high-specific and takes
place due to the followings types of bonds, except:
A. Hydrogenic
B. Electrostatic
C. * Peptide
D. Vandervaal's
E. Hydrophobic
864.
An antigen after incorporation into an organism contacts with the receptors of
lymphocytes, causes the transition of cells to a mitotic cycle. Transfer of the signal from
a membrane is carried out with the help of mediators. Which from them does not
participate in this process?
A. Inositol triphosphate
B. Diacylglycerol
C. Ions of Ca++
D. * UTP
E. cGМP
865.
Antibodies are powerful weapons in the body's defense against microorganisms.
However, there are limits to what an antibody can actually do. Which of the following is
NOT an action that an antibody can actually accomplish?
A. cause an agglutination of antibodies and antigens, forming an antibody–antigen
complex
B. attach to a bacterial cell antigen, preventing the bacterium from attaching to
anything else
C. start a complement protein cascade
D. * poke microscopic "holes" in a bacterial cell membrane, causing it to die
E. Both A and D are correct.
866.
As a result of development of kidney insufficiency a patient has a necessity for the
transplantation of a kidney. Which analysis must be done to avoid tearing away of
transplanted organ?
A. To define the amount of gamma-globulins in blood
B.
C.
D.
E.
To define the amount of lymphocytes in blood
* To define the proteins of main complex of histocompatability in leucocytes
To discover state of the system of complement in blood of recipient
To define A/G coefficient.
867.
As result of incorporation of antigen in an organism takes place a complex of
biochemical processes, directed on it neutralization and deletion. Choose from the below
mentioned an incorrect immune responses of organism:
A. Binding of antigen to the proteins-receptors of lymphocytes
B. * Activating of gluconeogenesis
C. Activating, prolipheration, differentiation of T-cell
D. Modification of B-lymphocytes in plasmatic cells and synthesis of antibodies
E. Activating of the system of complement, endocytosis and lysis of the antigen by
tissue macrophages
868.
Crioglobulin – the protein of C-globulin fraction, which absent in blood plasma of
healthy people, appears at:
A. Diabetus Mellitus
B. Wilson disease
C. * Leykoses, mielom disease
D. Starvation
E. Lung emphysema
869.
During the complex inspection of 48-years-old patient was determined HDL/LDL
which used for diagnostic:
A. Diabetes mellitus
B. Chronic pancreatitis
C. Hypothyroidism
D. * Atherosclerosis
E. Myocardium infarction
870.
During the complex inspection of 65-years-old patient was determined HDL/LDL
which used for diagnostic of:
A. Diabetes mellitus
B. Chronic pancreatitis
C. Hypothyroidism
D. * Atherosclerosis
E. Myocardium infarction
871.
Essence of immune reaction of organism is formation of antibodies against
foreign factors. Choose what from below mentioned functions are not specific for the
antibodies:
A. Fastening and activating of complement
B. * Ability to change membrane potential of the antigen
C. Binding to the receptors on the cells surface of macrophages
D. Binding to the receptors of mast cell
E. Ability to penetrate the placenta barrier
872.
How is it a mother who is breast feeding positively affects her baby's immune
system?
A. she gives her baby permanent antibodies she has produced
B. she gives her baby antigens she has produced in her breast milk
C. * she gives her baby antibodies she has produced in her breast milk
D. she gives her baby immune cells to fight incoming invaders
E. Both C and B are correct.
873.
If all of your cells are covered in antigens (and they are), why doesn't your
immune system kill/attack all cells?
A. because your immune system is dedicated to finding invaders
B.
C.
D.
E.
* because your immune system is very sophisticated
because your healthy cells are not "tagged" in any way
because your cells are "tagged" healthy by cell membrane protiens.
all of the above
874.
In the patient - cirrhosis of liver. What changes on the electrophoregramme of
proteins of blood plasma can be here?
A. * Decrease fractions of albumins and D- globulins
B. Increases fractions of I- and - globulins
C. Increases fractions of albumins and lowering of I- and - globulins
D. Increase fractions of albumins and lowering of f- globulins
E. Changes are not observed
875.
Intoxication can occur as a result of the increase of carbon monoxide
concentration in the air. Thus, transport of oxygen from the lungd to tissues realized by
hemoglobin breaks. What hemoglobin derivative appers in this case?
A. Methemoglobin
B. Oxyhemoglobin
C. Carboxyhemoglobin
D. Carbhemoglobin
E. Hemochromogen
876.
?On the surface of lymphoid cells (B-lymphocytes) proteins -receptors which
recognize and specifically link antigens are placed. Which chemical nature of these
receptors?
A. Histons
B. Proteins
C. Krioglobulines
D. * Immunoglobulines
E. Globin
877.
On the surface of lymphoid cells (B-lymphocytes) proteins -receptors which
recognize and specifically link antigens are placed. Which chemical nature of these
receptors?
A. Histons
B. Proteins
C. Krioglobulines
D. * Immunoglobulines
E. Globin
878.
Once vaccinated, you have had a primary exposure to specific antigens. If you
ever encounter this antigen again, you will mount a rapid immune response due to:
A. cytotoxic T cells
B. antibodies
C. antigen presenting cells
D. * memory cells
E. all of the above
879.
Patient has ketonemia and ketonuria, amount of glucose in blood 3,5 mM/l,
cholesterol – 4,5 mM/l. What malfunctions could cause this?
A. * diabetes mellitus
B. carbohydrates deficit in nutrition
C. atherosclerosis
D. excessive usage of fats
E. liver disease
880.
Pollen often causes such allergic reactions as itch, edem Simultaneously in an
organism the enhanceable amount of histamine accompanies:
A. * Dilatation of blood vessels and increase their permeability
B.
C.
D.
E.
High blood pressure
Diminishing of the synthesis of immunoglobulins
Degradation of antibodies
Activation of a histidin decarboxylase
881.
Pollen often causes such allergic reactions as itch, edema. Simultaneously in an
organism the enhanceable amount of histamine accompanies:
A. * Dilatation of blood vessels and increase their permeability
B. High blood pressure
C. Diminishing of the synthesis of immunoglobulins
D. Degradation of antibodies
E. Activation of a histidin decarboxylase
882.
Proteins of main complex of histocompatability are the main proteins of
immunological individuality of organism. All below mentioned functions inherent them
EXEPT:
A. Participating is in cooperation between lymphoid cells
B. They are proteins of transplantation
C. * Execute a catalytic function
D. Participating in cooperating with an antigen on the cells surface
E. Send cytotoxic T-effectors to the infected „target”.
883.
Recognition of foreign factors (antigens) in an organism carries out lymphocytes
with the help of proteins-receptors. How many molecules of immunoglobulin are placed
on the surface of lymphoid cell:
A. * About 105
B. 10-20 molecules
C. Near 1000 molecules
D. 1010
E. None of above
884.
Recognition of foreign factors (antigens) in an organism carries out lymphocytes
with the help of proteins-receptors. How many molecules of immunoglobulin are placed
on the surface of lymphoid cell:
A. * About 105
B. 10-20 molecules
C. Near 1000 molecules
D. 1010
E. None of above
885.
Reliability of implementation of protective function of organism is provided by
the numerous factors of the immune system. Immune function is inherent to all below
mentioned factors except:
A. Plenty of clones of B- lymphocytes
B. A high affinity of membranes immunoglobulins to the antigens
C. Cooperation of many clones of B- lymphocytes with antigen
D. Presence in the organism of activated B- lymphocytes as cells of „memory” to the
certain antigens
E. * Sufficient content of proteins in blood
886.
Technogenic, ecological, social and other factors often result in the damage of the
immune system of organism, reduce resistance of human organism to the infections.
Immunological insufficiency can be result of such disorders except:
A. * Insufficient synthesis by the liver of gamma-globulins
B. Deficiency of stem cells of bony marrow
C. Disorders of activating of T-cells
D. Disorders of function B-lymphocytes and secretion of antibodies
E. Deficiency of the system of complement
887.
The allergic reaction of organism is related to activating of complement by a
partial hydrolysis. Among the below named functions of the low-molecular peptides
choose correct:
A. Diminish the amount of eosinophils and basophiles
B. Weaken construction of smooth muscles
C. * Increase permeability of walls of capillaries
D. Diminish permeability of walls of capillaries
E. Strengthen the chemo taxis of leucocytes.
888.
The allergic reaction of organism is related to activating of complement by a
partial hydrolysis. Among the below named functions of the low-molecular peptides
choose correct:
A. Diminish the amount of eosinophils and basophiles
B. Weaken construction of smooth muscles
C. * Increase permeability of walls of capillaries
D. Diminish permeability of walls of capillaries
E. Strengthen the chemo taxis of leucocytes.
889.
The amount of urea in the patient's blood is 16 mmol/l, in daily urine 6 g. Which
of the following is the possible reason for this:
A. liver disease
B. starvation
C. * kidney disease
D. acidosis
E. thyrotoxicosis
890.
The amount of urea in the patient's blood is 16 mmol/l, in daily urine 6 g. Which
of the following is the possible reason for this:
A. liver disease
B. starvation
C. * kidney disease
D. acidosis
E. thyrotoxicosis
891.
The concentration of urea in the blood of healthy adult is:
A. 10-12 mM/l
B. 12-20 mM/l
C. 1-2 mM/l
D. * 3-8 mM/l
E. 15-18 mM/l
892.
The damage of the immune system reduces resisting of human organism to the
infections. Immune status of organism depends on the followings structures, except:
A. Bony marrow
B. Thymus
C. Tissue macrophages
D. Lymphatic nodes
E. * Hypophysis
893.
The damage of the immune system reduces resisting of human organism to the
infections. Immune status of organism depends on the followings structures, except:
A. Bony marrow
B. Thymus
C. Tissue macrophages
D. Lymphatic nodes
E. * Hypophysis
894.
The disease AIDS is caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). One of
the reasons why this disease has resisted a cure is because it attacks the body's immune
system, the very system that is designed to resist viral infections. Which of the immune
system cells does the AIDS virus specifically target for infection?
A. B cells
B. * Helper T cells
C. memory cells
D. natural killer cells
E. none of the above
895.
The following acute phase protein increase dramatically in concentration during
inflammation :
A. ceruloplasmin
B. haptoglobulin
C. C-reactive protein
D. fibrinogen
E. C3
896.
The immunological response of organism for foreign factors is closely related to
the functions of proteins of main complex of histocompatability that initiate the lysis of
cells. The mechanism of their action includes the row of processes, except:
A. Proteins of main complex of histocompatability send cytotoxic T-effectors to the
antigen
B. Lymphocyte throws out on a membrane of the „target”-cells (antigen) protein
perphorin
C. Perphorin forms pores in the cellular membrane of „target” -cells
D. * Electrochemical potential changes on the membrane of „target” -cells
E. Through pores in a membrane water and electrolytes flow and cause lysis of
„target” -cells
897.
The patient has symptoms of general adiposity and atherosclerotic changes. From
the list of possible reasons should be ixcluded:
A. * lack of carbohydrates in food
B. smoking
C. alcohol addiction
D. genetic factors
E. excess of carbohydrates and lipids in nutrition
898.
The patient possibly has atherosclerosis. What of the below helped to prove this?
A. increase of general lipids in blood
B. increase of ketone bodies in blood
C. increase of high density liporoteins
D. decrease of phospholipids in blood
E. * increase of low density liporoteins
899.
The surface of bacterial cells is covered with proteins that the human body can
recognize as belonging to a foreign, invading microorganism. These molecules are
collectively referred to as ...
A. antibiotics
B. antiseptics
C. * antigens
D. antibodies
E. none of the above
900.
The wide spectrum of immunological effects is related to the row of soluble
factors of protein nature, which produced by T-cell, mast cells, macrophages, fibroblasts.
All below named proteins belong to these factors, except:
A. * Liberines and statins
B. Cytokines, monokines
C. Lymphokines, lymphotoxins
D. Interleukins
E. Interferon
901.
To the deficiency of which immune proteins AIDS related?
A. B1- antitrypsin
B. * ? - globulins
C. С-reactive protein
D. Macroglobulin
E. Ceruloplazmin
902.
Transplantation of organs and cells between persons, which are not relatives,
frequently leads to tearing away of transplanted organ. What proteins are unique for each
organism and serve as the markers of immunological individuality of organism?
A. Immunoglobulins of B- lymphocytes
B. Proteins-receptors of T-cell
C. Proteins of the system of complement
D. * Proteins of I class of main complex of histocompatability
E. Proteins of II class of main complex of histocompatability
903.
Which class of antibody is secreted into breast milk where it is delivered to the
suckling neonate, and transported through the gut lumen into blood of the neonate?
A. * IgA
B. IgG
C. IgM
D. IgD
E. IgE
904.
A new-born child manifests symptoms of icterus. The introduction of low doses of
Phenobarbital (the inductor of the synthesis of UDP-glucuronyltransferase) promoted the
improvement of the clinical state. Which of the biochemical processes listed below is
activated by the Phenobarbital-induced enzyme?
A. Gluconeogenesis
B. Microsomal oxidation
C. Tissue respiration
D. * Conjugation
E. Glycogen synthesis
905.
In a patient increased rotting of proteins in an intestine. How are the toxic
products of this process harmless?
A. Hydrolysis
B. Isomerisation
C. Solvatacion
D. Partial proteolisis
E. * Conugation with sulphuric and glucuronic acids
906.
50-years patient is disturbed by pains in right underrib after the reception of fatty
food. Esteblish yellow colour of sclerotic and skin, acholic excrement, urine, – to the
color of beer. Presence of what matter in urine of patient did stipulate the dark coloure of
urine?
A. Bilirubinglucoronids
B. Ketone bodies
C. Urobilin
D. Sterkobilin
E. Urea
907.
A 16-year patient is diagnosedwith hereditary deficiency of UDPglucuronyltransferase. Laboratory investigation showed hyperbilirubinemia conditioned
mainly by the increase of concentration of….. in the blood.
A. Urobilinogen
B.
C.
D.
E.
Direct bilirubin
* Indirect bilirubin
Stercobilinogen
Biliverdin
908.
A 20-year-old patient is diagnised with inherited deficiency of UDPglucuronyltransferase. The increased concentration of what blood component confirms
the diagnosis?
A. Stercobilinogen
B. Direct (conjugative) bilirubin
C. Urobilin
D. * Indirect (conjugation) bilirubin
E. Indican
909.
A 26 years-old women complain the lowering concentration of urea in blood on
such conditions, except:
A. Defeat of liver by a pathological process
B. Insufficiency one of enzymes which form urea
C. Acidosis
D. Protein starvation
E. * Surplus using of proteins
910.
A 26 years-old women on 2-7 days of complete starvation maintenance of glucose
in blood of healthy man is supported within the limits of norm to due to:
A. Gluconeogenesis from lactat and pyruvat
B. Breaking up to glucose of glycogen of liver
C. * Gluconeogenesis from amino acids and glycerin
D. Breaking up to glucose of glycogen of muscles
E. Converting into glucose of fatty acids
911.
A 35-year-old developed immune hemolytic anemia. The level of what substance
increase in the serum of blood to the utmost?
A. Mesobilinogen
B. Direct bilirubin
C. Stercobilinogen
D. * Indirect bilirubin
E. Protoporphyrin
912.
A 46-year women, suffering from cholelithiasis developed icterus. The urine
become dark-yellow colour and the feces discolored. The concentration of what
substance in the blood serum woulde rise mostly?
A. Non-conjugation bilirubin
B. * Conjugation bilirubin
C. Biliverdin
D. Mesobilirubin
E. Urobilinogen
913.
A 54 years-old man at the short starvation after the consumption of carbohydrate
meal, hexosis in a liver transform into glucose-6-phosphate, which can feel farther
transformations, except:
A. * Gluconeogenesis
B. Pentosophosphate cycle
C. Synthesis of glycogen
D. Glycolysis
E. Synthesis of fatty acids
914.
A 57-year-old woman suffered an attack of hepatic colic followed by jaundice.
Ultrasound examination revealed an accluson of the general bile duct with a stone. The
rising level of what substance in blood is indicative of mechanical jaundice?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Verdohemoglobin
Biliverdin
* Direct bilirubin
Indirect bilirubin
Stercobilin
915.
A 68-year-old woman visits her physician complaining of labored breathing and
swelling in her lower extremities. Physical examination is consistent with a diagnosis of
congestive heart failure. An increase in which of the following is the most likely
explanation for the swelling in her legs?
A. Interstitial colloid osmotic pressure
B. Lymph flow
C. Plasma colloid osmotic pressure
D. * Right atrial pressure
E. Stroke volume
916.
A 70 years –old man have fatty infiltration of liver, which often drive to fatty
degeneration, can cause all factors, except:
A. Exessive arrive of fats from fatty tissues
B. Lag of metabolisation of fat from arrive
C. Chronic protracted and infectious illnesses
D. Arrive to organism galogen derivatives of carbochydrates
E. * Predominance in a ration of proteins
917.
A new-born child shows signs of yellow coloring of skin and mucous membranes.
A possible cause of this state is the provisional deficiency of the enzyme:
A. * UDP-glucuronyltransferase
B. Uridine transferase
C. Heme synthetase
D. Heme oxygenase
E. Biliverdin reductase
918.
A newborn child is found to have physiological icterus. The level of free bilirubin
in the blood considerably exceeds the normal range. The deficiency of what enzyme is
status conditioned by?
A. Heme oxygenase
B. Transaminase
C. Xanthine oxidase
D. D.Adenosine deaminase
E. * UDP-glucuronyltransferase
919.
A newborn with hemolytic illness has developed encephalopathy. The increased
level of what substance in blood caused the lesion of the CNS?
A. * Bilirubin unrelated to albumin
B. Bilirubin-albumine complex
C. Bilirubin-glucuronide complex
D. Verdohemoglobin
E. Bile asids
920.
A pacient with concentration of cholesterol in blood - higher 7 mmol/l can result
in such changes, except:
A. Formation of cholesterol stones in a gall-bladder
B. Atherosclerosis
C. Strengthening selection through an intestine
D. Deposit in a skin and other tissues
E. * Oxidation to CO2 and H2O
921.
A patient appealed to the hospital with complaints about a general weakness,
aching stomach-aches, bad appetite, yellowing skin. In the blood serum of patient 77,3
mkM/l of general bilirubin and 70,7 mkM/l conjugated. Which most credible pathology
for a patient?
A. * Mechanical jaundice
B. Sharp hepatitis
C. Cirrhosis of liver
D. Hemolitic jaundice
E. Hepatic jaundice
922.
A patient has yellow coloring of the skin, dark urine and yellow –colored feces.
The increase concentration of what substance will be observed in the blood serum?
A. Conjugation bilirubin
B. * Non-conjugation bilirubin
C. Mesobilirubin
D. Verdoglobin
E. Biliverdin
923.
A patient with complaints of general weakness, stomachache and bad appetite was
admitted to a clinic. A doctor suspected icterus. In the blood serum the total bilirubin
content is 77>3 mM/l, the direct bilirubin content is 70,76 mM/l. What type of icterus is
the most credible in this case?
A. * Mechanical icterus
B. Acute hepatitis
C. Liver cirrhosis
D. Hepatic icterus
E. Hemolitic icterus
924.
A toxic waste product of protein metabolism that produced in the liver must be
excreted from the body is
A. * Ammonia
B. Carbon dioxide
C. Urea
D. Uric acid
E. Only B and D
925.
A woman with chronic hepatitis complains of sensitivily to barbiturates which she
tolerated before without of the liver is damaged?
A. Excretory
B. * Disintoxification
C. Hemodinamic
D. Hemopoetic
E. Cytophagus
926.
After blood transfusion in a patient a skin and mucus shells yellow colour,
increase the level of general and nondirect bilirubin in blood, maintenance of urobiline in
urine increase, in feces – appear level of stercobilin. Which type of jaundice does it
testify?
A. Inherited jaundice
B. * Hemolitic jaundice
C. Obstructive jaundice
D. Hepatic jaundice
E. Jaundice of new-born
927.
After hard physical work during rest there are stimulation some metabolic ways of
carbohydrates, except:
A. Glycogenes
B. Gluconeogenesis from lactat
C. Gluconeogenesis from glycerin
D. * Glycolysis, Krebs cycle
E. Gluconeogenesis from amino acids
928.
At complete starvation during 12-24 ours maintenance of glucose level in blood of
healthy man in norm is supported within the limits mainly to:
A. Gluconeogenesis from amino acids
B. Gluconeogenesis from lactat
C. Breaking up of glycogen in muscles
D. * Breaking up of glycogen in a liver
E. Transformation of proteins on glucose
929.
At the inspection of blood of patient found out the considerable increase level
isoenzyme LDG5 and activity of AlAT. Do supposition about possible disease:
A. Heart attack of myocardium
B. * Hepatitis
C. Rheumatism
D. Pancreatitis
E. Gout
930.
At the inspection of patient found out stagnation of bile and stone in a gallbladder. Name the basic component of stones which appeared in this state:
A. Protein
B. * Cholesterol
C. Triglycerides
D. Direct bilirubin
E. Mineral salts
931.
Excess intake of iron may be pathological because it may accumulate in the liver
and cause cirrhosis. The term used to describe excess iron accumulation in the body is
A. Anemia
B. Polycythemia
C. Erythrocythemia
D. * Hemochromatosis
E. Xeropthalmia
932.
For a child which borned 2 days ago, observe the yellowing colour of skin and
mucus shells. Reason of such state can be a lack of enzyme:
A. * UDP-glyucuroniltransferase
B. Sulphontransferase
C. Hemshyntetase
D. Hemoxigenase
E. Biliverdinreductase
933.
For a patient 27 years found out the pathological changes of liver and brain. In
blood plasma decrease, and in urine – increases maintenance of copper. Diagnosed Vilson disease. Activity of what enzyme does need investigate in blood plasma for
conformation of diagnosis?
A. Xantinoxidase
B. Carboangidrase
C. * Ceruloplasmin
D. Leycinaminopeptidase
E. Alkogoldehydrogenase
934.
For a patient 45 years with the intoxication of liver during the leadthrough of test
with the bensoate of sodium (test of Kvik) on detoxification ability found out a low level
in urine:
A. * Hipuric acid
B. Oxiproline
C. Kreatinine
D. Urea
E. Amino acids
935.
For a patient edemata appeared with the cirrhosis of liver. What is possible reason
of their appearance?
A. * Diminishing maintenance of albumin in blood
B. Diminishing maintenance of haptoglobin
C. Increase in blood of ceruloplasmin
D. Diminishing in blood of Na+ ions
E. Lowering maintenance of glucose in blood
936.
For a patient increase in the blood plasma conjugated (direct) bilirubin is set at a
simultaneous increase unconjugated (undirect) and decrease in fecees and urine of
stercobilinogen. What type of jaundice does it testify?
A. * Obstractive
B. Hepatic
C. Hemolitic
D. Jilbert disease
E. Jaundice is absent
937.
For a patient which practises upon smoking, found out a tumour of lung. What is
condition the carcinogenic action of tobacco?
A. * Transformation of benzpiren into oxibenzpiren in a liver
B. Disintegration of benzpiren of tobacco to NH3 in tissues
C. Binding of benzpiren with glucuronic acid in a liver
D. Dissolution of benzpiren in blood plasma
E. Accumulation of benzpiren in tissues
938.
For a patient which use a dicoumarol, found the decreasing level of protrombin
from a 0,15 g/l to 0,05g/l, necessity for a hemopexis – formation of blood clot. It took a
place as a result:
A. * Insufficiency of vitamin K
B. Insufficiency of vitamin B2
C. Insufficiency of vitamin C
D. Lowering concentration of calcium in blood
E. Lowering maintenance of globulins
939.
For a patient with surplus formation of ketone bodies in liver, which shows
hyperketonemia, ketonuria and smell of acetone is named - ketosis. He is in such cases,
except:
A. Starvation
B. Diabetes Mellitus
C. * Diabetes insipidus
D. Surplus use of alcohol
E. In pregnant woman at protracted vomiting
940.
For youth 16 years diagnosed the deficit of UDP-glyucuroniltransferase.
Laboratory determined a hyperbilirubinemia, predefined mainly an increase in blood
concentration of:
A. Direct bilirubin
B. * Undirect bilirubin
C. Urobilin
D. Biliverdin
E. Transferrin
941.
For youth 18 years with sharp toxic hepatitis in the blood serum will be
enhanceable level:
A. * Alaninaminotransferase
B. Creatinkinase
C. Alkilane phosphatase
D. D-amilase
E. Laktatdehydrogenase-1 (LDG1)
942.
Harmless of xenobiotis (medications, epoxides, aldehydes, nitroderivatives and
others) and endogenous metabolits (estradiol, prostaglandins, leukotrienes) takes place in
a liver by them conjugation with:
A. * Glutation
B. Aspartat
C. Glycine
D. S-adenosilmetionin
E. Phosphoadenosine
943.
Hepatic detoxification of natural metabolites and xenobiotics in the patients liver
is broken. Name the cytochrome, the activity of which is presumably decreased:
A. Cytochrom c1
B. Cytochrome oxidase
C. Hemoglobin
D. Cytochrom b
E. * Cytochrom P450
944.
Hepatitis can cause the urine to be the color
A. * Yellow
B. Black
C. Amber
D. Greenish-brown
E. Blue
945.
Hepatitis, cirrhosis and tumours of liver, can take a place such violations of
protein metabolism, except:
A. Hypoalbuminemia
B. Hypoprothrombinemia
C. Gemoraggi
D. Asotemia
E. * Hyper-gamma-globulinemia
946.
In a patient cirrhosis of liver. Research of which from the adopted matters which
are exreted with urine can characterize the state of antitoxic function of liver?
A. Creatinine
B. Amino acids
C. Uric acid
D. Ammonia salts
E. * Hypuric acid
947.
In a patient with jaundice arose up: increase in blood plasma of general bilirubin
due to nondirect (free), in feces and urines – high maintenance of stercobilin, level of
direct bilirubin (conjugative) in blood plasma within the limits of norm. About which
type of patology of liver is it possible?
A. * Hemolitic jaundice
B. Hepatic jaundice
C. Mechanical jaundice
D. Cirrhosis
E. Hepatitis
948.
In blood of healthy adult man and nonpregnant women this protein does not
appear. But at primary liver cancer his level grows. Name him:
A. Transferrin
B. Feritin
C. * C-fetoprotein
D. Tiroxintranspoting protein
E. Crioglobulin
949.
In man 70 years predefined an enhanceable level of blood clotting, conditioned by
a decrease in blood plasma:
A. Albumin
B. Immunoglobulin A
C. * Heparin
D. Vitamin D
E. Calcium
950.
? In sick M. 24 years during starvation, glycogen in liver decompose to glucose-1phosphate. How does from him free glucose formed , which can act from a liver to the
brain in time of hypoglicemia?
A. Glucose-1-phosphate split on glucose and inorganic phosphate in a liver
B. Glucose-1-phosphate disintegrates on constituent component in blood
C. * Glucose-1-phosphate transforms at first on glucose-6-phosphate, on which act
specific phosphatase
D. Glucose-1-phosphate at first passes on fructose-6-phosphate
E. Glucose-1-phosphate experience changes from the side of phosphofructikinase
951.
In sick with complaints about feeling of heaving in right anderib, itch of skin,
crabbiness, fatigueability, it is discovered at a laboratory inspection: hyperbilirubinemia
with predominance of conjugative bilirubin, tymol test in a norm. What pathology testify
these changes?
A. Sharp hepatitis
B. * Mechanical jaundice
C. Gemolitic jaundice
D. Cirrhosis of liver
E. Pancreatitis
952.
In the girl of 23 years, exhausted starvation, more reliable in liver increases:
A. Synthesis of triacylglicerol
B. * Gluconeogenesis
C. Synthesis of cholesterol
D. Formation of uric acid
E. Formation of conjugative bilirubin
953.
Liver cirrhosis of a patient was diagnosed. Determination of which of the
compounds exreted with irine characterizes the state of antitoxic function of the licer?
A. * Hippuric acid
B. Ammonia salts
C. Creatinine
D. D.Uric acid
E. Amono acid
954.
The increase of conjugated (direct) bilirubin is revealed in the patients blood
plasma, and the simultaneous increase of non-conjugated (indirect) bilirubin level as well
as the dramatic decrease of stercobilinogen content in the feces and urine are discovered.
What type of icterus takes place?
A. Aminolevulinate synthase
B. UDP-glucuronyltransferase
C. Heme oxigenase
D. Heme synthetase
E. Biliverdin reductase
F. Hemolitic
G. Hepatic
H. Posthepatic
I. Jaundice of newborn
J. Gilbert disease
955.
The new-born have violation in binding of bilirubin reason of heavy forms of
jaundice in hepatocytes. What matter is used for formation of conjugate?
A. * Glucuronic acid
B. Sulphuric acid
C. Uric acid
D. Lactic acid
E. Piruvat
956.
To the patient which suffers on chronic hepatitis, for verification of detoxification
function of liver was conducted loading of sodium benzoate. Exreated of what matter
with urine will testify the detoxification function of liver?
A. Fenilacetic acid
B. Citric acid
C. * Hypuric acid
D. Oxalic acid
E. Mevalonic acid
957.
To the patient with suspicion pathology of liver with diagnostic purpose appoint
research of such biochemical indexes, except:
A. Proteins fractions of blood, AlAT/AsAT
B. Alkaline phosphatase, arginase
C. Laktatdegidrogenaze, urea
D. Protrombin, ceruloplasmin
E. * Cholesterol, triacylglicerol
958.
Vilson disease found (hepatocerebral dystrophy) in blood lowering maintenance
of ceruloplasmin. Violation of which processes it can cause?
A. * Complexformation of amino acids with copper
B. Disintegration of tissue proteins
C. Decarboxilation of amino acids
D. Intensification synthesis of urea
E. Intensification synthesis of uric acid
959.
Visual inspection of a patient revealed the presence of bilirubin and increased
pigmentation of skin that evolves after ultraviolet irradiation. The patients urine becones
red in the open air. Wich of the following urine constituent determination is required for
the vertification of Gunter disease.
A. Acetone
B. Hemoglobin
C. Bilirubin
D. Creatinine
E. * Uroporphyrinogen 1
960.
Which transformation of carbohydrates will prevail in a liver, if the concentration
of glucose in blood equal 3 mmol/l?
A. Gluconeogenesis
B. * Transformation of glycogen to free glucose
C. Pentosophosphate cycle
D. Glycolisis
E. Formation of UDP-glucuronic acid
961.
Worker of dry-cleaning had fatty dystrophy of liver. Violation synthesis of what
matter in a liver can result in such situation?
A. Tristearine
B. * Cholin phosphatidic
C. Urea
D. Phosphatidic acid
E. Cholic acid
962.
Yellowish skin and mucous membranes of a patient are observed after blood
transfusion. There also increased levels of total and indirect bilirubin in the blood,
urobilin in the urine and stercobilin in the feces. What type of icterus is observed in this
case?
A. Icterus of newborn
B. Inherited icterus
C. Posthepatic icterus
D. Hepatic icterus
E. * Hemolytic icterus
963.
You are presented with a patient’s liver specimen and you notice that the cells
seem to have an abnormally large amount of smooth endoplasmic reticulum for liver
cells. You conclude that this sample is probably from a patient.
A. Who cannot break down fats
B. With a bacterial infection
C. Who is a habitual user of narcotics
D. * Who may be exposed to toxic chemicals i.e. in their workplace
E. A, c. and d are correct
964.
Patient has increased amount of urea and creatinine in blood and their decrease in
urine. Possible reason of this state are:
A. this state is observed at muscle disease
B. main reason – liver disease
C. * diseases, which cause kidney failure
D. the main reason are affection of neutralization, transportation and excretion of
ammonia with urine
E. this state is observed as a result of acid-base equilibrium in the organism
965.
Patient has increased amount of urea and creatinine in blood and their decrease in
urine. Possible reason of this state are:
A. this state is observed at muscle disease
B. main reason – liver disease
C. * diseases, which cause kidney failure
D. the main reason are affection of neutralization, transportation and excretion of
ammonia with urine
E. this state is observed as a result of acid-base equilibrium in the organism
966.
Sportsman who was on a diet with great amount of protein has acidic reaction of
urine. Presence of which substances causes such change?
A. urates and sulphates
B. * chlorides and phosphates
C. chlorides and sulphates
D. phosphates and sulphates
E. urates and chlorides
967.
The of 56 years old patient complains for general weakness, nausea, bad appetite.
Is observed icteric discolor of skin, hyperbilirubinemia (direct bilirubin), urine is foamy,
acholic stool. Which state are these changes characterized?
A. * obturative jaundice
B. hepatocellular jaundice
C. hemolytic jaundice
D. Gilbert's syndrome
E. Johnson's syndrome
968.
? Urine transparency is one of the parameters, evaluated by the analysis. Presence
of what substance causes turbidity of alkaline urine?
A. * calcium phosphate
B.
C.
D.
E.
magnesium sulfate
ammonium acids
uric acid salts
chloride salts
969.
52-years old patient for few days suffered from pain in the right hypogastrium
after having of fatty meal. It was observed sclera and skin yellowing, acholic stool, darkcolored urine. Diagnosis is obstructive jaundice. Presence of which substanse in the urine
caused its dark colour?
A. bilirubinglucuronid
B. ketone bodies
C. urobilin
D. stercobilin
E. glucose
970.
A 2 years old child showed the symptoms of psychomotor development
inhibition, thin hair. Laboratory tests: increased amount of ammonia and arginino
succinate in blood and urine. What enzyme deficiensy in liver causes argininosuccinic
acidemia?
A. * argininosuccinatliase
B. ornithyn carbamoil transferase
C. arginase
D. glutaminase
E. xanthine oxidase
971.
A 45 years old patient suffers from pain in lumbar department of the back and its
limited mobility. It is takes place darkening of urine with air. What inherited disease has
the patient?
A. Phenylketonuria
B. Galactosemia
C. * Alkaptonuria
D. Cystinosis
E. Syndrome of Fankoni
972.
A 6 years old child suffers from glomerulonephritis. Which of the below
mentioned indexes prove it?
A. * proteinuria
B. phosphaturia
C. glycosuria
D. ketonuria
E. creatinuria
973.
A 6 years old child suffers from glomerulonephritis. Which of the below
mentioned indexes prove it?
A. * proteinuria
B. phosphaturia
C. glycosuria
D. ketonuria
E. creatinuria
974.
A 6 years old child suffers from glomerulonephritis. Which of the below
mentioned indexes prove it?
A. proteinuria
B. phosphaturia
C. glycosuria
D. ketonuria
E. creatinuria
975.
A man after 1,5 litres blood loss has suddenly reduced diuresis. The increased
secretion of what hormone caused such diuresis alteration?
A. Corticotropin
B. Natriuretic factor
C. Parathormone
D. Cortisol
E. * Vasopressin
976.
A patient complains about acute stomach-ache, nausea, vomit. Diastase activity is
800 grammes/l• hour What diagnosis is the most possible?
A. Acute cholecystitis
B. * Acute pancreatitis
C. Ulcer of stomach
D. Acute appendicitis
E. Enterocolitis
977.
A patient, which visited a doctor, has increased level of glucose in blood and
urine. Diabetes mellitus is suspecteds. What changes in lipid metabolism can cause this
disease?
A. hyperketonemia
B. hypercholesterolemia
C. * hypoketonemia, ketonuria
D. hyperphospholipidemia, hyperketonemia
E. hypophospholipidemia , hypoketonemia
978.
A specific test on the damage of kidneys tissues for the proof of diagnosis inflammatory process in kidneys of the patient was conducted. This test is determination
in urine:
A. Concentrations of creatin
B. Activity of creatin phosphokinase MB
C. Presence of lactose
D. * Activity of transamidinase
E. Activity of pepsin
979.
A two years old child was delivered to the hospital with symptoms of mental and
physical underdevelopment, which suffers from the frequent vomiting after meal. In urine
found out phenyl-pyruvic acid. Disorder of which substances metabolism is this
pathology?
A. Phosphorus-calcium metabolism
B. Water-salt metabolism
C. * Metabolism of amino acids
D. Carbohydrates metabolism
E. Lipids metabolism
980.
A woman of 58 years, сondition is hard. Consciousness is blear, skin is dry, and
eyes are sunken, cyanosis, the smell of rotting apples from the mouth. Laboratory test:
blood glucose 15,1 mmol/l, urine glucose 3,5%. What is the most real reason for such
condition?
A. uremic coma
B. hypovalemic coma
C. anaphylactic shock
D. * hyperglycemic coma
E. hypoglycemic coma
981.
An acute pancreatitis and parotitis are diagnosed. How will it influence on the
activity of amylase in urine?
A. * High activity of amylase is in urine.
B. Low activity of amylase is in urine.
C. No any of amylase in urine.
D. No any changes.
E. All answers are correct.
982.
At a biochemical inspection of a patient were found a hyperglycemia, glucosuria,
high urine’s density, in blood found - enhanceable amount of glucocorticoids. At the
same time in blood and urine found excess of 17 – ketosteroids. What type of diabetes
developed:
A. * Steroid diabetes
B. Diabetes Mellitus, the I type
C. Diabetes Mellitus , the II type
D. Kidney diabetes
E. Hepatic diabetes
983.
At what disease glomerular filtration is always decreased?
A. Acute nephritis
B. Chronic glomerulonephritis
C. Acute pyelonephritis
D. Amyloidosis of kidneys
E. * Acute kidney’s insufficiency
984.
At what disease in urine appears the protein of Bens - Jones?
A. * Myeloma
B. Amyloidosis of kidneys
C. Glomerulonephritis
D. Tuberculosis of kidneys
E. Pyelonephritis
985.
At what disease in urine appears the protein of Bens - Jones?
A. * Myeloma
B. Amyloidosis of kidneys
C. Glomerulonephritis
D. Tuberculosis of kidneys
E. Pyelonephritis
986.
At what disease more frequent alkaline reaction of urine?
A. * Uremia
B. Acute nephritis
C. Festering pyelitis
D. Abscess of kidneys
E. Diabetes insipidus
987.
At what disease more frequent alkaline reaction of urine?
A. * Uremia
B. Acute nephritis
C. Festering pyelitis
D. Abscess of kidneys
E. Diabetes insipidus
988.
Decreased diuresis, hypernatremia, hypokaliemia were observed. Hypersecretion
of which hormone can cause such changes?
A. Parathormone
B. Epinephrine
C. Vasopressin
D. Natriuretic factor
E. * Aldosterone
989.
For a patient was found the increase of maintenance of urea and creatinine in
blood and diminishing in urine. What are possible reasons of such state?
A. Main reason of such state it is disorder of detoxification, transport and excretion
of ammonia with urine
B. Main reason is a disease of liver
C. Such state appears at the disease of muscles
D. * Diseases which result in insufficiency of kidneys
E. Such state appears as a result of disorder of acid-base balance in an organism
990.
For a patient which suffers from chronic kidney insufficiency, developed
osteoporosis. Disorder of what process is a principal reason of osteoporosis
development?
A. Hydroxylating of proline
B. Hydroxylating of lysine
C. Carboxylation of glutamate
D. * Formation of 1,25(ОН)2 D3
E. Hydroxylating of cortisol
991.
For diagnostic of acute inflammatory process in kidneys was conducted a specific
test - determination in urine of such substance:
A. Content of lactose
B. Activity of creatinkinase
C. Concentrations of creatin
D. Activity of pepsin
E. * Activity of alanine amino peptidase
992.
How many proteins do excrete daily with urine healthy adult?
A. * 30 mg
B. 50 mg
C. 60 mg
D. 100 mg
E. 120 mg
993.
How uric acid excretes from an organism?
A. With saliva
B. With feces
C. With sweat
D. * With urine
E. With hepato-enteral circulation
994.
Hyperuricemia is increase of uric acid level more than:
A. * 0,5 mmol/l
B. 0,1 mmol/l
C. 10 mmol/l
D. 1 mmol/l
E. 2 mmol/l
995.
Hyperuricuria is observed at all of diseases which are accompanied the increased
disintegration:
A. Glycoproteins
B. Phosphoproteins
C. * Nucleoproteins
D. Lipoproteins
E. Chromoproteins
996.
In a norm reabsorption of glucose is:
A. * 100%
B. 90%
C. 96%
D. 30%
E. 10%
997.
In a norm the clearance of endogenous creatinine is:
A. * 110 – 150 ml/min
B. 100 – 250 ml/min
C. 110 – 200 ml/min
D. 10 – 150 ml/min
E. 10 – 100 ml/min
998.
In blood and urine of a patient it was takes place increase value of pyruvic and ?ketoglutaric acids. The deficiency of which coenzyme causes these changes?
A. Pyridoxal phosphate
B. * Thiamin pyrophosphate
C. Flavin mononucleotide
D. Biotin
E. Ubiqinon
999.
In blood of patient hypercalciemia, hypophosphatemia were observed, in urine –
hyperphosphaturia. The possible reason of such state is:
A. Depression of parathormone secretion
B. Increased secretion of calcitonine
C. Depression of calcitonine secretion
D. * Increased secretion of parathormone
E. Increased secretion of thyroxine
1000.
In the normal state reabsorption of water is:
A. * 98%
B. 40%
C. 55%
D. 79%
E. 100%
1001.
In the urine of a 42 years man, who was in stress for a long time, the amount of
17-ketosteroids is increased. This testifies about the increased secretion of:
A. * Cortisol
B. Estradiol
C. Epinephrine
D. Norepinephrine
E. Aldosterone
1002.
In what part of nephron does take place filtration of urine?
A. * In a glomerulus
B. In the loop of Henle
C. In a proksimal canaliculi
D. In a distal canaliculi
E. In the collective tubes
1003.
In which units the clearance of endogenous creatinine determined?
A. Mm/minute
B. Gramm/l
C. Mmol/l
D. Ml/hour
E. * Ml/minute
1004.
Indicate the credible index of albumin-globulin coefficient in the case of kidney
disease:
A. 2,8
B. * 0,8
C. 1,5
D. 2,5
E. 2,0
1005.
indicator of glomerular function is
A. Serum urea
B. Serum creatinine
C. Urea clearance
D. * Creatinine clearance
E. Both A and D
1006.
Interpret the results of urine analysis - a color is dark, foamy, density - 1,022,
bilirubin - positive, urobilin – negative:
A. * Mechanical jaundice
B. Hepatic jaundice
C. Hemolytic jaundice
D. Normal condition
E. No any correct answer
1007.
Interpret the results of urine analysis: a color is dark, foamy, density - 1,026,
bilirubin - positive, urobilins – positive:
A. * Hepatic jaundice
B. Mechanical jaundice
C. Hemolytic jaundice
D. Normal condition
E. No any correct answer
1008.
Interpret the results of urine analysis: color – brown – orange, density - 1,020,
bilirubin – negative, urobilin – positive:
A. * Hemolytic jaundice
B. Hepatic jaundice
C. Mechanical jaundice
D. Normal condition
E. No any correct answer
1009.
Inulin clearance in an average adult man is about
A. 54 ml/min
B. 75 ml/min
C. 110 ml/min
D. * 130 ml/min
E. 250 ml/min
1010.
It was determinate high activity of amylase in urine of a patient. How properly
interpret this analysis?
A. * It is possible acute pancreatitis, parotitis.
B. Pathology of liver.
C. This analysis testifies disorders of gastrointestinal tract.
D. It is possible at nephropathies
E. This analysis testifies disorders of carbohydrate metabolism in an organism.
1011.
Laboratory test of a patient’s urine with intestines dysbacteriosis established the
increase of indican. It testifies:
A. kidney disease
B. normal neutralization liver function
C. increased fat hydrolysis
D. * liver malfunction
E. vitamins F hypovitaminosis
1012.
Laboratory test of a patient’s urine with intestines dysbacteriosis established the
increase of indican. It testifies:
A. kidney disease
B. normal neutralization liver function
C. increased fat hydrolysis
D. * liver malfunction
E. vitamins F hypovitaminosis
1013.
Mother with her 5 years old child visited a doctor. Child after beeing under
sunlight has the erythema of skin. Laboratory tests showed decrease of iron in blood
plasma, increase of uroporphyrinogen I excretion with urine. The most possible
pathology is:
A. erythropoietic porphyria
B. methemoglobinemia
C. hepatic porphyria
D. coproporphyria
E. hemolytic jaudice
1014.
Name laboratory tests which should be conducted for the patients with suspicion
on a acute pancreatitis:
A. total blood test
B. Activity of LDH
C. Activity of AlAT
D. * Activity of amylase in urine and blood
E. A level of sugar in blood
1015.
Name the pathological compounds of urine at diabetes mellitus:
A. bile pigments, acetone
B. * acetone, glucose
C. blood, bilirubin
D. protein, blood
E. bile pigments, indican
1016.
Name the pathological compounds of urine at diabetes mellitus:
A. bile pigments, acetone
B. * acetone, glucose
C. blood, bilirubin
D. protein, blood
E. bile pigments, indicant
1017.
Name the pathological compounds of urine at diabetes mellitus:
A. bile pigments, acetone
B. * acetone, glucose
C. blood, bilirubin
D. protein, blood
E. bile pigments, indican
1018.
Name the pathological compounds of urine at diabetes mellitus:
A. bile pigments, acetone
B. * acetone, glucose
C. blood, bilirubin
D. protein, blood
E. bile pigments, indican
1019.
Name the pathological compounds of urine at diabetes mellitus:
A. bile pigments, acetone
B. * acetone, glucose
C. blood, bilirubin
D. protein, blood
E. bile pigments, indicant
1020.
of which of the following hormones?
A. Cortisol
B. Insulin
C. * Vasopressin
D. Glucagon
E. Aldosterone
1021.
Patient B. suffers from polyuria. Pathological components do not discovered in
urine. What possible reason of this state?
A. Deficiency of oxytocin
B. Excess of vasopressin
C. * Deficiency of vasopressin
D. Excess of oxytocin
E. Disorders of liver and kidney’s functions
1022.
Patient has increased amount of urea and creatinine in blood and their decrease in
urine. Possible reason of this state are:
A. this state is observed at muscle disease
B. main reason – liver disease
C. * diseases, which cause kidney failure
D. the main reason are affection of neutralization, transportation and excretion of
ammonia with urine
E. this state is observed as a result of acid-base equilibrium in the organism
1023.
Phenylketonuria of newborn may be diagnosed after a reaction of urine with:
A. * FeCI3
B. CuSO4
C. NaCl
D. Fe+
E. Na3PO4
1024.
Polyuria of patients with diabetes insipidus appears as a result:
A. * Insufficient level of antidiuretic hormone in blood
B. Insufficient level of insulin in blood
C. Disorders of reabsorption of water in canaliculies as a result of high osmotic
pressure of urine
D. Excessive intake of liquid
E. Disorders of reabsorption of water in canaliculies as a result of low osmolality of
urine
1025.
Polyuria of patients with diabetes mellitus appears as a result:
A. * Disorders of reabsorption of water in canaliculies as a result of high osmotic
pressure of urine
B. Insufficient level of glucagon in blood
C. Excessive intake of liquid
D. Insufficient level of antidiuretic hormone in blood
E. Disorders of reabsorption of water in canaliculies as a result of low osmolality of
urine
1026.
Possible reasons of hypoproteinemia at a nephrotic syndrome are all the following
except:
A. * Convertion of proteins into fats
B. Diet with the deficiensy of proteins
C. Diarrea
D. Proteinuria
E. Increased catabolism
1027.
Sportsman who was on a diet with great amount of protein has acidic reaction of
urine. Presence of which substances causes such change?
A. urates and sulphates
B. * chlorides and phosphates
C. chlorides and sulphates
D. phosphates and sulphates
E. urates and chlorides
1028.
The amount of urea in the patient's blood is 16 mmol/l, in daily urine 6 g. The
possible reason for this is the following:
A. Liver disease
B. Starvation
C. * Kidney disease
D. Acidosis
E. Thyrotoxicosis
1029.
The analysis demonstrated a 10 times increase of diastase activity. The danger of
autolysis of a patient’s pancreas caused with activating of enzyme:
A. Amylase
B. Pepsin
C. * Trypsin
D. Lipase
E. Nuclease
1030.
The density of urine of a healthy adult is:
A. * 1,012 – 1,020
B. 1,020 – 1,050
C. 1,025 – 1,045
D. 1,005 – 1,010
E. 1,010 – 1,035
1031.
The most dangerous for life such effect of acute kidney insufficiency:
A. Overhydratation
B. Hypokaliemia
C. Hypermagniyemia
D. * Hyperkaliemia
E. Hyperkal'ciemia
1032.
The patient complains of polyuria. The pathological components in urine are not
detected. The deficiency of what hormone can result in such state?
A. Insulin
B. Glucagon
C. Epinephrine
D. * Vasopressin
E. Cortisol
1033.
The patient L., 46 years, complains for dry mouth, thirst, quickened urination,
general weakness. Biochemical blood investigation showed hyperglycemia,
hyperketonemia. In the urine glucose, ketone bodies were found. Electrocardiogram
showed diffuse myocardial changes. Possible diagnosis is:
A. * A.diabetes mellitus
B. alimentary hyperglycemia
C. acute pancreatitis
D. diabetes insipidus
E. ischemic heart disease
1034.
The results of Zimnytskiy's test showed density of urine about 1.003-1.008. Name
this state?
A. hypersthenuria
B. * hyposthenuria and isosthenuria
C. hyposthenuria
D. oliguria
E. pyuria
1035.
The results of Zimnytskiy's test showed density of urine about 1.003-1.008. Name
this state?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
hypersthenuria
* hyposthenuria and isosthenuria
hyposthenuria
oliguria
pyuria
1036.
Urine of patient after staying with oxygen becomes red. Biochemical research of
urine set the enhanceable excretion of protoporphyrin IX that is the marker of disorders
of synthesis:
A. Bilirubin
B. Purine nucleotides
C. Amino acids
D. * Hem
E. Pyrimidine nucleotides
1037.
Urine transparency is one of the parameters, evaluated by the analysis. Presence
of what substance causes turbidity of acidic urine?
A. calcium phosphate
B. magnesium sulfate
C. ammonium acids
D. * uric acid salts
E. chloride salts
1038.
Urine transparency is one of the parameters, evaluated by the analysis. Presence
of what substance causes turbidity of alkaline urine?
A. * calcium phosphate
B. magnesium sulfate
C. ammonium acids
D. uric acid salts
E. chloride salts
1039.
Urine transparency is one of the parameters, evaluated by the analysis. Presence
of what substance causes turbidity of acidic urine?
A. calcium phosphate
B. magnesium sulfate
C. ammonium acids
D. * uric acid salts
E. chloride salts
1040.
What basic event in pathogenesis of chronic kidney’s insufficiency?
A. * All below transferred
B. Decline of glomerular filtration
C. Hyperazotemia
D. Disorders of water – electrolyte metabolism
E. Hyperkaliemia
1041.
What method of research is characterized concentration property of kidneys?
A. Creatinine of blood
B. * Zimnitskiy’s test
C. Glomerular filtration
D. Electrolytes of blood
E. All of the above
1042.
Which method is used for determination of acid-base state of organism?
A. Determination of creatinine of blood
B. Zimnitskiy’s test
C. Research of kidney blood flow
D. Test of Reberga
E. * Excretion of bicarbonates with urine
1043.
With urine of a healthy adult is excreted the following product of bilirubin
disintegration:
A. urobilin
B. * stercobilin
C. mesobilin
D. biliverdin
E. verdoglobin
1044.
With urine of newborn was done a reaction with FeCI3 and a positive reaction
(dark color) got. What disease is possible?
A. Galactosemia
B. Tirosinosis
C. * Phenylketonuria
D. Alkaptonuria
E. Aminoaciduria.
1045.
You suspect that your 12 year old male patient has an inborn error in methionine
metabolism. His methionine levels are low and his homocysteine levels are high. A liver
biopsy indicates that his cystathionine synthase and cystathionase levels are normal. This
patient may have a deficiency:
A. Of vitamin B12
B. Of folic acid
C. A deficiency in the pathway that synthesizes methyl cobalamin
D. A deficiency in the pathway that synthesizes N5-methyl tetrahydrofolate
E. * All of the above
1046.
43 years old man suffers from muscle spasms as a result of intensive physical
action. Muscle biopsy discovered increased concentration of glycogen. This state appears
as a result of transformation affection of:
A. Glucose-6-phosphate > glycogen
B. * Glycogen > glucose-6-phosphate
C. Creatine > creatinine
D. Myoglobine ? heme >?bilirubin
E. Lactate >?glucose
1047.
A doctor with the purpose of conformation diagnosis sent a patient with the early
stage of muscular dystrophy in a biochemical laboratory for the leadthrough of blood test.
Growth activity of what enzyme can be observed in this patient?
A. * Creatinkinase
B. Alaninaminotransferase
C. Colagenase
D. Gialuronidase
E. Glutaminases
1048.
A patient has a general tooth pain, bleeding of gums, depolamerisation of
proteoglycans and destruction of odontoblasts and ostepblasts, loosen of teeth. Reason of
such state is hypovitaminoses of:
A. Vitamin A
B. Vitamin E
C. * Vitamin C
D. Vitamin B6
E. Vitamin D
1049.
A patient has a making progress muscular weakness and low capacity, in skeletal
and to cardiac muscles, liver and plasma of blood, maintenance of carnitin goes down.
Which amino acids insufficient in food stuffs?
A. Alanine and proline
B. * Lysine and methionine
C. Arginine and valine
D. Aspartic and Glutamic acids
E. Histidine and serine
1050.
A patient have the frequent bleeding from internalss, mucus shells. Analysis found
out insufficiency of hydroxyproline and hydroxilisine in composition of collogen tissue.
Deficiency of what vitamin broken the processes of hydroxylating of adopted amino
acids in the organism of patient?
A. Vitaminu H
B. * Vitaminu C
C. Vitaminu PP
D. Vitaminu A
E. Vitaminu K
1051.
A patient is hospitalized in a hospital with a diagnosis is a syndrome of the
protracted squashing. Finiteness at a review – filling out, “wooden”. Anurya. At taking
by a catheter urine of red color. The presence of what matter does influence on the color
of urine?
A. Haemoglobin
B. Bilirubin
C. * Myoglobin
D. Coproporphyrin III
E. Porfobilinogen
1052.
A patient, which grumbles about pain in front breast area which is not taken off
nitroglycerine, weakness, enhanceable perspire, is hospitalized in a clinic. For him
cyanosys of lips, pallor of skin, is marked, bradicardia. 4 hours passed from the moment
of beginning of anginose attack. Determination activity of what enzyme will allow to
diagnose – heart attack of myocardium?
A. * Creatinkinase (MB)
B. LDG1
C. LDG5
D. AsAT
E. AlAT
1053.
A sportsmen leg has been injured during training. A traumatologist has diagnosed
tendon rupture. What type of connective tissue forms this organ?
A. Cartilaginous
B. Dense irregular connective tissue
C. Loose connective tissue
D. Reticular
E. * Dense regular connective tissue
1054.
A woman of 30 years has disease for about a year, when she first felt pain in the
joints region, intumescence, skin reddening. Probable diagnosis is pseudorheumatism.
One of the possible reasons of this disease is the change in the structure of connective
tissue protein:
A. Mucin
B. Ovoalbumin
C. Troponin
D. * Colagene
E. Myosin
1055.
?After myocardial infarction pacients morphological heart wall integrity was
regenerated. Owing to what tissues did the regeneration take place?
A. A Nerve
B. B. Smooth muscle
C. C. Striated muscle
D. D. Epithelial
E. * E. Connective
1056.
At a sprint the untrained people have a muscle pain as a result of piling up of
lactat. With strengthening of what biochemical process can it be constrained in organism?
A. * Glycogenolysis
B. Gluconeogenesis
C. Pentosophosphate cycle
D. Lipogeneses
E. Glycogeneses
1057.
By myocardial ischemia are characteristic decrease of oxidative phosphorylation
and increase of aerobic metabolism. By this there is an increased activity of
phosphorylase A and phosphofructokinase. This is connected with the increase in
myocard of:
A. Catecholamine
B. * Glycogen
C. Glucocorticoid
D. Mineral corticoid
E. Glucose
1058.
For a patient the weakness of muscles, osteoporosis, atrophy of skin, bad
cicatrization of wounds, is marked, laying of fat is increased in overhead part of body (on
face, neck). At a blood test found out the increase of sodium and chlorine, and
diminishing of potassium. What disease in this patient?
A. Addison disease
B. Reklingauzen disease
C. * Icenko-kushing disease
D. Bazedov disease
E. Syndrome of Konn
1059.
For a patient which has scurvy, violate the processes formation of connective
tissue which resulted in dicking and fall of teeth. Violation activity of what enzyme does
cause these symptoms?
A. Glycosiltransferase
B. Lizyloxidase
C. * Lisynhydroxilase
D. Prokolagenpeptidase N- terminal peptide
E. Prokolagenpeptidase C - terminal peptide
1060.
For a patient which suffers on chronic kidney insufficiency, developed
osteoporosis. Violation of what process is principal reason development of osteoporosis?
A. Hydroxylating of proline
B. Hydroxylating of lysine
C. Carboxylation of glutamate
D. * Formation of 1,25(ОН)2 D3
E. Hydroxylating of cortisol
1061.
For a patient with systematic scleriasis increased the biosynthesis of collogen and
his disintegration. Concentration of what amino acid will be increased in urine of this
patient?
A. * Oxyproline
B. Lysine
C. 5-Oxitryptophan
D. Serine
E. Dioksiphenilalanine
1062.
For patients with collagenose takes a place the process destruction of connective
tissue. It is confirmed an increase in blood:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Activity of isoenzymes of LDG
Activity of transaminase
Contents of urates
Contents of creatin and creatinine
* Contents of hydroxyproline and oxylisine
1063.
For pregnant 28 years determine enzymes in the cells of amniotic liquid.
Appeared insufficiensy activity of glucuronidase. What pathological process is observed?
A. Aglicogenose
B. Collagenoses
C. * Mucopolysaccharidoses
D. Glycogenosis
E. Lipidosis
1064.
For sportsmen after the physical loading the process of gluconeogenesis is
activated after some time. Specify, what substrate is used in this process:
A. * Lactat
B. Valine
C. Leucine
D. Isoleucine
E. Phenylalanine
1065.
For the increase of results to sportsman recommended to accept preparation which
contains carnitin. Which process in a most measure activated by carnitin?
A. Synthesis of steroids hormones
B. Synthesis of ketone bodies
C. Synthesis of lipids
D. Tissue respiration
E. * Transport of fatty acids in mithohondria
1066.
In a 23-years-old man diagnosed muscle dystrophy. Doctor for strengthening
synthesis of pirimidine nucleotides appointed him:
A. Ascorbic acid
B. * Potassium orotat
C. Lipoic acid
D. Cokarboxilase
E. Cyancobalamin
1067.
In a clinic with the break of ribs got a patient with a hypercorticoidism.
Roentgenologic analisis found out the osteoporoses changes of skeleton. Name one of
reasons of such violations:
A. Excessive synthesis of glycosaminoglycans
B. * Ingibition of collagen synthesis
C. Ingibition of vitamin D synthesis
D. Excessive of calcium salts
E. Excessive of phosphates
1068.
In a hospital put got patient which have previous diagnosis – progressive muscular
dystrophy. The presence of what substance in urine can confirm this diagnosis?
A. * Creatin
B. Creatine phosphate
C. Creatinine
D. Protein
E. Hydroxyproline
1069.
In blood of patient found out the increase activity of LDG1, LDG2, AsAT,
creatinkinase. In which organ of patient the most reliable development of pathological
process?
A. Kidney
B.
C.
D.
E.
Liver
Skeletal muscles
* Heart
Pancreas
1070.
In the organism of 7 years old girl was discovered lack of copper. The possibility
of break of flexible fibres, in which desmosine and isodesmosine are absent, grows. This
is caused by the decrease of activity of coppercontaining enzyme:
A. Lysyl oxidase
B. Proline hydrooxilase
C. * Cytochrome oxidase
D. Clastase
E. Peptidase
1071.
In the organism of patient found out the decline of synthesis of collogen and
diminishing of calcium in bone tissues. Contents of hyaluronic acid is enhanceable, and
chondroitin silphate is mionectic. The deficit of what vitamin does cause these changes?
A. Vitamin C
B. * Vitamin A
C. Vitamin D
D. Vitamin P
E. Vitamin B1
1072.
In the patient's blood plasma is discovered the increase of hyaluronidase activity.
What biochemical figure of blood plasma determination will allow to prove the
connective tissue pathology?
A. * Sialic acid
B. Bilirubin
C. Uric acid
D. Glucose
E. Galactose
1073.
It is known that possibilities of sportsman run on short or long distances
determines by correlation of red and white muscular fibres, to what is related different
speed breaking up of ATP. Which component of muscles does carry out this process?
A. Troponin
B. * Miosin
C. Creatin
D. Aktin
E. Carnosine
1074.
Patient complains for pain in joints. By sight can be seen edemas and reddening in
the joints area. What enzyme activity to be investigated to draw out a diagnosis?
A. Hyaluronidase
B. * Creatine kinase
C. Alkaline phosphatase
D. Acidic phosphatase
E. Urease
1075.
Patient has muscle atony. Name the muscle tissue enzyme, which activity can be
decreased by this state:
A. A-glutamine transferase
B. Amylase
C. Transketolase
D. * Creatine phosphokinase
E. Catalase
1076.
Patient has progressive myodystrophy. Name the figure of urine nitrogen
metabolism, characteristic for this state.
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Creatine
Ammonium salts
* Creatinine
Uric acid
Urea
1077.
Patient of 18 years has the diagnosis of muscle dystrophy. What matter increase in
the blood plasma is the most possible by this pathology?
A. Myoglobine
B. * Creatine
C. Myosin
D. Lactate
E. Alanine
1078.
Patient of 46 years for a long time suffers from childhood pseudohypertrophic
muscular (Duchenne's) dystrophy. What blood enzyme increase is the diagnostic test in
this case?
A. Adenylate kinase
B. Lactate dehydrogenase
C. Pyruvate dehydrogenase
D. Glutamate dehydrogenase
E. * Creatine phosphokinase
1079.
Patient of 62 years has diabetes mellitus. Glomerulosclerosis has evolved. The
most possible reason for this complication is the affection in renal plexus of:
A. Calcium excretion
B. Formation of primary urine
C. Gluconeogenesis process
D. Glucose reabsorption
E. * Colagene structure
1080.
Patient of 63 years has rheumatism. The concentration of oxiprolin in blood and
urine is increased. What is the main reason of hyperoxiprolinemia?
A. Hyaluroprotein degradation
B. Colagene degradation
C. Kidney malfunction
D. Cathepsin activation
E. * Prolyl hydroxylase activation
1081.
Patient of 63 years has symptoms of pseudorheumatism. Which of the
belowmentioned blood figures level increase will be the most important for diagnosis
provement?
A. General cholesterol
B. Lipoprotein
C. Total glycoaminglycans
D. * Acid phosphatase
E. R-glycosidase
1082.
The increase fragility of vessels, destruction of enamel and dentine of teeth, at
scurvy in majority is predefined a dyspoiesis stable triple spiral of collogen. What stage
of modification of procollagen is violated at this avitaminosis?
A. Formation of polipeptide chains
B. * Hydroxylating of proline
C. Glicolisation of hydroxilic tailings
D. Pinch off from procollagen of С-final peptid
E. Pinch off of N- final peptid
1083.
The patient has myopathy. There is observed acute decrease of myofibrillar
proteins in muscles. What urine component amount increase accompanies this disease?
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
* Creatine
Creatinine
Urobilin
Amylase
Ketone bodies
1084.
To the clinic got the child of 1 year with the signs of defeat of muscles. After
inspection found out the deficit of carnitine in muscles. Violation of what process is
biochemical basis of this pathology?
A. Regulation level of Ca2+ in mitochondria
B. * Ttransport of fatty acids in mitochondria
C. Substrate phosphorylating
D. Utilization of lactic acid
E. Synthesis of actin and miosin
1085.
To the cosmetologist a patient appealed with a request to deprive him tattoo on a
shoulder. What matter which is contained in connective tissue does limit distribution of
paint and does possible such type of “painting”?
A. * Elastin
B. Heparin
C. Fibrinogen
D. Hyaluronic acid
E. Gamma-globulin
1086.
To the patient with ischemic heart trouble appointed riboxine (Inosinum), which is
an intermediate metabolite synthesis of:
A. Metalloproteins
B. Lipoproteins
C. * Purine nucleotides
D. Glycoproteins
E. Ketone bodies
1087.
To the patient with the torn tendon muscle of foot a doctor in a holiatry appointed
ascorbic acid which will be instrumental in formation of mature collagen by
hydroxylating of some amino acids. Which amino acids do test such changes?
A. * Proline, lysine
B. Phenilalanine, glycine
C. Valine, leucine
D. Tryptophane, treonine
E. Histidin, arginine
Test questions for figures
1. Different types of muscle tissue is shown in figure 135. What type is indicated by letter
A.
A. * Skeletal muscle
B. Heart muscle
C. Smooth muscle
D. Intestinal muscle
E. Bronchi muscle
2. Different types of muscle tissue is shown in figure 135. What type is indicated by letter
B.
A. Skeletal muscle
B. * Heart muscle
C. Smooth muscle
D. Intestinal muscle
E. Bronchi muscle
3. Different types of muscle tissue is shown in figure 135. What type is indicated by letter
A.
A. Skeletal muscle
B. Heart muscle
C. * Smooth muscle
D. Diaphragm muscle
E. None of the above
4. DNA replication scheme is shown in figure 134. What enzyme is indicated by the digit
1?
A. Primase
B. DNA-polymerase
C. Ligase
D. * Helicase
E. Transferase
5. DNA replication scheme is shown in figure 134. What enzyme is indicated by the digit
4?
A. Primase
B. * DNA-polymerase
C. Ligase
D. Helicase
E. Transferase
6. DNA replication scheme is shown in figure 134. What is indicated by the digit 2?
A. Primase
B. DNA-polymerase
C. Ligase
D. Helicase
E. * Primer
7. DNA replication scheme is shown in figure 134. What is indicated by the digit 3?
A. Primase
B. DNA-polymerase
C. Ligase
D. Helicase
E. * Okazaki fragments
8. Lipoproteins shown in figure 130 contain about:
A. 95 % of TAG
B. 95 % of proteins
C. 50 % of proteins
D. 50 % of TAG
E. * 50 % of cholesterol
9. Normal metabolism of bile pigments is shown in figure 124. Which compound is
replaced with character 1 in this scheme?
A. * Verdoglobin
B. Biliverdin
C. Indirect bilirubin
D. Mesobilirubin
E. Mesobilinogen
10. Normal metabolism of bile pigments is shown in figure 124. Which compound is
replaced with character 2 in this scheme?
A. Verdoglobin
B. * Biliverdin
C. Indirect bilirubin
D. Mesobilirubin
E. Mesobilinogen
11. Normal metabolism of bile pigments is shown in figure 124. Which compound is
replaced with character 3 in this scheme?
A. Verdoglobin
B. Biliverdin
C. * Indirect bilirubin
D. Mesobilirubin
E. Mesobilinogen
12. Normal metabolism of bile pigments is shown in figure 124. Which compound is
replaced with character 5 in this scheme?
A. Verdoglobin
B. Biliverdin
C. Indirect bilirubin
D. * Mesobilirubin
E. Mesobilinogen
13. Normal metabolism of bile pigments is shown in figure 124. Which compound is
replaced with character 6 in this scheme?
A. Verdoglobin
B. Biliverdin
C. Indirect bilirubin
D. Mesobilirubin
E. * Mesobilinogen
14. Normal metabolism of bile pigments is shown in figure 124. Which compound is
replaced with character 7 in this scheme?
A. Verdoglobin
B. Biliverdin
C. Indirect bilirubin
D. Mesobilirubin
E. * Stercobilinogen
15. Normal metabolism of bile pigments is shown in figure 124. Which compound is
replaced with character 8 in this scheme?
A. Verdoglobin
B. Biliverdin
C. Indirect bilirubin
D. * Stercobilin
E. Stercobilinogen
16. Normal metabolism of bile pigments is shown in figure 124. Which compound is
replaced with character 9 in this scheme?
A. Verdoglobin
B. Biliverdin
C. Indirect bilirubin
D. * Stercobilin
E. Stercobilinogen
17. Normal metabolism of bile pigments is shown in figure 124. Which enzyme is replaced
with character 4 in this scheme?
A. * UDP-glucoronyltransferase
B. Glucoronidase
C. Bilirubinidase
D. Stercobilinidase
E. Mesobilinidase
18. Normal metabolism of bile pigments is shown in figure 124. Which enzyme is replaced
with character 10 in this scheme?
A. UDP-glucoronyltransferase
B. * Glucoronidase
C. Bilirubinidase
D. Stercobilinidase
E. Mesobilinidase
19. Scheme of monooxygenase system is shown in figure 126. Which components are
replaced with character 1 in this scheme?
A. TPP and TMP
B. * FAD and FADH2
C. PLP and PMP
D. Cytochrome b5 and cytochrome c
E. Cytochrome P450 (Fe2+) and Cytochrome P450 (Fe3+)
20. Scheme of monooxygenase system is shown in figure 126. Which components are
replaced with character 2 in this scheme?
A. TPP and TMP
B. FAD and FADH2
C. PLP and PMP
D. Cytochrome b5 and cytochrome c
E. * Cytochrome P450 (Fe2+) and Cytochrome P450 (Fe3+)
21. Scheme of monooxygenase system is shown in figure 126. Which components are
replaced with character 3 in this scheme?
A. H2
B. * H2O
C. O2
D. H2O2
E. OH
22. Scheme of regulation of blood pressure by kidneys is shown in figure 127. Which
component is replaced with character 1 in this scheme?
A. * Rhenin
B. Angiotensin I
C. Kallikrein
D. Kallikreinogen
E. Aldosteron
23. Scheme of regulation of blood pressure by kidneys is shown in figure 127. Which
component is replaced with character 2 in this scheme?
A. Rhenin
B. * Angiotensin I
C. Kallikrein
D. Kallikreinogen
E. Aldosteron
24. Scheme of regulation of blood pressure by kidneys is shown in figure 127. Which
enzyme is replaced with character 3 in this scheme?
A. Dehydrogenase
B. Angiotensin I isomerase
C. Angiotensin I hydratase
D. Rhenin
E. * Angiotensin-converting enzyme
25. Scheme of regulation of blood pressure by kidneys is shown in figure 127. Which
component is replaced with character 4 in this scheme?
A. Rhenin
B. Angiotensin I
C. Kallikrein
D. Kallikreinogen
E. * Aldosteron
26. The clinical symptom shown in figure 131 appears in familial hypercholesterolemia and
is called:
A. * Xanthomas
B. Tophus
C. Paetechia
D. Edema
E. Dermatitis
27. The clinical symptom shown in figure 131 is called xanthomas and this is:
A. * Nodules of cholesterol
B. Nodules of urates
C. Nodules of adipose tissue
D. Nodules of oxalates
E. Nodules of connective tissue
28. The clinical symptom shown in figure 131 is specific for:
A. Scurvy
B. * Familial hypercholesterolemia
C. Gout
D. Rickets
E. Pellagra
29. The disease, symptoms of which are shown in figure 129, is caused by the:
A. chronic hypovitaminosis P
B. chronic hypovitaminosis B12
C. chronic hypovitaminosis D
D. chronic hypovitaminosis K
E. * chronic hypovitaminosis B5
30. The main function of lipoproteins shown in figure 130 is:
A. Transport of diet TAG
B. Transport of endogenic TAG
C. * Transport of cholesterol from liver to tissues
D. Transport of cholesterol from tissues to liver
E. Transport of phospholipids
31. The medical symptom shown in figure 123 is specific for:
A. The deficit of STH in the organism of adults
B. * The excess of STH in the organism of adults
C. The deficit of ACTH in the organism of children
D. The excess of ACTH in the organism of children
E. The deficit of TTH in the organism of adults
32. The medical syndrome shown in figure 116 is specific for:
A. * The deficit of STH in the organism
B. The excess of STH in the organism
C. The deficit of ACTH in the organism
D. The excess of ACTH in the organism
E. The deficit of TTH in the organism
33. The medical syndrome shown in figure 122 is specific for:
A. The deficit of STH in the organism of adults
B. The excess of STH in the organism of adults
C. The deficit of ACTH in the organism of children
D. The excess of ACTH in the organism of children
E. * The excess of STH in the organism before puberty
34. The muscle structure is shown in figure 128. What component is indicated by character
1?
A. * Myofibril
B. Plasma membrane
C. Transverse tubule
D. Cisterna of sarcoplasmic reticulum
E. Tubules of sarcoplasmic reticulum
35. The muscle structure is shown in figure 128. What component is indicated by character
2?
A. Myofibril
B. * Plasma membrane
C. Transverse tubule
D. Cisterna of sarcoplasmic reticulum
E. Tubules of sarcoplasmic reticulum
36. The muscle structure is shown in figure 128. What component is indicated by character
3?
A. Myofibril
B. Plasma membrane
C. * Transverse tubule
D. Cisterna of sarcoplasmic reticulum
E. Tubules of sarcoplasmic reticulum
37. The muscle structure is shown in figure 128. What component is indicated by character
4?
A. Myofibril
B. Plasma membrane
C. Transverse tubule
D. * Cisterna of sarcoplasmic reticulum
E. Tubules of sarcoplasmic reticulum
38. The muscle structure is shown in figure 128. What component is indicated by character
5?
A. Myofibril
B. Plasma membrane
C. Transverse tubule
D. Cisterna of sarcoplasmic reticulum
E. * Tubules of sarcoplasmic reticulum
39. The muscle structure is shown in figure 128. What component is indicated by character
6?
A. * I band
B. A band
C. H zone
D. Z disk
E. Sarcomere
40. The muscle structure is shown in figure 128. What component is indicated by character
7?
A. I band
B. * A band
C. H zone
D. Z disk
E. Sarcomere
41. The muscle structure is shown in figure 128. What component is indicated by character
8?
A. * I band
B. A band
C. H zone
D. Z disk
E. Sarcomere
42. The muscle structure is shown in figure 128. What component is indicated by character
9?
A. I band
B. A band
C. * H zone
D. Z disk
E. Sarcomere
43. The muscle structure is shown in figure 128. What component is indicated by character
10?
A. I band
B. A band
C. H zone
D. * Z disk
E. Sarcomere
44. The scheme of digestion of nucleoproteins is shown in figure 132. Which enzyme is
indicated by digit 1?
A. Phosphatase
B. Nucleosidase
C. Nucleotidase
D. Nuclease
E. * Pepsin
45. The scheme of digestion of nucleoproteins is shown in figure 132. Which enzyme is
indicated by digit 2?
A. Phosphatase
B. Nucleosidase
C. Nucleotidase
D. * Nuclease
E. Pepsin
46. The scheme of digestion of nucleoproteins is shown in figure 132. Which enzyme is
indicated by digit 3?
A. Phosphatase
B. Nucleosidase
C. * Phosphodiestherase
D. Nuclease
E. Pepsin
47. The scheme of digestion of nucleoproteins is shown in figure 132. Which enzyme is
indicated by digit 4?
A. * Phosphatase
B. Nucleosidase
C. Nucleotidase
D. Nuclease
E. Pepsin
48. The scheme of digestion of nucleoproteins is shown in figure 132. Which enzyme is
indicated by digit 5?
A. Phosphatase
B. * Nucleosidase
C. Nucleotidase
D. Nuclease
E. Pepsin
49. The structure of myofibril is shown in figure 136. What is indicated by character 1?
A. * Sarcomere
B. Sarcoplasm
C. A band
D. I band
E. Sarcolemma
50. The structure of myofibril is shown in figure 136. What is indicated by character 2?
A. Sarcomere
B. * Myosin filament
C. A band
D. I band
E. Actin filament
51. The structure of myofibril is shown in figure 136. What is indicated by character 3?
A. Sarcomere
B. Myosin filament
C. A band
D. I band
E. * Actin filament
52. The structure of myofibril is shown in figure 136. What is indicated by characters 4?
A. I disk
B. * Z disk
C. A disk
D. Sarcomere
E. Actin filament
53. The structure shown in figure 125 is called:
A. Liposome
B. Vesicle
C. * Lipoprotein
D. Globule
E. Fibrin
54. The symptoms depicted in figure 115 are specific for:
A. Phenylketonuria
B. Diabetes mellitus
C. Uremia
D. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
E. * Gout
55. The symptoms depicted in figure 118 are specific for:
A. * Gout
B. Diabetes mellitus
C. Uremia
D. Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
E. Phenylketonuria
56. The symptoms of which disease is shown in figure 129?
A. Scurvy
B. * Pellagra
C. Berry-Berry
D. Rickets
E. Pernicious anemia
57. What is the name of enzyme E1 shown in figure 133?
A. Hexokinase
B. * Arginase
C. Xanthine oxidase
D. Catalase
E. Glucose oxidase
58. What is the name of enzyme E2 shown in figure 133?
A. Hexokinase
B. Arginase
C. * Xanthine oxidase
D. Catalase
E. Glucose oxidase
59. What process is shown in figure 134?
A. * Replication
B. Transcription
C. Translation
D. Posttranslational DNA modification
E. Recognition
60. What type of lipoprotein is shown in figure 130?
A. Chylomicrones
B. VLDL
C. IDL
D. * LDL
E. HDL
61. Which compound is indicated by digit 1 in figure 133?
A. Urea
B. Uric acid
C. * Xanthine
D. Adenine
E. Guanine
62. Which compound is indicated by digit 2 in figure 133?
A. Urea
B. * Uric acid
C. Xanthine
D. Adenine
E. Guanine
63. Which compound is replaced with character 1 in scheme shown in figure 114?
A. * 7-dehydrocholesterol
B. Cholecalciferol
C. 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol
D. 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol
E. Ergocalciferol
64. Which compound is replaced with character 2 in scheme shown in figure 114?
A. 7-dehydrocholesterol
B. Cholecalciferol
C. * 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol
D. 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol
E. Ergocalciferol
65. Which compound is replaced with character 3 in scheme shown in figure 114?
A. 7-dehydrocholesterol
B. Cholecalciferol
C. 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol
D. * 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol
E. Ergocalciferol
66. Which compounds are indicated by character 1 in figure 125?
A. Phospholipids
B. Apolipoproteins
C. * Triacylglycerols, esters of cholesterol
D. Monoacylglycerols, free fatty acids
E. Free cholesterol, free fatty acids
67. Which compounds are indicated by character 2 in figure 125?
A. * Phospholipids
B. Apolipoproteins
C. Triacylglycerols, esters of cholesterol
D. Monoacylglycerols, free fatty acids
E. Free cholesterol, free fatty acids
68. Which compounds are indicated by character 3 in figure 125?
A. Phospholipids
B. * Apolipoproteins
C. Triacylglycerols, esters of cholesterol
D. Monoacylglycerols, free fatty acids
E. Free cholesterol, free fatty acids
69. Which diet can cause the disease shown in figure 129?
A. Black bread
B. Meat
C. Rice
D. Eggs
E. * Corn
70. Which disease can be developed in the disorders of the biochemical pathway shown in
figure 114?
A. Scurvy
B. Pellagra
C. Berry-Berry
D. * Rickets
E. Pernicious anemia
71. Which hormone stimulates the formation of the compound 3 (see figure 114)?
A. Thyroxin
B. Triiodthyronin
C. * Parathormone
D. Insulin
E. Glucagon
72. Which metabolism is affected by hormones which are produced in the glands indicated
by question mark in figure 121?
A. Protein
B. Lipid
C. Carbohydrate
D. * Mineral
E. Nucleic acid
73. Which of the below coenzymes is required for the reactions indicated by arrows in figure
113?
A. * TPP
B. TGFA
C. Methycobalamin
D. PLP
E. PMP
74. Which of the below vitamins is required for the biochemical pathway III shown in figure
112?
A. C
B. * B5
C. B6
D. B10
E. B12
75. Which of the below vitamins is required for the biochemical pathway III shown in figure
112?
A. C
B. * B1
C. B6
D. B10
E. B12
76. Which of the below vitamins is required for the biochemical pathway III shown in figure
112?
A. C
B. * B2
C. B6
D. B10
E. B12
77. Which of the below vitamins is required for the biochemical pathway III shown in figure
112?
A. C
B. * B3
C. B6
D. B10
E. B12
78. Which of the following function is specific for hormones which are produced in the
cortex of glands indicated by question mark in figure 120?
A. * Stimulates gluconeogenesis
B. Promotes moving of Са from bones into blood
C. Inhibits gluconeogenesis
D. Activate glycolysis
E. Inhibits transamination of amino acids
79. Which of the following functions is specific for hormones which are produced in the
glands indicated by question mark in figure 121?
A. Stimulates synthesis of proteins
B. * Promotes moving of Са from bones into blood
C. Inhibits gluconeogenesis
D. Stimulates lipolysis
E. Inhibits transamination of amino acids
80. Which of the following hormone is produced in the glands indicated by digit 1 in figure
119?
A. Thyroxin
B. * Testosterone
C. Cortisol
D. Glucagon
E. ACTH
81. Which of the following hormone is produced in the glands indicated by digit 2 in figure
119?
A. Thyroxin
B. Testosterone
C. * Estradiol
D. Glucagon
E. ACTH
82. Which of the following hormone is produced in the glands indicated by question mark in
figure 120?
A. Thyroxine
B. Insulin
C. * Cortisol
D. Glucagon
E. ACTH
83. Which of the following hormones are produced in the glands indicated by question mark
in figure 121?
A. Thyroxine
B. Triiodthyronine
C. ACTH
D. * Parathyroid hormone
E. Insulin
84. Which of the following hormones is produced in the gland indicated by digit 2 in figure
117?
A. Somatoliberin
B. Thyroliberin
C. Corticoliberin
D. Foliliberin
E. * Somatotropic hormone
85. Which of the following hormones is produced in the gland indicated by digit 2 in figure
117?
A. Somatoliberin
B. * ACTH
C. Corticoliberin
D. Foliliberin
E. Thyroliberin
86. Which of the following hormones is produced in the gland indicated by digit 2 in figure
117?
A. Somatoliberin
B. Thyroliberin
C. Corticoliberin
D. Foliliberin
E. * Thyrotropic hormone
87. Which of the following hormones is produced in the gland indicated by digit 1 in figure
117?
A. STH
B. ACTH
C. TTH
D. * Somatostatin
E. Luteinizing hormone
88. Which of the following hormones is produced in the gland indicated by digit 1 in figure
117?
A. STH
B. ACTH
C. TTH
D. * Luteinising-hormone liberin
E. Luteinizing hormone
89. Which of the following hormones is produced in the gland indicated by digit 1 in figure
117?
A. STH
B. ACTH
C. TTH
D. * Somatoliberin
E. Luteinizing hormone
90. Which of the following symptoms are specific for the disease shown in figure 129?
A. * Dermatitis, diarrhea, dementia
B. Dermatitis, xerophthalmia, keratomalacia
C. Dermatitis, hemorrhage, loss of teeth
D. Dermatitis, sterility, muscle atrophy
E. Dermatitis, pernicious anemia, growth retardation
91. Which pathway is shown in figure 133?
A. Synthesis of urea
B. * Synthesis of uric acid
C. Synthesis of ketone bodies
D. Glycolysis
E. Gluconeogenesis
92. Which vitamin is required for the biochemical pathway I shown in figure 112?
A. B1
B. * B5
C. B6
D. B10
E. B12
93. Which vitamin is required for the biochemical pathway I shown in figure 112?
A. Thiamin
B. Folic acid
C. * Nicotinamide
D. Retinol
E. Tocopherol
94. Which vitamin is required for the biochemical pathway II shown in figure 112?
A. * B1
B. B3
C. B6
D. B10
E. B12
95. Which vitamin is required for the biochemical pathway II shown in figure 112?
A. B2
B. * B5
C. B6
D. B10
E. B12
96. Which vitamin is required for the biochemical pathway II shown in figure 112?
A. * Thiamin
B. Folic acid
C. Ribiflavin
D. Retinol
E. Tocopherol
97. Which vitamin is required for the biochemical pathway II shown in figure 112?
A. * Niacin
B. Folic acid
C. Ribiflavin
D. Retinol
E. Tocopherol
98. Which vitamin is required for the biochemical pathway IV shown in figure 112?
A. B2
B. * B5
C. B6
D. B10
E. B12
99. Which vitamin is required for the biochemical pathway IV shown in figure 112?
A. Thiamin
B. Folic acid
C. Ribiflavin
D. Retinol
E. * Nicotinamide
100.
Which vitamin is required for the reactions indicated by arrows in figure 113?
A. Cyanocobalamin
B. Ascorbic acid
C. Folic acid
D. * Thyamin
E. Retinol
101.
Which vitamin is required for the reactions indicated by arrows in figure 113?
A. * B1
B. B6
C. B10
D. B12
E. C
102.
Which vitamin is required for the reactions indicated by arrows in figure 113?
A. Cyanocobalamin
B. Ascorbic acid
C. Folic acid
D. * Riboflavin
E. Retinol
103.
Which vitamin is required for the reactions indicated by arrows in figure 113?
A. Cyanocobalamin
B. Ascorbic acid
C. Folic acid
D. * Pantothenic acid
E. Retinol
104.
Which vitamin is required for the reactions indicated by arrows in figure 113?
A. Cyanocobalamin
B. Ascorbic acid
C. Folic acid
D. * Niacin
E. Retinol
105.
Which vitamin is the precursor for coenzyme that is required for the reactions
indicated by arrows in figure 113?
A. * B1
B. B6
C. B10
D. B12
E. C
106.
Which vitamin is the precursor for coenzyme that is required for the reactions
indicated by arrows in figure 113?
A. * B2
B. B6
C. B10
D. B12
E. C
107.
Which vitamin is the precursor for coenzyme that is required for the reactions
indicated by arrows in figure 113?
A. * B3
B. B6
C. B10
D. B12
E. C
108.
Which vitamin is the precursor for coenzyme that is required for the reactions
indicated by arrows in figure 113?
A. * B5
B. B6
C. B10
D. B12
E. C