* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit: World War II Topic: War in the Pacific
Empire of Japan wikipedia , lookup
Wang Jingwei regime wikipedia , lookup
American mutilation of Japanese war dead wikipedia , lookup
American Theater (World War II) wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of the attack on Pearl Harbor wikipedia , lookup
Allied war crimes during World War II wikipedia , lookup
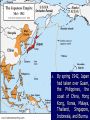
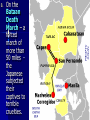
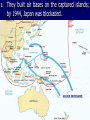
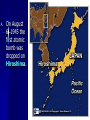
Unit: World War II Topic: War in the Pacific 1. A Japanese Empire A. The Japanese saw World War II as their chance to build an overseas empire. B. They had a scarce supply of natural resources and not a lot of land for their people. 2. Japanese Victories A. By spring 1942, Japan had taken over Guam, the Philippines, the coast of China, Hong Kong, Korea, Malaya, Thailand, Singapore, Indonesia, and Burma. B. C. Under the slogan “East Asia for the Asians,” the Japanese created the Greater East Asia CoProsperity Sphere. After victory, however, the Japanese treated people with cruelty. 3. The Bataan Death March A. The Japanese reserved the most brutal treatment for Allied POWs. B. On the Bataan Death March – a forced march of more than 50 miles the Japanese subjected their captives to terrible cruelties. Of approx. 70,000 54,000 survived. POWS, only I was questioned by a Japanese officer, who found out that I had been in a Philippine Scout Battalion. They took me outside and I was forced to watch as they buried six of my Scouts alive. They made the men dig their own graves, and then had them kneel down in a pit. The guards hit them over the head with shovels to stun them and piled earth on top. - Lieutenant John Spainhower, War Diary 4. The Pacific Theater A. In April 1942, 16 B-25 bombers under Lt. James Doolittle bombed Tokyo and several other cities. B. In the Battle of the Coral Sea (1942), the Allies stopped a potential Japanese takeover of Australia. C. When Japan targeted Midway Island, 1500 miles away from Japan, the Allies stopped them this turned the tide of the war in the Pacific. 5. An Allied Offensive A. Under the command of General Douglas MacArthur, the Marines conducted an “island-hopping” campaign. B. They built air bases on the captured islands; by 1944, Japan was blockaded. C. The Japanese were suffering, but would not consider surrendering. 5. V-J Day The Decision to Drop the Bomb: Alternative Possibilities 1. 2. 3. 4. A massive invasion of Japan, expected to cost millions of Allied causalities A naval blockade to starve Japan, along with conventional bombing A demonstration of the atomic bomb on a deserted island to pressure Japan to surrender A softening of Allied demands for an unconditional surrender MORE ALLIED LIVES – WAR DRAGS ON President Truman considered the bomb to be a military weapon and had no doubt that it should be used. “You should do your weeping at Pearl Harbor,” he told his critics. A. On August 6, 1945 the first atomic bomb was dropped on Hiroshima. B. Nagasaki was next on August 9. C. The Japanese surrendered on September 2, 1945.