* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lipids • Triglycerides –Fats and oils • Phospholipids
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Cholesterol wikipedia , lookup
Low-density lipoprotein wikipedia , lookup
High-density lipoprotein wikipedia , lookup
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
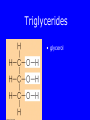
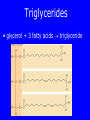
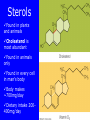
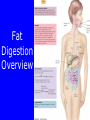
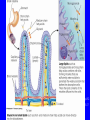
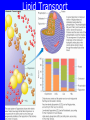
Lipids • Triglycerides –Fats and oils • Phospholipids – Lecithin • Sterols – Cholesterol Objectives • After reading Chapter 4, class discussion and learning activities, you will be able to – Identify types (classification) of lipids – Describe the role of lipids in the body – Discuss lipid digestion, absorption and transport – Calculate calories from fat Objectives • Identify food sources of fats • Discuss the health related effects of lipids – Blood lipid profile – Omega fatty acids – Trans fatty acids – Hydrogenation Triglycerides p. 128 Fig 4-1 4 Triglycerides • glycerol Triglycerides • glycerol + 3 fatty acids triglyceride Fatty Acids • Length of fatty acid – 18-24 carbons in length • Degree of Saturation –Saturated fatty-acid –Monounsaturated fatty-acid –Polyunsaturated fatty-acid p. 129 Fatty Acids • Point of unsaturation • Location of double bonds –Omega number •Omega-3 fatty acid •Omega-6 fatty acid Triglycerides • Degree of saturation determines: –Firmness –Stability •Oxidation –Antioxidants Rancidity • Definition: Deterioration of fat; resulting in undesirable flavor/odor – Flavor Reversion-soy oil; Cu, Fe • Hydrolytic: Separation of glycerol from fatty acids – Short chain fatty acids – Butyric fatty acid; butter • Oxidative: Loss of hydrogen in presence of air/heat – Oxidation of double bonds – Polyunsaturated fatty acids Trans Fats • Degree of unsaturation revisited –Hydrogenation –Cis vs. trans-fatty acids •Trans fat occurs naturally in meat and dairy foods – Conjugated linoleic in milk » Possibly positive for heart health p. 108 NRAEF p. 135-137 Fig 4-9 Phospholipids Phospholipids • Phospholipids in foods-Lecithin • Roles of phospholipids –Plasma membrane –Emulsifiers Phospholipids Sterols Found in plants and animals Cholesterol is most abundant Found in animals only Found in every cell in man’s body Body makes ~700mg/day Dietary intake 200400mg/day Dietary Cholesterol Sterols • Roles of sterols –Manufacture bile acids –Make hormones •Estrogen and testosterone –Make adrenal hormones –Make Vitamin D –Maintain cell membranes Fat Digestion • Hydrolysis –Triglycerides monoglycerides, fatty acids, glycerol Fat Digestion • Mouth – Melting – Lingual Lipase • Stomach – Churning and mixing – Gastric Lipase Fat Digestion • Small intestine –Fat triggers the release of hormone • Cholecystokinin (CCK) –Gallbladder releases bile –Bile emulsifies fat so it can be more fully digested • Pancreatic lipase • Intestinal lipase Fat Digestion Fat Digestion • Enterohepatic circulation • How bile travels through the body Fat Digestion Overview p.152 5-17 Lipid Transport • Lipoproteins –Chylomicrons –VLDL = very-low-density lipoproteins –LDL = low-density lipoproteins –HDL = high-density lipoproteins Lipid Transport Lipid Transport • Lipoproteins and health –LDL: carries cholesterol from liver to the cells of the body •High=Less healthy –HDL: carries cholesterol from the cells back to the liver •High=More healthy Roles of Triglycerides • Fat stores – Energy – Protection – Insulation • Provide essential fatty acids • Insure efficient use of protein and carbohydrate Essential Fatty Acids • Linoleic acid and the omega-6 family – Arachidonic acid • Linolenic acid and the omega-3 family – Alpha omega 3 fatty acids – Marine omega 3 fatty acid •EPA =eicosapentaenoic acid •DHA = docosahexaenoic acid Sources Essential Fatty Acids Health Effects of Lipids • Blood lipid profile – Cholesterol=<200mg/dL – LDL=<100 – HDL=>60 – TG=<150 • Risks from saturated fats, trans fats, cholesterol • Benefits from polyunsaturated fats monosaturated, omega-3 Health Effects of Lipids • Risks from trans fats – Alter blood cholesterol like saturated fats – Raise LDL cholesterol – Lower HDL cholesterol at high intakes – Increase inflammation & insulin resistance – AI = 5 gm/day • Risks from cholesterol – Not as implicated as saturated or trans fats – Beware cholesterol sensitivity • Limit intake <300 mg/day Health Effects of Lipids • Benefits from monounsaturated fats and polyunsaturated fats –Olive oil (monounsaturated) •Lowers LDL and total cholesterol •Lowers blood clotting factors •Lowers blood pressure •Provides phytochemicals which act as antioxidants Health Effects of Lipids • Benefits from omega-3 fats – Prevent arrhythmias – Lower blood pressure – Improve blood vessel function – May ease inflammation – Prevent repeat heart attack •1 gm supplement daily for 3 years • Balance omega-6 and omega-3 intakes How Dietary Fat Affects Blood Lipids Type of Fatty Acid • Saturated • Polyunsaturated • Monounsaturated • Omega-3 • Trans Effects on Blood Lipids - G Total Cholesterol G LDL Cholesterol - H Total, LDL, HDL Cholesterol - H Total, LDL G HDL Cholesterol - H Triglycerides, Total Cholesterol - G Total, LDL H HDL Cholesterol Health Benefits of Lipids Recommended Intakes of Fat • DRI: 20-35% of energy intake • Cholesterol: 200-300 mg/day • Linoleic acid AI –5% - 10% of energy intake • Linolenic acid AI –0.6 - 1.2% of energy intake Guidelines to Groceries • Avoid ADDED and Invisible Fat • Avoid Tropical oils – Coconut oil – Palm oil Fat Distribution in Diet Guidelines to Groceries • Use whole, unprocessed vegetables, fruits, and grains without added fats Guidelines to Groceries • Use fat free milk and milk products Guidelines to Groceries • Use meat sparingly • Use lean meats • Use meat alternatives Beware the Label • “0 Trans Fat” – can still contain up to 0.5 grams • Look for “partially hydrogenated vegetable oil” or “vegetable shortening” • IOM recommends trans fat intake be “as low as possible” Fat Substitutes • “New” vegetable oils from “new” seed – Soybean & other seeds with very low levels of linolenic acid • More stable but less omega-3 fatty acid • Fat substitues – Z-Trim made from corn, soy, oat fiber – Oatrim made from whole oats • Fat replacers –Artificial fats •Olestra Changing Guidelines for Fat Intake Changing Guidelines • Cook with olive oil or canola oil • Monounsaturated fatty acids • Nibble on nuts • Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids • Feast on fish • Marine omega-3 PUFA • But beware of mercury • Limit fatty meats, whole milk products, and tropical oils Changing Guidelines • Limit hydrogenated fat foods – Fried foods (fried in solid fats) – Fast foods (prepared in partially hydrogenated oils/fats – Commercial baked goods – Snack foods Replacing Saturated Fat with Unsaturated Fat Objectives • After reading Chapter 4, class discussion and learning activities, you will be able to – Identify types (classification) of lipids – Describe the role of lipids in the body – Discuss lipid digestion, absorption and transport – Calculate calories from fat Objectives • Identify food sources of fats • Discuss the health related effects of lipids – Blood lipid profile – Omega fatty acids – Trans fatty acids – Hydrogenation