* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Cryobiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
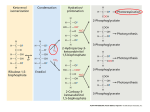
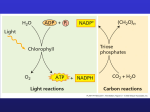
Alternative Mechanisms of Carbon Fixation C3 plants C4 plants CAM plants The story so far…. Rubisco • Catalyzes 2 reactions: ▫ Addition of CO2 to RuBP (carboxylation) Photosynthesis ▫ Addition of O2 to RuBP (oxidation) Photorespiration BOTH happening inside plants! What Weather Has To Do With It… • Stomata gas exchange & temperature control • When it is hot, stomata openings shrink to conserve water ▫ CO2 concentrations decline inside the leaf • Cells continue to undergo photosynthesis ▫ oxygen levels increase – can’t exit via stomata • Oxygen competes with CO2 for Rubisco’s active site ▫ Oxygen has a higher affinity ∴ less CO2 binds Photorespiration • “Photo” – needs products from light reactions • Removes PGA from Calvin Cycle…slowing carbohydrate production. • C3 plants lose up to ¼ of the carbon they fix to photorespiration. Don’t’ Copy… Just Look Photosynthesis Rubisco Substrate: Products: CO2 Glucose O2 What Happens? Rubisco Substrate: Products: O2 PGA CO2 What Happens? Calvin cycle proceeds “normally” Optimal Temperature: Photorespiration 15-25°C - No ATP produced - No G3P produced - Loses C Optimal Temperature: 30-47°C Photorespiration • As C3 photosynthesis declines, photorespiration increases … could kill the plant due to lack of food. • Then why??? ▫ Rubisco a remnant of earlier mechanisms better suited to high atmospheric CO2 C4 Plants (4-Carbon molecule) Enzyme: Phosphoenol pyruvate Carboxylase (PEP carboxylase) Intermediary Molecule: Oxaloacetate (OAA) & Malate Drought resistant Ex. corn, sugarcane Types of Plants: Types of Cells: Bundle sheath: surround veins Mesophyll – around bundle sheath Purpose: Keep [CO2] high to compete with O2 for Rubisco Energy Comparison to C3 Plants: Requires more energy ATP required to convert pyruvate into PEP C4 Plant Photosynthetic Cells • Bundle Sheath: site of Calvin cycle • Mesophyll ▫ No mesophyll cells are more than 3 cells away from any bundle sheath cell at anytime. How Do C4 Plants Reduce Photorespiration? • Continually move CO2 into bundle sheath cells, via malate • Keeps CO2 concentrations high so that it may outcompete oxygen. • 10-120x higher than normal • Using more ATP is still advantageous in a HOT climate! CAM Plants Crassulacean Acid Metabolism Stomata Action: NIGHT: Enzyme: Night – open Day – closed PEP carboxylase Storage Location: Vacuole DAY: What happens? - Malic acid broken down - CO2 released - Calvin cycle occurs Why? Conserve water Intermediary: Malic acid In Summary… Classwork/Homework