* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download QS6U22
Thermal runaway wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Semiconductor device wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
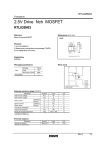
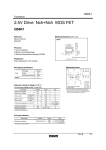
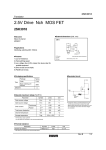
QS6U22 Transistors 2.5V Drive Pch+SBD MOS FET QS6U22 zStructure Silicon P-channel MOS FET Schottky Barrier DIODE zExternal dimensions (Unit : mm) TSMT6 1.0MAX 2.9 1.9 0.95 0.95 (5) 0.85 0.7 (4) 1.6 2.8 (2) (1) 0~0.1 0.3~0.6 zFeatures 1) The QS6U22 combines Pch MOS FET with a Schottky barrier diode in a TSMT6 package. 2) Low on-state resistance with fast switching. 3) Low voltage drive (2.5V). 4) Built-in schottky barrier diode has low forward voltage. (6) (3) 1pin mark 0.16 0.4 Each lead has same dimensions Abbreviated symbol : U22 zApplications Load switch, DC / DC conversion zPackaging specifications Package Type Code Basic ordering unit (pieces) zEquivalent circuit Taping (6) (5) (4) TR 3000 QS6U22 ∗2 ∗1 (1) (2) ∗1 ESD PROTECTION DIODE ∗2 BODY DIODE (3) (1) Anode (2) Source (3) Gate (4) Drain (5) N / C (6) Cathode ∗A protection diode has been in between the gate and the source to protect against static electricity when the product is in use. Use the protection circuit when rated voltages are exceeded. Rev.A 1/4 QS6U22 Transistors zAbsolute maximum ratings (Ta=25°C) <MOSFET> Symbol VDSS VGSS ID IDP ∗1 IS ISP ∗1 Tch PD ∗3 Limits −20 ±12 ±1.5 ±6.0 −0.75 −6.0 150 0.9 Unit V V A A A A °C W / ELEMENT <Di> Repetitive peak reverse voltage Reverse voltage Forward current Forward current surge peak Junction temperature Power dissipation VRM VR IF IFSM Tj PD 25 20 0.7 3.0 150 0.7 V V A A °C W / ELEMENT <MOSFET AND Di> Total power dissipation Range of Storage temperature PD ∗3 Tstg 1.25 −55 to +150 W / TOTAL °C Parameter Drain-source voltage Gate-source voltage Drain current Source current (Body diode) Continuous Pulsed Continuous Pulsed Channel temperature Power dissipation ∗2 ∗3 ∗1 Pw≤10µs, Duty cycle≤1% ∗2 60Hz•1cyc. ∗3 Mounted on a ceramic board zElectrical characteristics (Ta=25°C) 〈MOSFET〉 Parameter Symbol Min. − Gate-source leakage IGSS Drain-source breakdown voltage V(BR) DSS −20 − Zero gate voltage drain current IDSS Gate threshold voltage VGS (th) −0.7 − Static drain-source on-state ∗ − RDS (on) resistance − Yfs ∗ 1.0 Forward transfer admittance Ciss − Input capacitance − Coss Output capacitance − Crss Reverse transfer capacitance − td (on) ∗ Turn-on delay time − tr ∗ Rise time − td (off) ∗ Turn-off delay time − tf ∗ Fall time − Qg ∗ Total gate charge − Qgs ∗ Gate-source charge − Qgd ∗ Gate-drain charge Typ. − − − − 155 170 310 − 270 40 35 10 12 45 20 3.0 0.8 0.85 Max. ±10 − −1 −2.0 215 235 430 − − − − − − − − − − − Unit µA V µA V mΩ mΩ mΩ S pF pF pF ns ns ns ns nC nC nC Conditions VGS=±12V, VDS=0V ID= −1mA, VGS=0V VDS= −20V, VGS=0V VDS= −10V, ID= −1mA ID= −1.5A, VGS= −4.5V ID= −1.5A, VGS= −4V ID= −0.75A, VGS= −2.5V VDS= −10V, ID= −0.75A VDS= −10V VGS=0V f=1MHz ID= −0.75A VDD −15V VGS= −4.5V RL=20Ω RG=10Ω VDD −15V VGS= −4.5V RL=10Ω / RG=10Ω ID= −1.5A Min. − Typ. − Max. −1.2 Unit V Conditions IS= −0.75A, VGS=0V Min. − − Typ. − − Max. 0.49 200 Unit V µA IF=0.7A VR=20V ∗Pulsed 〈Body diode (source−drain)〉 Parameter Forward voltage Symbol VSD 〈Di〉 Parameter Forward voltage drop Reverse current Symbol VF IR Conditions Rev.A 2/4 QS6U22 Transistors 1 Ta=125°C Ta=75°C Ta=25°C Ta= −25°C 0.01 0.001 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 VGS= −10V Pulsed Ta=125°C Ta=75°C Ta=25°C Ta= −25°C 1000 100 0.1 1 GATE-SOURCE VOLTAGE : −VGS (V) VGS= −4V Pulsed Ta=125°C Ta=75°C Ta=25°C Ta= −25°C 1000 100 0.1 1 10 1200 1000 900 800 700 600 500 400 300 200 2 4 6 8 10 12 1000 VGS=0V Pulsed Ta=125°C Ta=75°C Ta=25°C Ta= −25°C 14 16 0.1 Ta=25°C f=1MHz VGS=0V 100 0.5 1 1.5 2 SOURCE-DRAIN VOLTAGE : −VSD (V) Ciss Fig.7 Reverse Drain Current vs. Source-Drain Voltage 10 0.01 0.1 1 10 10000 Ta=25°C Pulsed VGS= −4.0V VGS= −4.5V VGS= −10V 1000 100 0.1 10 100 DRAIN-SOURCE VOLTAGE : −VDS (V) Fig.8 Typical Capacitance vs. Drain-Source Voltage 1 10 DRAIN CURRENT : −ID (A) Fig.6 Static Drain-Source On-State Resistance vs. Drain Current ( ) 1000 Ta=25°C VDD= −15V VGS= −10A RG=10Ω Pulsed 100 tf td (off) 10 td (on) tr Coss Crss 0.01 0.0 1 Fig.3 Static Drain-Source On-State Resistance vs. Drain Current (ΙΙ) Fig.5 Static Drain-Source On-State Resistance vs. Gate-Source Voltage CAPACITANCE : C (pF) REVERSE DRAIN CURRENT : −IS (A) 0 Ta=125°C Ta=75°C Ta=25°C Ta= −25°C 100 0.1 GATE-SOURCE VOLTAGE : −VGS (V) Fig.4 Static Drain-Source On-State Resistance vs. Drain Current (ΙΙΙ) 1 Ta=25°C Pulsed ID= −1.2A ID= −0.6A 1100 DRAIN CURRENT : −ID (A) 10 1000 VGS= −4.5V Pulsed DRAIN CURRENT : −ID (A) Fig.2 Static Drain-Source On-State Resistance vs. Drain Current (Ι) STATIC DRAIN-SOURCE ON-STATE RESISTANCE : RDS (on) (mΩ) STATIC DRAIN-SOURCE ON-STATE RESISTANCE : RDS (on) (mΩ) Fig.1 Typical Transfer Characteristics 10000 10 10000 DRAIN CURRENT : −ID (A) STATIC DRAIN-SOURCE ON-STATE RESISTANCE : RDS (on) (mΩ) 0.1 10000 STATIC DRAIN-SOURCE ON-STATE RESISTANCE : RDS (on) (mΩ) VDS= −10V Pulsed SWITCHING TIME : t (ns) DRAIN CURRENT : −ID (A) 10 STATIC DRAIN-SOURCE ON-STATE RESISTANCE : RDS (on) (mΩ) zElectrical characteristic curves <MOSFET> 1 0.01 0.1 1 10 DRAIN CURRENT : −ID (A) Fig.9 Switching Characteristics Rev.A 3/4 QS6U22 Transistors GATE-SOURCE VOLTAGE : VGS (V) 8 Ta=25°C VDD= −15V ID= −1.2A RG=10Ω Pulsed 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2 1.4 1.6 1.8 2 TOTAL GATE CHARGE : Qg (nC) Fig.10 Dynamic Input Characteristics zMeasurement circuits Pulse Width VGS ID VDS VGS 10% 50% 50% 90% RL 10% D.U.T. 10% RG VDD VDS 90% td(on) 90% td(off) tr ton Fig.11 Switching Time Measurement Circuit tr toff Fig.12 Switching Waveforms VG VGS ID VDS RL IG(Const) D.U.T. Qg VGS Qgs RG Qgd VDD Charge Fig.13 Gate Charge Measurement Circuit Fig.14 Gate Charge Waveform Rev.A 4/4 Appendix Notes No technical content pages of this document may be reproduced in any form or transmitted by any means without prior permission of ROHM CO.,LTD. The contents described herein are subject to change without notice. The specifications for the product described in this document are for reference only. Upon actual use, therefore, please request that specifications to be separately delivered. Application circuit diagrams and circuit constants contained herein are shown as examples of standard use and operation. Please pay careful attention to the peripheral conditions when designing circuits and deciding upon circuit constants in the set. Any data, including, but not limited to application circuit diagrams information, described herein are intended only as illustrations of such devices and not as the specifications for such devices. ROHM CO.,LTD. disclaims any warranty that any use of such devices shall be free from infringement of any third party's intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights, and further, assumes no liability of whatsoever nature in the event of any such infringement, or arising from or connected with or related to the use of such devices. Upon the sale of any such devices, other than for buyer's right to use such devices itself, resell or otherwise dispose of the same, no express or implied right or license to practice or commercially exploit any intellectual property rights or other proprietary rights owned or controlled by ROHM CO., LTD. is granted to any such buyer. Products listed in this document are no antiradiation design. The products listed in this document are designed to be used with ordinary electronic equipment or devices (such as audio visual equipment, office-automation equipment, communications devices, electrical appliances and electronic toys). Should you intend to use these products with equipment or devices which require an extremely high level of reliability and the malfunction of with would directly endanger human life (such as medical instruments, transportation equipment, aerospace machinery, nuclear-reactor controllers, fuel controllers and other safety devices), please be sure to consult with our sales representative in advance. About Export Control Order in Japan Products described herein are the objects of controlled goods in Annex 1 (Item 16) of Export Trade Control Order in Japan. In case of export from Japan, please confirm if it applies to "objective" criteria or an "informed" (by MITI clause) on the basis of "catch all controls for Non-Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction. Appendix1-Rev1.1