* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11-7 Adolescent Psychosocial Development
William E. Cross Jr. wikipedia , lookup
Belongingness wikipedia , lookup
Sexual fluidity wikipedia , lookup
Introspection illusion wikipedia , lookup
Heterosexuality wikipedia , lookup
Attitude (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Peer pressure wikipedia , lookup
Personal identity wikipedia , lookup
Unpopularity wikipedia , lookup
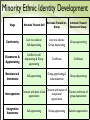
Adolescent Relationships July 26, 2011 Review • Emergence of sexuality: childhood, adolescence? • Sexual scripts? • Sexual orientation • Invisible norm • Conclusions about development of samesex sexual attraction? Teens’ Sexual Behavior • From where do teens learn about sex? • Peers: “Don’t trust adults. I mean, they don’t know what we’re going through. Just want to scare you from having sex, like you’ll die if you do. Gotta ask your friends for advice on how to do it,” (Archibald, Jacoby, Davies, 2010) • Parents: often misperception between teens and parents • Schools: sex education ranges from abstinenceonly to harm reduction Adolescent-Adult R’ships • Positive relationships with adults highly correlated with positive youth outcomes • Conflictual familial r’ships • • Push-pull of gaining/giving independence • Influenced by cultural norms Close familial r’ships • Communication, support, connectedness, control Peer Relationships • Brain maturation, cognitive development, and psychosocial advances allow teens to develop close and important friendships • Symbols of friendships and group identity tantamount in teens’ lives • Peer pressure: encouragement to conform with peer group in behavior, dress, attitude Adolescent Psychosocial Development Identity • Identity vs. Diffusion (Erikson) • Answer “Who am I?” • Identity achievement: adopt some roles, reject others as set forth by culture Not Yet Achieved • • Identity diffusion • Lack of commitment to any goals • Motto is “whatever” Identity foreclosure • • Limit role exploration Identity moratorium • Postponement, “time out” Minority Ethnic Identity Development Stage Attitude Toward Self Attitude Toward InGroup Attitude Toward Dominant Group Conformity Low race salience Self-depreciating Low race salience Group depreciating Group-appreciating Dissonance & Appreciating Conflict b/t selfdepreciating & Group appreciating Conflictual Conflictual Resistance & Immersion Self-appreciating Group-appreciating & culturocentrism Group-depreciating Introspection Concern with basis of selfappreciation Integrative Awareness Self-appreciating Concern with nature of Concern with basis of unequivocal group-depreciation appreciation Group-appreciating Selective appreciation Emotional Changes in Adolescence • Drop in self-esteem among girls and boys • Girls’ athletic involvement buffers SE drop • Increased moodiness, angriness • Minority of teens experience clinical depression Suicidal Ideation & Behavior • • Thinking about suicide • Continuum ranging from thoughts of own death to serious, planful contemplation of taking own life • Most people fall somewhere on the continuum at sometime Nonfatal suicidal behavior • Self-injurious behavior that does not result in death Adolescent Fatal Suicidal Behavior • Rates increasing since 1960 due to • Availability of guns • Parental supervision • Drug/alcohol availability • Culture Ethnic & Gender Differences in Fatal Suicidal Behavior • American Indian & Alaska Native have highest rates of fatal suicidal behavior • Boys of all ethnicities have higher rates of fatal suicide than girls Risk Factors for Suicide • #1 risk factor: relationship to someone who has died of suicide • Accessibility to means • Previous suicidal behavior • Drug/alcohol use • Social isolation