* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ReV W6 Project MDA
Gluten-free diet wikipedia , lookup
Vegetarianism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Calorie restriction wikipedia , lookup
Food studies wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Food politics wikipedia , lookup
Food coloring wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
Raw feeding wikipedia , lookup
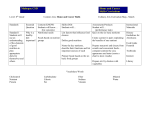
Week Six Project Instructions MyDietAnalysisVersion Objectives Compare your average intakes for many of the analyzed nutrients to your recommendations. Then explore the relationship between the balance, variety and nutrients density of your diet and your nutrient intakes. Source of information • Diet Analysis Reports Log onto to your on-line diet software account and click on REPORTS. For this project, use the following reports, always view the AVERAGE values. (When viewing your reports in the software, be sure all five days are CHECKED to see the averages.) ✴Actual Intakes vs Recommended Intakes ✴Calories and Fat Sources ✴MyPyramid • Case Study: Eddy • Case Study: Annette • Week 3 Diet Project: Fiber & Balance Part One Download the Project Form (see link in Week Six folder). Complete the form using your diet analysis reports. Give a conclusion about your intake for each nutrient in just a few words, such as met, exceeded, within range, below maximum recommendation, short. Note: Do not be concerned if the percentages for any vitamin/mineral are over 100%. Consuming large amounts of nutrients from foods is rarely a health problem. The one exception is SODIUM. The recommended MAXIMUM intake (tolerable upper intake level) is 2300 mg. 20 points Part Two OPTIONAL Discuss how the balance, nutrient density and variety of your diet relates to your average intakes of the above nutrients. 10 POINTS-which you can apply to any previous case study or diet project (Week 2, Week 3, Week 4). Word length: 300 to 600 Suggestions: Consider reviewing the case studies on Eddy and Annette and your Week 3 Diet project. Additional information: Balance Apply the Food Guide Pyramid/My Plate to check the balance of your diet. See the our case study on Eddy and your Week 3 Project Nutrient Density Nutrient Density is a very simple idea--it's a way to judge a food by comparing calories to the overall nutritional value. This is not a hard and fast definition; it is a judgment call! Picture nutrient density as a scale: on the lower end are lower nutrient density items (typically high calorie and low nutrient content) like soda and candy. Moving up the scale to the higher end we find higher nutrient density items (typically lower calorie, higher nutrient content) like broccoli, legumes, non-fat dairy foods. Click here to see >> an example scale of the Nutrient Densities of various foods. (Disclaimer! This scale is NOT the final word, just a way I judged the nutrient densities of various foods.) Some tips when judging the nutrient density (ND) of a food: Higher ND: Most whole grains, fruits and vegetables with little added fat and sugar. TIP: • Vegetables are some of the most nutrient dense sources of food--often low calories and rich in nutrients. When judging animal foods: Higher ND foods are lower in fat. Examples: non-fat or 1% milk and • lean cuts of meat. Compare a food against other foods from the same food group. Not really fair to compare • spinach to bread or a grapefruit to cheese. Some high calorie/high fat foods are tricky to judge. For example, we know that some high-fat • foods are rich in healthy oils like salmon, seeds and avocados. So the high fat content in foods that provide us with essential fatty acids adds and not reduces the nutrient density of a food. Nutrient density is not related to organic. Also processing may impact the nutrient density of a • food but it may also improve it! Depends on the extent and type of processing. Variety Focus on the Pyramid Food Groups that provide a great variety of choices: Grains, Vegetables and the Meat & Bean groups. Examine the variety of the foods you consumed from within each of these groups, Grains, Vegetables and Meat& Bean. Discuss how the variety of foods consumed relates to the intake of nutrients in your diet? How many different types of grains were consumed? Vegetables? [TIP: See the Food Guide Pyramid’s FIVE SUBGROUPS listed for vegetables.] Did choices from the Meat & Bean group include seafood? nuts&seeds? legumes?