* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 6 Magnetism
Insulator (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
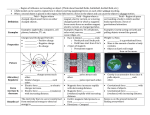
Unit 6 Magnetism Chapter 8 Pages 226-255 Magnets • Two magnets exert a force on each other • The magnetic force is the interaction you feel before the two magnets even touch each other • The strength of this force increases as you move the magnets closer together • The magnetic field exerts the magnetic force • Each magnet has a north and south pole • This is where the magnetic force is the strongest • Like poles repel • Opposite poles attract Earth’s Magnetic Field • On a compass, the needle points to geographic North • This is because earth’s south magnetic pole is located in Canada • So opposites attract • The north on the compass to the “south” in Canada Magnetic Domains • Groups of atoms with aligned magnetic poles are called magnetic domains • This allows the object to behave like a magnetic with a north and south pole • Ex: Placing a magnet against an iron nail will cause all the atoms to orient themselves in the same direction and temporarily cause the nail to act as a magnet Electric Current and Magnetism • Moving charges produce magnetic fields • The direction of the field depends on the direction of the current • The strength of the field depends on the amount of current flowing through the wire Electromagnets • An electromagnet is a temporary magnet made by placing iron inside a current carrying coil of wire • The more the wire is coiled around the iron, it causes a stronger magnetic field • When current flows through the electromagnet it moves toward or away from another magnet, converting electric energy into mechanical energy to do work • Ex: stereo speakers contain electromagnets Galvanometers • Gauges are your dashboard of your car are galvanometers • They measure the current being sent from sensors which in turn register the amount of ex: gasoline you have left Electric Motors • An electric motor is a device that changes electrical energy into mechanical energy • Like galvanometers, electric motors use an electromagnet • The movement of the current is constantly switched back and forth to maintain the rotation of the coil • Some motors use a commutator to do this, others use household alternating current • Electric motors are most useful if their rotation speed is controlled • Today’s motors are smaller, more powerful, and more efficient than the first ones developed in the late 1800s Electric Generators • Electromagnetic induction is caused when a magnetic is moved through a wire coil or rotating a coil of wire through a magnetic field • This is how generators produce electricity • Again, the current flow must constantly switch directions in order for the coil to turn continuously Types of Generators • In your car, it is called an alternator • Power plants use generators to allow electricity to reach your home • Here the electromagnets are connected to a turbine pushed by either water, wind, or steam Direct and Alternating Currents • A battery produces a direct current, which flows in only one direction of a wire • Generators produce alternating current, which reverses the direction of current flow in a regular way Transformers • Alternating current traveling through power lines is a high voltage so as to reduce the amount of energy lost as heat • A transformer can either decrease the voltage (step down) or increase it (step up) • Step up transformers have more turns of wire in the secondary coil than in the primary coil