* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Magnetism_and_Electromagnetism_Review
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
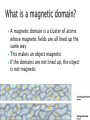
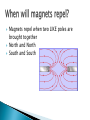
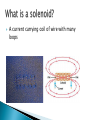
The two smaller magnets will have their own north and south poles You get two separate magnets, NOT a north “magnet” and a south “magnet” This is due to the direction of the domains On its poles Magnets have two poles: A north pole A south pole Electrons Electrons spin in orbit around the nucleus A moving electron produces a magnetic field This movement makes each atom like a tiny bar magnet The magnetic field This allows magnets to interact without touching Magnetic field lines start at one pole and return to the opposite pole A magnetic domain is a cluster of atoms whose magnetic fields are all lined up the same way This makes an object magnetic If the domains are not lined up, the object is not magnetic Magnets will attract when two OPPOSITE poles are brought together North and South A ferromagnetic material Some ferromagnetic materials are: Iron Nickel Cobalt By rubbing a ferromagnetic material with one pole of a strong magnet By placing a ferromagnetic material in a strong magnetic field Attaching a ferromagnetic material to an electric circuit Magnets repel when two LIKE poles are brought together North and North South and South The solar wind is a stream of charged particles ejected from the upper atmosphere of the sun. It mostly consists of electrons and protons. Particles from the solar wind travel along the magnetic field lines If they come close enough to Earth, they interact with the atmosphere This causes the bright colors An aurora is only seen near the poles because that is the only place where the magnetic field lines come close to Earth The angle between geographic north and magnetic north This is different depending on where you are on Earth Magnetic declination changes over time because the magnetic poles move very slowly Drop it repeatedly Strike it hard Heat it All of these cause the domains to move in different directions This causes the magnet to lose its magnetic properties An electric current produces a magnetic field. Remember that an electric current is the flow of electrons. Remember also that the movement of electrons is what creates a magnetic field. A current carrying coil of wire with many loops Increase the current in the solenoid Add more loops of wire Wind the coils of wire closer Use a stronger ferromagnetic material for the core Induced emf A current can be produced by a changing magnetic field First shown in an experiment by Michael Faraday A primary coil is connected to a battery A secondary coil is connected to an ammeter Electromagnetic Induction When a magnet moves toward a loop of wire, the ammeter shows the presence of a current (a) When the magnet is held stationary, there is no current (b) When the magnet moves away from the loop, the ammeter shows a current in the opposite direction (c) If the loop is moved instead of the magnet, a current is also detected Electromagnetic Induction – Results of the Experiment A current is set up in the circuit as long as there is relative motion between the magnet and the loop The same experimental results are found whether the loop moves or the magnet moves The current is called an induced current because it is produced by an induced emf Applications of Faraday’s Law – Apnea Monitor The coil of wire attached to the chest carries an alternating current An induced emf produced by the varying field passes through a pick up coil When breathing stops, the pattern of induced voltages stabilizes and external monitors sound an alert Application – Tape Recorder A magnetic tape moves past a recording and playback head The tape is a plastic ribbon coated with iron oxide or chromium oxide x Application – Tape Recorder, cont. To record, the sound is converted to an electrical signal which passes to an electromagnet that magnetizes the tape in a particular pattern To playback, the magnetized pattern is converted back into an induced current driving a speaker



























![magnetism review - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002621376_1-b85f20a3b377b451b69ac14d495d952c-150x150.png)




