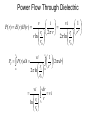* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Co-Axial Cable Analysis - Prescott Campus, Arizona
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Partial differential equation wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
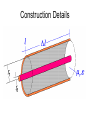
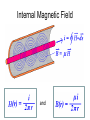
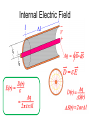
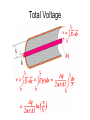
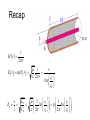
Co-Axial Cable Analysis Construction Details Question 1 What is the fundamental equation relating the magnetic field surrounding a conductor and the current in the conductor? Ampere’s Law: i H dS Internal Magnetic Field and Question 2 By what method is the total flux passing through a given area computed? B dA A Total Flux in Short Section Definition of inductance: Ratio of total flux to total linked current causing the flux. Incremental Inductance: Inductance per Unit Length Question 3 What is the fundamental equation relating the electric field surrounding a charged body and the charge on that body? Gauss’s Law: q D dA A Internal Electric Field Question 4 What is the fundamental equation relating the electric field in the region about two bodies and the potential difference (voltage) between those two bodies? a vba E dS b Total Voltage E Field Relation to Voltage We showed previously that: ..and since... ..therefore... Definition of capacitance: Ratio of total charge to the voltage resulting from the charge. Incremental Capacitance Capacitance per Unit Length Question 5 What is the fundamental relationship between the magnitudes of Electric and Magnetic fields when Energy is propagating through a medium? Ohm’s Law E H where is the intrinsic impedance of the dielectric material Induced Co-ax Voltage We previously determined that the magnetic field strength associated with a current in the co-ax is given by: H (r ) i 2r , thus E (r ) 2 r i ..and the voltage between inner and outer conductor will be: Characteristic Impedance We see now that the ratio of voltage to current associated with energy propagating in a coaxial cable is: .. but, from our previous discussion of inductance and capacitance per unit length, r1 ln 2 2 r0 1 r1 L0 2 ln Z 0 2 C0 2 r0 r1 ln r0 L0 v Z0 i C0 Recap H r i 2 r i E r H r 2 r L0 v Z0 i C0 v r1 r ln r0 1 r1 1 r1 ln ln 2 r0 2 r0 Question 6 What is the fundamental equation relating the Power density flowing through a region and the fields in that region? P EH Power Transfer The Poynting Vector is used to represent the power transferred by electromagnetic fields: P EH If the fields are perpendicular, as they are in this case, then i Pr E r H r 2r 2 in watts per square meter Question 7 How do we compute the total power flowing through a surface if we know the power density at all points on that surface? r1 PT Pr dA r0 Power Transfer (cont) To find the total power transfer (watts) we must integrate P(r) over the entire cross section of the dielectric, between r0 and r1. . . We’ll integrate using a ring of thickness dr ... u i 1 u i2 PT 2 2rdr 2 r0 r 2 PT i 2 Z 0 iv 2 r1 dr 2 1 r r i 2 0 r1 r1 ln r0 Power Flow Through Dielectric v i P(r ) E (r ) H (r ) r1 2 r ln r0 r1 r1 r vi 1 2 r1 r 2 ln r0 vi 1 PT P(r )dA 2 2rdr r1 r0 r r0 2 ln r0 r1 vi dr vi r1 r0 r ln r0 Traveling Waves If one applies Kirchhoff’s Laws to a differential length of transmission line having Inductance and Capacitance per unit length of L0 and C0 respectively, and excited by a source with radian frequency w, solution of the resulting differential equations yields a solution for the voltage function of the form: j wt x V t , x Vi e Vi represents a complex amplitude. The + preceding the w t term indicates that solutions will exist in complex conjugates to yield a real valued time function. As per our long standing convention, we will only explicitly carry the + term through our derivations. The + preceding the x term indicates solutions exist representing waves traveling in the positive and negative directions. Let’s see how this works. Traveling Waves (cont) Consider the solution having the phase term (wt-x). This represents the instantaneous phase of the voltage function. Now consider The waveform peaks, where the instantaneous phase equals 2N (or any point of constant phase). If we solve for x, we get 2 N wt 2 w xN N t Two important observations can be made. 1. The distance between adjacent peaks (wavelength) is 2. The position of the peaks is increasing at a velocity vp 2 vp f w 1 1 L0C0