* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electromagnetic Induction - Lompoc Unified School District
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Skin effect wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
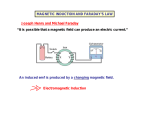
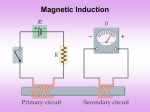
Electromagnetic Induction Faraday Discovered basic principle of electromagnetic induction Whenever the magnetic field around a conductor is moving or changing magnitude, a current is induced in the conductor Torus Ring When switch is turned on, a magnetic field is created in coil A and the entire iron ring becomes magnetized Sudden increase in magnetic field causes a current to momentarily be induced in coil B Once the field becomes steady in the ring, induced current no longer exits When switch is turned off, the sudden demagnetization causes current to be again momentarily induced but in opposite direction Factors Affecting Current Induced Number of loops Rate of motion of magnetic field More loops, greater current Faster motion, greater current Strength of magnetic field Stronger field, greater current Faraday’s Law Amount of emf induced is proportional to: Rate of change in magnetic field (called flux) Flux is directly proportional to B and A Unit of flux is the Weber (Wb) = BA cos Number of loops in the wire Rate of change = -N (/t) Example A conductive wire consisting of 3 loops and enclosing an area of .020 m2 is perpendicular to a uniform magnetic field of .030T. If the field goes to zero in .0045sec, what is the magnitude of the induced emf? Example The magnetic flux through a 60 turn coil of wire is reduced from 35Wb to 5.0Wb in .10sec. The average induced current is .0036 A, what is the wire’s resistance? Direction emf acts in direction opposite to the flux Induced emf gives rise to current whose magnetic field opposes original field Lenz’s Law Current flows in a direction such that the induced field they create opposes the action of the inducing field Work done moving a magnetic field against its opposing force is transformed into electric energy