* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download MAGNETIC INDUCTION AND FARADAY`S LAW
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
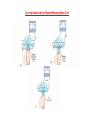
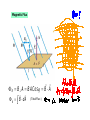
MAGNETIC INDUCTION AND FARADAY’S LAW Joseph Henry and Michael Faraday “It is possible that a magnetic field can produce an electric current.” An induced emf is produced by a changing magnetic field. Electromagnetic Induction Current Induced by Magnet Moving Near Coil Magnetic Flux r r Φ B = B⊥ A = BACosq = B ⋅ A r r Φ B = ∫ B ⋅ dA ( Total Flux ) Faraday’s Law of Induction e i= R N loops r r ΦB = B⋅ A dΦ B e =− dt Induced emf E is caused by the change in the magnetic flux. How about minus sign? Lenz ‘ s law Lenz’s Law An induced emf is always in a direction that “opposes” the change in the flux. • flux increasing • flux decreasing induced emf will create a current to reduce it. induced emf will create a current to increase it. Three ways to change the magnetic flux. 1) By changing intensity of the magnetic field B 2) By changing area A of the loop. 3) By changing orientation of the loop with respect to the field (changing Q). What is the direction of the induced current? A square coil of wire with side 5.0 cm contains 100 loops and is perpendicular to a uniform 0.60 T magnetic field. It is quickly and uniformly pulled from the field to a region where B drops to zero. At t=0, the right edge of the coil is at the edge of the field. It takes 0.100 s to move the whole coil into the field free region. (a) Find the rate of change of the flux. (b) Find the emf and induced current. (c) How much energy is dissipated in the coil if its resistance is 100 ohms. (d) What was the average force required? EMF Induced by a moving conductor EMF Induced by a moving conductor The distance the rod travels: dx dx = v ⋅ dt The area swept by the rod: Change in the flux: dA = l ⋅ vdt df B = B ⋅ dA = Blvdt df B Blvdt e= = = Blv dt dt Magnitude of emf AC GENERATOR