* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electromagnetic Induction
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Michael Faraday wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
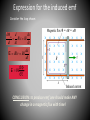
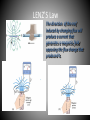
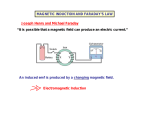
Electromagnetic Induction Ways of generation emf (electromotive force) • Chemical Reaction (batteries). • Use of Active transducers. e.g.. photocell or thermocouples. • Principal of Electromagnetic Induction. Electromagnetic Induction. • Electromagnetic Induction is the phenomenon of voltage induction in a conductor placed in the magnetic field. • The generation of emf due to Electromagnetic Induction was first obtain by the English scientist Michael Faraday in 1831. Laws of Electromagnetic Induction. • Faraday’s First law • Faraday’s Second law • LENZ’S Law Faraday’s First law • The first law states that whenever the magnetic lines of force linking with a coil or conductor changes • An emf gets induced in the coil or conductor. Faraday’s Second law • The magnitude of induced emf is directly proportional to the rate of change of flux linkage. • where flux linkage=Flux X No. of coils Expression for the induced emf Consider the loop shown: d m d dx Bl x Bl dt dt dt dx E Blv Bl dt CONCLUSION: to produce emf one should make ANY change in a magnetic flux with time! LENZ’S Law The direction of the emf induced by changing flux will produce a current that generates a magnetic field opposing the flux change that produced it. Lenz’s Law B, H N S Iinduced V+, V- Lenz’s Law: emf appears and current flows that creates a magnetic field that opposes the change – in this case an decrease – hence the negative sign in Faraday’s Law. Lenz’s Law B, H N S Iinduced V-, V+ Lenz’s Law: emf appears and current flows that creates a magnetic field that opposes the change – in this case an increase – hence the negative sign in Faraday’s Law. Thank you……..