* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3 Generators, Motors, Eddy Currents, Maxwell`s Four Equations
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
High voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electroactive polymers wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Computational electromagnetics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electrical injury wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Friction-plate electromagnetic couplings wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Electric machine wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
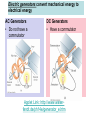
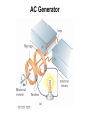
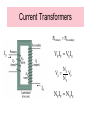
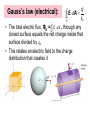
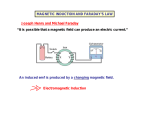
-Generators -Motors -Eddy Currents -Maxwell’s Four Equations AP Physics C Mrs. Coyle Electric generators convert mechanical energy to electrical energy AC Generators • Do not have a commutator DC Generators • Have a commutator Applet Link: http://www.walterfendt.de/ph14e/generator_e.htm AC Generator Rotating Loop in a Generator • Loop has N turns • The flux through the loop at any time t : FB = BA cos q FB =BA cos wt dFB ε N dt NABω sin ωt Induced emf in a Rotating Loop dFB ε N dt NABω sin ωt emax = NABw Induced emf in a Rotating Loop emax occurs when wt = 90o or 270o – This occurs when the magnetic field is in the plane of the coil and the time rate of change of flux is a maximum e = 0 when wt = 0o or 180o – This occurs when B is perpendicular to the plane of the coil and the time rate of change of flux is zero DC Generators • The DC (direct current) generator has essentially the same components as the AC generator • The main difference is that the contacts to the rotating loop are made using a split ring called a commutator DC Generators • In this configuration, the output voltage always has the same polarity and pulsates with time • To obtain a steady DC current, commercial generators use many coils and commutators distributed so the pulses are out of phase Motors • A motor is a generator operating in reverse • Electrical energy is converted to mechanical energy • A current is supplied to the coil by a battery and the torque acting on the current-carrying coil causes it to rotate Back emf of a Motor • As the coil rotates in a magnetic field, an emf is induced in the coil – This induced emf always acts to reduce the current in the coil and is called back emf – The back emf increases in magnitude as the rotational speed of the coil increases • The power requirements for starting a motor and for running it are greater for heavy loads than for light ones Voltage Transformers F solenoid NP o IP A dF B Vs N s dt dF B VP N P dt NS NP step up transformer NP NS step down transformer dF B VP VS dt N P NS Current Transformers PPr imary PSecondary VP IP VSIS IP NS VS VP NP IS NP IP NSIS Eddy Currents • Circulating currents that are induced in bulk pieces of metal moving through a magnetic field • The eddy currents are in opposite directions as the plate enters or leaves the field • Are often undesirable because they represent a transformation of mechanical energy into internal energy Maxwell’s Equations q S E dA εo B dA 0 Gauss's law electric Gauss's law in magnetism S dFB E ds dt Faraday's law dFE B ds μo I εo μo dt Ampere-Maxwell law q Gauss’s law (electrical): S E dA εo • The total electric flux, ΦE = E dA , through any closed surface equals the net charge inside that surface divided by eo • This relates an electric field to the charge distribution that creates it Gauss’s law (magnetism): B dA 0 S • The total magnetic flux F dA through any closed surface is zero • The number of field lines that enter a closed volume must equal the number that leave that volume • The magnetic field lines cannot begin or end at any point • Isolated magnetic monopoles have not been observed in nature Faraday’s law of Induction: dFB E ds dt • An electric field is created by a changing magnetic flux • Induced voltage Emf=- E ds around any closed path, equals the rate of change of the magnetic flux through any surface bounded by that path • Example: A current is induced in a conducting loop placed in a time-varying B Ampere-Maxwell Law dFE B ds μo I εo μo dt • A generalization of Ampere’s law • Creation of a magnetic field by a changing electric field and electric currents • The line integral of the magnetic field around any closed path is the given sum The Lorentz Force Law F = qE + qv x B • Maxwell’s equations, together with this force law, completely describe all classical electromagnetic interactions