* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Superior mesenteric artery
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
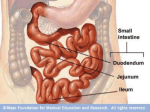
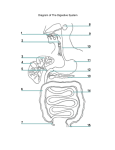
Esophagus Length:- 10 inches = 25 cm Length of the abdominal part:- 0.5 inch = 1.25 cm Relations:A- Anteriorly:1- Left lobe of liver 2- Left vagus N. B- Posteriorly:1- Left crus of diaphragm 2- Left vagus N. Blood supply:A- Arterial supply:- Branches from left gastric A. B- Venous drainage:- Into left gastric V. → Into portal V. Lymph drainage:- To left gastric L.Ns. Nerve supply:1- Parasympathetic:- Anterior & posterior gastric Ns. = Left & right vagus Ns. 2- Sympathetic:- From thoracic part of sympathetic trunk N.B. 1- Esophageal opening of diaphragm is an opening through the right crus 2- Esophagus enters the right side of stomach 3- Gastro-esophageal sphincter:- In the form of circular muscle layer at the lower end of esophagus - It isn’t an anatomical sphincter = It is a Physiological sphincter - Its closure is controlled by vagi Stomach Parts:1- Fundus:- Above the cardiac orifice 2- Body:- Extends between a- Level of cardiac orifice b- Level of incisura angularis 3- Pyloric antrum:- Between a- Incisura angularis b- Pylorus 4- Pylorus:- One inch long - Its cavity is called pyloric canal - Its muscular wall is called pyloric sphincter Relations:A- Anteriorly:1- Anterior abdominal wall 2- Diaphragm 3- Left lobe of liver 4- Left costal margin 5- Left lung & pleura B- Posterior relations = stomach bed:- Formed by 1- Pancreas 2- Splenic Artery 3- Spleen 4- Left kidney 5- Left suprarenal gland 6- Transverse colon 7- Transverse mesocolon 8- Diaphragm 9- Lesser sac Blood supply:A- Arterial supply:1- Left gastric A.:- From celiac trunk - Runs along lesser curvature - Supplies the lower 1/3 of esophagus & upper right part of stomach 2- Right gastric A.:- From hepatic artery - Runs along lesser curvature - Supplies the lower right part of stomach 3- Short gastric A.:- From splenic A. - Supply the fundus 4- Left gastro-epiploic A.:- From splenic A. - Supplies stomach along upper part of greater curvature 5- Right gastro-epiploic A.:- From gastro-duodenal A. that is a branch of hepatic A. - Supplies stomach along lower part of greater curvature B- Venous drainage:1- Left gastric vein:To portal V. 2- Right gastric vein:To * * 3- Short gastric Vs.:To splenic V. 4- Left gastro-epiploic V.:To * * 5- Right gastro-epiploic vein:- To superior mesenteric V. Lymph drainage:A- Lymph vessels pass with the As. to reach 1- Right & left gastric L.Ns. 2- Right & left gastro-epiploic L.Ns. 3- Short gastric L.Ns. B- Then to celiac L.Ns. Nerve supply:A- Parasympathetic nerve supply:- From right & left vagi - Secretomotor to gastric glands, motor to muscles of stomach but inhibitory to pyloric sphincter B- Sympathetic supply:- Form celiac plexus - Motor to pyloric sphincter C- Pain transmitting nerve fibers:- Pass with the sympathetic fibers Peritoneal covering:- completely covered by peritoneum except for bare area of the stomach Peritoneal folds and ligaments:1- Greater omentum:- Connects the greater curvature with the transverse colon 2- Lesser omentum:- Connects the lesser curvature with the liver 3- Gastro-splenic ligament:- Connects the fundus with the spleen 4- Gastro-phrenic ligament:- Connects the fundus with the diaphragm N.B. 1- Capacity of stomach = 1500 mL 2- Shape of stomach a- J-shaped stomach = Vertical:- In tall thin persons b- Steer-horn stomach = High & transverse:- In short obese persons 3- Steer horn = قرن الثور 4- Openings of stomach:a- Cardiac orifice b- Pyloric orifice 5- Stomach is relatively fixed at its ends by very mobile in between 6- Incisura angularis = Constant notch in the lower part of lesser curvature 7- Fundus contains gases 8- Pylorus is the most tubular part of stomach 9- Lesser curvature of stomach a- It is the right border of stomach b- Suspended to the liver by lesser omentum 10- Peritoneal ligaments & folds attached to the greater curvature of stomach a- Gastro-splenic ligament:- Attached to its upper part & to spleen b- Greater omentum:- Attached to its lower part & to transverse colon 11- Pyloric sphincter:- Anatomical & physiological - Circular muscle fibers 12- Pylorus:- Lies on transpyloric plane - Can be recognized by a constriction on its surface 13- Rugae = Mucosal folds of stomach:- Mainly longitudinal 14- Muscle fibers of stomach are longitudinal, transverse & oblique 15- Left gastric A. supplies a- Lower 1/3 of esophagus b- Upper right part of stomach 16- Left gastro-epiploic A. & short gastric As. arise from splenic A. at the hilum → Then pass through gastro-splenic ligament Small intestine Parts:1- Duodenum 2- Jejunum 3- Ileum Duodenum Shape:- C-shaped Length:- 10 inches = 25 cm Position:- Retroperitoneal (fixed to the posterior abdominal wall) except the 1st one inch that is mobile Parts:1- First = 2 inches 2- Second = 3 inches 3- Third = 4 inches 4- Fourth = 1 inch Blood supply:A- Arterial supply:1- Superior pancreaticoduodenal artery:- Branch of gastroduodenal A that is a branch of hepatic A. - Supplies the upper half 2- Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery:- Branch of superior mesenteric A. - Supplies the lower half B- Venous drainage:1- Superior pancreaticoduodenal V.:- Drains into portal V. 2- Inferior pancreaticoduodenal V.:- Drains into superior mesenteric V. Lymph drainage:- Lymphatics follow As. 1- Upward through pancreatico-duodenal L.Ns. → To gastro-duodenal L.Ns → To celiac L.Ns. 2- Downwards through pancreatico-duodenal L.Ns → To superior mesenteric L.Ns. Nerve supply:- By celiac & superior mesenteric plexuses that consist of 1- Sympathetic fibers 2- Parasympathetic fibers:- From vagus nerves Peritoneal covering:1- The 1st one inch:- Resembles the stomach - The peritoneum covers its anterior & posterior surfaces - Lesser omentum is attached to its upper border - Greater omentum is attached to its lower border 2- The remainder:- Retro-peritoneal - The peritoneum covers its anterior surface partially Directions of the 4 parts:A- First part:- Begins at pylorus - Runs upward, backward & to the right on transpyloric plane - At the level of 1st lumbar vertebra B- Second part:- Vertical - On the right side of 2nd & 3rd lumbar vertebrae C- Third part:- Horizontal - Directed to the left - Along subcostal plane - Passes in front of vertebral column D- Fourth part:- Upward & to the left - Ends at duodeno-jejunal flexure Relations of duodenum Relations of the 1st part A- Anteriorly:1- Quadrate lobe of liver 2- Gall bladder B- Posteriorly:1- Portal V. 4- Lesser sac:- Behind the 1st one inch 2- Bile duct 5- Gastroduodenal A. 3- I.V.C. C- Superiorly:- Epiploic foramen D- Inferiorly:- Head of pancreas Relations of the 2nd part Anteriorly:1- Right lobe of liver 2- Transverse colon B- Posteriorly:1- Hilum of right kidney C- Laterally:1- Ascending colon 2- Right colic flexure D- Medially:1- Head of pancreas 2- Bile duct 3- Coils of small intestine 4- Fundus of gall bladder 2- Right ureter 3- Right lobe of liver 3- Main pancreatic duct Relations of the 3rd part A- Anteriorly:1- The root of mesentery of small intestine 2- Superior mesenteric vessels in the root of mesentery of small intestine 3- Coils of jejunum B- Posteriorly:1- Right ureter 3- I.V.C. 2- Right psoas major 4- Aorta C- Superiorly:- Head of pancreas D- Inferiorly:- Coils of jejunum Relations of the 4th part Anteriorly:1- Beginning of the root of mesentery of small intestine 2- Coils of jejunum B- Posteriorly:1- Left margin of aorta 2- Medial border of left psoas major N.B. 1- Lesser sac is behind a- Stomach b- First one inch of duodenum c- Lesser omentum d- Greater omentum 2- Duodenum lies in epigastric & umbilical regions 3- Ampulla of Vater opens into the medial border of 2nd part of duodenum 4- Plicae circularis = Circular mucosal folds = In duodenum, jejunum & ileum 5- Major & minor duodenal papillae = Rounded elevations in the medial wall of 2nd part of duodenum:- Produced by …………. & ………. 6- Minor duodenal papilla is 2 cm above the major one 7- Duodeno-jejunal flexure is held in position by a peritoneal fold called ligament of Treitz 8- Ligament of Treitz is attached to a- Right crus of diaphragm b- Duodeno-jejunal flexure Jejunum & ileum Arterial supply:A- Jejunum:- Supplied by jejunal branches of S.M.A. B- Ileum:- Supplied by 1- Ileal branches of S.M.A. 2- Ileocolic A.:- From S.M.A. Venous drainage:- The same as arterial supply A- Jejunum:- Drained by jejunal Vs. to S.M.V. B- Ileum:- Drained by 1- Ileal Vs. to S.M.V. 2- Ileocolic V.:- To S.M.V. Lymph drainage:- To intermediate mesenteric L.Ns. → Then to superior mesenteric L.Ns. Nerve supply:- By superior mesenteric plexus that consists of 1- Sympathetic fibers 2- Parasympathetic fibers:- From vagus nerves Differences between jejunum and ileum 1- Length 2- Site 3- Mesentery 4- Wall 5- Lumen 6- Colour 7- Vessels 8- Mesenteric fat 9- Plicae circularis 10- Payer's patches 11- Windows 12- Intestinal villi Jejunum The upper 2/5 of the free part of small intestine - 240 cm In the upper part of peritoneal cavity Attached to posterior abdominal wall above & to the left of aorta Thicker Wider Redder a- 1 – 2 rows of arcades b- Long terminal vessels Lesser Larger & more numerous Absent Present Larger and more numerous Ileum - The lower 3/5 - 360 cm a- In the lower part of peritoneal cavity b- In the pelvis Attached to posterior abdominal wall below & to the right of aorta a- 3 – 4 rows b- Short terminal vessels Greater amount a- In the upper part:- Smaller & fewer than in jejunum b- In the lower part:- Absent Present in the antimesenteric border of lower part of ileum Absent Small and few N.B. 1- Length of jejunum + Ileum = 20 feet = 6 meters 2- Jejunum begins at duodeno-jejunal flexure 3- Ileum end at ileo-cecal junction 4- Coils of jejunum & ileum - Freely mobile - Attached to the posterior abdominal wall by the mesentery of small intestine 5- Mesentery of small intestine has 2 edges 1- Long free edge:- Contains jejunum & ileum 2- Short attached edge = The root:- Continuous with parietal peritoneum on the posterior abdominal wall 6- The root of mesentery of small intestine extends a- From the left side of 2nd lumbar vertebra b- To the region of right sacro-iliac joint 7- Superior mesenteric L.Ns. lie around the origin of S.M.A. 8- Peyer’s patches = Aggregations of lymphoid tissue Differences between large and small intestine A- External differences:Small intestine Large intestine 1- Mobility Mobile except duodenum Mobile except ascending & descending colon 2- Caliber Smaller Larger 3- Mesentery Has a mesentery except duodenum Transverse colon, sigmoid colon & appendix have mesenteries 4- Longitudinal muscle layer Forms a continuous layer around small intestine = No teniae coli Collected into 3 longitudinal bands (Teniae coli) except in appendix, rectum & anal canal Absent 5- Appendices epiploica = Fatty tags attached to the walls 6- Saccules in the walls Absent → Smooth wall Present present B- Internal differences:- Plicae circularis Intestinal villi Peyer’s patches Small intestine Present Present Present Large intestine Absent Absent Absent Caecum Position:- In the right iliac fossa Length:- 6 cm Peritoneal covering:- Completely covered by peritoneum → Mobile Caecal peritoneal recesses:1- Retrocecal recess 2- Superior ileocaecal recess 3- Inferior * * Relations:A- Anteriorly:1- Anterior abdominal wall 2- Coils of small intestine 3- Part of greater omentum B- Posteriorly:1- Psoas major 2- Iliacus 2- Femoral N. 3- Lateral cutaneous femoral nerve 4- Appendix C- Medially:- Appendix Arterial supply:- Anterior and posterior cecal arteries that are branches of ileocolic artery that is a branch of S.M.A. Venous drainage:- By anterior & posterior ileo-cecal Vs. → To ileo-colic V. → To S.M.V. Lymph drainage:- To mesenteric L.Ns. → To superior mesenteric L.Ns. Nerve supply:- By superior mesenteric plexus that consists of 1- Sympathetic fibers 2- Parasympathetic fibers:- From vagus nerves Appendix Length:- 8 – 13 cm Site:- In right iliac fossa - Its base lies deep to McBurney’s point - McBurney’s point is at the junction between the latera 1/3 & medial 2/3 of a line drawn between a- A.S.I.S. b- Umbilicus Attachment to caecum:- Its base is attached to the posteromedial aspect of caecum. One inch below the ileocaecal junction Positions of the tip:1- In the pelvis:- Common 2- Behind caecum:- Common 3- Lateral to caecum 4- In front of or behind terminal part of ileum Peritoneal covering:- Completely covered by peritoneum - Has a mesentery (mesoappendix) Arterial supply:- Appendicular artery that is a branch of posterior caecal A. Venous drainage:- Appendicular V. → To posterior caecal V. Lymph drainage:- To 1 – 2 L.Ns. in meso-appendix → To superior mesenteric L.Ns. Nerve supply:- By superior mesenteric plexus that consists of 1- Sympathetic fibers 2- Parasympathetic fibers:- From vagus nerves 3- Sensory afferent fibers:- Accompany the sympathetic fibers → Reach 10th thoracic segment of spinal cord Surface anatomy:- The base of appendix is represented by McBurney's point - McBurney's point is a point at the junction between the lateral 1/3 and medial 2/3 of a line drawn between the right A.S.I.S. and umbilicus N.B. 1- Caecum lies below the ileocecal junction 2- Ileocecal junction is at the junction between caecum & ascending colon 3- Ileocaecal opening is guarded by 2 horizontal mucosal folds (Called ileocecal valve) 3- Teniae coli converge at the base of appendix 4- No teniae coli in appendix, rectum nor anal canal 6- Meso-appendix is attached to the mesentery of small intestine 7- Appendicular vessels & nerves pass through meso-appendix 8- Base of appendix can be found by identifying the teniae coli of caecum → Trace these teniae coli → They converge towards the base of appendix Ascending and descending colon Length Peritoneal covering Anterior relations Posterior relations Ascending colon Descending colon 13 cm 25 cm Peritoneum covers the anterior surface and the sides → Binds the ascending & descending colon to the posterior abdominal wall 1- Anterior abdominal wall 2- Coils of small intestine 3- Greater omentum 1- Iliacus muscle 2- Iliac crest 3- Quadratus lumborum 4- Origin of transversus abdominis 5- Right kidney 6- Iliohypogastric N. 7- Ilioiguinal N. 1- ………… 2- ………… 3- ………… 4- ………… 5- ………… 6- ………… 7- ………… 8- Left psoas major 9- Femoral N. 10- Lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh By branches of I.M.A.:1- Right colic A. 2- Ileo-colic A. Right colic & Ileocolic Vs. Venous → To S.M.V. drainage To colic L.Ns. → To Lymph superior mesenteric L.Ns. drainage Nerve supply By superior mesenteric plexus that consists of 1- Sympathetic fibers 2- Parasympathetic fibers from vagus nerves Arterial supply By branches of I.M.A.:1- Left colic A. 2- Sigmoid As. Left colic & Sigmoid Vs. → To I.M.V. To colic L.Ns. → To inferior mesenteric L.Ns. By inferior mesenteric plexus that consists of 1- Sympathetic fibers 2- Parasympathetic fibers from pelvic splanchnic nerves Transverse colon Length:- 38 cm Relations:Anteriorly:1- Greater omentum 2- Anterior abdominal wall (Umbilical & hypogastric regions) Posteriorly:1- Second part of duodenum 2- Head of pancreas 3- Coils of jejunum & ileum Arterial supply:A- Proximal 2/3:- Supplied by middle colic A. that is a branch of S.M.A. B- Distal 1/3:- Supplied by left colic A. that is a branch of I.M.A Venous drainage:- The same as the arterial supply A- Proximal 2/3:- drained by middle colic V. that drains to S.M.V. B- Distal 1/3:- Drained by left colic V. that drains to I.M.V. Lymph drainage:A- Proximal 2/3:- Drain to colic L.Ns. → Then to superior mesenteric L.Ns. B- Distal 1/3:- Drain to colic L.Ns. → Then to inferior mesenteric L.Ns. Nerve supply:A- Proximal 2/3:- The same as ascending colon B- Distal 1/3:- The same as descending colon Peritoneum of transverse colon 1- Transverse mesocolon:- Attached to a- Anterior border of pancreas b- Upper border of transverse colon 2- Posterior layers of greater omentum:- Attached to lower border of transverse colon Peritoneal covering:- Completely covered by peritoneum except its first part where the peritoneum covers its anterior surface only but the posterior surface lies directly on the 2nd part of duodenum and head of pancreas N.B. 1- Descending colon ends at the pelvic brim by continuation as pelvic colon 2- Ascending colon is in front of the lower pole of right kidney. 3- Descending colon is in front of the lateral border of left K. 4- Left colic flexure is a- Higher than the right one b- Suspended from diaphragm by phrenico-colic ligament 5- Transverse colon is suspended from pancreas by transverse mesocolon Celiac artery Beginning:- From the commencement of abdominal aorta at the level of last thoracic vertebra Branches:1- Left gastric A. 2- Splenic A. 3- Hepatic A. Splenic artery Course:- Originates from celiac trunk → Runs to the left on the upper border of pancreas behind the stomach → In front of left kidney →Passes through lieno-renal ligament → Enters the hilum of spleen Branches:1- Pancreatic branches 2- Left gastro-epiploic A. 3- Short gastric As.:- 5-6 in number Hepatic artery Course:- Arises from celiac trunk → Runs to the right &→ Ascends in the right free margin of lesser omentum (In front of portal V. & to the left of bile duct) → Ends at porta hepatis by dividing into right & left branches Branches:1- Right gastric A. 2- Gastro-duodenal A.:- Descends behind first part of duodenum then divides into a- Right gastro-epiploic A. b- Superior pancreatico-duodenal A. 3- Terminal branches:a- Right branch:- Gives the cystic A. b- Left branch Superior mesenteric artery Course:- Begins from the anterior surface of abdominal aorta at the level of 1st lumbar vertebra → Descends in front of the 3rd part of duodenum → Descends in the root of mesentery of small intestine → Ends at the ileocaecal junction by anastomosis with the ileal branch of ileocolic A. Course and relations:- descends in front of the uncinate process of pancreas Branches:1- Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery:- Single or double - Passes between head of pancreas & 3rd part of duodenum - Supplies pancreas & duodenum 2- Middle colic artery:- Passes through the transverse mesocolon - Supplies the right 2/3 of transverse colon - Divides into right and left branches 3- Right colic artery:- Supplies ascending colon (the upper 2/3) and right colic flexure - Divides into ascending & descending branches - Usually a branch of ileocolic A. 4- Jejunal and ileal branches - 12 – 15 in number - Supply jejunum & ileum - Form arcades 5- Ileocolic artery that divides into A- Superior branch:- Anastomoses with the right colic A. B- Inferior branch:- Anastomoses with the end of S.M.A. & gives 1- anterior cecal A. 2- posterior cecal A.:- Gives appendicular A. Collectively:- Aorta → S.M.A. → Ileocolic A. → Inferior division → Posterior cecal A. → Appendicular A. Inferior mesenteric artery Course:- Begins from the anterior surface of abdominal aorta 3.8 cm above its bifurcation → Descends downward & to the left → Ends by passing in front of the left common iliac artery → continues as the superior rectal artery in the medial limb of sigmoid mesocolon Branches:1- Left colic artery:-Supplies the left 1/3 of transverse colon , left colic flexure & upper part of descending colon -Divides into ascending & descending branches 2- Sigmoid arteries:- - 2 – 3 in number -Supply the sigmoid colon and lower part of descending colon 3- Superior rectal artery:- It is the continuation of I.M.A. as it crosses in front of left C.I.A. - Supplies the rectum and upper 1/2 of anal canal Marginal artery Definition:- Anastomosis of colic As. around the concave margin of large intestine Formation:1- Anastomosis between a- Ileal branch of ileocolic A. = Inferior branch of ileocolic A. b- S.M.A. 2- Anastomosis between a- Superior branch of ileocolic A. b- Descending branch of right colic A. 3- Anastomosis between a- Ascending branch of right colic A. b- Right branch of middle colic A. 4- Anastomosis between a- Left branch of middle colic A. b- Ascending branch of left colic A. 5- Anastomosis between a- Descending branch of left colic A. b- First sigmoid A. 6- Anastomosis between a- Sigmoid As. b- Superior rectal A. Splenic vein Course:- Begins at hilum of spleen by the union of several veins → Passes to the right inside splenico-renal ligament → Runs behind tail & body of pancreas → Ends behind the neck of pancreas by uniting with S.M.V. to form portal V. Tributaries:1- Inferior mesenteric V. 2- Pancreatic Vs. 3- Short gastric Vs. 4- Left gastro-epiploic V. Inferior mesenteric vein Course:- Begins as a continuation of superior rectal A. → Ascends on the left side of inferior mesenteric A. & duodeno-jejunal flexure → Joins the splenic V. behind the body of pancreas Tributaries:1- Sigmoid Vs. 2- Left colic V. 3- Superior rectal V. Superior mesenteric vein Course:- Begins at ileo-cecal junction → Ascends in the root of mesentery of small intestine on the posterior abdominal wall → Passes in front of 3rd part of duodenum → Passes behind neck of pancreas → Ends behind the neck of pancreas by uniting with ………… to form ………. Tributaries:1- Inferior pancreatico-duodenal V. 2- Right gastro-epiploic V. 3- Jejunal Vs. 4- Ileal Vs. 5- Ileo-colic V. 6- Right colic V. 7- Middle colic V. N.B. 1- Celiac trunk = Artery of the foregut 2- Foregut includes 1- Lower 1/3 of esophagus 2- Stomach 3- First part of duodenum 4- Upper ½ of 2nd part of duodenum 3- Midgut includes 1- Lower ½ of 2nd part of duodenum 2- Third & fourth parts of duodenum 3- Jejunum & ileum 4- Caecum & appendix 5- Ascending colon 6- Proximal 2/3 4- Hindgut includes 1- Distal 1/3 of transverse colon 2- Descending colon 3- Sigmoid colon 4- Rectum 5- Upper ½ of anal canal 5- Celiac trunk a- Surrounded by celiac plexus b- Behind lesser sac 6- Gastric As. a- Between the 2 layers of lesser omentum b- Run along the lesser curvature of stomach c- Anastomose together 7- Gastro-epiploic As. a- Between the 2 layers of greater omentum b- Run along the greater curvature of stomach c- Anastomose together 8- Short gastric As. anastomose with the left gastric & left gastro-epiploic As. 9- Right gastric A. arises from hepatic A. at the upper border of pylorus 10- Superior pancreatico-duodenal A. runs between the head of pancreas & 2nd part of duodenum 11- Superior rectal A.:- Descends behind the rectum - Anastomoses with the middle & inferior rectal As. 2- S.M.V. is on the right side of S.M.A. Veins of the portal system 1- Portal vein 2- Splenic vein 3- Superior mesenteric vein 4- Inferior mesenteric vein Portal vein Length:- 2 inches = 5 cm Course:- Begins behind the neck of pancreas by the union of S.M.V. and splenic V. → Ascends behind the 1st part of duodenum → Ascends in the free margin of lesser omentum in front of epiploic foramen → Ends at porta hepatis by dividing into right and left branches Tributaries:1- splenic vein 2- superior mesenteric vein 3- right gastric vein 4- left gastric vein 5- cystic vein:- to the right branch of portal vein. 6- Inferior mesenteric V. drains into the splenic V. 7- paraumbilical veins:- connect the veins of anterior abdominal wall with the left branch of portal vein Sites of portosystemic anastomosis 1- In the lower 1/3 of esophagus:A- Between 1- Esophageal tributaries of azygos vein (systemic tributaries) 2- Esophageal tributaries of left gastric vein (portal tributaries) B- Significance = in portal hypertension → esophageal varices. 2- Halfway down the anal canal:A- Between 1- Superior rectal vein (portal tributaries) 2- Middle & inferior rectal Vs. that drain into internal iliac & internal pudendal Vs. (systemic tributaries) B- Significance = in portal hypertension → piles = hemorrhoids 3- Paraumblical Vs.:A- Connect 1- Left branch of portal V. With 2- Superficial veins of anterior abdominal wall (Systemic tributaries) B- Significance = in portal hypertension → caput medusae 4- Anastomosis between A- Veins of ascending colon, descending colon, duodenum, pancreas & liver (Portal tributaries) B- Renal, lumbar & phrenic Vs. (Systemic tributaries) N.B. 1- Portal hepatic vein = Portal vein 2- Portal V. drains a- Abdominal part of G.I.T. (From lower 1/3 of esophagus to upper ½ of anal canal) b- Spleen c- Pancreas d- Gall bladder 3- Cystic V. drains into either a- To right branch of portal V. b- Directly to the liver 4- Para-umbilical Vs. accompany ligamentum teres inside the lower margin of falciform ligament 5- Left gastric V. drains the stomach and lower 1/3 of esophagus. 6- The systemic veins = the veins that drain into I.V.C. and S.V.C. 7- Caput medusae = Varicose veins radiating from umbilicus 8- Portal vein and its tributaries have no valves