* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Session 1 Framework
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Cyberwarfare wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Access control wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
Cyberattack wikipedia , lookup
Cyberterrorism wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Cybercrime countermeasures wikipedia , lookup
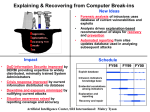
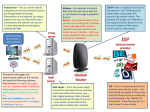
Session 1 Framework Security Threat Responsibility and Policy Architecture Response Flow Preparation Emergency Response Yan Wang 2006.09 Agenda Framework & Technology Security Monitoring Response Measure Case Study & Discussion Security Threat Threat Evolution and Trends Threat Categories Attacks Fundamental Evolution of Availability Threats Exploit Trends Three Key Threat Categories • Reconnaissance Unauthorized discovery and mapping of systems, services, or vulnerabilities • Access Unauthorized data manipulation, system access, or privilege escalation • Denial of Service Disable or corrupt networks, systems, or services How do these impact ISPs? • Reconnaissance – Happens all the time. It is part of the “attack noise” of the Internet (along with low level attacks and backscatter). • Access – Break-ins on the edge of an ISP’s network (I.e. customer CPE equipment) can impact the ISP’s core. • DOS – The core threat to an ISP – knocking out customers, infrastructure, and services. Reconnaissance Methods • Common commands and administrative utilities nslookup, ping, netcat, telnet, finger, rpcinfo, File Explorer, srvinfo, dumpacl • Public tools Sniffers, SATAN, SAINT, NMAP, custom scripts Network Sniffer nmap nmap Why Do We Care? Why Do We Care? Access Methods Access Methods (cont.) Denial of Service Methods • Resource Overload Disk space, bandwidth, buffers, ... Ping floods, SYN flood, UDP bombs, ... • Software bugs Out of Band Data Crash: Ping of death, fragmentation… • Toolkits TRINOO, Tribal Flood Net and friends • Distributed attacks for amplification DoS DoS type • Resource Overload Disk space, bandwidth, buffers, ... Ping floods, SYN flood, UDP bombs, ... • Out of Band Data Crash Ping of death, ... • Routing Capacity Fill up packet buffers, queues, flow tables, and processing capabilities. DoS Sequence DDoS DDoS Step 1: Crack Handlers and Agents DDoS Step 2: Install Trojan & Covert Communication Channel DDoS Step 3: Launch the Attack DDOS Attack Characteristics • DDOS Arrays (handlers and agents) a maintenance intensive. Take time and effort to create. • Launching attacks from an agent can be considered a one shot weapon. Once the attack is launched, there is a risk of traceback. If someone traces back to the agent, they could watch and wait to see if the perpetrator returns to the agent. Attacks Fundamental Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) ARP Datagram Internet Protocol IP Header Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) User Datagram Protocol (UDP) Transport Control Protocol TCP Header TCP Establishment and Termination Packet Spoofing IP Spoofing TCP Blind Spoofing TCP blind spoofing (Cont.) ARP Based Attacks Gratuitous ARP Misuse of Gratuitous ARP A Test in the Lab A Collection of Tools to Do: ARP spoof in Action More on ARP Spoof Selective Sniffing SSL/SSH Interception SSL/SSH Interception SSL/SSH Interception ICMP Based Attacks-smurf Smurf’s Script Kiddy Tool ICMP Unreachable Teardown IP Based Attacks IP Normal Fragmentation IP Normal Fragmentation (Cont.) IP Normal Reassembly IP Reassembly Attack IP Reassembly Attack (Cont.) Ping of Death Attack Denial of Service Ping of Death Attack Denial of Service UDP Based Attacks Looping UDP DoS - Fraggle Attack TCP Based Attacks SYN Attack TCP SYN Flood TCP SYN Flood TCP Session Hijacking TCP DDOS Reflection Attacks TCP DDOS Reflection Attacks TCP DDOS Reflection Attacks TCP DDOS Reflection Attacks Other Attacks Incident Response Team A Computer Security Incident Response Team (CSIRT) is a team that performs, coordinates, and supports the response to security incidents that involve sites within a defined constituency. ISP Security ISP need to: • Protect themselves • Help protect their customers from the Internet • Protect the Internet from their customers • At any given time there are between 20 to 40 DOS/DDOS attacks on the Net Role of Service Providers Role of Service Providers Role of Service Providers ISP Security Actions Policy Policy • Avoid extensive damage to data, systems and networks due to not taking timely action to contain an intrusion • Minimize the possibility of an intrusion affecting multiple systems both inside and outside an organization because staff did not know who to notify and what actions to take. • Avoid negative exposure in the news media that can damage an organization’s public image and reputation. • Avoid possible legal liability and prosecution for failure to exercise due care when systems are inadvertently or intentionally used to attack others. Preparing to Respond • Create an archive of original media, configuration files, and security-related patches for all router and host operating systems and application software versions • Ensure that backup tools and procedures are working • Create a database of contact information • Select and install tools to use when responding to intrusions Preparing to Respond (Cont.) • Develop a plan and process to configure isolated test systems and networks when required • Keep response plans, procedures and tools up to date • Consider performing a practice drill to test tools and procedures CERT Infrastructure • Information Platform(Website) • Tel, Mail • Event Processing System • Traffic Monitoring System • Intrusion Detection System Security System Architecture emergency response service system information issue system Leak Scan Cooperation Security Monitoring System Distributing IDS Traffic Analyse and Account Traffic Collection Identity Authen Infrastructure IP info Event Clock Synchronization CCERT Framework CERNET Committee of Experts Center CCERT CCERT Expert Team Regional CCERT R&D Interprovincial CCERT Campus CCERT Secretariat CCERT Framework Committee of Experts CCERT Liaison Training R&D Service Analysis Monitoring Response Flow ① ② ③ ④ ⑤ ⑥ ⑦ Preparation Detection Analysis Decision Control Announcement Statistic Response Flow CERNET management helpdesk Traffic analyzing and monitoring Important Event Investigation NOC Other IRTs Common Event Users Administrators Signature based IDS tools patches Whois info Attack Incident signature database CNCERT/CC advisories 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 1st Qtr 2nd Qtr 3rd Qtr 4th Qtr What Do ISPs Need to Do? Components of Response Analyze the event Contain the incident Eliminate intruder access Restore operations Update procedures based on lessons learned Analyze Event • What systems were used to gain access • What systems were accessed by the intruder • What information assets were available to those systems? • What an intruder did after obtaining access • What an intruder is currently doing Contain the Intrusion • Gain control of the systems involved • Attempt to deny an intruder access to prevent further damage • Monitor systems and networks for subsequent intruder access attempts Eliminate Intruder Access • Change all passwords on all systems accessed • Restore system and application software and data, as needed • What other systems might be vulnerable? Restore Operations • Validate the restored system • Monitor systems and networks • Notify users and management that systems are again operational Other • Build the Communications Channels to your Peers and Customers • Build the Communications Channels to your Vendors Preparation • Securing the Router and the Management Plane • Securing the Network and Data Plane • Securing the Routing Protocol and Control Plane • Anycast as a Security Tool • Using IP Routing as a Security Tool Terminology Securing the Router and the Management Plane Routers do get Directly Attacked Routers do get Directly Attacked Router Security Global Services You Turn OFF Global Services You Turn OFF Interface Services You Turn Off Interface Services You Turn Off Cisco Discovery Protocol Cisco Discovery Protocol Cisco Discovery Protocol Use Enable Secret Securing Access to the Router RISK Assessment Lock Down the VTY and Console Ports VTY and Console Port Timeouts VTY Security VTY Security Encrypt the Traffic from Staff to Device SSH Support in ISP Code Cisco IOS SSH Configuration SSH Server Implementation SSH Server Configuration Prerequisites SSH Server Configuration SSH Server Configuration (cont.) SSH Server Configuration Summary SSH Client Access SSH Terminal-Line Access Secure Copy (SCP) Secure Copy (SCP) Staff AAA to get into the Device What is ISP AAA and ISP AA? Separate Security Domains!