* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hand SGD
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
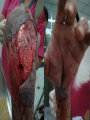
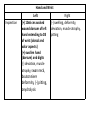
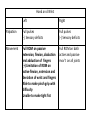
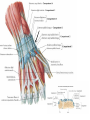
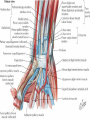
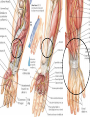
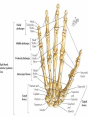
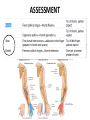
Hand SGD August 1, 2011 Block 10A PATIENT PROFILE • • • • • • Lope S. Ampalayo, 70 y.o/M, from Paco, Manila Married, with 2 children Filipino, Roman Catholic Baker Right-handed Chief Complaint • Open wound on dorsum of hand with fx of metacarpal bones – July 31, 2011 – No prior history of trauma. HISTORY OF PRESENT ILLNESS: • • • • DOI: 7/30/11 TOI: 8 PM POI: Paco, Manila MOI: Degloving Injury, L • Left hand caught in mechanical rolling pin Ospital ng Maynila ATS and Teana; x-ray done showed hand: fx, closed, complete, oblique, displaced, D3 of 3rd metacarpal, L PGH REVIEW OF SYSTEMS: • • • • • • • (-) cough, colds, fever, headache (-) dizziness (-) BOV (-) dysphagia (-) nausea , (-) vomiting (-) DOB, palpitations (-) bladder and bowel changes (-) joint pain (+) polyphagia, polydipsia, polyuria PAST MEDICAL HISTORY • • • • • (+) DM (since 2006)– no medications taken (+) HPN (since 2006)– uncontrolled PTB, BA, CA, liver/kidney disease, CVDs (-) food/drug allergies No other previous hospitalization and surgeries FAMILY MEDICAL HISTORY • (-) HPN, DM, PTB, BA, CA, liver/kidney disease, CVD, allergy PERSONAL AND SOCIAL HISTORY • • • • • • (-) smoker (-)alcoholic drinker (-) illicit drug use Elementary graduate (Bohol). Baker since 1980s. Married but wife lives in Bohol; has 2 children but one died. Physical Examination • Awake, coherent, ambulatory, NICRD. • BP 120/80 HR 88 RR 20 T: 36.7 • Pink conjunctivae, anicteric sclerae, (-) CLAD, NVE, ANM, trachea midline • ECE, CBS, (-) ABS • AP, NRRR, DHS, (-) murmurs, heaves, thrills • Round abdomen, NABS, (-) masses/tenderness • PNB, FEP, (-) cyanosis Hand and Wrist Left Inspection (+) 10x6 cm avulsed wound dorsum of left hand extending to D3 of wrist (dorsal and volar aspects) (+) swollen hand (dorsum) and digits (-) deviation, muscle atrophy, swan neck, boutonniere deformity, (-) pitting, onycholysis Right (-) swelling, deformity, deviation, muscle atrophy, pitting Hand an d Wrist Left Right Palpation Full pulses (-) Sensory deficits Full pulses (-) Sensory deficits Movement Full ROM on passive extension, flexion, abduction and adduction of fingers (+) Limitation of ROM on active flexion, extension and deviation of wrist and fingers Able to make pinch grip with difficulty Unable to make tight fist Full ROM on both active and passive mov’t on all joints Manual Muscle Testing Left Right C5 (Elbow flexor) 5/5 5/5 C6 (Wrist extensor) 0/5 5/5 C7 (Elbow extensor) 5/5 5/5 C8(Finger flexor) 4/5 5/5 T1 (Small finger abductors) 4/5 5/5 Hand Habitus: Slightly flexed wrist, slightly flexed 3rd, 4th, 5th digits, extended 2nd digit, and extended thumb Diagnostics Assessment Degloving Injury, Left Hand Hand: Fx, closed, complete, oblique, displaced, 3rd metacarpal, L Fx, closed, complete, transverse, displaced, proximal phalanx, base of 5th, L Musculature • Extrinsic muscles • Extrinsic extensor tendons cross the wrist and are surrounded by tendon sheaths in six compartments* bounded by the extensor retinacular ligament. • Extrinsic finger and thumb flexor tendons and the median nerve enter the hand through the carpal canal. * Compartments and anatomy illustrated next Musculature • Intrinsic musculature includes thenar, hypothenar, and interosseous muscles . • Thenar muscles: abductor pollicis brevis, the opponens pollicis, and the superficial head of the flexor pollicis brevis. • Hypothenar muscles: abductor digiti quinti, the opponens digiti quinti, and the flexor digiti quinti. • The dorsal interossei (4), commonly referred to as dorsal intrinsics, abduct the fingers; the palmar interossei (3)(palmar intrinsics) adduct the fingers. ASSESSMENT Radial Nerve Palsy Median Nerve Palsy • Loss of palmar sensation along the volar aspect of the thumb, index, long, and radial border of the ring finger • Motor strength deficits include loss of thumb opposition (APB), loss of thumb interphalangeal (IP) joint flexion (FPL), and loss of index distal interphalangeal joint flexion (FDP). Ulnar Nerve Palsy • • • • • “Clawhand” = Duchenne's sign Wartenberg's sign Froment's sign Pollock's sign. Masse's sign. Radial Nerve Palsy • Extension posturing of the hand is important in grasping and releasing functions. • Most often caused by injuries following a spiral fracture of the humerus – The sharp bony ends of the fracture can impale the radial nerve along its course. • Loss of radial nerve function at this level results in loss of wrist and finger extension (Wrist Drop) Degloving Injuries • Common with crush or shear mechanisms of injury • Zone of internal injury is often greatly underestimated by the external appearance of the limb. – Skin and subcutaneous tissue are separated from the underlying fascia in an open wound, or without break in the skin. • Degloved areas may lead to infected hematomas • It is generally recommended that the degloving injury be treated and healed before an incision is made in the area to treat the fracture. – Antibiotics and pain meds