* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Science of Recovery - AAP
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
NMDA receptor wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Polysubstance dependence wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
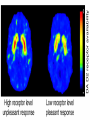
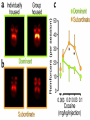
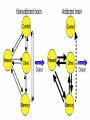
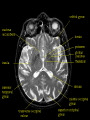
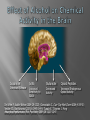
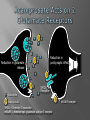
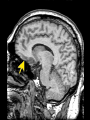
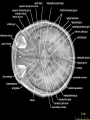
Cardwell C. Nuckols MA, PhD [email protected] (407) 758-1536 Facilitated by: NOVELTY ENVIRONMENTAL ENRICHMENT PHYSICAL EXERCISE NUTRITION Group Therapy Individual Counseling Sober Living Higher Power Assessment Alcohol/Drug Psyhosocial Recovery housing Healthy milieu Self help meetings Church From isolation to living “one day at a time” in the presence of others striving for a more fulfilling life Stimulates production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) Neurotrophin that governs maturation and development of neural systems Enhances executive functioning Obey social rules Adapt to changing & unpredictable environment Short term working memory Multi-tasking Self-directedness Self-directedness Responsible Purposeful Resourceful Increases neurotransmitters Monoamines Serotonin Dopamine Norepinephrine Association between DA D2 receptor numbers and drug self-administration Increased D2 receptors reduced alcohol consumption Decreased D2 receptors higher risk DA D2 receptor levels influenced by stress and social hierarchy Helps explain influence of environment and genes Subordinate animals more likely to selfadminister cocaine Dominant animals no more likely to selfadminister cocaine than placebo Social interventions can change neurobiology Increased DA D2 receptors Reduced self-administration Behavioral interventions could counteract the aversive effects of drug abuse and reinforce the power of group approaches Group Therapy Milieu Active participation Successful completion of assignments Leadership Modeling Self help Coffee and chairs “Telling story” Acute intoxication results in activation and deactivation of regions connected to the DA system These regions are involved in REWARD MEMORY MOTIVATION/DRIVE CONTROL Reward Circuit-Nucleus Accumbens and Ventral Pallidum Motivation/Drive Circuit-Orbitofrontal Cortex Memory & Learning Circuit-Amygdala and Hippocampus Control Circuit-Prefrontal Cortex & Anterior Cingulate Gyrus Volkow, N. D. et al. J. Clin. Invest. 2003;111:1444-1451 Copyright ©2003 American Society for Clinical Investigation Location Nucleus Accumbens (NAc) Ventral Tegmental Area (VTA) Impact of drugs of abuse Increased extracellular levels of DA in striatum (NAc) Reinforcing effects related to: Magnitude of DA increase Abruptness of DA increase Reduced sensitivity to natural reinforcers Goals: Management of craving Reduce reward value of drugs Reduce pleasure (create unpleasantness) from drug experience Situational triggers Emotional triggers Environment (People, Places And Things) Internal (Hungry, Angry, Lonely, Tired, Reward and Bored) Acute Abstinence Syndrome Stress In presence of: › › › Alcohol and drugs Alcohol and drug users Places where used to use or purchase Negative feeling states particularly anger but also: › › › › Boredom Loneliness Fear Anxiety Positive feeling states Physical pain Use of mood-altering prescription drugs Suddenly having a lot of cash Complacency Insomnia Sexual functioning Psychotherapy Behavior Therapy Structure Recovery Foundation Program Changing patterns Safety Plan Pharmacological Acute Maintenance 31 yo Nicki-a recovering methamphetamine addict- just got her first paycheck. She cashed her check and cruised thru the neighborhood where she used to score dope. Rock music blared from her speakers. Soon she was thinking, "I worked hard all week. I deserve a little fun.” In an inpatient setting the patient schedule serves this purpose On an outpatient basis or upon discharge from inpatient a recovery plan or contract is appropriate Remember that most addicts have little or no recent experience living a drug free lifestyle TASK SH TX FUN NUT PEX MON TU WED THU FRI SAT SUN Carter is 24 yo and just getting out of treatment for alcohol and drug addiction His early A/D history included…. Started drinking on Friday nights with friends in high school Turned-on to cocaine and marijuana by friends on weekends Started to buy drugs to sell from a distributor on Wed nights MY PERSONAL SAFETY PLAN • • • • • • Remember that craving go away I can write in my journal I can call my sponsor (299-289-5555) I can call my lover (299-426-1776) I can read from my favorite recovery book I can read affirmations TH: “On the back of the index card, come up with a saying or a prayer that gives you strength.” CT: “ I have always liked ‘Lord help me to be the best possible person I can be today’.” Opioid Maintenance Medications Methadone LAAM Buprenorphine Naltrexone Naltrexone (Revia, Vivitrol) Pure antagonist Poor compliance Less than 10% for street addicts Better compliance Healthcare professionals Parole/Probation New suspension with q30d administration should dramatically increase compliance and reliability of drug Subutex-Buprenorphine. sublingual (SL) 2mg and 8mg tablets Suboxone-Buprenorphine/Naloxone SL tablets Buprenorphine 25-50 x’s more potent than morphine Partial agonist Increasing dose does not increase effect like a full agonist Very high affinity for mu opioid receptor Mu receptor will choose buprenorphine over other opioids Buprenorphine will displace other opioids Slow dissolution from mu receptor Half-life on receptor is 34-36 hrs Heroin on and off receptor in millisecond At Buprenorphine dose of 16mg almost no binding to other opioids If taken under the tongue you get predominant buprenorphine effect If dissolved and injected get predominant naloxone effect (precipitates withdrawal) Buprenorphine equally effective as 60 mg of Methadone per day If patient needs 80-100 or more mgs of Methadone to be comfortable, Buprenorphine probably will not work With client dependent on short-acting opioids Instruct client to abstain for 12-24 hours Need to be in mild withdrawal before first dose Disulfiram, 1951 Acamprosate, 2004 Oral naltrexone, 1994 Injectable extended-release naltrexone, 2006 NONE OF THESE ARE ADDICTIVE Dopamine Increased Release GABA Glutamate Opioid Peptides Increased Sensitivity to GABA Decreased Activity Increased Endogenous Opioid Activity De Witte P. Addict Behav 2004;29:1325; Gianoulakis C. Curr Top Med Chem 2004;4:39-50; Nestler EJ. Nat Neurosci 2005;8:1445-1449; Tupala E, Tiihonen J. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2004;28:1221-1247. Glutamate System Acute Alcohol Effect Administration of Alcohol Chronic Alcohol Use Inhibits NMDA receptors Effect: anxiety, sedation Alcohol-Free Adaptation # and/or function of NMDA receptors on neurons CNS Equilibrium Withdrawal Increased glutamatergic activity Effect: - Acute: dysphoria, hallucinations - Post-acute: sleep/mood disturbances Littleton. Alcohol Health Res World 1998;22:13. Balances acute alcohol effect Effect: tolerance, dependence Removal of Alcohol N = 605 Fuller RK, et al. JAMA 1986;256:1449-1455. * N = 605 * p < .05 Fuller RK, et al. JAMA 1986;256:1449-1455. a Reduction in postsynaptic effects a Reduction in glutamate release a a Glutamate NMDA Receptor a Acamprosate NMDA = N-methyl-D-aspartate mGluR5 = metabotropic glutamate subtype 5 receptor a mGluR5 receptor N = 272 Sass H, et al. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1996;53:673-680. Location Orbitofrontal Cortex (OFC) Impact of Drugs of Abuse Drug as reinforcer far exceeds that of natural reinforcers OFC hypoactive during AAS Exposure to drug or other “cues” during withdrawal precipitates craving and compulsive drug use Hypothalamus Amygdala Reticular formation Head ganglion of ANS & locus of drive Brainstem regulation of arousal Frontal cortex Modulates instinctive behavior and internal drives Processes face and voice information for appraisal of external environment Therefore, integrates external and internal environment Early developmental trauma has negative impact on OFC AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PARASYMPATHETIC DISSOCIATION (FREEZE) SYMPATHETIC HYPERAROUSAL (FIGHT/FIGHT) Increase value of non-drug reinforcers Positive Connection to Others Therapeutic Relationship How we communicate “Mirror” neurons Family and couples therapy 12 step meetings Connection to Higher Power of Your Choice Mindfulness Meditation Location Amygdala Hippocampus Impact of Drugs of Abuse People, Places and Things (“cues” or “triggers”) create an intense desire to use (“craving”) Impact of Drugs of Abuse (cont.) These cues automatically trigger habit learning Release of DA Declarative learning links emotional states to use (“Hungry, Angry, Lonely and Tired”) Behavioral Extinguish learned positive association with drug or drug “cues” Promote reinforcement of positive behaviors Recovery in neuropsychological functioning › › Most of treatment is during time of greatest dysfunction Recovery is; Time-dependent Due to sustained abstinence Experiencedependent Active rehabilitation or repetitive behavior Repetitive recovery-oriented behaviors Repetitive recovery-oriented thoughts Neurons that “fire together, wire together” Location Prefrontal Cortex Anterior Cingulate Gyrus Impact of Drugs of Abuse Disruption of prefrontal cortical functions removes self-directed behavior in favor of sensory-driven behavior Lack of vertical integration Control Strengthen Prefrontal Cortical Control Cognitive Therapy Education Exercises Puzzles Computer Games Crossword Puzzles Vertical Integration PFC plastic especially between 0-5 and 10-20 years of age Developmental delays occur secondary to early life trauma and early onset alcohol/drug abuse. Treatment Positive role models (Sponsor) Surrogate family (Home Group) “Growing Up In AA” Coordinate the many brain activities needed to utilize: Executive Functions Set goals Make plans to attain those goals Organize steps to carry out the plans Ensure that desired outcomes are achieved Conscience Pursue Reward Within the Law Why give an alcoholic or addict a 60 minute didactic or video? A new format 15-20 minute simple didactic How to participate in treatment 10 minute questionnaire 30 minute discussion group I THINK……….. I FEEL………….. I LEARNED…… MY FUTURE BEHAVIOR WILL CHANGE… BE KIND, CONSIDERATE, FORGIVING AND COMPASSIONATE AT ALL TIMES, PLACES AND UNDER ALL CONDITIONS WITH EVERYONE, AS WELL AS, YOURSELF http://www.jci.org/cgi/content/full/111/1 0/1444 Nestler, Eric. “The Neurobiology of Cocaine Addiction”. Science & Practice Perspectives. December 2005, pgs 4-12. http://www.medscape.com/viewprogram /3023_pnt Cloninger, Robert. Feeling Good: The Science of Well-Being. Oxford University Press, New York, 2004. Panksepp, Jaak. Affective Neuroscience. Oxford University Press, New York,1998, pg 255. Schore, Allan. Affect Regulation & the Repair of the Self. WW Norton, New York, 2003, pg 29-31. Scaer, Robert. The Trauma Spectrum. WW Norton, New York, 2005, pgs 62-64. http://www.msu.edu/~brains/humanatla s/search.html Nuckols, Cardwell C. THE SCIENCE OF RECOVERY: “Connecting to Others and a Higher Power of Your Choice”. Counselor Magazine. Vol. 7, No. 1, Feb., 2006. Nuckols, Cardwell C. THE SCIENCE OF RECOVERY: "Incorporating Neuroscience into Your Practice”. Counselor Magazine. December 2005, Vol. 6, no.,6, pgs 24-31. Gazzaniga, Michael (Editor). The Cognitive Neurosciences III. The MIT Press, London2004. Rossi, Ernest. The Psychobiology of Gene Expression. WW Norton, New York,2002. Blumenfeld, Hal. Neuroanatomy Through Clinical Cases. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA., 2002. McGlynn EA, et al. “The Quality of Healthcare Delivered to Adults in America”. New England Journal of Medicine. 2003;348:2635-2645. http://draonline.org - Dual Recovery Anonymous Http://www.alcoholics-anonymous.org – Alcoholics Anonymous http://www.wsoinc.com – Narcotics Anonymous http://www.ca.org – Cocaine Anonymous http://www.whitebison.org – Wellbriety http://www.nami.org – National Alliance for the Mentally Ill www.facesandvoicesofrecovery.org – Faces and Voices of Recovery (FAVOR) www.gwcinc.com/drnuck ols.htm www.hcionline.com/cnuckols http://www.hazelden.org /OA_HTML/hazCSrdSrchR esults.jsp?event=&cg=200&kw=NUCKOLS