* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 12: Transport and Immunity
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
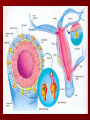
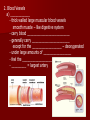
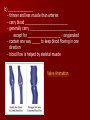
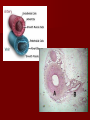
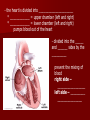
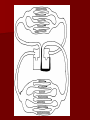
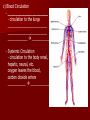
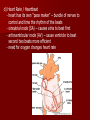
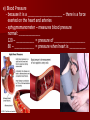
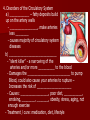
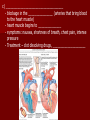
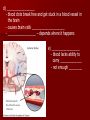
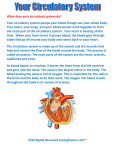
Unit 12: Transport and Immunity Absorption, circulation, and protection A. Adaptations for Transport - Transport is the life process in which substances are _____________ of cells or are _____________________ - In complex organisms a ________________ is to move material to and from the cells 1. Transport in Protists - no circulatory system needed – single celled and small organisms - cells are ______________________________________ - use __________ and ____________________ - _____________ inside the cell - _________________ ______________ _______________ 2. Transport in Hydra - no circulatory system - two cell layers – _______________________________ Endoderm has _____________________________ - use ________ and ____________ to move materials then cyclosis inside the cells - movement of tentacles also helps to circulate water What happens to the digested materials in the gastrovascular cavity? What about the undigested materials? What is the link between nutrition and transport? 3. Transport in the Earthworm - has _________________________ with organs (groups of specialized tissues and cells) - has a _____________, system of _______________, and a means to __________________________ - most of the Earthworm is ______________________ ____________________ a) ____________ - carries dissolved __________________________________ ______________________________________ - Earthworm blood is ___ has ______________________ b) ________________ - “_________” near the front of the earthworm - beat to help ____________________ - connect _____________________________________ c) _________________________ - runs along the ___________ of the digestive tube - divides into ___________________ - ________ – __________________________ site where _____________________________ between the body cells and blood d) _______________________ - runs along the _____ of the digestive tube - ________ to help push blood - ________________________ - formed from _____________ ________________________ e) _________________________ - blood is always _____________________________ inside the body - blood __________________ 4. Transport in the Grasshopper a) _________________________ - blood is ____________________________ - blood flows ___________________________________ ___________________________ b) ______________ - colorless – _______________________ - ___________________________________ - used to transport ____________________________ c) _________________ - _________________ - pumps blood out the ______________ - blood is also moved by _______________________ - _________ – stop the ________________________ d) ______________ - blood vessel that ______________________________ - blood flows out of the aorta ______________________ spaces and finally _______________________________ B. Human Circulatory System 1. _______________ - blood contains both dissolved substances and specialized cells - humans have ~ 5 L of blood - Blood is composed of 4 different parts a) ______________________________________________ - most numerous cell in the body - __________________ - ____________ = _______ on RBC used to ___________ ________________________ - made in _______________ – on the end of long bones - mature red blood cells do not have nuclei become filled with hemoglobin - live for ~ 120 days - destroyed by liver and spleen b) _________________________________________ - ________________________________________ - made in red bone marrow and lymph nodes - attack _________________ and organisms cancer cells, transplants, allergens, virus, bacteria - ______ in number when the body is ________________ c) ___________________ - cell fragments made in bone marrow - involved in __________ combine with blood proteins to stop bleeding d) ___________________ - yellow _______________ of blood makes up 55% of blood - 90% water - 10% dissolved _____, _____, _____________________ ________________, _______, ________, ___________ _______________, and ___________________ 2. Blood Vessels a) ____________ - thick walled large muscular blood vessels smooth muscle – like digestive system - carry blood __________________________ - generally carry _______________________ except for the __________________ – deoxygenated - under large amounts of _________________ - feel the __________________ - _________ = largest artery b) _______________ - thinner and less muscle than arteries - carry blood __________________________ - generally carry ____________________________ except for ____________________ - oxygenated - contain one way _____ to keep blood flowing in one direction - blood flow is helped by skeletal muscle Valve Animation c) _________________ - site where ______________________________________ __________________________ - _______________________________________________ - blood passes through 1 cell at a time – single file 3. _________________ a) Structure - _________ organ with thick muscular walls - myocardium - muscle = _____________________ * specialized muscle tissue Make a fist demo - the heart is divided into _____________________ * ____________ = upper chamber (left and right) * ____________ = lower chamber (left and right) pumps blood out of the heart - divided into the _____ and ______ sides by the _________ prevent the mixing of blood right side – _________________ left side – _________ _______________ b) Blood Flow Through the Heart - acts as _________________ - 1 pump - right side – ___________________ pumps to the lungs - other pump – left side – ______________ pumps to the body - Atria Valve Ventricle Artery right side - tricuspid valve left side - bicuspid valve c) Blood Circulation - _____________________ - circulation to the lungs ________________________ ________________________ ____________ ___________ - Systemic Circulation - circulation to the body renal, hepatic, neural, etc. oxygen leaves the blood, carbon dioxide enters ___________ ____________ Blood returns to the heart through the __________ _____________ _______________ _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________– the _____________ _____________ _____________ ____________ ___________ ____ _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________ – the _____________ _____________ _____________ _____________– to do it all again! Heart Lungs Heart Body it takes ~7 minutes for a red blood cell to complete the trip d) Heart Rate / Heartbeat - heart has its own “pace maker” – bundle of nerves to control and time the rhythm of the beats - sinoatrial node (SA) – causes atria to beat first - artioventricular node (AV) – cause ventricle to beat second two beats more efficient - need for oxygen changes heart rate e) Blood Pressure - because it is a _____________________ – there is a force exerted on the heart and arteries - sphygmomanometer – measures blood pressure normal: _____________ 120 – ___________ = pressure of ___________________ 80 – ____________ = pressure when heart is __________ 4. Disorders of the Circulatory System a) ____________ – fatty deposits build up on the artery walls - _________________, make arteries less ________ - causes majority of circulatory system diseases b) _____________________________ - “silent killer” - a narrowing of the arteries and/or more __________ to the blood - Damages the __________________________ to pump Blood, could also cause your arteries to rupture – Increases the risk of _____________________ - Causes: _________________, poor diet, ___________, smoking, ________, _______, obesity, stress, aging, not enough exercise - Treatment / cure: medication, diet, lifestyle c) ___________________________________ - blockage in the _______________ (arteries that bring blood to the heart muscle) - heart muscle begins to ______________ - symptoms: nausea, shortness of breath, chest pain, intense pressure - Treatment – clot dissolving drugs, ____________________ d) _________________ - blood clots break free and get stuck in a blood vessel in the brain - causes brain cells ____________________ - _________________ – depends where it happens e) _________________ - blood lacks ability to carry _____________ - not enough ________