* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
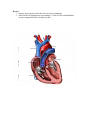
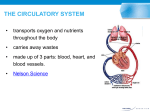
Circulatory System General Information: 1. supplies body’s cells with nutrients and oxygen 2. removes carbon dioxide and other wastes 3. helps fight disease Structure: 1. Heart – myocardium (thick muscle layers of the heart) contracts to pump blood into the arteries and to the rest of the body 2. Sinoatrial (SA) node – group of cardiac muscle cells start the contraction and cause heart muscle cells of the atria to contract together a. The pacemaker of the heart 3. Atrioventricular (AV) node – similar group of muscle cells causing the cells of the ventricles to contract a. Two beats together make the characteristic “lub-dub” heartbeat sound 4. Arteries – blood vessels with thick walls a. Carry blood away from the heart b. Blood pressure (force of blood on walls) is felt in arteries 5. Capillaries – smallest vessels (walls are one cell thick) a. Bring nutrients and oxygen to cells and absorb carbon dioxide and wastes b. Blood cells are carried single file 6. Veins – blood vessels with thin walls and valves to prevent backflow a. Carry blood toward the heart Blood – connective tissue that is half fluid (plasma) and half blood cells 1. Transport of oxygen (hemoglobin in red blood cells) 2. Guard against infection (white blood cells) 3. Production of antibodies (lymphocytes) 4. Blood clotting (platelets) 5. Lymphatic system – collects lymph (fluid that leaks from blood into surrounding tissues) and returns it to the blood a. Absorbs nutrients b. Fights infections Cardiovascular Disease – diseases of the circulatory system 1. buildup of fatty deposits in arteries results in high blood pressure (called hypertension) and atherosclerosis (hard deposits called plaque) 2. blood clots and blockage of arteries (from atherosclerosis) block blood flow to heart muscle cells (causing heart attacks) and to brain cells (causing strokes) Review: 1. immune system protects the body from invasion of pathogens 2. white blood cells (lymphocytes, macrophages, T-cells, B-cells, and antibodies) are also components of the circulatory system