* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What Is Heart Disease?
Survey
Document related concepts
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Congenital heart defect wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
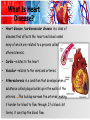
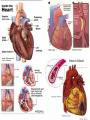
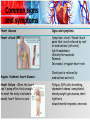
What Is Heart Disease? • Heart disease /cardiovascular disease is a class of diseases that affects the heart and blood vessel many of which are related to a process called atherosclerosis. • Cardio –relates to the heart • Vascular –relates to the veins and arteries • Atherosclerosis is a condition that develops when a substance called plaque builds up in the walls of the arteries This buildup narrows the arteries, making it harder for blood to flow through. If a blood clot forms, it can stop the blood flow. COMMON TYPES OF HEART DISEASE Preventable – • Heart disease can affect the structure of the heart –valves ,muscles ,fibers and blood supply e.g. coronary heart disease – disease of the blood vessels supplying the heart muscle. • The common cause of coronary heart disease result from - Atherosclerosis –this is a condition that develops when a substance called plaque builds up in the walls of the arteries. Coronary arteries that supply the heart muscle become blocked And as a result can cause: • Hypertension (increased pressure ) • Angina /Ischemic heart disease (partially blocked) • Heart attack /M.I(Fully blocked ) • Heart failure (damaged valves and enlargement),arrythmias (damaged heart fibers) COMMON TYPES OF HEART DISEASE • Heart disease can also result from infection –rheumatic heart disease – damage to the heart muscle and heart valves from rheumatic fever, caused by streptococcal bacteria ,and endocarditis . Non-preventable – • Heart disease can also be congenital -congenital heart disease - malformations of heart structure existing at birth Risk Factors Modifiable risk factors-Some risk factors can be avoided or altered, potentially slowing the disease process or even reversing it. These factors include: • elevated serum lipid levels • hypertension • cigarette smoking • diabetes mellitus • sedentary lifestyle • stress • obesity—especially abdominal (waist measurement greater than 40″ [101.6 cm] in men and greater than 35″ [88.9 cm] in women) • excessive intake of saturated fats, carbohydrates, and salt. Risk Factors Con’t Non-modifiable risk factors- there are four non-modifiable factors increase a person's risk of cardiovascular disease: • age • male gender • family history • race. Common signs and symptoms Heart disease Signs and symptoms Hypertension -A sustained blood pressure above 140/90mmhg . Dizziness ,or may be ASYMPTOMATIC Complications- Cardiac complications include CAD, angina, MI, heart failure, arrhythmias, and sudden death,stroke,blindness,kidney failure Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy— primary disease of the heart muscle that's characterized by a thickened, inflexible heart muscleresults from extensively damaged myocardial muscle fibers shortness of breath,fatigue dry cough at night,palpitations,nausea Edema of the legs , chest pain Common signs and symptoms Heart disease Signs and symptoms Heart attack /MI Symptoms: chest /thumb /back pains that is not relieved by rest or medications .(nitrates) light headedness Anxiety/nervousness Paleness Increased, irregular heart rate Angina /ischemic heart disease Heart failure -When the heart can't pump effectively enough to meet the body's metabolic needs, heart failure occurs Chest pain is relieved by medications and rest. Fatigue, Difficulty breathing, dependent edema, unexplained, steady weight gain,nausea,chest tightness slowed mental response, anorexia How is heart disease diagnosed? LABORATORY TESTING –measures heart enzymes/proteins and reveals the extent of damage and monitor healing. • Creatine kinase (CK)-Elevated levels indicate death to heart muscles. • Ischemia-modified albumin (IMA)-indicates lack of oxygen supply to the heart . • Myoglobin- indicates damage to the heart muscle • Troponin I and T-indicates heart damage • Cholesterol levels-detects cholesterol levels-LDL/HDL GRAPHIC RECORDING STUDIES –used to detect heart disorders . • ECG- graphically records electrical current generated by the heart. • Exercise ECG(stress test)-assess heart response to an increased workload. How is heart disease diagnosed? Imaging studies – • Chest X-ray-may detect enlargement or structural changes of the heart • Echo- visualize heart size and shape, heart wall thickness and motion, and cardiac valve structure and function • CT /MRI-detect changes in the structure of the heart Interventional studies – • Cardiac catheterization and coronary angiographydetermines location of blockage ,pressure and oxygen levels of the heart. How is heart disease treated ? Treatment of heart disease depends on the causative factor or the disorder present; • Pharmacological –medications may be used to reduce blood pressure(anti –hypertensives),control heart rate(antarrythmias) ,reduce pain(anti –anginal) ,lower cholesterol(anti –lipidemics),dissolve or prevent blood clots (anti –platelet /thrombolytics)and reduce fluid accumulation(diuretics) How is heart disease treated ? • Non –pharmacological -lifestyle changes-education,diet (DASH diet ),exercise • Invasive interventions (surgery) • Coronary artery with an autogenous graft-restores blood flow to the heart • Bypass grafting -bypasses the obstruction resulting from arteriosclerosis • Embolectomy- removes the blockage (blood clot) Valve repair HOW CAN HEART DISEASE BE PREVENTED ? DIETARY MEASURES-These are based on the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) • •Limiting use of salt to less than 2.4 grams of sodium (6 gm salt) per day i.e. no added salt in cooking or at table); avoid canned foods, salted meat, etc. • •Reducing excessive dietary fat (especially saturated fat and trans-fatty acids) to no more than 30% of calories. Saturated fat should not exceed 10% of total calories. • •Ensuring intake of fibre of at least 30-40 gm/day. • •Ensuring intake of potassium between 70-80 mmol/l daily. This can be achieved by a good selection of fruits and vegetables especially bananas,tomatoes and oranges as well as coconut water. • Avoiding red meat . HOW CAN HEART DISEASE BE PREVENTED ? Physical Exercise • This should be undertaken for 30-60 minutes at least five times each week,but preferably daily. Walking is the easiest form of exercise for most people. Weight Management • This aims at the attainment and maintenance of desirable body weight i.e. • BMI <25 or at least a significant reduction, if overweight or obese. There is a possibility of 5-20 mmHg decrease in systolic pressure for every 10kg (22lb) weight loss. HOW CAN HEART DISEASE BE PREVENTED ? Reduction of Alcohol Intake • Alcohol use should not exceed 2 drinks/day for men and 1 drink/day for women. (1 drink = one ounce of spirits or 1 bottle of beer or 1 glass of wine) Cessation of Tobacco Use • Tobacco should be avoided. Education • Every opportunity should be taken for education of the patient, with partner and relatives. The education should include diet, exercise and other lifestyle advice(stress reduction)