* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 37-1
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
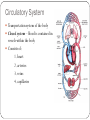
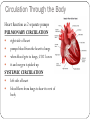
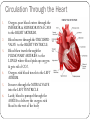
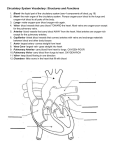
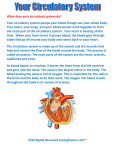
Chapter 37-1 Circulatory System Circulatory System Transportation system of the body Closed system – blood is contained in vessels within the body Consists of: 1. heart 2. arteries 3. veins 4. capillaries Heart Composed of mostly cardiac muscle Size of a closed fist Enclosed in the PERICARDIUM: - protective tissue Surrounded by the MYOCARDIUM: - thick layer of muscle -contractions of this pumps the blood throughout the body Heart Heart muscle contracts about 72 times per minute Divided into 2 halves (right & left) by the septum: - prevents mixing of oxygen-poor blood with oxygen-rich blood Upper portion – right & left ATRIUM - receives blood Lower portion – right & left VENTRICLE - pumps blood out Circulation Through the Body Heart function as 2 separate pumps PULMONARY CIRCULATION right side of heart pumps blood from the heart to lungs when blood gets to lungs, CO2 leaves it and oxygen is picked up SYSTEMIC CIRCULATION left side of heart blood flows from lungs to heart to rest of body Circulation Through the Heart 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Oxygen-poor blood enters through the INFERIOR & SUPERIOR VENA CAVA to the RIGHT ARTRIUM. Blood moves through the TRICUSPID VALVE to the RIGHT VENTRICLE. Blood then travels through the PULMONARY ARTERIES to the LUNGS where blood picks up oxygen & gets rid of CO2. Oxygen-rich blood travels to the LEFT ATRIUM It moves through the MITRAL VALVE into the LEFT VENTRICLE Lastly, blood is pumped through the AORTA to delivery the oxygen-rich blood to the rest of the body Blood Vessels 3 types: 1. arteries: - pump oxygen-rich blood away from heart to tissues 2. capillaries: - where oxygen is dropped off & carbon dioxide and other wastes are picked up 3. veins: - pump oxygen-poor blood back to heart Blood Pressure Force of blood on the arteries walls Decrease when the heart relaxes Increases during exercise Average of healthy person – 120/80 Diseases of the Circulatory System High Blood Pressure - Hypertension - forces heart to work harder - may weaken or damage heart muscle & blood vessels - may lead to coronary heart disease - increases risk of heart attack & stroke Diseases of the Circulatory System ATHEROSCLEROSIS - fatty deposits called PLAQUE build up on the walls of arteries - dangerous in coronary arteries - if blocked, part of heart muscle will die due to lack of oxygen - leads to heart attack - can also form blood clots - if clot breaks free – can go to brain and cause a stroke Heart Attack Symptoms: 1. nausea 2. shortness of breath 3. severe, crushing chest pain Stroke Brain tissue will eventually die due to lack of oxygen Brain function may be lost in that area Causes: 1. paralysis 2. loss of the ability to speak 3. death Circulatory System Health Cardiovascular disease is easier to prevent than to cure To prevent: 1. regular exercise 2. eating healthy 3. avoid smoking